Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy NCERT Solutions
Before getting into the details of Sources Of Energy Class 10 NCERT Solutions, let us look at the topics and subtopics under class 10 science chapter 14 notes:
- Sources Of Energy
- What Is A Good Source Of Energy?
- Conventional Sources Of Energy
- Alternative Or Non-Conventional Sources Of Energy
- Environmental Consequences
- How Long Will An Energy Source Last Us?
- उर्जा के स्रोत कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Sources of Energy Important Questions
- Sources of Energy Class 10 Notes
- Sources of Energy NCERT Exemplar Solutions
- Sources of Energy Class 10 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Science Sources of Energy Mind Map
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Intext Questions
Page Number: 243
Question 1
What is a good source of energy?
Answer:
A good source of energy is one that
- does a large amount of work per unit volume or mass
- can be easily accessible
- is easy to store and transport, and
- is economical.
Question 2
What is a good fuel ?
OR
Write any three characteristics of a good fuel. [AICBSE 2015]
Answer:
A good fuel is one which has the following properties :
- It should be fairly cheap.
- It should be easily available.
- Its ignition temperature should be well above normal temperature.
- It should be conveniently handled and transported.
- It should not produce any poisonous material during burning.
- Its combustion rate should be steady and controllable.
- It should not leave any residue or ash after burning.
- A good fuel should have high calorific value so that higher amount of heat may be obtained by burning a little fuel.
Question 3
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one should you use and why ?
Answer:
I would prefer to use cooking gas like LPG. It fulfils many of the criteria of a good fuel like its ignition temperature, good calorific value and non-polluting characteristics.
Page Number: 248
Question 1
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels ?
Answer:
(i) The burning of fossil fuels produces large amount of carbon dioxide that causes increased greenhouse effect.
(ii) The burning of fossil fuels (such as coal) produces smoke which pollutes the air.
(iii) The burning of fossil fuels produces acidic gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide. These acidic gases cause acid rain that affects our water and soil resources.
(iv) Fossil fuels cannot be replenished in short time because it takes millions of years to form them.
Question 2
Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy ?
Answer:
We are looking at alternate sources of energy because of the following reasons.
- The fossil fuels and nuclear fuels on the earth are limited which may not last for long.
- The undesirable effects of pollution, both from the burning of fossil fuels and from the radioactive nuclear wastes of nuclear power plants are creating threat to our environment.
Question 3
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for convenience ?
Answer:
(i) Wind mill farms are constructed to produce electricity.
(ii) The traditional use of energy of flowing water has been modified by establishing hydro-power plants. At hydro-power plants, the energy of falling water or flowing water is tapped by using a water turbine and then made to drive generators.
Page Number: 253
Question 1
What kind of mirror-concave, convex or plane – would be the best suited for use in a solar cooker ? Why ?
Answer:
A concave mirror would be best suited in a solar cooker because it focuses the sunlight in a very small area of the solar cooker and a high temperature is produced in it which is sufficient to cook the food.
Question 2
What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Answer:
The energy from the oceans can be obtained mainly in three forms. These are
(i) tidal energy
(ii) wave energy and
(iii) ocean thermal energy
- Limitations of Tidal Energy :
(i) There are very few sites around the world which are suitable for building tidal dams.
(ii) The rise and fall of sea-water during high and low tides is not enough to generate electricity on a large scale. - Limitations of wave energy : The movement of ocean waves is associated with kinetic energy. Such sites in the world are limited where the waves strike the shore lines with sufficient power.
- Limitations of ocean thermal energy : NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of EnergyTo convert ocean thermal energy into electricity, a temperature difference of 20°C (or more) between the surface water of ocean and deeper water is needed for operating OTEC power plants. This involves high cost.
Question 3
What is geothermal energy ?
Answer:
Energy stored as heat in certain regions of the earth (called hot spots) is called geothermal energy. Hot spots are the locations below earth’s crust where upward moving magma gets collected due to geological changes. When underground water comes in contact with the hot spots, steam is generated. This steam is utilised to generate electricity using pipes and turbines. Sometimes hot water from the hot spot finds outlet at the surface. Such outlets are called hot springs.
Question 4
What are the advantages of nuclear energy ?
Answer:
The advantages of nuclear energy are that :
- It produces a large amount of useful energy from a very small amount of a nuclear fuel (like uranium-235).
- Once the nuclear fuel (like uranium-235) is loaded into the reactor, the nuclear power plant can go on producing electricity for two to three years at a stretch. There is no need for putting in nuclear fuel again and again.
- It does not produce gases like carbon dioxide which contributes to greenhouse effect or sulphur dioxide which causes acid rain.
Page Number: 253
Question 1
Can any source of energy be pollution free ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
No source of energy can be pollution free because even if it is clean, its assembly could have caused some environmental damage.
Question 2
Hydrogen has been used as rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG ? Why or why not ?
Answer:
Hydrogen is cleaner fuel than CNG. This is because the burning of hydrogen produces only water, which is totally harmless. On the other hand, burning of CNG produces carbon dioxide gas and water. The carbon dioxide can produce greenhouse effect in the atmosphere and lead to the excessive heating of the environment in long run.
Page Number: 243
Question 1
Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
(i) Energy derived from biomass is a renewable source of energy because waste products are continuously produced. Plants and trees are also grown at reasonable intervals.
(ii) The energy derived from flowing water, wind, sun and ocean are renewable sources because these sources can be harnessed into energy so long as the present solar system exists.
Question 2
Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are exhaustible sources of energy. The estimated reserves of these fuels are said to last us for about another 200 years, while it takes millions of years for these to be formed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day
(b) a cloudy day
(c) a hot day
(d) a windy day
Answer:
(b) A cloudy day.
Question 2
Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source ?
(a) Wood
(b) Gobar gas
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Coal
Answer:
(c) Nuclear energy.
Question 3
Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the sun’s energy ?
(a) Geothermal energy
(b) Wind energy
(c) Nuclear energy
(d) Biomass
Answer:
(a) Geothermal energy.
Question 4
Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the sun as direct sources of energy Ans
Answer:
| Fossil fuels | Sun |
| (i) Non-renewable source of energy. | (i) Renewable source of energy. |
| (ii) Cause a lot of air pollution. | (ii) Pollution-free, doesn’t cause any pollution. |
| (iii) They will exhaust in future. | (iii) It is a non-exhaustible source. |
| (iv) Energy can be tapped throughout the year. | (iv) Energy cannot be tapped during night and cloudy and rainy days. |
Question 5
Compare and contrast biomass and hydro-electricity as sources of energy. Ans.
Answer:
| Biomass | Hydroelectricity |
| (i) Renewable source of energy. | (i) Renewable source of energy. |
| (ii) Biomass plants can be installed at any place to produce biomass as energy source. | (ii) Plants can be installed only at the places where dams can be constructed. |
| (iii) To collect waste materials is a tough and costly process. | (iii) Once the plants start to work, it is not difficult to collect water. |
Question 6
What are the limitations of extracting energy from
(a) the wind ?
(b) waves ?
(c) tides ?
Answer:
(a) Limitations of wind energy
(i) Wind energy farms cannot be established everywhere. The wind energy farms can be established only at those places, where wind blows for most part of the year.
(ii) The wind required for generating electricity should be strong and steady to maintain the desired level of generation. The minimum wind speed necessary for satisfactory working of the wind generator is about 15 km/h. This is not always so.
(iii) The wind energy farms require a large area of land.
(iv) The setting up of wind energy farms is very expensive.
(b) Limitations of wave energy : The harnessing of sea-waves energy would be a viable proposition only at those places where sea-waves are very strong. This has constraints of time and location.
(c) Limitations of tidal energy :
(i) There are very few sites around the world which are suitable for building tidal dams.
(ii) The rise and fall of sea-water during high and low tides is not enough to generate electricity on a large scale.
Question 7
On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable ?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible ?
Are the options given in (a) and (b) the same ?
Answer:
(a) Renewable sources : The sources of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and are inexhaustible, are called renewable sources of energy. The energy derived from flowing water, wind, tides, ocean waves, or wood are examples of energy from such sources.
Non-renewable sources : These sources are produced over million of years under special conditions. Once consumed, these are not replaceable for a very long time. Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas are non-renewable sources.
(b) Exhaustible sources are non-renewable sources, while inexhaustible sources are renewable sources.
Yes, the options given in (a) and (b) are the same.
Question 8
What are qualities of an ideal source of energy ?
Answer:
An ideal source of energy
- Must give an adequate amount of net energy.
- Must be convenient to use so as to give energy at a steady rate.
- Must be easy to store and transport.
Question 9
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker ? Are there places where solar cookers would have limited utility ?
Answer:
Advantages of using solar cooker :
- The use of solar cooker for cooking food saves precious fuels like coal, kerosene and LPG.
- The use of solar cooker does not produce smoke due to which it does not pollute air.
- When food is cooked in solar cooker, its nutrients do not get destroyed. This is because in a solar cooker, food is cooked at a comparatively lower temperature.
- In a solar cooker, up to four food items can be cooked at the same time.
Disadvantages of using solar cooker :
- The solar cooker cannot be used to cook food during night because sunshine is not available at that time.
- If the day sky is covered with clouds, even then solar cooker cannot be used to cook food.
- The direction of reflector of solar cooker has to be changed from time-to-time to keep it facing the sun.
Sources of Energy - The box-type solar cooker cannot be used for baking (making chappattis, etc.) or for frying.
The places that receive rain most of the year or where the sky remains cloudy, the solar cooker has limited utility.
Question 10
What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption ?
Answer:
Some of the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy are the following :
- The combustion of fossil fuels is producing acid rain and damaging plants (crops), soil and aquatic life.
- The burning of fossil fuels is increasing the amount of greenhouse gas carbon-dioxide in the atmosphere. It has also affected the rainfall.
- The cutting down of trees from the forest for obtaining fire-wood is causing soil erosion and destroying wild life.
