Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Solutions
You can also Download NCERT Solution Class 10 science to help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Students can also find NCERT intext, exercises and back of chapter questions. Also working on Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Solutions will be most helpful to the students to solve their Homeworks and Assignments on time. Students can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations PDF to access them even in offline mode. Not only that, but you will also have access to all the FREE PDFs of study materials and solutions along with absolutely FREE Online Tests to enhance your problem-solving speed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science provided herein are designed by our subject matter experts in a simple and precise manner.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Before getting into the details of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions And Equations, let’s have an overview of a list of topics and subtopics under Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions And Equations:
- Chemical Reactions And Equations
- Chemical Equations
- Types Of Chemical Reactions
- Have You Observed The Effects Of Oxidation Reactions In Everyday Life? Y Life?
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
- रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ और समीकरण कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Chemical Reactions and Equations Mind Map
- Chemical Equation
- Oxidation in Everyday Life
- Types of Chemical Reactions
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Intext Questions
Page Number: 6
Question 1
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air ?
Answer:
Magnesium gets covered with a layer of magnesium oxide when kept in air for a long time. This layer hinders the burning of magnesium. Hence, it is to be cleaned before burning.
Question 2
Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
(i) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(ii) 3 BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → BaSO4 + 2 AlCl3
(iii) 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2↑
Question 3
Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions :
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
(i) BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl (aq)
(ii) NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Page Number: 10
Question 1
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer:
(i) The substance whose solution in water is used for white washing is calcium oxide (or quick lime). Its formula is CaO.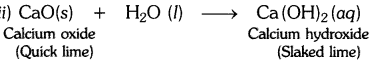
Question 2
Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in text book Activity 1.7 (i.e., electrolysis of water) double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer:
In Activity 1.7, water is electrolysed to give H2 gas at one electrode and O2 gas at the other electrode.
2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Thus two molecules of water on electrolysis give two molecules of hydrogen gas and one molecule of oxygen gas or in other words the amount of hydrogen gas collected would be double than that of oxygen gas.
Page Number: 13
Question 1
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it ?
OR
An iron nail is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate for about 30 minutes. State the change in colour observed. Give reason for the change. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer:
When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, the displacement reaction takes place. The colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate.![]()
Question 2
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10 (NCERT Text Book).
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react to form sodium chloride and water.![]()
Question 3
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances which are reduced in the following reactions.
(i) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(ii) CuO (s) + H2(g) → Cu (s) + H2O(l)
Answer:
(i) Substances oxidised is Na as it gains oxygen and oxygen is reduced.
(ii) Substances reduced is Cu as hydrogen is oxidised as it gains oxygen.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect ?
2 PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb (s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced.
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) All
Answer:
(i) (a) and (b)
Question 2
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction
(b) double displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) displacement reaction
Answer:
(d) Displacement reaction.
Question 3
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings ? Tick the correct answer :
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer:
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Question 4
What is a balanced chemical equation ? Why should chemical equations be balanced ?
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products.
The chemical equations should be balanced to satisfy the law of conservation of mass.
Question 5
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:
(a) 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) → 2NH3 (g)
(b) H2S (g) + 3O2 (g) → SO2 (g) + 2H2O(l)
(c) 3BaCl2 (aq) + Al2(SO4)3 (aq) → 2AlCl3 (aq) + 3BaSO4 ↓(s)
(d) 2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Question 6
Balance the following chemical equations :
(a) HNO3 + Ca (OH)2 → Ca (NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Answer:
(a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 7
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions :
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer:
(a) Ca (OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2 Ag
(c) 2Al + 3 CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3 Cu
(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
Question 8
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case :
(a) Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide (aq) → Potassium iodide (aq) + Barium
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g) bromide(s)
(c) Hydrogen (g) + Chloride (g) → Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid (aq) → Magnesium chloride (aq) + Hydrogen (g)
Answer:
(a) 2KBr (aq) + Bal2(aq) → 2Kl(aq) + BaBr2(s)
Type : Double displacement reaction
(b) ZnCO3 (s) → ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
Type : Decomposition reaction
(c) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g)
Type : Combination reaction
(d) Mg (s) + 2HCl (aq) → MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Type : Displacement reaction
Question 9
What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions ? Give examples.
Answer:
Exothermic reactions : Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions. An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing “+ Heat”on the products side of an equation.
Example :
(i) C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + Heat
(ii) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) + Heat
Endothermic reactions : Those reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions. An endothermic reaction is usually indicated by writing “Heat” on the product side of a chemical equation.
Examples :
(i) C (s) + 2S (s) → CS2 (l) – Heat
(ii) N2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO(g) – Heat
Question 10
Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction ? Explain.
Answer:
Respiration is an exothermic process because during respiration glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body to form carbon dioxide and water along with the production of energy.![]()
Question 11
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In a decomposition reaction, a single compound breaks down to produce two or more simpler substances.
For example: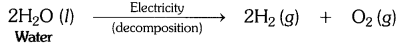
While, in a combination reaction, two or more substances simply combine to form a new substance.
For example:![]()
Question 12
Write one equation each for the decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
OR
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity. [CBSE 2015 (Delhi)]
Answer: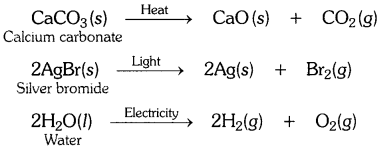
Question 13
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In displacement reactions, a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its solution. For example,
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq)
This is a displacement reaction where iron displaces copper from its solution.
In double displacement reactions, two reactants in solution exchange their ions. For example,
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3 (aq)
This is a double displacement reaction where silver nitrate and sodium chloride exchange Cl– and NO3– ions between them.
Question 14
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer:![]()
Question 15
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction ? Explain by giving examples.
Answer:
A reaction in which an insoluble solid called precipitate is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction.
Example : When a solution of iron (III) chloride and ammonium hydroxide are mixed, a brown precipitate of iron (III) hydroxide is formed.![]()
Question 16
Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each:
(a) Oxidation and
(b) Reduction.
Answer:
(a) Oxidation : The addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation.
Example :
(i) S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) (Addition of oxygen to sulphur)
(ii) 2Mg(s) + O2 (g) → 2MgO(s) (Addition of oxygen to magnesium)
(b) Reduction : The removal of oxygen from a substance is called reduction.
Example: (i) CuO + H2
Here, copper oxide is being reduced to copper because oxygen gets removed from copper oxide.
(ii) ZnO + C → Zn + CO
Here, zinc oxide is being reduced to zinc because oxygen gets removed from zinc oxide.
Question 17
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer:
Element ‘X’ is copper (Cu).
The black coloured compound is copper oxide (CuO). The reaction involved is![]()
Question 18
Why do we apply paint on iron articles ?
Answer:
Paint does not allow iron articles to come in contact with air, water and saves iron articles from damage due to rusting.
Question 19
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why ?
Answer:
To keep food items fresh and save from getting oxidised, food items are flushed with nitrogen.
Question 20
Explain the following terms with one example each (a) Corrosion, (b) Rancidity.
Answer:
(a) Corrosion : It is the process in which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid) on their surface.
Example : When iron is exposed to moist air for a long period of time, its surface acquires a coating of a brown, flaky substance called rust. Rust is mainly hydrated iron (III) oxide [Fe2O3.xH20].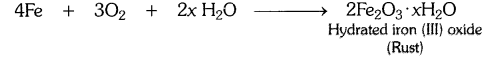
(b) Rancidity : The condition produced by aerial oxidation of fats and oils in foods marked by unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
Rancidity spoils the food materials prepared in fats and oils which have been kept for a considerable time and makes them unfit for eating.
Rancidity can be prevented by adding anti-oxidants to foods containing fats and oils. It can also be prevented by flushing fat and oil containing foods with nitrogen before sealing.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 |
| Chapter Name | Chemical Reactions and Equations |
| Number of Questions Solved | 28 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science. Here we have given Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 1.
Question 1
Which of the given statements about the reaction below are incorrect?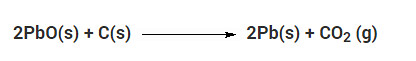
a. Lead is getting reduced
b. Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised
c. Carbon is getting oxidised
d. Lead oxide is getting reduced
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Solution:
(i) (a) and (b)
Question 2![]()
The above reaction is an example of a
(i). Combination reaction
(ii). Double displacement reaction
(iii). Decomposition reaction
(iv). Displacement reaction
Solution:
(iv) Displacement reaction
Question 3
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
a. Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced
b. Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced
c. No reaction takes place
d Iron salt and water are produced
Solution:
Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced
Question 4
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Solution:
An equation for a chemical reaction is an equation in which the number of atoms for each element in the reaction and the total charge is the same for both the reactants and the products. In other words, the mass and the charge are balanced on both sides of the reaction.
Question 5
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
a. Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia
b. Hydrogen sulfide gas burns in air to give water and sulfur dioxide
c. Barium chloride reacts with Aluminium sulfate to give Aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate
d. Potassium metal reacts with water to give a potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Solution:
a. 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
b. 2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2
c. 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4
d. 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
Question 6
Balance the following chemical equations.
a. HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
b.NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
C. NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
d. BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Solution:
a. 2HNO3 + 2Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
b. 6NaOH + 3H2SO4 → 3Na2SO4 + 6H2O
C. NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCI + NaNO3
d. BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 7
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chlorideAnswer:(a) Ca (OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2 Ag(c) 2Al + 3 CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3 Cu(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
Question 8
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction of each case.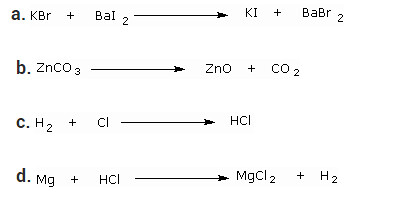
Solution:
a. 2KBr + BaI2 → 2KI + BaBr2 — Double Displacement reaction
b. ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 — Decomposition reaction
c. H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl — Combination reaction
d. Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 — Displacement reaction
Question 9
What is meant by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Solution:
An exothermic reaction is one that releases heat.
