Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Animals and Plants NCERT Solutions
Topics and Sub Topics in Chapter 10 Respiration in Animals and Plants:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 10 | Respiration in Organisms |
| 10.1 | Why do we respire? |
| 10.2 | Breathing |
| 10.3 | How do we Breathe? |
| 10.4 | What do we breathe out? |
| 10.5 | Breathing in Other Animals |
| 10.6 | Breathing under water |
| 10.7 | Do plants also respire? |
Q1. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Answer:
During the run, the demand of energy is high but the supply of oxygen to produce energy is limited. Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscle cells to fulfill the demand of energy. After finishing the race, an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual so that more oxygen is supplied to the cells.
Q2. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
Similarity:
(i) In both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, food is broken down to release energy.
(ii) Both takes place inside cells.
(iii) Both produces byproducts.
Differences:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| (i) It takes place in the presence of oxygen. | (i) It takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| (ii) Energy is released in higher amount. | (ii) Energy is released in lesser amount. |
| (iii) Carbon dioxide and water are produced as byproducts. | (iii) Carbon dioxide and water are produced as byproducts. |
| (iv) It is a slow process. | (iv) It is a fast process. |
| (v) Examples: Animals and plants cells. | (iv) Examples: Human cells, yeast, Bacteria etc. |
Q3. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Answer:
We often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air to expel out these foreign particles. These particles get past the hair in the nasal cavity and irritate the lining of the cavity which results in sneezing.
Q4. Take three test-tubes. Fill each of them with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO2 ?
Answer:
Test-tube A will have the highest concentration of CO2 because snail will take in oxygen and gives out CO2.
In test-tubes B and C, the CO2 will be utilized by the water plant for synthesizing food and hence there will be less concentration of CO2 in these.
Q5. Tick the correct answer:
(a) In cockroaches, air enters the body through
(i) lungs
(ii) gills
(iii) spiracles
(iv) skin
Answer: (iii) spiracles
(b) During heavy exercise, we get cramps in the legs due to the accumulation of
(i) carbon dioxide
(ii) lactic acid
(iii) alcohol
(iv) water
Answer: (ii) lactic acid
(c) Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is:
(i) 9 – 12
(ii) 15 – 18
(iii) 21 – 24
(iv) 30 – 33
Answer: (ii) 15 – 18
(d) During exhalation, the ribs
(i) move outwards
(ii) move downwards
(iii) move upwards
(iv) do not move at all
Answer: (ii) move downwards
Q6. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (i) Earthworm |
| (b) Diaphragm | (ii) Gills |
| (c) Skin | (iii) Alcohol |
| (d) Leaves | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (e) Fish | (v) Stomata |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
| – | (vii) Tracheae |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Yeast | (iii) Alcohol |
| (b) Diaphragm | (iv) Chest cavity |
| (c) Skin | (i) Earthworm |
| (d) Leaves | (v) Stomata |
| (e) Fish | (ii) Gills |
| (f) Frog | (vi) Lungs and skin |
Q7. Mark T if the statement is true and F if it is false:
(i) During heavy exercise the breathing rate of a person slows down. (T/ F)
(ii) Plants carry out photosynthesis only during the day and respiration only at night. (T/ F)
(iii) Frogs breathe through their skins as well as their lungs. (T/ F)
(iv) The fishes have lungs for respiration. (T/ F)
(v) The size of the chest cavity increases during inhalation. (T/ F)
Answer:
(i) F
(ii) F
(iii) T
(iv) F
(v) T
Q8. Given below is a square of letters in which are hidden different words related to respiration in organisms. These words may be present in any direction – upwards, downwards, or along the diagonals. Find the words for your respiratory system. Clues about those words are given below the square.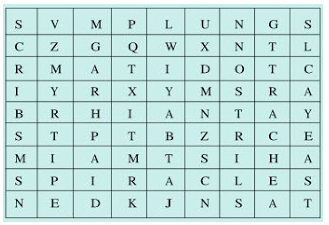
(i) The air tubes of insects
(ii) Skeletal structures surrounding chest cavity
(iii) Muscular floor of chest cavity
(iv) Tiny pores on the surface of leaf
(v) Small openings on the sides of the body of an insect
(vi) The respiratory organs of human beings
(vii) The openings through which we inhale
(viii) An anaerobic organism
(ix) An organism with tracheal system
Answer: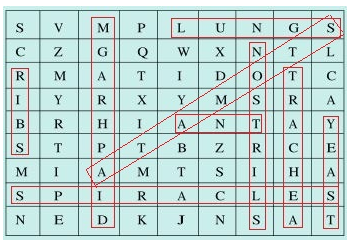
(i) The air tubes of insects → Trachea
(ii) Skeletal structures surrounding chest cavity → Ribs
(iii) Muscular floor of chest cavity → Diaphragm
(iv) Tiny pores on the surface of leaf → Stomata
(v) Small openings on the sides of the body of an insect → Spiracles
(vi) The respiratory organs of human beings → Lungs
(vii) The openings through which we inhale → Nostrils
(viii) An anaerobic organism → Yeast
(ix) An organism with tracheal system → Ant
Q9. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because:
(a) At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air.
(b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
(c) The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground.
(d) The pressure of air is higher than that on the ground.
Answer:
The mountaineers carry oxygen with them because (b) The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Heat
- Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7 Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8 Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9 Soil
- Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12 Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- Chapter 14 Electric Current and Its Effects
- Chapter 15 Light
- Chapter 16 Water: A Precious Resource
- Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline
- Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
.png)
.png)