- The construction of hydro-power plants is disturbing ecological balance.
- Nuclear power plants are increasing radioactivity in the environment.
The following steps can be taken to reduce energy consumption :
- Switch off lights, fans, TV. and other such electrical appliances when not needed, to save electricity.
- Use energy efficient electrical appliances to save electricity. This can be done by using compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) and tube lights in place of conventional filament- type electric bulbs.
- Good quality stoves should be used to burn fuels like kerosene and LPG so as to obtain maximum heat.
- Pressure cookers should be used for cooking food to save fuel.
- Solar cookers should be used to cook food whenever possible and solar water heaters should be used to get hot water.
- The use of biogas as fuel should be encouraged in rural areas.
- Bicycles should be used for short distances to save fuel like petrol which is used in cars, scooters and motorcycles.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
Sources of energy : Different forms of energy, conventional and non-conventional sources
of energy: Fossil fuels, solar energy; biogas; wind, water and tidal energy; Nuclear energy, Renewable versus non-renewable sources of energy.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 14 |
| Chapter Name | Sources of Energy |
| Number of Questions Solved | 24 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Question 1
What is a good source of energy?
Solution:
A good source of energy would be one,
i) Which would do a large amount of work per unit volume or mass.
ii) Be easily accessible.
iii) Be easy to store and transport, and
iv) Perhaps most importantly, be economical.
Question 2
What is a good fuel?
Solution:
A good fuel would be one,
i) Which is easily available.
ii) It should not produce too much of smoke.
iii) On burning should release less amount of heat.
Question 3
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Solution:
Solar energy can be used for heating food because it is easily available, it will not produce smoke and it will not release any amount of heat.
Question 4
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Solution:
Fossil fuels are non-renewable. Burning of coal or petroleum products causes the air pollution. The oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur that are released on burning fossil fuels are acid oxides. These lead to acid rain, which affects water and soil resources.
Question 5
Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Solution:
The fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy. So we need to conserve them. If we were to continue consuming these sources at such alarming rates, we would soon run out of energy. In order to avoid this, alternate sources of energy were explored.
Question 6
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Solution:
The wind possesses kinetic energy. This energy was harnessed by windmills in the past to do mechanical work. Today, wind energy is also used to generate electricity.
Another traditional source of energy was the kinetic energy of flowing water or the potential energy of water at a height. Hydropower plants convert the potential energy of falling water into electricity.
Question 7
What kind of mirror – concave, convex or plane – would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Solution:
Plane mirror would be best suited for use in a solar cooker. A plane mirror is used as a reflector. The reflector is used to increase the area over which the solar energy is collected so that more and more heat rays of the sun may enter the solar cooker.
Question 8
What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Solution:
The energy from the oceans can be obtained mainly in three forms,
a) Tidal energy
b) Ocean waves energy
c) Ocean thermal energy
The energy potential from sea is quite large, but efficient commercial exploitation is difficult.
Question 9
What is geothermal energy?
Solution:
‘Geo’ means ‘earth’ and ‘thermal’ means ‘heat’. Thus the geothermal energy is the heat energy from the hot rock present inside the earth. This heat can be used as a source of energy to produce electricity.
Question 10
What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Solution:
The advantages of nuclear energy is as follows,
(a) It generates electricity.
(b) Disease like cancer can be treated.
(c) It helps for the improvement in the agriculture and industry.
Question 11
Can any source of energy be pollution-free? Why or why not?
Solution:
Yes, Solar energy does not cause any pollution. Solar cells make use of the ‘everlasting solar energy’ and their use does not produce any environmental pollution.
Question 12
Hydrogen has been used as a rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG? Why or why not?
Solution:
Yes, hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than CNG because of its very high colorific value, hydrogen is an extremely good fuel.
Question 13
Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Solution:
Hydro Energy and Solar Energy
Hydro energy or water energy is renewable source of electric energy, which will never get exhausted, since water is available in plenty.
Solar energy is also known as light energy, which is obtained from the sun and it will never get exhausted.
Question 14
Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Solution:
Coal and petroleum are the two energy sources that are considered to be exhaustible. They are non-renewable sources of energy and are present in a limited amount in the earth. Once exhausted, they will not be available to us again.
Question 15
A solar water heater can be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day.
(b) a cloudy day.
(c) a hot day.
(d) a windy day.
Solution:
(a) a sunny day.
Question 16
Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(a) wood
(b) gobar-gas
(c) nuclear energy
(d) coal.
Solution:
(c) nuclear energy.
Question 17
Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy.
Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) geothermal energy
(b) wind energy
(c) nuclear energy
(d) bio-mass.
Solution:
(c) nuclear energy.
Question 18
Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the Sun as direct sources of energy.
Solution:
Fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy. These non-renewable sources of energy (like coal, petroleum, natural gas) are present in a limited amount in the earth. Once exhausted, they will not be available to us again.
The sun is the source of all energy. The sun is a renewable source of energy, provides us heat and light energy free of cost. The energy obtained from the sun is called solar energy. The energy coming from the sun contains heat rays, visible light, ultra-violet rays and some gamma rays.
Question 19
Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydro electricity as sources of energy.
Solution:
The waste material of living things and the dead parts of living things is called bio-mass. Bio-mass contains carbon compounds and it is the oldest source of heat energy for domestic purposes. The important examples of bio-mass being used as a fuel are wood, cattle dung and agriculture wastes like bagasse.
Hydropower plants convert the potential energy of falling water into electricity. Water energy is a renewable source of electric energy, which will never get exhausted. The construction of dams on rivers helps in controlling floods and in irrigation.
Question 20
What are the limitations of extracting energy from
(a) the wind?
(b) waves?
(c) Tides?
Solution:
a) There are many limitations in harnessing wind energy. Wind energy farms can be established only at those places where wind blows from the greater part of a year. The wind speed should also be higher than 15 Km/h to maintain the required speed of the turbine. There should be some back-up facilities to take care of the energy needs during a period when there is no wind.
b) The waves are generated by strong winds blowing across the sea. Wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong.
c) Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam across a narrow opening, the location where such dams can be built are limited.
Question 21
On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible?
Are the options given in (a) and (b) the same?
Solution:
The options given in (a) and (b) are the same.
Those sources of energy, which are being, produced continuously in nature and are inexhaustible are called renewable sources of energy.
Those sources of energy, which have accumulated in nature over a very, very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted are called non-renewable sources of energy.
Question 22
What are the qualities of an ideal source of energy?
Solution:
The important qualities of an ideal source of energy is
a) It should be a renewable source of energy.
b) It should be pollution-free.
c) It should be economical.
d) It should be easily accessible.
Question 23
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker? Are there places where solar cookers would have limited utility?
Solution:
The advantages of a solar cooker
i) The use of solar cooker for cooking food saves fuel.
ii) The use of solar cooker does not produce smoke due to which the environment also does not get polluted.
iii) When food is cooked in a solar cooker, its nutrients do not get destroyed. This is because in a solar cooker, food is cooked at comparatively lower temperature.
iv) In a solar cooker, upto four food items can be cooked at the same time.
The disadvantages of a solar cooker
i) The box-type solar cooker cannot be used to make chappaties.
ii) The box-type solar cooker cannot be used for ‘frying’.
The limited utility of a solar cooker is
i)The solar cooker cannot be used to cook the food during nighttime.
ii) If the day-sky is covered with clouds, even then the solar cooker cannot be used to cook the food.
iii) The direction of reflector of solar cooker has to be changed from time to time to keep it facing the sun.
Question 24
What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Solution:
Exploiting any source of energy disturbs the environment in some way or the other. The source we would choose depends on factors such as the case of extracting energy from that source, the economics of extracting energy from the source, the efficiency of technology available and the environmental damage that will be caused by using that source.
We cannot depend on the fossil fuels for much longer, if we manage bio-mass by replacing the trees we cut down for fire-wood, we can be assured of a constant supply of energy at a particular rate. Renewable energy is available in our natural environment, in the form of some continuing or repetitive current of energy, or is stored in such large under ground reservoirs that the rate of depletion of reservoirs because of extraction of usable energy is practically negligible.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Question 1.
Which of the following is a non-renewable source of energy? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Wood
(b) Sun
(c) Fossil fuel
(d) Wind
Answer:
(c) The fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy whereas wood, the Sun and wind are renewable sources of energy. Non-renewable sources of energy are those which are exhaustible and cannot be replaced, once they have been used. They are also known as conventional sources of energy.
Question 2.
Fuel used in thermal power plant is [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) water
(b) uranium
(c) bio-mass
(d) fossil fuels
Answer:
(d) The thermal power plant generates electric power from heat produced by burning fossil fuel, i.e. coal and petroleum. Everyday we burn a large amount of fossil fuels to heat up water to produce steam. The steam so produced runs turbines to generate electricity.
Question 3.
In a hydroelectric power plant more electrical power can be generated, if water falls from a greater height because [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) its temperature increases
(b) a large amount of potential energy is converted into kinetic energy
(c) the electricity content of water increases with height
(d) more water molecules dissociate into ions
Answer:
(b) In a hydroelectric power plant, more electrical power can be generated, if water falls from a greater height, because the rise in water level causes the increase in potential energy of water. Thus, when it flows from higher position more amount of kinetic energy is formed by the conversion of higher potential energy and this kinetic energy in the form of moving water can produce more electrical power.
Question 4.
The power generated in a windmill [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) is more in rainy season, since damp air would mean more air mass hitting blades
(b) depends on the height of the tower
(c) depends on wind velocity
(d) can be increased by planting tall trees close to the tower
Answer:
(c) Wind energy farms can be located only in vast open areas located in favourable wind conditions as the minimum velocity for a windmill to functions is 11-16 km/h and is called as cut in speed. Thus, the power generated in a windmill depends on wind velocity.
Question 5.