If 1 mole of N2 molecule reacts with 1 mole of O2 molecule, the heat of 184 KJ has to be supplied to initiate the reaction to give 1 mole of NO molecule. This means that the bonds between N – N and O – O are so strong that they do not break easily. N2 has triple covalent bond between the two N atoms. O2 has a double covalent bond. Thus energy has to be put into the reaction to break the strong bonds. Thus the above reaction is a good example of an endothermic reaction.
Question 10
Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction?
Solution:
During respiration, glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body to form carbon dioxide and water along with the production of energy.
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
It is an exothermic reaction, because energy is produced during this process.
Question 11
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for decomposition reactions.
Solution:
Essentially, decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions. A compound decomposes (i.e., “splits-up”) into two or more compounds and/or elements. For example, mercury (II) oxide will, decompose into mercury metal and oxygen, upon heating:
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
Since heat had to be added to make this reaction occur, it is an endothermic reaction. Most decomposition reactions are endothermic. Another example of decomposition reaction is the heating of calcium carbonate (sea shells, chalk):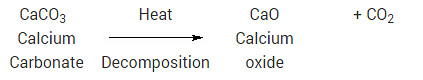
Question 12
Write one equation each for decomposition reactions in which energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity?
Solution:
When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide: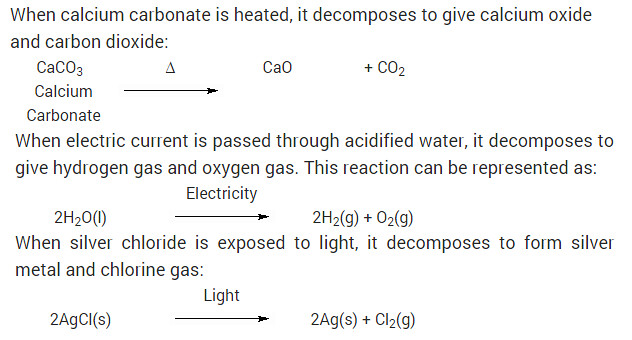
Question 13
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write relevant equations for the above?
Solution:
The difference between the displacement and double displacement reactions is that in a displacement reaction one element displaces another by virtue of it being more reactive whereas in a double displacement two anions and two cations switch places between two compounds respectively.
For example:
CuSO4 (aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4 + Cu(s)
Blue copper sulphate solution reacting with solid zinc will give rise to colourless zinc sulphate solution and solid copper. Thus Zn displaces Cu in the salt form. Zn is more reactive than Cu.
An example of double displacement reaction is the reaction between sodium carbonate and calcium chloride, both in aqueous
Solution:
Na2CO3 (aq) + CaCl2 (aq) → CaCO3 (ppt) + 2NaCl(aq)
Question 14
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involves displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Solution:![]()
Question 15
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples:
Solution:
A precipitation reaction is a reaction in which soluble ions in separate solutions are mixed together to form an insoluble compound that settles out of solution as a solid. This insoluble compound is called a precipitate.
An example of a precipitation reaction
Aqueous silver nitrate (AgNO3), when added to a solution containing potassium chloride (KCl), precipitates a white solid, and silver chloride is observed.
AgNO3 (aq) + KCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq)
The silver chloride (AgCl) has formed a solid, which is observed as a precipitate.
Question 16
A shiny brown colored element ‘X’ on heating in the air becomes black in color. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Solution:
The shiny brown colored element X is copper metal (Cu). When copper metal is heated in air, it forms a black colored compound copper oxide. So, the black colored compound is the copper oxide or copper (II) oxide, CuO.
Question 17
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Solution:
Rust is a soft and porous substance, which gradually falls from the surface of an iron object, and then the iron below starts rusting. Thus, rusting of iron (or corrosion of iron) is a continuous process which, if not prevented in time, eats up the whole iron object. So, when we apply paint on iron articles it reduces the rusting of iron.
Question 18
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Solution:
Packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas can prevent rancidity. When the fat and oil present in food materials gets oxidised (in air), their oxidation products have an unpleasant smell and taste. When it is surrounded by unreactive gas, nitrogen, there is no oxygen (of air) to cause its oxidation and make it rancid.
Question 19
Explain the following terms with one example each.
a. Corrosion
b. Rancidity
Solution:
a. Corrosion is the process in which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical on their surface. Corrosion is caused mainly by the oxidation of metals by the oxygen of air.
Example: Rusting of iron is the most common form of corrosion. When an iron object is left in damp air for a considerable period of time, it gets covered with a red-brown flaky substance called ‘rust’. This is called rusting of iron.
b. The condition produced by aerial oxidation of fat and oil in food which is marked by an unpleasant smell and taste is called rancidity.
Example: Rancidity can be retarded by keeping food in a refrigerator.
The refrigerator has a low temperature inside it. When the food is kept in a refrigerator, the oxidation of fat and oil in it is slowed down due to low temperature. So, the development of rancidity due to oxidation is retarded.
Question 20
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Solution:
To remove the oxide layer and facilitates rapid burning.
Question 21
Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions.
i. Hydrogen + Chloride → Hydrogen chloride
ii. Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
iii. Sodium + water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Solution:
i. H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
ii. 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 3BaSO4 + 2AlCl3
iii. 2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
Question 22
Write a balanced chemical equation and state symbols for the following reactions.
a. Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride
b. Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Solution: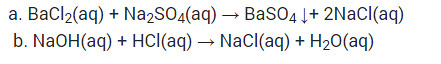
Question 23
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for white washing.
Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(i) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X; named in (ii) above with water
Solution:
Question 24
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped into it?
Solution:
In this reaction, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The deep blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of light green solution of iron sulphate. A red-brown coating of copper metal is formed on the surface of the iron metal. This displacement reaction occurs because iron is more reactive than copper.
Question 25
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions.
i. 4Na(s) + O2 (g) → 2Na2O(s)
ii. CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Solution:
i. 4Na(s) + O2 (g) → 2Na2O(s)
Here oxygen is added to sodium. The addition of oxygen is Called oxidation. So the substance that is oxidized is sodium Na.
ii. CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
In this reaction, copper oxide (CuO) gives the oxygen required for the oxidation of hydrogen; therefore, copper oxide is the oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is responsible for removing oxygen from copper oxide; therefore, hydrogen is the reducing agent here.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Question 1.
When crystals of lead nitrate are heated strongly in a dry test tube
(a) crystals immediately melt
(b) a brown residue is left
(c) white fumes appear in the test tube
(d) a yellow residue is left
Answer:
(b)Pungent smelling, brown fumes are evolved due to NO2 gas and brown coloured residue of lead oxide (PbO) is left.![]()
Question 2.
A dilute ferrous sulphate solution was gradually added to the beaker containing acidified permanganate solution. The light purple colour of the solution fades and finally disappears. Which of the following is the correct explanation for the observation? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) KMnO4 is an oxidising agent, it oxidises FeSO4
(b) FeSO4 acts as an oxidising agent and oxidises KMnO4
(c) The colour disappears due to dilution, no reaction is involved
(d) KMnO4 is an unstable compound and decomposes in the presence of FeSO4 to a colourless compound
Answer:
(a)Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in the presence of dil. H2SO4, i.e. in acidic medium, acts as a strong oxidising agent. In acidic medium, KMnO4 oxidises ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate.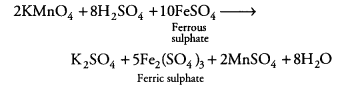
Question 3.
Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc taken in a test tube. The following observations are recorded. Point out the correct observation.
(a) The surface of metal becomes shining
(b) The reaction mixture turns milky
(c) Odour of a pungent smelling gas is recorded
(d) A colourless and odourless gas is evolved
Answer:
(d)Zinc metal reacts with dil. HCl to form zinc chloride and bubbles of colourless and odourless hydrogen gas is evolved.![]()
Question 4.
When a magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, the ash formed is
(a) black
(b) white
(c) yellow
(d) pink
Answer:
(b)When a Mg ribbon is burnt in air, the ash formed is of magnesium oxide which is white in colour.
2Mg(r) + O2(g) → 2MgO(f)
Question 5.
Three beakers labelled as A, B and C each containing 25 mL of water were taken. A small amount of NaOH, anhyd. CuSO4 and NaCl were added to the beakers A, B and C, respectively. It was observed that there was an increase in the temperature of the solutions contained in beakers A and B whereas, in case of beaker C, the temperature of the solution falls. Which one of the following statements is/are correct?
I. In beakers A and B, exothermic process has occurred.
II. In beakers A and B, endothermic process has occurred.
III. In beaker C, the exothermic process has occurred.
IV. In beaker C, endothermic process has occurred. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) I and IV
(d) II and III
Answer:
(c)As in case of beakers A and B, heat is given out, so temperature became high, hence it is an exothermic reaction while in beaker C, heat is absorbed from water, so temperature falls, hence it is an endothermic process.
Question 6.
Which of the following will be required to identify the gas evolved when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc metal?
(a) Red litmus paper
(b) pH paper
(c) Lime water
(d) A burning splinter
Answer:
(d)On reacting with dil. HCl, zinc metal forms zinc chloride and hydrogen gas is evolved. Presence of hydrogen gas can be checked by a burning splinter because H4 gas burnt in a splinter with a pop sound.![]()
Question 7.
On immersing an iron nail in CuSO4 solution for few minutes, you will observe that
(a) no reaction takes place
(b) the colour of solution fades away
(c) the surface of iron nails acquire a black coating
(d) the colour of solution changes to green
Answer:
(b)Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
Fe is present above in the reactivity series of metals. Hence, Fe displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution. And the colour of the solution fades away. This is an example of displacement reaction.
