Class 7 Geography Social Science Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife NCERT Solutions
1. Answer the following questions briefly.
- Which are the two factors on which the growth of vegetation mostly depends?
- Which are the three broad categories of natural vegetation?
- Name the two hardwood trees commonly found in tropical evergreen forest
- In which part of the world is tropical deciduous forests found?
- In which climatic conditions are citrus fruits cultivated?
- Mention the uses of coniferous forest.
- In which part of the world is seasonal grassland found?
Answer:
- Two factors on which growth of vegetation mostly depends:
- Climate (Temperature and Moisture).
- Height
- Slope
- The thickness of the soil.
(Any two factors)
- Three broad categories of natural vegetation:
- Forests: Grow in regions of high temperature and rain.
- Grasslands: Grow in regions of moderate rainfall.
- Thorny shrubs and scrubs: Grow in dry regions.
- Two Hardwood Trees:
- Rosewood
- Ebony
- Mahogany (Any Two)
- Tropical deciduous forest is found in the following parts of the world:
- Large parts of India.
- Northern Australia
- Central America
- Citrus fruits are cultivated in the Mediterranean climatic conditions.
- Four uses of coniferous forests:
- Coniferous forests provide softwood.
- It is used in making pulp. The pulp is used in making paper and newsprint.
- The matchmaking industry gets softwood from coniferous forests.
- Softwood is also used in making package boxes.
- Seasonal grassland is found in the Savannah region of Africa. It gets dried up in the dry season.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(a) Mosses and Lichens are found in
(i) Desertic vegetation
(ii) Tropical vegetation (iii) Tundra vegetation.
(b) Thorny bushes are found in
(i) Hot and humid tropical climate
(ii) Hot and dry desertic climate
(iii) Cold polar climate.
(c) In tropical evergreen forest, one of the common animals is
(i) Monkey (ii) Giraffe
(iii) Camel.
(d) One important variety of coniferous forest is
(i) Rosewood (ii) Pine
(iii) Teak.
(e) Steppe grassland is found in
(i) S. Africa (ii) Australia
(iii) Central Asia.
Answer: (a)—(iii), (b)—(ii), (c)—(i), (d)—(ii), (e)—(iii).
Question 3.
Match the following.
(i) Walrus (a) Softwood tree
(ii) Cedar (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest
(iii) Olives (c) A polar animal
(iv) Elephants (d) Temperate grassland in Australia
(v) Campos (e) Thorny shrubs
(vi) Downs (f) A citrus fruit
(g) Tropical grassland of Brazil
Answer.
(i) Walrus (c) A polar animal
(ii) Cedar (a) Softwood tree
(iii) Olives (f) A citrus fruit
(iv) Elephants (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest
(v) Campos (g) Tropical grassland of Brazil
(vi) Downs (d) Temperate grassland in Australia
4. Give reasons:
- The animals in the polar region have thick fur and thick skin.
- Tropical deciduous trees shed their leaves in the dry season.
- The type and thickness of vegetation changes from place to place.
Answer:
- The animals in the polar region have thick fur and thick skin because of the following reasons:
- Polar regions are very cold. .
- Animals that do not have thick fur and thick skin cannot survive in these harsh and cold climates.;
- They have to protect themselves from cold by thick fur and thick skin.
- Tropical deciduous trees shed their leaves in the dry season because of the following reasons:
- During the dry season, rainfall is scarce and water supply to plants and trees through their roots is reduced.
- Transpiration occurs through leaves.
- To reduce transpiration in dry season, trees shed their leaves.
- The short supply of moisture through their roots keeps them alive during the dry season.
- The type and thickness of vegetation changes from place to place because of the following reasons:
- Climate (temperature and moisture)
- Height from mean sea level – Slope
- The thickness of the soil.
- As these conditions vary from place to place, natural vegetation (types and thickness) also varies from place to place.
5. Activity:
(a) Collect pictures and photographs of forests and grasslands of different parts of the world. Write one sentence below each picture.
(b) Make a collage of rainforest, grassland, and coniferous forests.
Answer:
(a) Pictures and photographs of forests and grasslands of different parts of the world.
These forests are found in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics. These regions are hot and receive heavy rainfall throughout the year. These trees do not shed their leaves altogether.
These forests are the monsoon forests found in the large part of India, northern Australia and in central America. Trees shed their leaves in dry season.
These forests are commonly found along the eastern margin of the continents and comprise both hard and softwood trees like oak, pine etc.

The grass can grow veiy tall, about 3 to 4 metres in height. Savannah grasslands of Africa are of this type.