Choose the correct statement. [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Sun can be taken as an inexhaustible source of energy
(b) There is infinite storage of fossil fuel inside the Earth
(c) Hydro and wind energy plants are non-polluting sources of energy
(d) Waste from a nuclear power plant can be easily disposed off
Answer:
(a) The Sun has been radiating an enormous amount of energy at the present rate for nearly 5 billion years and will continue radiating at that rate for about 5 billion years more, so the Sun can be taken as an inexhaustible source of energy.
Question 6.
Which part of the solar cooker is responsible for greenhouse effect? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Coating with black colour inside the box
(b) Mirror
(c) Glass sheet
(d) Outer cover of the solar cooker
Answer:
(c) Glass sheet present in the solar cooker easily passes the radiation into the solar cooker and the radiation gets absorbed and that reflected back by the black coating is of longer wavelength and cannot pass back out through the glass. Thus, glass sheet produces greenhouse effect in solar cooker.
Question 7.
Ocean thermal energy is due to [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) energy stored by waves in the ocean
(b) temperature difference at different levels in the ocean
(c) pressure difference at different levels in the ocean
(d) tides arising out in the ocean
Answer:
(b) The water at the surface of the sea or ocean is heated by the Sun, while the water in deeper sections is relatively cold. This difference in temperature between these layers ranges from 10-30 °C and is exploited to obtain energy. Thus, ocean thermal energy is due to temperature difference at different levels in the ocean.
Question 8.
The major problem in harnessing nuclear energy is how to [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) split nuclei
(b) sustain the reaction
(c) dispose off spent fuel safely
(d) convert nuclear energy into electrical energy
Answer:
(c) The major hazard of nuclear power generation is the storage and disposal of spent or used fuels. Improper nuclear waste storage and disposal result in environmental contamination as well as risk of accidental leakage of nuclear radiation. It happened in Chernobyl disaster 1986, Fukushima Nuclear disaster 2011 caused great damage to the living beings and habitats.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy (Hindi Medium)











Class 10 Science Sources of Energy Mind Map
SOURCES OF ENERGY
(Plants, winds, water, coal, bio-gas, natural gas etc.)
It should not affect the environment. It should be eco-friendly.
Biogas is a mixture of methane (75%) CO2, hydrogen and traces of hydrogen sulphide. Methane is an extremely good fuel
Environmential Consequences
- Air pollution and acid rain
- Green house effect
- Damage to water bodies and to human life.
Types of Sources of Energy
- Renewable Sources of Energy
- Non- Renewable Sources of Energy
Renewable Sources of Energy
Which can be easily generated and whose supply is unlimited.
Hydro Power Plants
The potential energy of falling water is converted into electricity.
- Limited Dams
- Construction needs a large area
- Eco-systems are destroyed
- High lost of installation
- About 20% of the power generated in India comes from hydro power plants
Wind Energy
When wind blows with a sufficient speed, it gets ability to do some work
It doesn’t pollute the air like power plants that rely on combustion of fossil fuels
Wind mill
It is a device which is used to convert wind energy into electrical energy. More than 25% of the electricity needs are generated through a vast network of wind mills.
Wind farm and power plants
It is basically used to generate electricity on a commercial basis, (large scale)
Wind power plants needs high maintenance and high wind speeds
Wind farms are noisy and may spoil the view for people living near them
Biomass
It means any organic matter from which we get energy on a renewable basis
Solar Energy
The energy coming with the rays of the sun. The ultimate source of energy
Solar Cooker
It is a device that uses solar energy to cook food
Solar Panel
It is a combination of large number of solar cells to draw high voltage for commercial purposes
Solar Cells
It is a device which converts solar energy into electric energy
Solar cells can be used in many small appliances like calculators and spacecrafts
Energy from the Sea
Form of energy obtained from the ocean in the form of tidal waves; wind blowing etc.
Tidal energy
It is a form of energy which is obtained from the ocean in the form of tidal waves
Wave energy
It is a another type of ocean based energy source that uses the power of waves to generate electricity
Ocean thermal energy (OTE)
This energy is obtained from using the temperature difference between deep cold ocean water ane warm surface water
Geothermal energy
It is the energy which is stored in the form of heat inside the earth
Characteristics of good sources of energy
- Easy storing and transportation
- Easy access
- Large amount of work per unit volume or mass
- Economical
Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
Which cannot be generated easily and whose supply is limited
Advantages
- High in energy
- Profitable
- Easy to use
- Cost effective
Disadvantages
- Time consuming to extract
- Dangerous for humans
- Contribution to acid rain
- Not viable for future generations
Fossil Fuels
These are hydrocarbons based natural resources that were formed 300 millions years ago.
Thermal Power Plant
Fuel is burnt to produce heat energy which is converted into electrical energy
Advantages
- Smaller space is required as compared to hydro power plant
- Running costs are less compared to gas plants or diesel
Major Hazards
Causes Air Pollution Green House Effect and Acid Rain
Nuclear Energy
Energy released during nuclear reactions
Types of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Fission
It is a process in which a heavy nucleus splits up into two lighter nuclei
→ 92U235 + 0n1
56Ba141 + 36Kr92 + 30n1 + energy
This principle is used in atom bomb
Moderator
Slow down fast moving neutrons e.g.: heavy water, graphite
Coolant
Remove heat e.g.: cold water, liquid oxygen
Control rods
Absorb neutrons e.g.: boron, cadmium
Nuclear Fusion
It is a process in which two lighter nuclei combine together to form a heavier nucleus
1H2 + 1H2 + 1H2 → 2He4 + 1H1 + 0n1 + 21.6 Mev
This principle is used in hydrogen bomb
Major Hazards
- Storage of spent fuels.
- Disposal of spent fuels.
- High cost of Installation
- Limited availability of fuel.
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources Of Energy and we hope this detailed article on sources of energy class 10 questions and answers are helpful. If you have any doubt regarding this article or cbse class 10 physics sources of energy questions and answers, drop your comments below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Important Questions of Sources of Energy Class 10 Science Chapter 14
Question 1.
The biggest source of energy on Earths surface is
(a) Biomass
(b) Solar radiations
(c) Tides
(d) Winds (2020)
Answer:
(b) The biggest source of energy on Earths surface is solar radiations.
Answer question numbers 2-5 on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts:
The Tehri dam is the highest dam in India and one of the highest in the World. The Tehri dam withholds a reservoir of capacity 4.0 km³ and surface area 52 km². It is used for irrigation, municipal water supply and the generation of 1000 MW of hydro electricity.
The Tehri Dam has been the object of protests. Environment activist Shri Sunder Lai Bahuguna led the “Anti Tehri Dam Movement” from 1980s to 2014. The protest was against the displacement of town inhabitants and environmental consequences of the weak ecosystem. The relocation of more than 1,00,000 people from the area has led to protracted legal battles over resettlement rights and ultimately resulted in the delayed completion of the project. (2020)
Question 2.
How is hydropower harnessed?
Answer:
Potential energy of water stored in a dam is converted into kinetic energy of falling water and then, this kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy.
Question 3.
Define 1 MW.
Answer:
1 MW is the power consumed or dissipated by a device which consumes or dissipates 1 mega joule of energy per second.
Question 4.
Mention two disadvantages of constructing Tehri Dam.
Answer:
For the construction of Tehri Dam, relocation of more than 100000 people was needed which led to widespread protests and legal battles. Also large ecosystems were destroyed when it submerged under the water in dams causing emission of large amounts of methane which is a green-house gas.
Question 5.
What happens when water from great heights is made to fall on blades of turbine?
Answer:
When water from great heights is made to fall, the potential energy of these waters get converted into kinetic energy and when it falls on the blades of turbines, it rotates the turbine of a generator, thus producing electricity.
Question 6.
Why is biogas considered an excellent fuel? (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Biogas is considered as excellent fuel because
- it does not produce smoke.
- slurry left behind can be used as an excellent manure.
Question 7.
Name any two nutrients that the spent slurry has in the biogas plant. (AI 2019)
Answer:
Nitrogen and phosphorus.
Question 8.
Write the energy conversion that takes place in a hydropower plant. (2018)
Answer:
Hydropower plant converts the potential energy of stored yrater into electrical energy.
Question 9.
Name any two fossils fuels. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Coal and petroleum are two fossil fuels.
Question 10.
Name any two conventional sources of energy. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(i) Fossil fuels (ii) Wind energy
Question 11.
What is meant by the term ‘Biomass’? (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Biomass : Cow-dung, various plant materials like the residue after harvesting the crops, vegetable wastes and sewage which can be decomposed in the absence of oxygen is called biomass.
Question 12.
Write the characteristic features of the micro organisms which help in the production of biogas in a biogas plant. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
In a biogas plant, anaerobic micro-organisms are used. They do not require oxygen to decompose or break-down complex compounds of the cow- dung slurry.
Question 13.
What are fossil fuels? “Burning fossil fuels may lead to intense global warming.” Justify this statement. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Fossil fuels : The combustible substances formed from the dead remains of the animals and plants which were buried deep under the surface of the earth for over millions of years are called fossil fuels. Burning of fossil fuels produces carbon dioxide and excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere causes the greenhouse effect, leading to intense global warming.
Question 14.
What is the main constituent of biogas? How is biogas obtained from biomass? Write any two advantages of using this gas. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Tlie main constituent of biogas is methane (75%). Biogas is obtained by anaerobic decomposition of biomass in a biogas plant. The two advantages of using this gas are
- It does not produce smoke.
- It has high calorific value.
Question 15.
Define:
(i) Biomass
(ii) Anaerobic degradation (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
(i) Refer to answer 11.
(ii) Anaerobic degradation : Breaking of large organic molecules into simple molecules in the absence of air is called anaerobic degradation.
Question 16.
There are many limitations associated with the setting up of wind energy farms to harness energy. Raman wants to generate electricity by using wind mill in his parental village in Uttar Pradesh.
(i) Is it advisable to set up such wind energy farms in his village? Give reason for your answer.
(ii) Write any two limitations associated with the wind energy farms.