Question 8.
What happens when ferrous sulphate crystals are heated? [CCE 2014]
(a) A gas having the smell of burning sulphur is evolved
(b) No gas is evolved
(c) Brown coloured gas is evolved
(d) Colourless and odourless gas is evolved
Answer:
(a)The green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals changes to brownish black ferric oxide and smell of burning sulphur is evolved due to SO2 and SO3.![]()
Question 9.
The colour of the precipitate formed when barium chloride solution is mixed with sodium sulphate solution is [CCE 2014]
(a) blue
(b) black
(c) white
(d) green
Answer:
(c)This is an example of a double displacement reaction and a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.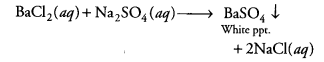
Question 10.
How the colour changes when the gases after thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate come in contact with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate?
(a) Green to orange
(b) Red to colorless
(c) Orange to green
(d) Blue to green
Answer:
(c) The color changes from orange to green due to the formation of iron (III) sulphate
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations (Hindi Medium)

















Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Mind Map
Chemical Equation
The representation of chemical reaction by means of symbols of substances in the form of formulae is called chemical equation.
For example N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation has equal number of atom of each element participating in the reaction on both left and right hand sides of the reaction.
According to Law of Conservation of Mass, total mass of the elements present in the products of a chemical reaction has to be equal to the total mass of the element present in the reactants.
Balancing Of A Chemical Equation
Total No of Atoms on R.H.S = Total no of Atoms on L.H.S.
Fe3O4 T H2 → Fe + H20
[Fe] Fe3O2 + H2 → 3Fe + H20
[0] Fe3O4 + H2 → 3Fe + 4H20
[H] Fe3O4 + 4H2 → 3Fe + 4H20
Oxidation In Everyday Life
Rusting
When iron reacts with oxygen and moisture it forms a red substance called rust.
Corrosion
Metals on coming in contact with oxygen, water, acids or gases presents in air changes its surface. This is called corrosion for e.g. black coating on silver and green coating on copper.
Prevention – painting, galvanization, oiling, greasing
Rancidity
Oil and fats on exposure to air show a change in taste and smell. This property is known as rancidity.
Prevention – adding antioxidants, Vacuum packing, refrigeration, flushing food with nitrogen
Types Of Chemical Reactions
The transformation of chemical substance into a new chemical substance by making and breaking of bonds between different atom is known a chemical reaction.
Combination Reaction
When two elements or one compound and one element or two compounds combine to form a new product.
Foi example
• H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
• Zn + CuS04 → ZnS04 + Cu
• NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
Exothermic Reactions
Reactions producing energy are called exothermic reactions.
Most of the combination reactions are exothermic in nature.
For example : CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + Heat
Oxidation
Gain of oxygen or removal of hydrogen is called oxidation eg.
• Zn + O2 → ZnO
• Mn + HCl → MnCl2 + H2
Reduction
Gain of hydrogen or removal of oxygen is called reduction.
e.g. CuO + H2 → Cu + H20
Redox Reactions
A chemical reaction in which both oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously are called redox reactions.
For example
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Decomposition Reaction
When a compound-split into two or more simple products for example![]()
Decomposition reaction require energy either in the form of heat, light or electricity for decomposing the reactions
Endothermic Reactions
Reactions which require energy to occur are known as endothermic reactions.
For example:![]()
Displacement Reactions
It takes place when a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal. For Example:
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Double Displacement Reactions
In this reactions ions are exchanged between two reactants and forming new compounds.
Precipitation Reaction :
In some reactions, an insoluble mass is formed which is known as precipitate and such reactions are called precipitation reaction.
For Example
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → 2NaCl + BaSO4 Precipitate
Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 1 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Students can get comprehensive practice of balancing different kinds of equations.
- Find out how to create a balanced chemical equation and learn about chemical reactions with CBSE Class 10 Chemistry learning resources.
- NCERT Solution will help you write different chemical equation appropriately Helps you get thorough practice of solving questions of varied difficulty before facing the main examination.
- Our comprehensive set of study materials acts as a perfect guide when doing homework and preparing for the examination.
- On LearnCBSE.in, our experts support you to understand chemistry with CBSE Class 10 Chemistry such as CBSE Class 10 Chemistry notes, MCQs and NCERT solutions as per the latest syllabus.
With LearnCBSE.in NCERT Solutions Learning App in your Mobile, you will get to attend FREE LIVE Master – Classes and FREE Conceptual videos. Get 100 percent accurate NCERT Book Solution for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 (Chemical Reactions and Equations) explained by expert Science teachers.
Thorough knowledge and good practice will help you score full marks on the questions asked in this chapter. Learning the fundamentals of Chemistry in CBSE Class 10 is now easy.
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding NCERT Solutions for 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and we hope this detailed NCERT Solutions are helpful. Students can also check out NCERT Books, CBSE Syllabus, CBSE Sample Papers, RD Sharma Solutions at LearnCBSE.in for free.
Important Questions of Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Chapter 1
Question 1.
Identify ‘x’, ‘y’ and ‘z’ in the following reaction :![]()
(a) x = gas; y = reaction condition; z = gas
(b) x = solid; y = liquid; z = gas
(c) x = number of moles of KClO3; y = reaction condition; z = number of molecules of oxygen
(d) x = physical state of KClO3 and KCl;
y = reaction condition, z = physical state of O2. (2020)
Answer:![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Following is a balanced chemical equation for the action of steam on iron : 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Reason (R): The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical equation.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. (2020)
Answer:
A balanced chemical equation must obey the law of conservation of mass.
Question 3.
(a) State the law that is followed by balancing a chemical equation.
(b) Balance the following chemical equation: Na + H3O → NaOH + H2 (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Law of conservation of mass is followed for balancing a chemical equation which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. That is, the total mass of the elements present in the products of a chemical reaction has to be equal to the total mass of the elements present in the reactants in a balanced equation.
(b) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Question 4.
Explain the significance of photosynthesis.
Write the balanced chemical equation involved in the process. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Photosynthesis means synthesis with the help of light. It is the process that gives life to all living beings.
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants utilize carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen.![]()
Question 5.
Write balanced chemical equations for the following chemical reactions:
(a) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(b) Lead + Copper chloride → Lead chloride + Copper
(c) Zinc oxide + Carbon → Zinc + Carbon monoxide (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(a) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
(b) Pb(s) + CuCl2(aq) → PbCl2(aq)+ Cu(s)
(c) ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Question 6.
Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
This reaction can be classified as
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Exothermic reaction
(C) Endothermic reaction
(D) Oxidation reaction
Which of the following is a correct option? (2020)
(a) (A) and (C)
(b) (C) and (D)
(c) (A), (C) and (D)
(d) (A) and (B)
Answer:
(d) The reaction between CaO and H2O to form Ca(OH)2 is an exothermic combination reaction.
Question 7.
When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a (2020)
(a) combination reaction
(b) displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) double displacement reaction.
Answer:
(d) CuSO4 + H2S → CuS + H2SO4
It is a double displacement reaction as in this reaction CuSO4 and H2S reacting by exchange of Cu2+ and H+ ions to from two new compounds i.e., CuS and H2SO4.
Question 8.
In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution :
(A) exchange of atoms takes place
(B) exchange of ions takes place
(C) a precipitate is produced
(D) an insoluble salt is produced
The correct option is (2020)
(a) (B) and (D)
(b) (A) and (C)
(c) only (B)
(d) (B), (C) and (D)
Answer:
(d) In this reaction exchange of Na+ and Ba2+ ions takes place forming BaSO4 which is a white precipitate i.e., an insoluble salt.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 ↓+ 2NaCl
Question 9.
In which of the following, the identity of initial substance remains unchanged? (2020)
(a) Curdling of milk
(b) Formation of crystals by process of crystallisation
(c) Fermentation of grapes
(d) Digestion of food
Answer:
(b): Formation of crystals is a physical change rest others are chemical change.
Question 10.
Study the following equation of a chemical reaction: (Board Term 1, 2015)
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
(i) Identify the type of reaction.
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation of another example of this type of reaction.
Answer:
(i) Combination reaction.
(ii) Another example of combination reaction is![]()
Question 11.
State the type of chemical reactions, represented by the following equations : (Board Term I, 2014)
(a) A + BC → AC + B
(b) A + B → C
(c) PQ + RS → PS + RQ
(d) A2O3 + 2B → B2O3 + 2A
Answer:
(a) Displacement reaction.
(b) Combination reaction.
(c) Double displacement reaction.
(d) Displacement reaction or redox reaction.
Question 12.
1 g of copper powder was taken in a China dish and heated. What change takes place on heating? When hydrogen gas is passed over this heated substance, a visible change is seen in it. Give the chemical equations of reactions, the name and the colour of the products formed in each case. (2020)
Answer:
When copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance which is copper oxide.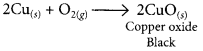
When hydrogen gas is passed over CuO, the black coating on the surface turned reddish brown due to the formation of Cu.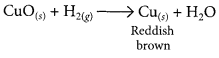
Question 13.
A compound ‘A’ is used in the manufacture of cement. When dissolved in water, it evolves a large amount of heat and forms compound ‘B’.
(i) Identify A and B.
(ii) Write chemical equation for the reaction of A with water.
(iii) List two types of reaction in which this reaction may be classified. (2020)
Answer:
(i) A is calcium oxide, CaO which is used in the manufacturing of cement.
B is calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)3.![]()
(iii) The given reaction is a combination reaction.
Example : NH3(g)(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(s)
2NO(g) + 02(g) → 2NO2(g)
Question 14.
Mention with reason the colour changes observe when:
(i) silver chloride is exposed to sunlight.
(ii) copper powder is strongly heated in the presence of oxygen.