(b) Students are suggested to do this activity themselves
6. For Fun:
In the crossword table given below, some words are hidden. They are all about vegetation and wildlife and are to be found horizontally and vertically. Two have been worked out for you. Work in pairs with a friend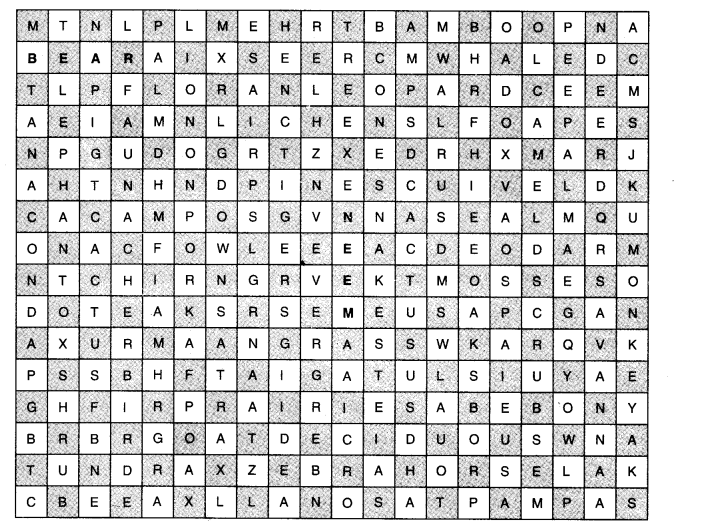
Answer:
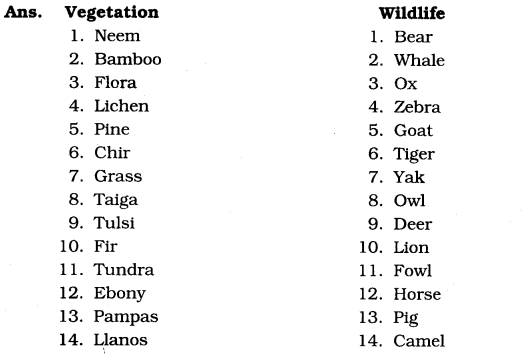
Class 7 Geography Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Intext Questions
Question 1.
Now can you tell why Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher? What type of vegetation did she see in the Himalayas starting with the foothills and going to the higher altitudes? (NCERT Page 39)
Answer.
Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher because of the following reasons:
- Change in a climate with an increase in height.
- Slope
- The thickness of the soil.
Types of vegetation she saw
- Sal and teak forests
- Coniferous forests
- Rhodo-dendrous
- Short grass
Question 2.
Like Salima, when you go to visit any new place, notice the type of natural vegetation occurring there and try to think of factors responsible for the growth of such vegetation in that habitat.
Note down if any human interference has taken place in that area in terms of deforestation, grazing, cultivation of cash crops, constructional activities, etc. (NCERT Page 39)
Answer.
In October to Nainital.
- Alpine and Montane vegetation.
Factors:
- Cold climate.
- Heavy rainfall.
- Mountainous soil.
Yes, for habitation and commercial activities.
Question 3.
Where in India do tropical evergreen and tropical deciduous forests occur? Name the states. (NCERT Page 41)
Which type of forest dominates most parts of India?
Answer.
- Western slopes of western ghats, N.E. India—Tropical evergreen (Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Goa, and N.E. states)
- Central India—Deciduous (M.P., Chhattisgarh), Jharkhand etc.
- Tropical Deciduous.
Question 4.
Look around in your surroundings and find out the articles made of hardwood and softwood.
Find out and learn the names of few trees of your locality. (NCERT Page 43)
Answer.
Hardwood: Steppers, bridges, furniture, doors, windows.
Softwood: Matches, packing material, false ceiling, boats etc.
Mango, neem, jamun, shisham, kikar, peepal, sal.
Question 5.
Can you name the great desert of India? Name some of the common animals of the desert. (NCERT page 44)
Answer.
Thar is the great Indian desert.
Camel, Snakes, lizards and many insects are found here.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife VSAQ
1. How is height of land and the character of vegetation related with each other? [V. Imp.]
Answer: With the change in height the climate changes and that changes natural vegetation.
2. Where are shrubs found?
Answer: Shrubs are found in the dry regions.
3. Why do trees of tropical evergreen forests not shed their leaves altogether?
Answer: It is because there is no particular dry season.
4. What is the special feature of tropical evergreen forests? [V. imp.]
Ans. Thick canopies of the closely spaced trees are found here. As a result sunlight do not reach inside the forest.
5. Name the trees found in the tropical deciduous forests.
Ans. Sal, teak, neem and shisham.
6. Where are temperate evergreen forests located?
Answer: These forests are located in the mid-latitudinal coastal region.
7. Why are only citrus fruits cultivated in Mediterranean regions? [V. Imp.]
Answer: It is because people have removed the natural vegetation in order to cultivate citrus fruits.
8. Mention one special feature of coniferous forests.
Answer: These forests have tall and softwood evergreen trees.
9. Name the animals found, in the coniferous forests.
Answer: Silver fox, mink, and polar bear.
10. Name the animals found in tropical grasslands. ,
Answer: Elephants, zebras, giraffes, dear and leopards.
11. Where are Savannah grasslands found?
Answer: They are found in East Africa.
12. Where are Llanos grasslands found?
Answer: They are found in Venezuela.
13. Which type of grassland Prairie is?
Answer: Prairie is temperate grassland.
14. Where are tropical deserts located?
Answer: They are located on the western margins of the continents.