(iii) Write the energy transformations which take place when wind mill is used for generating electricity? (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(i) No, it is not advisable to set up such wind energy farms in his village because wind energy farms can be established only at those places where wind blows for the greater past of a year. The wind speed should also be higher than 15 km/h to maintain the required speed of the turbine.
(ii) Limitation of wind energy:
(a) Initial cost of establishment of the farm is quite high.
(b) The tower and blades need a high level of maintenance.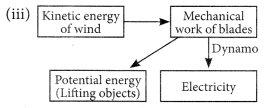
Question 17.
Explain with the help of labelled diagram the process of production of biogas in a biogas plant. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer: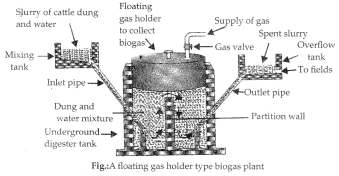
Working of the biogas plant:
Dung and domestic/agricultural wastes are mixed with water in the mixing tank. The slurry so obtained is fed into the digester through the inlet chamber. Gradually, the anaerobic fermentation sets in and biogas is produced. It takes about 6-8 weeks for a new biogas plant to start producing biogas at a reasonably fast rate. When the pressure of biogas inside the dome increases, it starts pushing the spent slurry into the outlet chamber, and finally into the overflow tank. The spent slurry being a rich source of plant nutrients is used as a manure in agricultural fields.
Biogas can be taken out for supply by spinning the gas valve. To make the biogas plant run continuously, dung slurry is fed into the digester and the spent slurry is removed from it from time to time.
Question 18.
List any four disadvantages of using fossil fuels for the production of energy. (AI 2011)
Answer:
Disadvantages of using fossil fuels for the production of energy are :
- Fossil fuels are non-renewable source of energy.
- It causes air pollution to the environment.
- It takes millions of years for its formation.
- It causes acid rain.
Question 19.
Which one of the following statement is not true about nuclear energy generation in a nuclear reactor?
(a) Energy is obtained by a process called nuclear fission.
(b) The nucleus of Uranium is bombarded with high energy neutrons.
(c) A chain reaction is set in the process.
(d) In this process a tremendous amount of energy is released at a controlled rate. (2020)
Answer:
(b) In a nuclear reactor, to produce nuclear energy, uranium is bombarded with low energy neutrons.
Question 20.
Assertion (A) : In the process of nuclear fission, the amount of nuclear energy generated by the fission of an atom of uranium is so tremendous that it produces 10 million times the energy produced by the combustion of an atom of carbon from coal. Reason (R) : The nucleus of a heavy atom such as uranium, when bombarded with low energy neutrons, splits apart into lighter nuclei. The mass difference between the original nucleus and the product nuclei gets converted to tremendous energy.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true. (2020)
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
Answer question numbers 21-24 on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts :
Geothermal energy is the energy produced by the heat of molten rocks formed in the deeper hot regions of the earth’s crust. This energy is harnessed to generate electricity. When water is made to flow deep underground in the rocks it returns as steam (or hot water, which is later converted to steam) to drive a turbine on an electric power generator.
In India, exploration and study of geothermal fields started in 1970. The Geological Survey in India has identified 350 geothermal energy locations in the country. The most promising of these is in Puga valley of Ladakh. The estimated potential for geothermal energy in India is about 10000 MW. There are seven geothermal provinces in India namely the Himalayas, Sohna, West coast, Cambay, Son-Narmada-Tapi; Godavari and Mahanadi. Most power station in India produce Alternating Current (AC). (2020)
Question 21.
What are geothermal energy hot-spots?
Answer:
Due to geological changes, molten rocks formed in the deeper hot regions of earths crust are pushed upward and trapped in certain regions. These regions are called hot spots.
Question 22.
Name two countries, other than India, where power plants based on geothermal energy are operational.
Answer:
Many geothermal power plants are operational in countries such as New Zealand and United States of America.
Question 23.
Name the phenomenon that explains the working of an electric generator.
Answer:
An electric generator works based on the principal of electromagnetic induction.
Question 24.
State an important advantage of using AC over DC.
Answer:
A.C. can be transmitted to distant places without much loss of electric power than D.C.
Question 25.
Name any one material used to make a solar cell and also mention the range of voltage produced by a typical cell. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Silicon is used to make a solar cell. A typical cell develops a voltage of 0.5 – 1 V.
Question 26.
Write the name of the substance whose vapours are used to run the turbine of the generator of ocean thermal energy plant. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
Volatile liquid ammonia.
Question 27.
Name the energy obtained from sea or ocean water due to the difference in temperature at the surface and in deeper sections of these water bodies. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Ocean thermal energy.
Question 28.
Explain the term ‘Hot Spots’ in the context of geothermal energy production. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
Refer to answer 21.
Question 29.
Name any two elements that are used in fabricating solar cells. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
Silicon, Silver.
Question 30.
Differentiate between energy obtained by burning fossil fuels and that obtained as solar energy. (Board Term I, 2017, 2013)
Answer:
- The reserves of fossil fuels are limited, i.e., exhaustible whereas solar energy is available in abundance (and that too without any cost), i.e., it is inexhaustible.
- Fossil fuels cause pollution on burning whereas solar energy is pollution free.
- Fossil fuels can provide energy at any required time whereas solar energy becomes unavailable when the sky is covered with clouds.
Question 31.
Define the process of nuclear fission. Write the steps involved in generating electricity in a nuclear reactor. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
The phenomenon of splitting up of a heavy nucleus, on bombardment with slow speed neutrons, into two fragments of comparable mass, with the release of two or more fast moving neutrons and a large amount of energy is known as nuclear fission.
Steps involved in generating electricity:
- Large atoms like uranium or plutonium are bombarded by slow moving neutron.
- Large atoms break and releases lots of heat energy.
- This heat is used to boil water to steam.
- This steam rotates the turbine which produces electricity.
Question 32.
Name the three forms in which energy from sea is available for our use and write one limitation of each. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
- Tidal Energy:
Limitation : The rise and fall of water during tides is not high enough to generate electrical energy on a large scale. There are very few places suitable for building dams. It is for these reasons, the tidal energy is not likely to be a major source of energy. - Wave energy:
Limitation : Wave energy would be a viable proposition only where waves are very strong. - Ocean thermal energy Limitation : The efficient commercial exploitation is difficult.
Question 33.
Nuclear power is an excellent non-conventional source of energy. Still it is not used commonly for power generation. Why? State three reasons. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Nuclear power can not be exploited easily because:
- the waste products of nuclear reactions (produced at nuclear power plants) are radioactive which keep on emitting harmful nuclear radiations for thousands of years. So, it is very difficult to store or dispose off nuclear wastes safely. Improper nuclear waste storage or disposal can pollute the environment.
- there is the risk of accidents in nuclear reactors (especially the old nuclear reactors). Such accidents lead to the leakage of radioactive materials which can cause serious damage to the plants, animals (including human beings) and the environment.
- the high cost of installation of nuclear power plants and the limited availability of uranium fuel make the large scale use of nuclear energy prohibitive.
Question 34.
Explain the principle and process of converting ocean thermal energy into electricity. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Principle : There is a temperature difference between the water at the surface of the sea and deep below the sea. The difference in temperature at many places is of the order of 20°C. This difference in temperature can be exploited to produce electric energy in ocean thermal energy conversion plant (OTEC).
Working : In one of the methods, a low melting point liquid or fluid such as ammonia (volatile liquid) or chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) is used to run the turbine of a generator. The warm surface water is used to boil the liquid like ammonia or CFC in a heat exchanger and vapours thus formed are used to drive the turbine of the generator. In another exchanger cold water from the depth of the ocean is pumped up to condense the vapours of the ammonia again to liquid. This ammonia is reused and the cycle repeats.
Question 35.
Give two examples each of the following :
(i) Renewable sources of energy
(ii) Non-renewable sources of energy (AI 2011)
Answer:
(i) Examples of renewable sources of energy are wind energy, solar energy, etc.
(ii) Coal, petroleum and natural gas are the examples of non-renewable sources of energy.
Question 36.
Write two points of difference between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. Give one example of each. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
| Renewable source of energy | Non-renewable source of energy |
| 1. These sources of energy are replenishable. | These sources of energy are not replenishable. |
| 2. It takes less time to form again. | It takes hundreds of years to form again. |
| 3. Examples: sun wind etc. | Example: coal, petroleum etc. |
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2015
37.Name any two fossil fuels.
Ans. A good fuel is the one which
- has high calorific value,
- is non-polluting,
- is easy to transport and easily available,
- has moderate ignition temperature.
38.Mention the purpose of blackening the interior of a solar cooker.
Answer. The purpose of blackening the interior of a solar cooker is that the black surface absorbs more heat radiations of incident solar energy (about 98%) as compare to white or other light coloured surface
Short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] – Year 2015
39.Why do people oppose the construction of Tehri Dam on the river Ganga and Sardar sarover project on the river Narmada. (Or)
Mention three disadvantage of producing hydroelectricity by constructing the dams.(Or)
List any three ways in which construction of dams for production of electricity adversely affects the environment of that place.
Answer.
- Large area is required to build the dam that result rehabilitation of displaced people.
- Large eco-systems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dams.
- The vegetation which is submerged rots under anaerobic conditions and gives rise to large amounts of methane gas which leads to a green-house effect.
40. Reena’s father works with a company that builds dams. Once he took her to the site where a dam was being built. Reena saw a group of people sitting there and shouting slogans against the building of dam. She talked the group of people and asked them about their problems and then discussed it with her father. She then tried to convince the people to talk with the authorities and come to an amicable solution. The discussion was successful. Reena’s father was very proud of his daughter. Now answer the following questions:
(i) Why was Reena’s father proud of his daughter?
(ii)Why was the group of people protesting against the building of dam?
(iii) Reena’s contribution to the peaceful resolution of the conflict proved to boon for many citizens of the country. How?