(iii) a piece of zinc is dropped in copper sulphate solution. (2020)
Answer:
(i) When white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight, its colour changes to grey as it decomposes to silver in the presence of sunlight.![]()
This type of reaction is called photodecomposition reaction.
(ii) When copper powder is strongly heated in presence of oxygen, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance which is copper oxide.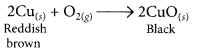
(iii) When a piece of zinc is dropped in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and reddish brown copper metal gets deposited on zinc piece.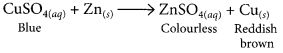
Question 15.
Lead nitrate solution is added to a test tube containing potassium iodide solution.
(a) Write the name and colour of the compound precipitated.
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
(c) Name the type of this reaction justifying your answer. (2020)
Answer:
(a) When lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide then yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed along with potassium nitrate.
(b) Balanced chemical reaction is as follows :![]()
(c) This type of reaction is called precipitation reaction in which one of the products formed is an insoluble substance or this is also called double displacement reaction.
Question 16.
2 g of silver chloride is taken in a China dish and the China dish is placed in sunlight for sometime. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Refer to answer 14(i).
Question 17.
Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(a) It is a displacement reaction.![]()
(b) Refer to answer 15.
Question 18.
2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube. (Al 2019, Board Term 1, 2017, 2016)
(a) List any two observations.
(b) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(c) Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the products formed.
Answer:
(a) Ferrous sulphate crystals (FeSO4.7H2O) lose water when heated and the colour of the crystals changes. It then decomposes to ferric oxide (Fe2O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2) and sulphur trioxide (SO3) with a smell of burning sulphur.
(b) This is a thermal decomposition reaction.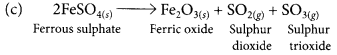
Question 19.
You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance. (AI 2019)
(a) Why has this black substance formed?
(b) What is the black substance?
(c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
(d) How can the black coating on the surface be turned reddish brown?
Answer:
(a) The black substance is formed because copper combines with oxygen.
(b) The black substance is copper oxide (CuO).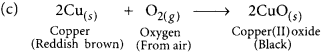
(d) The black coating on the surface can be turned reddish brown by passing hydrogen gas over the hot copper oxide.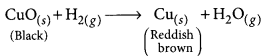
Question 20.
Decomposition reactions require energy either in the form of heat or light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light and electricity. (2018)
Answer:
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of heat:![]()
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of light:![]()
Decomposition reaction involving absorption of electrical energy:![]()
Question 21.
Take 3 g of barium hydroxide in a test tube, now add about 2 g of ammonium chloride and mix the contents with the help of a glass rod. Now touch the test tube from outside.
(i) What do you feel on touching the test tube?
(ii) State the inference about the type of reaction occurred.
(iii) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(i) When barium hydroxide is added into ammonium chloride, the bottom of test tube is found to be cooler.
(ii) It is an endothermic reaction.
(iii) Ba(OH)2 + 2NH4Cl → BaCl2 + 2NH4OH
Question 22.
(a) A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of the chemical reaction.
(b) Ferrous sulphate when heated, decomposes with the evolution of a gas having a characteristic odour of burning sulphur. Write the chemical reaction involved and identify the type of reaction. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(a)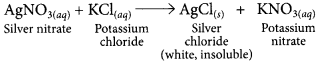
It is a double displacement reaction.
(b) Refer to answer 18(b) and (c).
Question 23.
Name the type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation: (Board Term I, 2016)
(i) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(ii) 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4![]()
Answer:
(i) Combination reaction.
(ii) Precipitation reaction or double displacement reaction.
(iii) Thermal decomposition reaction.
Question 24.
What is a reduction reaction?
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions. (Board Term I, 2015)
(a) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(b) 2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2
Answer:
Those reactions in which addition of hydrogen to a substance or removal of oxygen from a substance take place are called reduction reactions.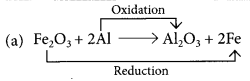
Fe2O3 is getting reduced to Fe and Al is getting oxidised to Al2O3.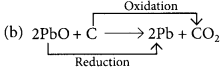
PbO is reduced to Pb and C is oxidised to CO2.
Question 25.
(a) Can a displacement reaction be a redox reaction? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Write the type of chemical reaction in the following:
(i) Reaction between an acid and a base
(ii) Rusting of iron. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(a) Consider the following displacement reaction:
Zn(s)+ CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Here, Zn has changed into ZnSO4 (i.e., Zn2+ ions) by loss of electrons. Hence, Zn has been oxidised. CuSO4 (i.e., Cu2+) has changed into Cu by gain of electrons. Hence, CuSO4 has been reduced. Thus, the above reaction is a displacement reaction as well as a redox reaction.
(b) (i) Neutralisation reaction
(ii) Oxidation reaction.
Question 26.
Mention the type of chemical reaction that takes place when: (Board Term I, 2013)
(i) a magnesium ribbon is burnt in air.
(ii) limestone is heated.
(iii) silver bromide is exposed to sunlight.
(iv) electricity is passed through acidified water.
(v) ammonia and hydrogen chloride are mixed with each other.
Write the chemical equation for each reaction.
Answer:![]()
This is a combination reaction.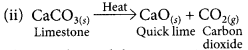
This is a thermal decomposition reaction.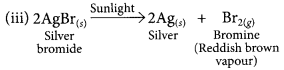
This is a photo decomposition reaction.![]()
This is electrolytic decomposition reaction.![]()
This is a combination reaction.
Question 27.
What happens when food materials containing fats and oils are left for a long time? List two observable changes and suggest three ways by which this phenomenon can be prevented. (2020)
Answer:
Food materials containing fats and oils change their taste and smell due to a process called rancidity. Rancidity is a process in which air reacts with fats and oils which changes the smell and taste of food.
Methods of prevention:
Vacuum packing,
refrigeration of food materials,
placing of food materials, away from direct sunlight.
Question 28.
(i) Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction?
(ii) Write chemical name and the formula of the brown gas produced during thermal decomposition of lead nitrate.
(iii) Why do chips manufactures flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen? (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
(i) The glucose produced in our body during digestion combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides energy. The special name of this reaction is respiration. Thus respiration is an exothermic process because energy is produced during this process.
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) + Energy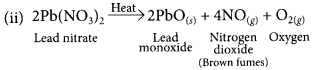
Brown gas evolved is nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
(iii) Chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen because atmospheric oxygen can react with chips which may cause change in colour, change in taste. So to cut the contact between air and the chips, nitrogen gas is used which do prevent its oxidation.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2015
29.“We need to balance a skeltal chemical equation.” Give reason to justify the statement.
Answer:
Skeltal chemical equation are unbalanced. We need to balance chemical equation because of law of conservation of mass. It states that ‘matter can neither be created nor be destroyed’. Therefore chemical equation must be balanced in each and every chemical reaction.
30. Name the reducing agent in the following reaction:
3MnO2 + 4Al———— > 3Mn + 2Al2O3
State which is more reactive, Mn or A1 and why?
Answer. ‘Al’ is reducing agent.
‘AT is more reactive than Mn v ‘Al’ displaces Mn from its oxide.
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2015
31.A Name the type of chemical reaction represented by the following equation: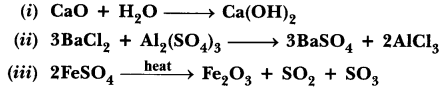
Answer.
(i) Combination reaction
(ii) Double displacement reaction (Precipitation reaction)
(iii) Decomposition reaction.
32. Write the chemical equation of the reaction in which the following changes have taken place with an example of each:
(i) Change in colour
(ii) Change in temperature
(iii) Formation of precipitate
Answer.
(i)Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq)———–> Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag
The solution will become blue in colour and shiny silver metal will be deposited.
(ii) NaOH + HCl ———–> NaCl + H2O+ heat
The temperature will increase because heat will be evolved.
(iii) Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq)———–> Pbl2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
Yellow ppt
Yellow precipitate of Pbl2will be formed.
33.State the type of chemical reactions and chemical equations that take place in the following:
(i) Magnesium wire is burnt in air.
(ii) Electric current is passed through water.
(iii) Ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases’are mixed.
Answer.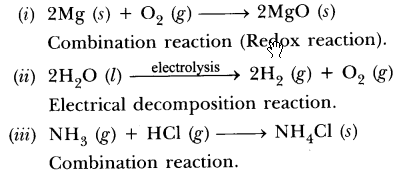
34. 2g of ferrous sulphate crystals are heated in a dry boiling tube.
(i) List any two observations.
(ii) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place.
(iii) ‘Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer.
(i) •Green colour of Fe SO4 disappears and reddish brown solid is formed.
• Smell of burning sulphur.
(ii) Decomposition reaction![]()
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2015
35. (a) Define a balanced chemical equation. Why should an equation be balanced?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
(i) Phosphorus burns in presence of chlorine to form phosphorus penta chloride.
(ii) Burning of natural gas.
(iii) The process of respiration.
Answer.
(a) Balanced chemical equation has an equal number of atoms of different elements in the reactants and products. According to law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created nor be destroyed in a chemical reaction.
(b)(i) P4 (s) + 10Cl2 (g) ———> 4PCl5 (S)
(i)CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) ———> CO2 (g) + 2H2O(l) + heat energy
(iii) C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) + 6H2O ———> 6CO2 (aq) + 12H2O (l) + energy
36.(a) Explain two ways by which food industries prevent rancidity.
(b) Discuss the importance of decomposition reaction in metal industry with three points.
Answer.
(a) (i) Rancidity can be prevented by adding antioxidants to food containing
fat and oil, e.g. butylated hydroxy anisole is added to butter as antioxidant.
(ii) It can be prevented by packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas.
(b) (i) Molten NaCl is electrolytically decomposed to form sodium metal.
(ii) Aluminium metal is obtained by electric decomposition of bauxite ore mixed with cryolite.