15. Name some animals found in polar regions.
Answer: Seal, walruses, musk-oxen, Arctic owl, polar bear, and snow foxes.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife SAQ
1. Mention the major features of tropical evergreen forests. [V. Imp.]
Answer: Major features of tropical evergreen forests are:
- These forests are so dense that thick canopies are developed which do not allow the sunlight to penetrate inside the forest.
- As there is no particular dry season, the trees do not shed their leaves altogether. This keeps the forest evergreen.
- Hardwood trees such as rosewood, ebony and mahogany are found here.
2. Mention the features of Mediterranean trees.
Answer: These trees adapt themselves to dry summers with the help of their thick barks and wax-coated leaves which help them reduce transportation.
3. Write a short note tropical grasslands. [V. Imp.]
Answer: Tropical grasslands occur on either side of the equator and extend till the tropics. This vegetation grows in the areas of moderate to low amount of rainfall. The grass can grow very tall, about 3 to 4 metres in height. Savannah grasslands of Africa are of this type. Common animals found here are elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer and leopards.
4. Give cm account of the natural vegetation and wildlife found in the polar regions.
Answer: Polar regions are extremely cold. Therefore the growth of natural vegetation is very limited here. Only mosses, lichens and veiy small shrubs are found here. They grow during the very short summer. This is called Tundra type of vegetation. This vegetation is found in the polar areas of Europe, Asia and North America. The animals found here have thick fur and thick skin which protect them from the cold climatic conditions. Seal, walruses, musk-oxen, Arctic owl, Polar bear and snow foxes are some of the animals found in these regions.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Long Answer Questions
1. Discuss various types of forests. [V. Imp.]
Answer: Types of forests: ,
- Tropical evergreen forests
- Tropical deciduous forests
- Temperate evergreen forests
- Temperate deciduous forests
- Mediterranean vegetation
- Coniferous forests
1. Tropical evergreen forests. These forest are very dense and found in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics. These regions receive heavy rain throughout the year. The trees of these forests do not shed their leaves altogether and therefore they remain green all the time. Hardwood trees like rosewood, ebony and mahogany are found here.
2. Tropical deciduous forests. These forest are found in the regions which experience seasonal changes. Trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water. The hardwood trees like sal, teak, neem and shisham are found here. Animals like tigers, lions, elephants, langoors and monkeys are common in these forests.
3. Temperate evergreen forests. These forests are commonly found along the eastern margin of the continents. They comprise both hard and softwood trees. For example, oak, pine, eucalyptus etc.
4. Temperate deciduous forests. Trees of these forests shed their leaves in dry ‘season’. Oak, ash, beech, etc. are common trees here. Deer, foxes, wolves, etc. are common animals in these forests.
5. Mediterranean vegetation. It is mostly found in the areas around the Mediterranean sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. Citrus fruits like oranges, figs, olives and grapes are commonly cultivated in the Mediterranean regions.
6. Coniferous forests. They are also called Taiga. They are tall, softwood evergreen trees. Chir, pine, cedar is an important variety of trees in these forests. Silver, fox, mink, polar bear are the common animals found here.
2. Describe different types of grasslands. [V. Imp.]
Answer: Different types of grasslands are:
- Tropical grasslands
- Temperate grasslands
- Thorny bushes
- Tropical grasslands. This type of vegetation grows in the areas of moderate to low amounts of rainfall. The grass here can grow very tall, about 3 to 4 metres in height. Savannah grasslands of Africa are of this type. Common animals found here are elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer, leopards etc.
- Temperate grasslands. This type of vegetation is found in the mid-latitudinal zones and in the interior part of the continents. Grass here is usually short and nutritious. Common animals found in this region are wild buffaloes, bison, antelopes etc.
- Thorny bushes. These are found in the dry desert-like regions. Tropical deserts are located on the western margins of the continents, which are characterised by scarce vegetation.
Vegetation in the polar regions is also limited. Only mosses, lichens, and very small shrubs are found here. It grows during the very short summer. This is called Tundra type of vegetation. Polar animals have thick fur and thick skin which protect them from the cold climate conditions, for example, seal, walruses, musk-oxen, Arctic owl, etc.
- Chapter 1 Environment
- Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth
- Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth
- Chapter 4 Air
- Chapter 5 Water
- Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
- Chapter 7 Human Environment – Settlement, Transport, and Communication
- Chapter 8 Human Environment Interactions – The Tropical and the Subtropical Region
- Chapter 9 Life in the Temperate Grasslands
- Chapter 10 Life in the Deserts
- Chapter 1 Tracing Changes Through A Thousand Years
- Chapter 2 New Kings and Kingdoms
- Chapter 3 The Delhi Sultans
- Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire
- Chapter 5 Rulers and Buildings
- Chapter 6 Towns, Traders, and Craftsperson
- Chapter 7 Tribes, Nomads and Settled Communities
- Chapter 8 Devotional Paths to the Divine
- Chapter 9 The Making of Regional Cultures
- Chapter 10 Eighteenth-Century Political Formations
.png)
.png)