Answer.
(i) Because she convinced the people by explaining them the advantage of constructing dam and come with a solution of rehabilitation of displaced peoples. So the contribution to the peaceful resolution of the conflict make Reena’s father proud of his daughter.
(ii)The group of people protesting against the building of dam because of following disadvantages
(a) A large area of agricultural land and human habitation are sacrificed as it get submerged at the dam site.
(b) Large ecosystems are destroyed when submerged under water.
(c) The decomposition of vegetation under anaerobic condition produces methane gas which is also a greenhouse gas.
(iii)(a) The citizens are not affected by flood as it can be controlled by storing the water behind the dam.
(b) Farmers get benefited as water for irrigation is available for the whole year.
(c) Low cost of production of electricity gives monetary gain which is a boon to citizens.
41.Bio gas is an excellent fuel. Justify the statement by giving two reasons. Mention the main constituents of bio gas along with its percentage.
Answer.
(i) It burns without smoke and leave no residue therefore causes no atmospheric pollution.
(ii)Its heating capacity is high, i.e. it has high calorific value. Main constituents of bio gas: The composition of bio gas varies depending upon the nature of organic matter feeding in’the digester and advanced waste treatment technology. The typical composition of bio gas is
Methane 50 – 75%
Carbon dioxide 25 – 50%
Nitrogen 0 – 10%
Hydrogen 0 – 1%
Hydrogen sulphide 0 – 3%
42.(a) Define tidal energy.
(b) Explain how the tidal energy is harnessed and write one limitation of the use of tidal energy.
Answer.
(a) Tidal energy: The energy produced by the surge of ocean water during high and low tides due to difference in sea-levels is called tidal energy. The high and low tides occur due to the gravitational pull of the moon. This causes enormous movement of water.
(b) Tidal energy is harnessed by constructing a dam near the shores. During the high tides water flows into the dam and during the low tides, water flows out. This flowing water rotates the turbine, present at the opening of the dam and produces electricity.
43. Define process of nuclear fission. Writ the steps involved in generating electricity in a nuclear reactor.
Answer. Nuclear Fission: The process in which a heavy nucleus (such as uranium, plutonium or thorium) is broken into two nearly equal fragments when bombarded with low-energy neutrons and a tremendous amount of energy is released. This process is called nuclear fission.
Steps involved in generating electricity:
- The fuel rods full of uranium pellets are placed in a nuclear reactor chamber.
- Low-energy neutrons are bombarded on uranium fuel rod.
- A self-sustaining fission chain reaction starts that releases energy at a controlled rate.
- With this heat the reactor converts water to steam at a high temperature and pressure.
- This high temperature and pressure steam spins generator turbines producing electricity.
- The steam cools back into water, which can then be used over again.
Long Answer Type Question [5 Marks] – Year 2015
44.Nikhil and Neha went to a remote village in Kerala to meet their grandmother. They were surprised to see a biogas plant in Mr. Nair’s house in the neighbourhood. There were plenty of livestocks and the household used cooking gas from the plant. Also their farms had rich vegetation. They contacted sarpanch of the village and convinced him to set up a biogas plant for village community.
(a) Mention the values displayed by Mr. Nair, Nikhil and Neha.
(b) Explain the possible arguments given by Nikhil and Neha to the sarpanch to convince him to set up community biogas plant.
Answer.
(a) Mr Nair: Higher degree of general awareness, helping nature.
Nikhil and Neha: Knowledge sharing.
• helping nature.
• concern for community advantage.
(b) Possible arguments given by Nikhil and Neha in favour to set up community biogas plant, to the sarpanch on
- Economical source of energy.
- Cleanliness of the whole village.
- Use of slurry left behind as mannar which is rich in nitrogen and phosphorous.
- It reduces air pollution and greenhouse effect.
- It raises the standard of living.
- It is beneficial to entire village community. Basically they discuss and explain the advantages of community bio gas plant for the’entire village.
45.Solar cooker takes more time as compared to the LPG to boil potato or rice, yet Kunal uses solar cooker for such type of cooking:
(i) Why does Kunal uses Solar cooker instead of LPG? Give reasons for your answer.
(ii) Name the phenomenon which is responsible for obtaining high temperature in solar cooker.
Answer.
(a)(i) There are no energy losses while cooking on the solar cooker as the food gets cooked in a controlled environment whereas cooking on the LPG leads to maximum percentage of energy loss.
(ii) Temperature controlled cooking retains the nutrient value of the food.
(iii) Using the solar cooker, LPG can be served which result reduction in the emission of CO2.
(iv) It saves a lot of prestigious time which is normally consumed for cooking purpose.
(b) Greenhouse effect.
46. Manoj’s father works in a nuclear power reactor. He asked his father to take him for a visit to nuclear power reactor. But his father was not keen to take him there. Now answer the following questions:
(i) What could be the possible reason of Manoj’s father not taking him to the nuclear power reactor?
(ii) Write one advantages and one disadvantage of setting up a nuclear power reactor. .
Answer.
(a) (i) Safety concerns.
(ii) Health concerns.
(b) Advantage: From a small amount of nuclear fuel, a large amount of energy is released in a nuclear power reactor.
Disadvantage: There is risk of harmful radiation leakage from nuclear waste.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2014
47. Name the part of a biogas plant where reactions take place in the absence of oxygen.
Answer. Digester chamber.
48. Name the kind of energy possessed by wind and the device used to harness it.
Answer. Kinetic energy, wind mill.
49. List two non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer. Geothermal, solar, biomass, water, wind are the non-conventional sources of energy, (any two)
50. A black surface absorbs more heat radiations as compared to a white or a
reflecting surface under identical conditions. List two solar devices which make use of this property in their design.
Answer. Solar cooker, solar water heater.
51. Name any two elements that are used in fabricating solar cells.
Answer. Germanium, Silicon.
52. Why a solar cooker painted black form outside?
Answer. Black surface absorbs more heat as compared to white or reflecting surface under identical conditions.
Short Answer Type Question [I] [2 Marks] – Year 2014
53. Define fuel. List any two characteristics that you would look for in a good fuel.
Answer. A substance that produces useful energy when it burn or undergoes a chemical f or nuclear reaction. The fuel such as coal, wood, oil, or gas provides energy when burned. A good fuel is the one which produces a huge amount of heat on burning. It does not produce a lot of smoke and is easily available.
Short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] – Year 2014
54. State any three reasons to justify that LPG is considered as an ideal fuel.
Answer. LPG is considered as an ideal fuel because
- It is easy to store, handle and transport.
- It produces large amount of heat on burning.
- It does not leave any residue on burning,
55. Sate any three advantages of charcoal over wood.
Answer. Advantages of charcoal over wood
- It has higher calorific value, i.e. higher heat generating efficiency.
- Charcoal does not produce smoke on burning so it is a clean fuel.
- It is easier to transport and ready to use in a convenient dry and broken-up form.
56. Ramesh is a student of standard X. He organized many activities in his school to convey the students about the various advantages and disadvantages of using renewable and non-renewable sources of energy. Many students of the school took part and concluded about the best choices of energy sources on this basis.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What activities Ramesh might have had assigned for the students?
(ii) Name any two renewable sources of energy.
(in) Which two values are reflected in Ramesh’s thought and action?
Answer.
(i) Activities that Ramesh have had assigned for the students are:
(a) Hands on projects related to renewable and non-renewable sources of energy.
(b) Photograph exhibitions on the topic “use of fossil fuel and its impact on the environment.”
(c) Essay writing competition on a “renewable energy technology that could potentially be used for community.”
(d) Group discussion on advantages and disadvantages of using renewable and non-renewable sources of energy for selection of best source of energy.
(ii) Solar energy, hydro energy.
(iii) Ramesh’s thought: Higher degree of general awareness proper use of renewable source of energy.
Ramesh’s action: Concern for community advantage and good management.
57. Megha asked her mother to install a solar water heater on the roof top. Her mother asked about the need of such installation. Megha convinced her mother and succeeded in setting up a solar water heater on her roof top.
(i) State one advantage of installing the solar water heater to Megha’s family and to the society.
(ii) What qualities of Megha are reflected in her action?
(iii) State one limitation in using solar water heater.
Answer.
(i) Advantage of solar water heater (any one)
(a) Once solar water heater installed, the family and society never need to pay for heating up the water again.
(b) Megha’s family and society make their contribution to the nation to curb the emission of green house gases.
(ii) General awareness, concern for community advantage and proper use of ‘ renewable source energy.
(iii) (a) It does not work at night as well as on cloudy day.
(b) Relatively low heating system efficiency of passive solar water.
58. Mariyam made a solar cooker on her own. She used a white metallic box with a lid. She put the food in the solar cooker for heating and closed the lid. But she did not get good results. She then consulted her teacher to know her mistakes. Her teacher pointed out her mistakes, which she later rectified.
(a) According to you, which two mistakes were made by Mariyam and what
did she do to rectify them?
(b) Which qualities of Mariyam are rectified in her action.
answer.
(a) The possible mistakes were made by Mariyam are:
- The outer and interior of solar cooker might not have been blackened.
- Instead of using glass lid she might have been used plastic cover.
- The solar cooker might not have been insulated properly.
- The cooker utensil used for cooking might not have been blackened.
(b) • Gaining practical knowledge of what she have learned in theory. She wanted to adopt the eco-friendly life style.
59. Aditya suggests his family to install a solar water heater at their residence. But
some of the family members were in favour of installing an electric geyser.
Ultimately the family got water heater installed.
(a) Which according to you was correct? Give two reasons in support of your answer.
(b) Mention two possible changes in the thinking of the family members
because of the arguments Given by Aditya.
answer. (a) The decision of installing the solar water heater was correct this is due to
(i) Their system use solar energy which is a renewable source of energy and free.
(ii)It will reduce our dependence on fossil fuel, improving on our energy security and reduce the country import bill for fuel.