(iii) Carbonate ores are thermally decomposed to give metal oxide which on reduction give metal.
Short Answer Type Question[I] [2 Marks] -Year 2014
37. What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead nitrate? Name the type of reaction. Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above chemical reaction.
Answer.Yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed. It is precipitation reaction.
Pb( NO3)2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) —-> Pbl2 (s) + 2KNO3 (aq)
It is also called double displacement reaction.
short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2014
38.Write chemical equation reactions taking place when carried out with the help of
(a) Iron reacts with steam
(b) Magnesium reacts with dil HCl
(c) Copper is heated in air.
Answer.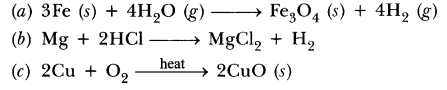
Long Answer Type Question [5 Marks] -Year 2014
39.(a) Write one example for each of decomposion reaction carried out with help of
(i) Electricity (ii) Heat (iii) Light
(b) Which of the following statements is correct and why copper can displace silver from silver nitrate and silver can displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
Answer.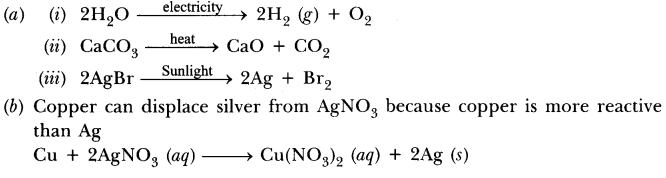
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2013
40. What is meant by skeltal type chemical equation? What does it represent? Using the equation for electrolytic decomposition of water, differentiate between a skeltal chemical equation and a balanced chemical equation.
Answer. The equations in which gaseous are written in atomic form instead of molecular form and equation is not balanced, are called skeltal type equation. They represent gaseous elements formed in atomic state and equation is not balanced
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks]-Year 2012
41.Identify the type of reaction(s) in the following equations.
(i)CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2 H2O
(ii) Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI ——–>Pbl2 + 2KNOs
(iii) CaO + H2O ——–> Ca(OH)2
(iv) CuSO4 + Zn ——–> ZnSO4 + Cu
Answer.
(i) Combustion reaction and oxidation reaction.
(ii)Double displacement reaction and precipitation reaction.
(iii) Combination reaction.
(iv) Displacement reaction.
42.What is the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this colour change after heating?
Answer.The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green. The colour changes to reddish brown on heating due to formation of iron (III) oxide.
Give an example each for thermal decomposition and photochemical decomposition reactions. Write relevant balanced chemical equations also.
Thermal decomposition reaction: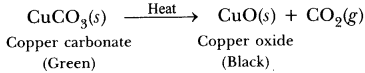
Photochemical decomposition reaction:![]()
43. Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it? Write two observations.
Answer. It is because displacement reaction takes place.
Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution and forms pale green
coloured solution of FeS04 and reddish brown copper metal gets deposited.
Fe(s) + CuS04(aq) ——–> FeS04(aq) + Cu(s)
44. Translate the following statement into chemical equation and then balance it Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate. State the two types in which this reaction can be classified.
Answer. 3BaCl2(aq) + A12(S04)3(aq) ——–> 3BaS04(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
It can be classified as double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.
45. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer. In decomposition reaction, a compound is broken down into simpler compounds or elements, e.g.![]()
Combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more elements or compounds combine to form a new compound, e.g.![]()
Thus, decomposition and combination reactions are opposite to each other.
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2012
46. What is rancidity? Mention any two ways by which rancidity can be prevented.
Answer. The process in which taste and smell of food gets spoiled is called rancidity. It happens due to oxidation.
Prevention from rancidity:
(i) Antioxidants are added to fatty acids to prevent oxidation, e.g. chips are packed in presence of nitrogen gas which prevents spoilage by oxidation.
(ii)Food should be kept in airtight container in refrigerator.
47.Write balanced chemical equation for the reactions that take place during respiration. Identify the type of combination reaction that takes place during this process and justify the name. Give one more example of this type of reaction.
Answer. CgH1206 + 6O2 —————> 6CO2 + 6H20 + heat
It is an exothermic combination reaction because heat is evolved.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) ————–>CO2 (g) + 2H20
Combustion of methane is another example of exothermic combination reaction.
48. What is redox reaction? Identify the substance oxidised and the substance reduced in the following reactions.
(i)2PbO + C —–> 2Pb + CO2
(ii)MnO2 + 4HCl —–> MnCl2 + 2H20 + Cl2
Answer. Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously are called redox reactions.
(i) PbO is getting reduced and C is getting oxidised.
(ii) MnOs is getting reduced and HCl is getting oxidised.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2011
49.State one basic difference between a physical change and a chemical change.
Answer. In physical change, no new substance is formed, whereas in a chemical change, new substance(s) is/are formed.
50. What is meant by a chemical reaction?
Answer. The reaction representing a chemical change is called a chemical reaction.
35.AgN03(aq) + NaCl(aq)——————– > AgCl(s)4↓ + NaN03(aq)
FeS + H2S04————- > FeS04 + H2S↑
Consider the above mentioned two chemical equations with two different kinds of arrows (↑and ↓) along with product. What do these two different arrows indicate?
Ans,↑shows the gas is evolved whereas ↓shows insoluble substance (precipitate) is formed.
51. Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water which is a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why?
Answer. It is because properties of compound (H2O) are different from properties of its constituting elements, i.e. H2and O2.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2011
52.Using a suitable chemical equation, justify that some chemical reactions are determined by:
(i) change in colour, (ii) change in temperature.
Answer.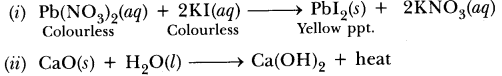
53.(a) A solution of substance ‘X’ is used for white washing. What is the substance ‘X’? State the chemical reaction of ‘X’ with water.
(b) Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer.
(a) ‘X’ is calcium oxide (CaO).
CaO(s) + H2O(l) —–> Ca(OH)2(aq) + heat
(a) It is because iron displaces copper from CuS04 to form FeS04 which is pale green.
Fe(s) + CUS04 (aq)—–> FeS04(aq) + Cu(s)
Blue Pale green
54.Write the balanced equation for the. following reaction and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(i) Potassium bromide + Barium iodide—-> Potassium iodide + Barium bromide.
(ii) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g)—-> Hydrogen chloride(g)
Answer.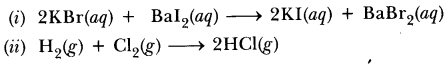
55. A zinc plate was put into a solution of copper sulphate kept in a glass container. It was found that blue colour of the solution gets fader and fader with the passage of time. After few days, when zinc plate was taken out of the solution, a number of holes were observed on it.
(i) State the reason for changes observed on the zinc plate.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer.
(i) It is because zinc has displaced copper from CuS04. Zinc metal has been used to form zinc sulphate, therefore, number of holes were observed.![]()
56. A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and a residue is left behind.
(i) Name the salt.
(ii) Write the equation for the decom-position reaction.
Answer.
(i) Lead nitrate is white salt.![]()
57. When a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate in a test tube, a reaction takes place.
(a) What type of reaction is this?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the above reaction.
Answer.
(a) Double displacement as well as precipitation reaction.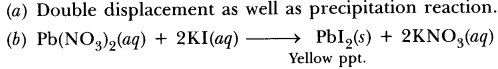
58. Write balanced equations for the following mentioning the type of reaction involved.
(i) Aluminium + Bromine —–> Aluminium bromide
(ii) Calcium carbonate—–> Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide
(iii) Silver chloride—–>Silver + Chlorine
Answer.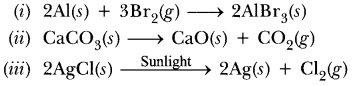
59.(a) Why is respiration considered as an exothermic reaction?
(b) Define the terms oxidation and reduction.
(c) Identify the substance that is oxidised and reduced in the following reaction.![]()
Answer. (a) It is because heat is evolved during respiration.
(b) Oxidation is a process in which O2 is added or H2 is removed or loss of electrons take place. Reduction is a process in which H2 is added or O2. is removed or gain of electrons take place.
(c) Zn is getting oxidised, CuO is getting reduced.
60.You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black colour substance.
(i) How has this black coloured substance formed?
(ii) What is that black substance?
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
Answer.
(i) Copper reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide which is black, i.e. oxidation of copper takes place.
(ii)Copper oxide![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2010
61. What happens chemically when quicklime is added to water filled in a bucket?
Answer. Quicklime reacts with water to form slaked lime and produces lot of heat and hissing sound.
62. On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
Answer. A chemical reaction is balanced on the basis of law of conservation of mass.
63. What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight? State the type of chemical reaction in this change.
Answer. Silver chloride becomes grey. It is a photochemical decomposition reaction.
64. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium chloride
and silver nitrate indicating the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Answer.![]()
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks]
65. What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride? State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction.
Answer. White precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
If both reactants are in solid state, then the reaction will not take place between them.![]()
It is a double displacement as well as a precipitation reaction.
66. What is a redox reaction? When a magnesium ribbon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash, is magnesium oxidised or reduced? Why?
Answer. The reactions in which oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons) take place simultaneously are called redox reactions.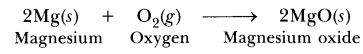
Magnesium is getting oxidised because it is losing electrons to form Mg2+ and oxygen is gaining electrons to form O2-, therefore it is getting reduced.
67. Write any two observations in an activity which may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give an example in support of your answer.
Answer. Any two of these observations will suggest chemical reaction has taken place.
(i) Change in state.
(ii)Change in colour.
(iii) Evolution of gas.
(iv)Change in temperature.