(b) Two possible changes in the thinking of the family members because of the arguments given by Aditya are:
(i) We should conserve the non-renewable fuels for application for which renewable source of energy is not easily available.
(ii)Solar water heating is good investment and cost effective. It is one of the safe and efficient way to deliver hot water free of cost.
60. Traffic jams, outside the school gate was a common sight since most of the students came on their own cars. This became a topic for discussion on every P.T.A meeting. On one such P.T.A meeting, the principle pointed out the examples of four of their teachers who were carpooling for the past several
years. She asked the parents to adopt this method to sort out the problem.
(i) List two values shown by the teachers mentioned by the principal.
(i) Explain two advantages that will occur if more parents emulate the examples of these teachers.
answer.
(a) The two values shown by the teachers mentioned by the principle are:
(i) Eco-friendly life style.
(ii) Co-ordination and friendship.
(b) (i) Reduction in air pollution and traffic congestion: Car pooling reduces the emission of CO2 into the atmosphere as every car pooling participant takes another car off the road.
(ii) Save money: Car pooling saves money by using less fuel. It reduces the cost involved in repetitive or long distance journey.
61. On returning home, Neha, a IXth std. student noticed that her 6 years old brother Neresh, watching T.V in the afternoon with all the lights and fans ‘on’. She noticed that the windows were closed and curtains were drawn, which made the room dark, so, Naresh had put on the lights. She calmly opened the windows, drew the curtain aside, which illuminated and aerated the room. Then she made Naresh put “off” the lights and made him understand the reason behind her action. (Assume that they are getting electric supply from Thermal Power Plant)
(a) List the two value exhibited by Neha.
(b) Explain how she tried to give same values to her brother.
answer.(a) The values exhibited by Neha are:
(i) Responsible citizen in the conservation of energy resources.
(ii) Adopt fuel and money saving technique in her life.
(b) Neha tried to give the same values to her brother Naresh by opening the windows, draw the curtain aside, which illuminated and aerated the room. This way she shows the practice of adopting renewable sources of energy like solar energy and conserve the fossil fuel like coal.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2013
62. What is acid rain?
answer. Acid rain: The rain containing the acidic oxides such as oxides of carbon, nitrogen and sulphur.
63.Write the name of the substance whose vapours are used to run the turbine of the generator of ocean thermal energy plant.
answer. Ammonia.
64. Mention the minimum temperature difference required between surface water and water at a depth of upto 2 km in an ocean thermal energy plant.
answer. 20 °C or 293 K in trapping geothermal energy
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] – Year 2013
65. State the principle of working of ocean thermal energy conversion plant.
Explain how the plant works? Write one essential condition for it to operate
properly.
answer. Principle of working of OTEC: The water at the surface of the ocean is warmer
than the water at deeper depths. This temperature difference can be used by
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) systems to generate electricity.
Working of OTEC:
- In OTEC plant, the energy of warm surface water is used to convert low i boiling point liquid ammonia into gaseous state.
- The vapour of ammonia at high pressure is used to spin the turbines of generators converting the Ocean thermal energy to electricity.
- The used vapour pass through the condenser where cold water, pumped from the deeper parts of ocean condenses ammonia vapour back into a liquid.
- This process is repeated again and again ,to get continuous production of electricity.
Essential condition for it to operate properly: The temperature difference between the warmer water at the surface and colder water at depths up to 2 km should be 293 K (20°C) or more.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2012
66.Name one fuel used in nuclear reactor.
answer. Uranium-235.
67.Name any two elements that are used in fabricating solar cells.
answer. Germanium, Silicon.
68.Name the reaction responsible for large energy production in the sun.
answer. Nuclear fusion.
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] – Year 2012
69.Mention why is it not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs? State three reasons to support your answer. Also mention three uses of solar cells.
answer. It is not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs because:
(i) of limited availability of special grade semiconducting materials such as silicon and germanium.
(ii)solar cells have lower efficiency as they depend entirely on intensity of solar radiation.
(iii) the process of manufacturing of solar cells is very expensive, silver used for interconnection of cells in the panel further adds to the cost.
Uses of solar cells:
(i) They provide electric power to satellites and space probes.
(ii) They provide electric power to off-shore drilling platforms and light houses.
(iii) TV relay stations or wireless transmission systems located in remote areas use solar panels to get electric power.
70.Out of two elements A and B with mass number 2 and 235 respectively, which one is suitable for making ,
(a) a nuclear reactor,
(b) a hydrogen bomb?
Name the nuclear reaction involved in each case. Write one difference between the two types of nuclear reactions.
answer.
(a) For a nuclear reactor— element ‘B’ with mass number 235 is suitable as a fuel in a nuclear reactor.
(b) For a hydrogen bomb— element ‘A’ with mass number 2 is suitable for making the hydrogen bomb.
The nuclear reaction involved in
(a) nuclear reactor is nuclear fission reaction and
(b) nuclear bomb is nuclear fusion reaction.
Difference between fission and fusion:
Fusion reaction releases much greater energy with non-radioactive products than the energy released in fission reaction with radioactive products.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] – Year 2011
71. List two nutrients that the slurry left behind in the biogas plant contain.
answer. Nitrogen and phosphorous.
72. Biogas is also known as gobar gas. Justify.
answer. Starting material for biogas is mainly cow dung. So, it is also known as gobar gas.
73. List two practical uses of biogas in rural areas.
answer. Practical uses of biogas in rural area are:
- It is an excellent fuel which burns without smoke with high heating capacity.
- It is also used for lighting.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] – Year 2011
74. Bio gas is considered to be a boon to the farmers. Give reasons.
answer.
- It is the source of excellent manure, rich in nitrogen and phosphorous which
can be obtained from the biogas plant in addition to biogas. - It provides the safe, efficient and profitable disposal method for bio-waste and sewage material.
75. What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
answer. Advantages of nuclear energy are:
- A small quantity of nuclear fuel is needed to produce a large amount of useful energy.
- Nuclear power plant produces less atmospheric pollution than thermal power plants, if the nuclear fission reaction is performed properly.
- Small amount of nuclear fuel can run a nuclear power plant over a long period of time. There is no need of inserting the nuclear fuel in the nuclear reactor again and again in a short period as in case of thermal power plant.
76. What is a solar cell panel? Mention any three of its applications.
answer. A large number of solar cells combined in an arrangement to obtain large electrical power is called solar cell panel.
Applications of solar cell panel are:
It provides the electric power for the:
- working of artificial satellites stationed in outer space,
- running of irrigation water pumps by the farmers in rural areas,
- street lighting in remote areas.
77. Out of two solar cookers, one was covered with a plane glass slab and the other was left open. Which of the two solar cookers will be more efficient and why?
answer. The solar cooker which was covered with a plane glass slab would be more efficient. The glass lid allows the heat radiation from sun to enter the solar cooker but does not allow the reflected heat radiation to escape or go outside the box. Thus, heat trapped inside the box increases the temperature. Glass lid also reduces heat loss due to reflection.
Short Answer Type Questions [II] [3 Marks] Year 2011
78.List any three hazards of nuclear waste. How does the disposal of nuclear waste pose a problem for the plant and animal life?
answer. Hazards of nuclear wastes are:
- Nuclear waste contains radioactive substances which emit harmful nuclear radiations.
- There is a high risk of environmental contamination.
- It is highly toxic.
Effect of nuclear waste on plant and animal life is:
The radiations emitted from the nuclear waste penetrate deep inside the human or animal body where they can damage biological cells thereby initiate cancer or causes genetic disease.
Increased mortality of plants, soil invertebrates and mammals and reproductive losses in plants and animals have also been observed.
79. (a) Charcoal is a better fuel than wood. Why? .
(b) How does biogas plant help to reduce the problem of pollution?
answer.
(a) Charcoal is considered to be a better fuel than wood because:
- It burns without flames.
- It is comparatively smokeless.
- It has higher calorific value, i.e. higher heat generating efficiency than wood.
(b) Biogas plant helps to reduce the problem of pollution in the following ways.
- It provides better sanitation due to safe disposal of bio-waste and sewage material.
- Biogas obtained from this plant produces less smoke on burning. (Hi) The residue left can be used as a manure which can be used as an alternative
of fertilizers. Thus, it prevents soil and water from degradation.
80. (a) What is geothermal energy?
(b) What are the advantages of wind energy?
answer.
(a) The heat energy obtained from the molten rocks formed in the deeper hot regions inside the earth are called geothermal energy.
(b) Advantages of wind energy are:
- It is an inexhaustible source of energy.
- It does not cause any environmental pollution.
- It is available at free of cost.
81. (a) How does construction of dams across the river get linked with production of greenhouse gases?
(b) How do technological inputs improve the efficiency of biomass fuels?
answer.
(a) A vast variety of plants get submerged in water, rot under anaerobic conditions and produce large amount of greenhouse gases such as methane.
(b) Traditional uses of biomass fuels are not only efficient but they also produce a lot of pollutants which are hazardous to health. Therefore, technological inputs are necessary to improve the efficiency of these fuels and make them environment friendly. With the help of technology, smokeless chulhas and biogas plants have been designed.
Short Answer Type Questions [2 Marks] -Year 2010
82. Mention any four limitations in harnessing wind energy on a large scale.
answer. Limitations in harnessing wind energy are:
- Speed of wind is not available at all time and at all places.
- To establish the wind energy farm, a large area of land is needed.
- Speed of wind should be higher than 15 km/h to harness the wind energy.
- Construction of windmill and its installation is very expensive.
83. What happens when wood is burnt in a limited supply of oxygen? Name the residue left behind after the reaction and state two advantages of using this residue as a fuel over wood.
answer. When wood is burnt in a limited supply of oxygen, volatile materials present in it get removed and cooled to get wood tar and wood gas.
The black residue left behind aftqr the reaction is known as charcoal. Advantages of using charcoal as a fuel over wood are:
- Burning of charcoal does not produce smoke. On the other hand, wood produces a lot of smoke on burning.
- For a given quantity, charcoal produces ,more heat than wood.
84. Name four gases commonly present in biogas. State two advantages of using this gas over fossil fuels.
answer. Methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
Advantages of using biogas over fossil fuels are:
- Biogas burns without smoke, leaves no residue unlike coal.
- Biogas is cheaper as compared to fossil fuels.
85. How are the wastes produced in nuclear power plants different from those produced in a thermal power plants ? What happens to the waste of a nuclear power plant?
answer.The waste obtained from nuclear power plants is highly radioactive in nature which emits harmful radiations, whereas waste produced in a thermal power plant is non-radioactive.
Management of nuclear waste is given as follows:
- Some products of nuclear waste are buried in sealed steel/lead containers for a long term storage, buried under the ground or dumped in vacated coal mines.
- Other waste products transforms into less harmful products or to products with a shorter half life.
Short Answer Type Questions [2 Marks] -Year 2009
86. In a solar cooker, the following arrangements are made. Write one function of each arrangement.
(a) The box is made of insulating material such as plastic or wood.
(b) The inner walls of the box are painted black.
(c) The box is covered with a transparent glass sheet.
(d) A plane mirror is hinged at an angle at the top of the box.
answer.
(a) To avoid loss of heat from solar cooker to the surroundings.
(b) Black surface absorbs more heat radiations of incident energy.
(c) Transparent glass sheet does not allow the reflected heat radiation to go outside the box.
(d) To increase the amount of solar energy incident on the transparent glass sheet.
87. Describe how hydro energy can be converted into electrical energy. Write any
two limitations of hydro energy.
answer. Conversion of hydro energy into electrical energy
- High rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water to collect it at a suitable height. The stored water has a lot of potential energy.
- The water from a suitable height is allowed to fall on the blades of a turbine located at the bottom of a dam through a pipe.
- Kinetic energy of flowing water rotates the turbine rapidly. Rotation of turbine helps the armature coil of generator to rotate rapidly in the magnetic field. Thus, hydroelectricity is generated.
Limitations of hydro energy:
(i) All river-sites are not suitable for construction of dams.
(ii) Large ecosystems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dam.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
Acids: Indicators, General characteristics, Properties of acids, Chemical nature of acids.
Sources of Energy: A source of energy is that which is capable of providing enough useful energy at a steady rate over a long period of time.
A Good source of energy should be :
- Safe and convenient to use, For example; energy nuclear can be used only by highly trained engineers with the help of nuclear power plants. It cannot be used for our household purpose.
- Easy to transport, For example; coal, petrol, diesel, LPG etc. have to be transported from the places of their production to the consumers.
- Easy to store, For example; huge storage tanks are required to store petrol, diesel, LPG etc.
Characteristics of a good fuel
- High calorific value.
- Less smoke.
- Less residue after burning.
- Easy availability.
- Inexpensive.
- Easy to store and transport.
Classification of Sources of energy
The sources of energy can be classified as follows :
- Renewable sources of energy.
- Non-Renewable sources of energy.
1. Renewable sources of energy: Renewable sources of energy are those which are inexhaustible, i.e., which can be replaced as we use them and can be used to produce energy again and again.
These are available in an unlimited amount in nature and develop within a relatively short period of time.
Example of Renewable Sources of Energy :
- Solar energy.
- Wind energy.
- Water energy (hydro-energy).
- Geothermal energy.
- Ocean energy.
- Biomass energy (firewood, animal dung and biodegradable waste from cities and crop residues constitute biomass).
Advantages of Renewable Sources of Energy
- These sources will last as long as the Earth receives light from the sun.
- These sources are freely available in nature.
- These sources do not cause any pollution.
2. Non-Renewable Source of Energy: Non-renewable sources of energy are those which are exhaustible and cannot be replaced once they have been used. These sources have been accumulated in nature over a very long period of millions of years.
Examples of Non-renewable Sources of Energy :
- Coal.
- Oil.
- Natural gas.
All these fuels are called fossil fuels.
Disadvantages of Non-renewable Sources of Energy
- Due to their extensive use, these sources are fast depleting.
- It is difficult to discover and exploit new deposits of these sources.
- These sources are a major cause of environmental pollution.
Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels are the remains of prehistoric plants and animals which got buried deep inside the early millions of years ago due to some natural processes.
These fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy and cause environmental problems due to pollution.
Formation of Fossil Fuels: During its formation, an entire organism or its parts often get buried in sand or mud. These, then decay and disintegrate leaving no signs of their existence. Infact, the harder parts of organisms after their death settle down and are covered by sediments and subjected to extreme pressure and temperature or the Earth converts them into fossil fuels, the process being referred to as fossilization.
Disadvantage of Fossil Fuels
- The fossils are non-renewable sources of energy and once used cannot be renewed.
- Burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution.
- The fossil fuels reserves in the Earth are limited and may get exhausted soon.
Thermal Power Plants: It generates electricity from heat produced by combustion of coal and petroleum. For example; fossil fuels.
Use coal, petroleum and natural gas produce thermal electricity.
Electricity transmission is very efficient.
The steam produced by burning fossil fuels nans the turbine to produce electricity.
Source of energy are also classified as
- Conventional sources of energy and
- Non- conventional sources of energy.
(i) Conventional Sources of Energy are those which are used extensively and meet a marked portion of our energy requirement and these are :
(a) Fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas) and
(b) Hydro energy (energy of water flowing in rivers).
Biomass energy and wind energy also fall in this category as these are being used since ancient times.
(ii) Non-conventional Sources of Energy are those which are not used as extensively as the conventional ones and meet our energy requirement only on a limited scale. Solar energy, ocean energy, (tidal energy, wave energy, ocean thermal energy, OTE), Geothermal energy and nuclear energy belong to this category. These sources of energy which have been tapped with the aid of advances in technology to meet our growing energy needs are also called alternative sources of energy.
Renewable Sources of Energies
1. Solar Energy: The energy produced by the sun in the form of heat and light energy is called as solar energy.
Solar radiations can be converted electricity through solar cells (Photovoltaic cells).
Photovoltaic cells convert solar radiations directly into electricity through silicon solar cells.
Solar cells arrange on a large flat sheets form a Mirror solar panel.
Solar cookers are painted black from outside and a large glass plate to trap solar radiations by green house effect.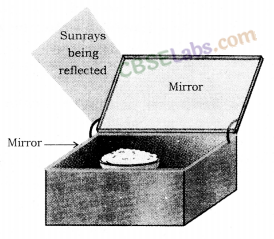
Advantages of Solar Cookers
- Eco-friendly.
- Renewable.
- Used in rural areas.
- Retains all the nutrients in food due to slow cooking.
Disadvantage of Solar Cookers :
- Silicon cells are expensive.
- Solar radiations are not uniform over the Earth’s surface.
- Cannot be used at night or on cloudy days.
- Cannot be used to make chapattis for frying as these require a temperature of 140°C or more. (Maximum temperature of 100°C only can be achieved in a solar cooker) Other Solar Devices are Solar water heater and Solar furnace.
2. Wind Energy: When large masses of air move from one place to another then it is referred to as wind. During this process, kinetic energy gets associated with it which is referred to as wind energy.
It can be converted into mechanical and electrical energy.
Kinetic energy of wind is used in running of windmills, which are used to lift water, grind grains etc.
Uses of Wind Energy
The important uses of wind energy are :
- It is used to drive windmills, water lifting pumps, and flour mills, etc.
- It is used to propel sale boats.
- It is used to fly engine fewer airplanes or gilders in the air.
- It is used to generate electrically used for various purposes like lightning, heating, etc.
Advantages:
- Eco-friendly
- Renewable.
Disadvantages :
- Wind speed does not uniform always.
- Needs a large area to erect series of windmills.
- Big amount of investment is needed.
- The output is less as compared to investment.
3. Hydro Power Plant (hydro energy): When the water flowing in a river is stored in a high rise dam and allowed to fall from the top of the dam. The water rushes down with a great force, which can be utilized to drive large water Lurbine. These turbines are connected with electric generators which generate electric current. The electricity generated in this process is termed as hydroelectricity or hydel power. In fact the process involves transference of potential energy of the water into kinetic energy’ and then into electric energy.
It is the most conventional renewable energy source obtained from water falling from a great height.
It is clean and nonpolluting source of energy.
Dams are constructed to collect water flowing in high altitude river. The stored water has a lot of potential energy.
When water is allowed to fall from a height, potential energy changes to kinetic energy which rotates the turbines to produce electricity.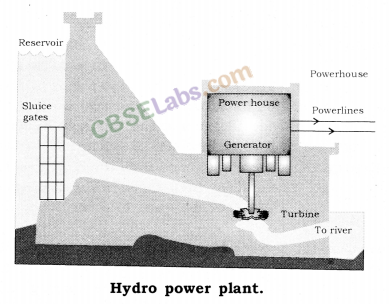
Advantages of Hydro Power Plant :
- It is readily and abundantly available everywhere free of cost.
- It is eco-friendly and does not produce any kind of environmental pollution.
- It is a renewable source as water itself is a renewable and inexhaustible resource.
- It is a cheap source of energy, as it does not involve any costly investment.
Disadvantages of Hydro Power Plant
- Highly expensive to construct.
- Dams cannot be constructed on all river sites.
- Large areas of human habitation and agriculture fields get submerged.
- People face social and environmental problems.
4. Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy is the heat of the Earth and is the naturally occurring thermal energy found within rock formations and the fluids held within those formations.
Energy harnessed from the heat of the Sun is called Geo Thermal Energy.
Magma is formed when this heat melts the rocks. The rocks and hot gases are called magma.
The magma gets collected at some depths below the Earth’s surface. These places are called ‘Hot spots’.
When underground water comes in contact these hot spots, it changes into steam, which can be used to generate electricity.
Advantages of Geo Thermal Energy
- Renewable
- Inexpensive
Disadvantages of Geo Thermal Energy
- Only a few sites are available for harnessing energy.