For example, lead nitrate is white crystalline solid which on heating gives yellowish brown solid (lead monoxide). A brown gas and a colourless gas is also evolved. It shows chemical reaction has taken place.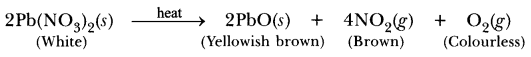
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2009
68.In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
Answer.It is because water contains hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2 : 1.
69.Balance the following chemical equations.
Answer.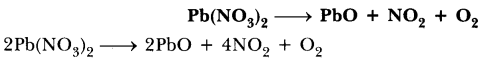
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2009
70. Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this change?
Answer.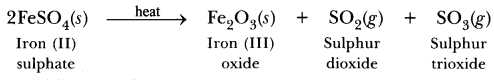
It is decomposition reaction.
71. What is an oxidation reaction? Give an example of oxidation reaction. Is oxidation an exothermic or an endothermic reaction?
Answer. The reaction in which oxygen or electronegative element is added or hydrogen or electropositive element is removed or loss of electrons takes place, is called an oxidation reaction, e.g. ,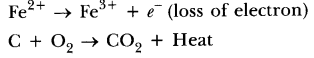
Oxidation reactions are mostly exothermic in nature because heat is evolved in this process.
72. Describe an activity to demonstrate the change that takes place when white silver chloride is kept in sunlight. State the type of chemical reaction which takes place.
Answer.
Aim: To demonstrate the change that takes place when white silver chloride is kept in sunlight.
Materials Required: AgNO3(aq), NaCl(aq), test tubes.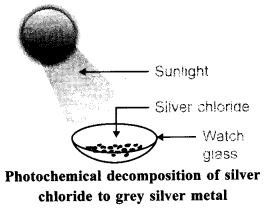
Procedure:
1. Take 5 ml of silver nitrate solution in a test tube.
2. Prepare sodium chloride solution in another test tube.
3. Add sodium chloride solution into test tube containing silver nitrate solution.
4. Observe the colour of silver chloride formed chloride to grey silver metal Dry it with the help of filter papers and place it on the watch glass.
5. Place the watch glass under sunlight for sometime.
6. Observe the colour of the silver chloride after sometime. Observation: White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because silver metal is formed.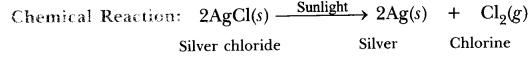
Explanation: Silver chloride is photosensitive. It decomposes in presence of sunlight to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
Conclusion: Decomposition of silver chloride in presence of sunlight is photochemical decomposition reaction.
73.When magnesium ribbon burns in air or oxygen, a product is formed. State the type of chemical reaction and name the product formed in the reaction. Write balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Answer.
![]()
The type of reaction is combination reaction and the product formed is magnesium oxide.
74.Distinguish between a displacement reaction and a double displacement reaction. Identify the displacement and the double displacement reaction from the following reactions.
Answer.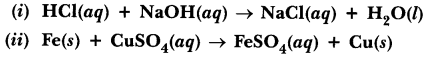
Displacement reaction is a reaction in which more reactive metal can displace less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Double displacement reaction are those reactions in which compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds (?) Double displacement reaction (ii) Displacement reaction
75.When you have mixed the solutions of lead(II) nitrate and potassium iodide,
(i) what was the colour of the precipitate formed and can you name the precipitate?
(ii) write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(iii) is this also a double displacement reaction?
Answer.
(i) The colour of the precipitate is yellow. The name of compound formed as a precipitate is Pbl2 (lead iodide).![]()
(iii) Yes, it is also a double displacement reaction.
76.What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer.Exothermic reactions are those in which heat is evolved, e.g.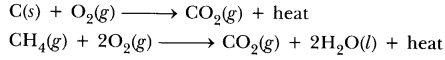
Endothermic reactions are those reactions in which heat is absorbed, e.g.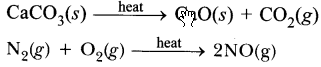
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reactions and Equations: Balanced and unbalanced chemical equations and balancing of chemical equations.
What is a chemical reaction Class 10?
Chemical Reaction: The transformation of chemical substance into another chemical substance is known as Chemical Reaction. For example: Rusting of iron, the setting of milk into curd, digestion of food, respiration, etc.
In a chemical reaction, a new substance is formed which is completely different in properties from the original substance, so in a chemical reaction, a chemical change takes place.
Only a rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemical reaction.
- The substances which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
- The new substances produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called products.
Example: The burning of magnesium in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of a chemical reaction.
2Mg(s) + O2(g)
Before burning in air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with sandpaper.
This is done to remove the protective layer of basic magnesium carbonate from the surface of the magnesium ribbon.
Reactant: Substances which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
Example: Mg and O2.
Product: New substance formed after a chemical reaction is called a product.
Example: MgO.
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions :
(i) Evolution of gas: The chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid is characterised by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) ↑
(ii) Change in Colour: The chemical reaction between citric acid and purple coloured potassium permanganate solution is characterised by a change in colour from purple to colourless.
The chemical reaction between sulphur dioxide gas and acidified potassium dichromate solution is characterized by a change in colour from orange to green.
(iii) Change in state of substance: The combustion reaction of candle wax is characterised by a change in state from solid to liquid and gas (because the wax is a solid, water formed by the combustion of wax is a liquid at room temperature whereas, carbon dioxide produced by the combustion of wax is a gas). There are some chemical reactions which can show more than one characteristics.
(iv) Change in temperature: The chemical reaction between quick lime water to form slaked lime is characterized by a change in temperature (which is a rise in temperature).
The chemical reaction between zinc granules and dilute sulphuric acid is also characterised by a change in temperature (which is a rise in temperature).
(v) Formation of precipitate: The chemical reaction between sulphuric acid and barium chloride solution is characterised by the formation of a white precipitate of barium sulphate.
BaCl2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) (ppt) + 2HCl(aq)
What is a chemical Equation Class 10?
Chemical Equation: Representation of chemical reaction using symbols and formulae of the substances is called Chemical Equation.
Example: A + B → C + D
In this equation, A and B are called reactants and C and D are called the products. The arrow shows the direction of the chemical reaction. Condition, if any, is written generally above the arrow.
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen, it gives water. This reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation:
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
H2 + O2 → H2O
In the first equation, words are used and in second, symbols of substances are used to write the chemical equation. For convenience, the symbol of substance is used to represent chemical equations.
A chemical equation is a way to represent the chemical reaction in a concise and informative way.
A chemical equation can be divided into two types: Balanced Chemical Equation and Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
(a) Balanced Chemical Equation: A balanced chemical equation has the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides.
Example: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
In this equation, numbers of zinc, hydrogen and sulphate are equal on both sides, so it is a Balanced Chemical Equation.
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. To obey this law, the total mass of elements present in reactants must be equal to the total mass of elements present in products.
(b) Unbalanced Chemical Equation: If the number of atoms of each element in reactants is not equal to the number of atoms of each element present in the product, then the chemical equation is called Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
In this example, a number of atoms of elements are not equal on two sides of the reaction. For example; on the left-hand side only one iron atom is present, while three iron atoms are present on the right-hand side. Therefore, it is an unbalanced chemical equation.
Balancing a Chemical Equation: To balance the given or any chemical equation, follow these steps:
Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Write the number of atoms of elements present in reactants and in products in a table as shown here.
| Name of atom | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | 1 | 3 |
| Hydrogen | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 1 | 4 |
Balance the atom which is maximum in number on either side of a chemical equation.
In this equation, the number of oxygen atom is the maximum on the RHS.
To balance the oxygen, one needs to multiply the oxygen on the LHS by 4, so that, the number of oxygen atoms becomes equal on both sides.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
Now, the number of hydrogen atoms becomes 8 on the LHS, which is more than that on the RHS. To balance it, one needs to multiply the hydrogen on the RHS by 4.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
After that, the number of oxygen and hydrogen atoms becomes equal on both sides. The number of iron is one on the LHS, while it is three on the RHS. To balance it, multiply the iron on the LHS by 3.
3 × Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
Now the number of atoms of each element becomes equal on both sides. Thus, this equation becomes a balanced equation.
| Name of atom | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | 3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen | 8 | 8 |
| Oxygen | 4 | 4 |
After balancing, the above equation can be written as follows:
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
To Make Equations More Informative:
Writing the symbols of physical states of substances in a chemical equation:
By writing the physical states of substances, a chemical equation becomes more informative.
- Gaseous state is represented by symbol (g).
- Liquid state is represented by symbol (l).
- Solid state is written by symbol (s).
- Aqueous solution is written by symbol (aq).
- Writing the condition in which reaction takes place: The condition is generally written above and/or below the arrow of a chemical equation.
Thus, by writing the symbols of the physical state of substances and condition under which reaction takes place, a chemical equation can be made more informative.
What are the types of a chemical reaction Class 10?
Types of Chemical Reactions: Combination Reaction, Decomposition Reaction, Displacement Reaction, Double Displacement Reaction, Neutralization Reactions, Exothermic – Endothermic Reactions and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions.
Types of Chemical Reactions:
Chemical reactions can be classified in following types:
(i) Combination Reaction: Reactions in which two or more reactants combine to form one product are called Combination Reactions.
A general combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation given here:
A + B → AB
Examples:
When magnesium is burnt in the air (oxygen), magnesium oxide is formed. In this reaction, magnesium is combined with oxygen.
Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide
When carbon is burnt in oxygen (air), carbon dioxide is formed. In this reaction, carbon is combined with oxygen.
C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
(ii) Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which one compound decomposes in two or more compounds or elements are known as Decomposition Reaction. A decomposition reaction is just the opposite of combination reaction.
A general decomposition reaction can be represented as follows :
AB → A + B
Examples:
When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s)
Calcium carbonate → Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide
When ferric hydroxide is heated, it decomposes into ferric oxide and water
2Fe(OH)3(s)
Thermal Decomposition: The decomposition of a substance on heating is known as Thermal Decomposition.
Example: 2Pb(NO3)2(s)
Electrolytic Decomposition: Reactions in which compounds decompose into simpler compounds because of passing of electricity, are known as Electrolytic Decomposition. This is also known as Electrolysis.
Example: When electricity is passed in water, it decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen.
2H2O(l)
Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction: Reactions in which a compound decomposes because of sunlight are known as Photolysis or Photo Decomposition Reaction.
Example: When silver chloride is put in sunlight, it decomposes into silver metal and chlorine gas.
2AgCl(s) (white)
Photographic paper has a coat of silver chloride, which turns into grey when exposed to sunlight. It happens because silver chloride is colourless while silver is a grey metal.
(iii) Displacement Reaction: The chemical reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound is known as Displacement Reactions. Displacement reactions are also known as Substitution Reaction or Single Displacement/ replacement reactions.
A general displacement reaction can be represented by using a chemical equation as follows :
A + BC → AC + B
Displacement reaction takes place only when ‘A’ is more reactive than B. If ‘B’ is more reactive than ‘A’, then ‘A’ will not displace ‘C’ from ‘BC’ and reaction will not be taking place.
Examples:
When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
When zinc reacts with copper sulphate, it forms zinc sulphate and copper metal.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
(iv) Double Displacement Reaction: Reactions in which ions are exchanged between two reactants forming new compounds are called Double Displacement Reactions.
AB + CD → AC + BD
Examples:
When the solution of barium chloride reacts with the solution of sodium sulphate, white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) (Precipitate) + 2NaCl(aq)
When sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and water are formed.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Note: Double Displacement Reaction, in which precipitate is formed, is also known as precipitation reaction. Neutralisation reactions are also examples of double displacement reaction.
Precipitation Reaction: The reaction in which precipitate is formed by the mixing of the aqueous solution of two salts is called Precipitation Reaction.
Example: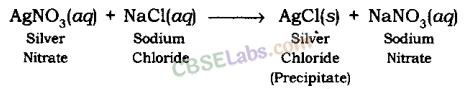
Neutralization Reaction: The reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water by an exchange of ions is called Neutralization Reaction.
Example: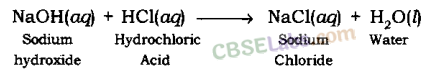
(v) Oxidation and Reduction Reactions:
Oxidation: Addition of oxygen or non-metallic element or removal of hydrogen or metallic element from a compound is known as Oxidation.
Elements or compounds in which oxygen or non-metallic element is added or hydrogen or metallic element is removed are called to be Oxidized.
Reduction: Addition of hydrogen or metallic element or removal of oxygen or non-metallic element from a compound is called Reduction.
The compound or element which goes under reduction in called to be Reduced.
Oxidation and Reduction take place together.
Oxidizing agent:
- The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an Oxidizing agent.
- The substance which removes hydrogen is also called an Oxidizing agent.
Reducing agent:
- The substance which gives hydrogen for reduction is called a Reducing agent.
- The substance which removes oxygen is also called a Reducing agent.
The reaction in which oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously is called Redox reaction.
When copper oxide is heated with hydrogen, then copper metal and hydrogen are formed.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(i) In this reaction, CuO is changing into Cu. Oxygen is being removed from copper oxide. Removal of oxygen from a substance is called Reduction, so copper oxide is being reduced to copper.
(ii) In this reaction, H2 is changing to H2O. Oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called Oxidation, so hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
- The substance which gets oxidised is the reducing agent.
- The substance which gets reduced is the oxidizing agent.
(vi) Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions:
Exothermic Reaction: Reaction which produces energy is called Exothermic Reaction. Most of the decomposition reactions are exothermic.
Example:
Respiration is a decomposition reaction in which energy is released.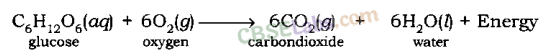
When quick lime (CaO) is added to water, it releases energy.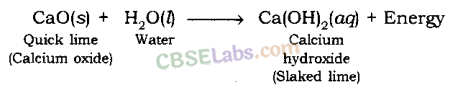
Endothermic Reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed is called Endothermic Reaction.
Example: Decomposition of calcium carbonate.
Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Everyday life: Corrosion and Rancidity.
Corrosion: The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to their reaction with oxygen, water, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is called Corrosion.
Example: Rusting of iron.
Rusting: Iron when reacts with oxygen and moisture forms red substance which is called Rust.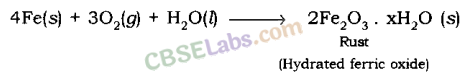
The rusting of iron is a redox reaction.
Corrosion (rusting) weakens the iron and steel objects and structures such as railings, car bodies, bridges and ships etc. and cuts short their life.
Methods to Prevent Rusting
- By painting.
- By greasing and oiling.
- By galvanisation.
Corrosion of Copper: Copper objects lose their lustre and shine after some time because the surface of these objects acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 when exposed to air.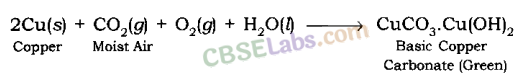
Corrosion of Silver Metal: The surface of silver metal gets tarnished (becomes dull) on exposure to air, due to the formation of a coating of black silver sulphide(Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
Rancidity: The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are left exposed to air for a long time. This is called Rancidity. It is caused due to the oxidation of fat and oil present in food materials.
Methods to prevent rancidity:
- By adding anti-oxidant.
- Vacuum packing.
- Replacing air by nitrogen.
- Refrigeration of foodstuff.
1. Chemical Reaction: During chemical reactions, the chemical composition of substances changes or new substances are formed.
2. Chemical Equation: Chemical reactions can be written in chemical equation form which should always be balanced.
3. Types of Chemical Reactions:
Combination reaction: A single product is formed from two or more reactants.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Decomposition reaction: A single reactant breaks down to yield two or more products.
- Thermal decomposition: 2Pb(NO2)2 → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
- Electrolysis: 2H20 → 2H2 + O2
- Photochemical reaction: 2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2
Displacement reaction: One element is displaced by another element.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Double displacement reaction: Exchange of ions between reactants.
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Redox reaction: Both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is evolved.
C + O2 → CO2 (g) + heat
Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed.
ZnCO3 + Heat → ZnO + CO2
Redox reaction: Chemical reaction in which both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously.
4. Oxidation: Reaction that involves the gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
5. Reduction: Reaction that shows the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ZnO is reduced to Zn—reduction. C is oxidized to CO—Oxidation.
6. Effects of Oxidation Reactions in Our Daily Life:
- Corrosion: It is an undesirable change that occurs in metals when they are attacked by moisture, air, acids and bases.
Example, Corrosion (rusting) of Iron: Fe2O3. nH2O (Hydrated iron oxide) - Rancidity: Undesirable change that takes place in oil containing food items due to the oxidation of fatty acids.
Preventive methods of rancidity: Adding antioxidants to the food materials, storing food in the airtight container, flushing out air with nitrogen gas and refrigeration.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions And Equation
Short Answer Type Questions
1.Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Thermit reaction, iron (III) oxide reacts with aluminium and gives molten iron and aluminium oxide.
(b) Magnesium ribbon is burnt in an atmosphere of nitrogen gas to form solid magnesium nitride.
(c) Chlorine gas is passed in an aqueous potassium iodide solution to form potassium chloride solution and solid iodine.
(d) Ethanol is burnt in air to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat.
Ans.
2.A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of the chemical reaction.
Ans.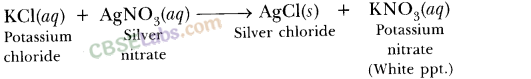
It is a double displacement reaction. It is also a precipitation reaction as AgCl is a white precipitate.
3.Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a)Sodium carbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid in equal molar concentrations gives sodium chloride and sodium hydrogen-carbonate.
(b)Sodium hydrogencarbonate on reaction with hydrochloric acid gives sodium chloride, water and liberates carbon dioxide.
(c)Copper sulphate on treatment with potassium iodide precipitates cuprous iodide
Ans.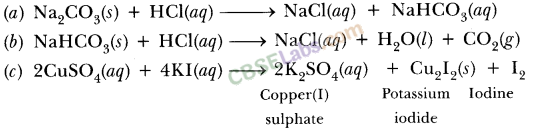
4.Why do fireflies glow at night?
Ans. It is because protein present in fireflies undergoes oxidation in presence of air and an enzyme. This chemical reaction involves emission of visible light. Therefore, fireflies glow at night.
5.Grapes hanging on the plant do not ferment but after being plucked from the plant can be fermented. Under what conditions do these grapes ferment? Is it a chemical or a physical change?
Ans. Grapes when attached to plants are living and therefore they have their immune system due to which they cannot get fermented. When microbes attack plucked grapes in absence of air, they undergo fermentation to form alcohol. This is a chemical process.
6.During the reaction of some metals with dilute hydrochloric acid, following observations were made.
(a) Silver metal does not show any change.
(b) The temperature of the reaction mixture rises when aluminium (Al) is added.
(c) The reaction of sodium metal is found to be highly explosive.
(d) Some bubbles of a gas are seen when lead (Pb) is reacted with the acid. Explain these observations giving suitable reasons.
Ans. (a) It is because silver is less reactive than hydrogen. It cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acid.
(b) It is because the reaction is exothermic.
(c) It is because sodium is highly reactive and forms hydrogen gas in the presence of moisture
(d) It is due to formation of hydrogen gas. The reaction becomes slow after some time as ![]()
7.A substance X, which is an oxide of a group 2 element, is used intensively in the cement industry. This element is present in bones also. On treatment with water, it forms a solution which turns red litmus blue. Identify X and also write the chemical reactions involved.
Ans.The substance ‘X’ is calcium oxide (CaO), element is calcium. Calcium oxide is used in cement industry. Calcium is present in bones in form of calcium phosphate.
Calcium oxide dissolves in water forming alkali which turns red litmus blue. CaO(s)+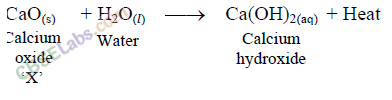
8.Why do we store silver chloride in dark coloured bottles?
Ans.It is because silver chloride decomposes to silver and chlorine gas in presence of sunlight.![]()
9.A magnesium ribbon is burnt in oxygen to give a white compound X accompanied by emission of light. If the burning ribbon is now placed in an atmosphere of nitrogen, it continues to burn and forms a compound Y.
(а)Write the chemical formulae of X and Y.
(b)Write a balanced chemical equation, when X is dissolved in water.
Ans.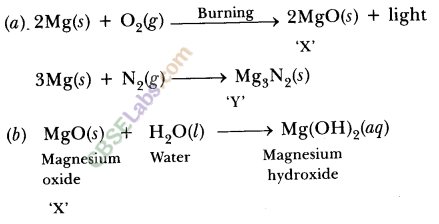
10.A silver article generally turns black when kept in the open for a few days. The article when rubbed with toothpaste again starts shining.
(a) Why do silver articles turn black when kept in the open for a few days? Name the phenomenon involved.
(b) Name the black substance formed and give its chemical formula.
Ans.(a) Silver reacts with
(b)
11.Write the balanced chemical equation for the following equations for the following reaction and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a)Nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst at 773 K to form ammonia gas.
(b)Sodium hydroxide solution is treated with acetic acid to form sodium acetate and water.
(c)Ethanol is warmed with ethanoic acid to form ethyl acetate in presence of cone.
(d)Ethene is burnt in presence of oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and releases heat and light.
Ans.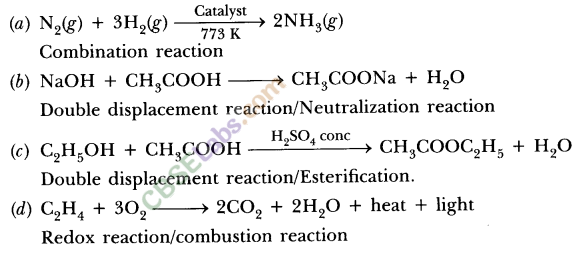
12.Complete the missing components/variables given as x and y in the following reactions :
Ans.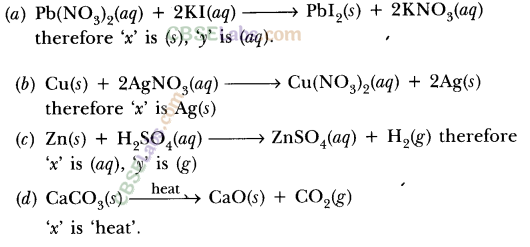
13.Which among the following changes are exothermic or endothermic in nature?
Ans.(a)Decomposition of ferrous sulphate
(b)Dilution of sulphuric acid
(c)Dissolution of sodium hydroxide in water
(d)Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water Ans. (a) It is endothermic reaction.
(b)It is exothermic process.
(c)It is exothermic process.
(d)It is endothermic process.
14. Identify the reducing agent in the following reactions :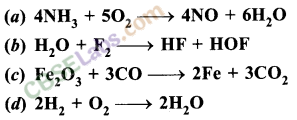
Ans.(a)
(b)
(c)CO (Carbon monoxide) is reducing agent.
(d)
15.Identify the oxidising agent (oxidant) in the following reactions :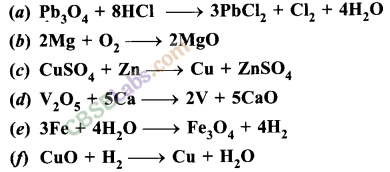
Ans.(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)CuO is oxidising agent.
16.Ferrous sulphate decomposes with the evolution of gas having a characteristic order of burning sulphur. Write the chemical reaction involved and identify the type of reaction.
Ans.![]()
It is decomposition reaction.
17.Which among the following are physical or chemical changes
(a)Evaporation of petrol.
(b)Burning of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
(c)Heating of an iron rod to red hot.
(d)Curdling of milk.
(e)Sublimation of solid ammonium chloride
Ans.(a)Physical change
(b)Chemical change
(c)Physical change
(d)Chemical change
(e)Physical change
18.Write a balanced chemical equation for each of the following reactions and also classify them.
(a)Lead acetate solution is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid to form lead chloride and acetic acid solution.
(b)A piece of sodium metal is added to absolute ethanol to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas.
(c)Iron (III) oxide on heating with carbon monoxide reacts to form solid iron and liberates carbon dioxide gas.
(d)Hydrogen sulphide gas reacts with oxygen gas to form solid sulphur and liquid water.
Ans.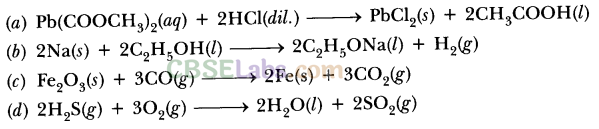
19.Balance the following chemical equations arid identify the type of chemical reaction: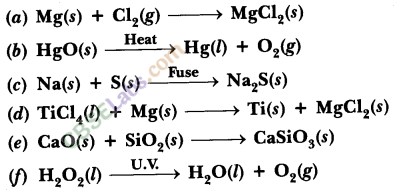
Ans.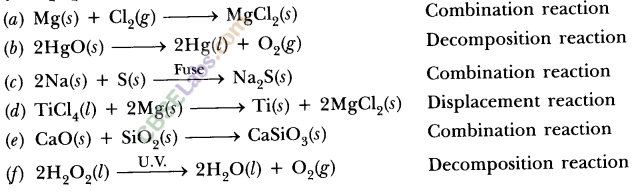
20.Zinc liberates hydrogen gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, whereas copper does not. Explain why?
Ans.Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen whereas copper is less reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, Zn displaces hydrogen from dil.HCl whereas copper does not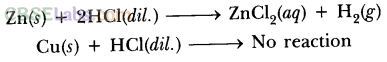
21.On heating blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in boiling tube, copper oxide (black), oxygen gas and a brown gas ‘X’ is formed.
(a)Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(b)Identify the brown gas ‘X’ evolved.
(c)Identify the type of reaction.
(d)What could be the pH range of aqueous solution of the gas ‘X’?
Ans.
(b) The brown gas ‘X,’ is nitrogen dioxide
(c) The reaction is a thermal decomposition reaction.
(d) The gas ‘X’ is acidic in nature because it is a non-metallic oxide. Its aqueous solution has pH less than 7.
22.Give the characteristic tests for the following gases.
(a)
Ans.(a)Pass the gas through limewater. Limewater turns milky which confirms the presence of 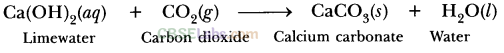
Limewater Carbon dioxide Calcium carbonate Water
(b) Pass the gas through acidified potassium dichromate solution (orange in colour). The solution will become green in colour due to formation of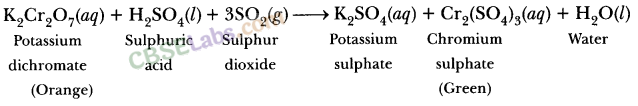
Alternative:
Pass the gas through acidified potassium permanganate solution (pink/purple in r colour). It will become colourless because 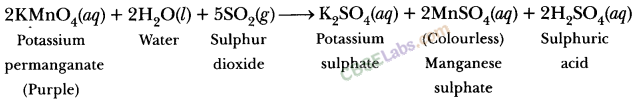
(c) Bring a candle near oxygen gas. The intensity of candle flame is increased, it shows the presence of oxygen gas which is a supporter of combustion.
(d) Bring a burning matchstick near hydrogen gas. The gas will burn explosively ‘ with a pop sound. It confirms the presence of hydrogen.
23.What happens when a piece of
(a)zinc metal is added to copper sulphate solution?
(b)aluminium metal is added to dilute hydrochloric acid?
(c)silver metal is added to copper sulphate solution? Also, write the balanced chemical equation if the reaction occurs.
Ans.(a)The solution will become colourless due to formation of zinc sulphate and reddish brown
(b)aluminium chloride solution will be formed.![]()
(c) No reaction will take place because silver is less reactive than copper, it cannot displace copper from copper sulphate.
24.What happens when zinc granules are treated with dilute solutions of
Ans.
25.On adding a drop of barium chloride solution to an aqueous solution of sodium sulphite, white precipitate is obtained.
(a)Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b)What other name can be given to this precipitation reaction?
(c)On adding dilute hydrochloric acid to the reaction mixture, white precipitate disappears. Why?
Ans.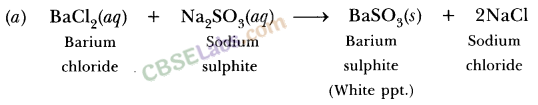
(b)It is also called double displacement reaction.![]()
It is because barium sulphite reacts with HC1 to form barium chloride which is soluble in water and liberates
26.You are provided with two containers made up of (A) copper and (B) aluminium. You are also provided with solutions of (a) dilute HCl (b) dilute
Ans.A. When solutions are kept in copper container-
(a)Dilute HC1: No reaction takes place as copper is less reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, dil. HC1 can be kept in copper container.
(b)Dilute HNOs: Copper will react with dil. HNOs as it is an oxidising agent and will form copper nitrate and nitrogen monoxide gas.![]()
Therefore,
(c)
(d)
Thus, dil. HCl,
B.When solutions are kept in aluminium container-
(a)Dilute HCl: Aluminium reacts with dil. HCl to form aluminium chloride . and hydrogen gas is formed.
So, dil. HCl cannot be kept in aluminium container.
(b)Dilute
(c)
Therefore, Zinc chloride cannot be stored in aluminium container.
(d)
A1 reacts with steam to form aluminium oxide and hydrogen
Thus.dil.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Subject NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
.png)
.png)