- Expensive
5. Ocean Energy: The oceans acquire almost 71% of the surface of the Earth. The enormous amount of water present in them did not act as a big collector of solar heat energy, but also store large amount of it due to its high specific heat. Thus, ocean water can be used as a renewable resource of energy.
The main forms of ocean energy are described as under :
(i) Ocean Thermal Energy: The energy available due to the temperature difference between the deeper levels and surface of an ocean is called as Ocean Thermal Energy,
(ii) Ocean Tidal Energy: The rise of ocean water due to the attraction of the moon is referred to as high tide and its fall as low tide. The enormous movement of water due to high and low tide provide a large amount of energy known as Ocean Tidal Energy. This tidal energy can be utilized by constructing a tidal barrage or dam.
(iii) Sea Wave Energy: The energy obtained from the high-speed sea waves is referred to as sea wave energy. Infact, these high-speed sea waves have a lot of kinetic energy associated with them, which can be used to drive dynamos which convert kinetic energy into electrical energy.
(iv) Energy from Nuclear Deuterium of Oceans: The oceans water contains an unlimited amount of heavy hydrogen isotope called as deuterium which is isotope hydrogen having one neutron in its nucleus. Scientists are working hard to produce energy by carrying the controlled nuclear fission of deuterium isotope. The process is still in its experimental stage.
(v) Energy From Salinity Gradient in Seas: The difference in the concentration of salts in the water of the two or more seas is called a salinity gradient. This salinity gradient is now a day used to obtain energy with the involvement of suitable techniques,
(vi) Energy From Sea Vegetation or Biomass: Sea vegetation or biomass is another direct source of energy because the enormous amount of seaweeds present in the sea water provides an endless supply of methane fuel.
Disadvantages: Uniform tidal action is not seen.
6. Bio-Mass: Biomass is defined as living matter or its residue and is a renewable sources of energy.
The biomass includes
- all the new plant growth
- agriculture and forest residues (like Bio-gases, dark, sea dust, wood savings, roots, animals dropping, etc..),
- Carbonaceous wastes (like sewage, garbage, night-soil, etc.)
- Biodegradable organic effluent from industries.
It is the source of the conventionally used fuels that are used in our country. For example; Cow dung cakes, fire-wood, coal, charcoal etc.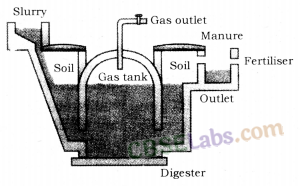
Bio-gas: It is a mixture of gases produced during decomposition of bio mass in the absence of oxygen. (Anaerobic Respiration). Methane is the major component of bio-gas.
Bio-gas plants: Animal dung, sewage, crop residues, vegetable wastes, poultry dropping, etc. are used to produce Bio-gas in Bio-gas plants.
Advantage of Bio-gas
- A Bio-gas plant, is quite simple, can easily be built in rural areas. A small plant using dung from 3 to 4 heads of cattle is capable of supplying Bio-gas for 6 hours daily for cooking purposes.
- Bio-gas is a clean fuel that burns without smoke and leaves no ash.
- The main constituent of Bio-gas, i.e., ethane has a higher calorific value (55 kj/g) that of petrol (50kj/g).
- The spent slurry, being rich in nitrogen and phosphorus is good manure.
- By using Bio-gas, firewood is saved and deforestation is reduced.
Composition of Bio-gas: Bio-gas is mainly composed of methane (up to 75%), C02 (25%) and traces of other gases such as nitrogen and hydrogen. Whereas methane is a high-value calorific fuel, carbon dioxide is an inert gas.
7. Nuclear Energy: A reaction in which, the nucleus of an atom undergoes a change to form a new atom and releases an enormous amount of energy is called as nuclear energy. There are two distinct ways of obtaining nuclear energy, (a) Nuclear fission and (b) Nuclear fusion.
Energy released when some changes take place in the nucleus of the atom of a substance is called Nuclear energy.
It is used for heat generation, fuel for marine vessels.
Advantages of Nuclear Energy
- The alternative source of energy due to depletion of fossil fuels.
- From a small amount of fuel, a large amount of energy is released.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy :
- Risk of nuclear waste leakage.
- High cost of setting up of nuclear plant.
- Pollution of environment.
Environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy :
- The combustion for fossil fuels produces acid rain and damages plants (crops), soil and aquatic life.
- The burning of fossil fuels is increasing the amount of greenhouse gas, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- The construction of hydropower plants is a disturbing ecological balance.
- Nuclear power plants are increasing radioactivity in the environment.
Difference between Nuclear Fission and Fusion
| Nuclear Fission | Nuclear Fusion |
| 1. It involves breaking of a heavy nucleus into lighter nuclei. | 1. It involves the binding of two nuclei. |
| 2. It is carried out by the bombardment of neutrons over a heavy nucleus. | 2. It is carried out by heating an extreme temperature. |
| 3. It is a chain reaction. | 3. It is not a chain reaction. |
| 4. It is a controlled process. | 4. It is an uncontrolled process. |
| 5. It produces an enormous amount of energy. | 5. It produces more energy than nuclear fission. |
| 6. Fission products are hazardous. | 6. It does not cause pollution. |
Need for Energy: The ability of a body to do work is called energy. No activity will occur without energy. So energy is required in all walks of life.
Characteristics of a good source of energy.
- It should be able to do a large amount of work for each unit of mass or volume.
- It should be easily accessible.
- It should be easily transported.
- It should be economical.
Conventional Sources of Energy.
The sources of energy which have been in use since a long time are called conventional sources of energy. For example, Coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydel energy, wind energy and nuclear energy are considered to be the conventional sources of energy. Firewood is also a conventional source of energy but its usage is now limited to kitchens in rural India.
Fossil Fuels.
Coal: Coal was formed millions of years ago. The plants got buried under swamps and due to high pressure and high temperature inside the earth; they were converted into coal. Coal is the highest used energy source in India. During the days of the steam engine, coal was used in steam engines. Moreover, coal was also used as kitchen fuel; before LPG became popular. Nowadays, coal is mainly being used in industries.
Petroleum: Petroleum was also formed millions of years ago. The animals got buried under the ocean surface and were converted into petroleum; in due course of time.
Petroleum is the third major source of energy being used today. Petroleum products are used as automobile fuel and also in the industries. Natural gas mainly comes from the oil wells and is also a major source of energy.
Non-renewable Sources of Energy.
It takes millions of years for the formation of fossil fuels. Since they cannot be replenished in the foreseeable future, they are known as non-renewable sources of energy.
Renewable Sources of Energy.
Those sources of energy which can be replenished quickly are called renewable sources of energy. Hydel energy, wind energy and solar energy are examples of renewable sources of energy.
Hydel Energy: Hydel energy is produced by utilizing the kinetic energy of flowing water. Huge dams are built over a source of water. Water is collected behind the dam and released. When the water falls on the turbine; the turbine moves; because of kinetic energy of water. Thus, electricity is generated by the turbine. Electricity; thus generated is called hydel energy or hydroelectricity.
Limitations of Hydroelectric Plants.
- Dams can be constructed only in a limited number of places, preferably hilly areas.
- Large areas of agricultural land and human habitation get destroyed by the cons¬truction of dams.
- Large eco-systems get submerged under water. The vegetation which is submerged underwater rots under anaerobic conditions and gives rise to large amounts of methane which is a greenhouse gas.
- Rehabilitation of displaced people is another major problem.
Thermal Power Plant: In a thermal power plant, coal or petroleum is used for converting water into steam. The steam is used to rim the turbine; to generate electricity.
Biomass: The material obtained from the bodies of plants and animals is called biomass.
Examples: cattle dung, sewage, crop residue, wood, etc.
Biogas: Biogas is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide. It contains 65% of methane gas. Biogas is produced by the anaerobic degradation of bio¬mass in the presence of water but in the absence of air.
Wind Energy: Wind energy has been in use since ages. Windmills have been in use; especially in Holland; since the medieval period. Nowadays, windmills are being used to generate electricity. The kinetic energy of wind is utilized to run the turbines; which generate electricity. At present, Germany is the leading country in terms of wind energy production and India comes at number five. In India, Tamil Nadu is the largest wind energy producing state. The largest wind farm in India is near Kanyakumari; in Tamil Nadu; which generates 380 MW of electricity.
Limitations of Wind Energy: Wind farms can only be established at those places where the wind speed is high enough and is more than 15 km/hr for most parts of the year. Wind farms need to be established on large tracts of land. The fan of the windmill has many moving parts; so the cost of maintenance and repair is quite high. The initial cost of establishing a wind farm is very high.
Non-conventional Sources of Energy: Energy sources which are relatively new are called non-conventional sources of energy, e.g., nuclear power and solar energy.
Solar Energy: The sun is the main source of energy for all living beings on this earth. Even the energy in the fossil fuels has come from the sun. The sun has an endless reservoir of energy which would be available as long as the solar system is in existence. Technologies for harnessing the solar energy have been developed in recent times.
Solar Cooker: Solar cooker is very simple in design and mode of function. It is usually made from mirrors. Plain mirrors are placed inside a rectangular box. The light reflected from the plain mirrors concentrates the solar energy inside the solar cooker which generates enough heat to cook food.
Solar Furnace: Solar furnace is made like a concave mirror. Large solar furnace has many smaller mirrors to compose a very large convex mirror. The thing to be heated is placed near the focus of the mirror.
Solar Cells: Solar cells are made from silicon. The solar panel converts solar energy into electrical energy which is stored in a battery; for later use.
Limitations of Solar Energy: The technologies for harnessing solar energy are at a nascent stage. At present, the cost-benefit ratio for using solar energy is not conducive. Using solar energy is exorbitantly costly.
Tidal Energy: Due to the gravitational pull of the moon, tides happen near seashores. Water rushes up near the seashore during high tide and goes down during low tide. Dams are built near seashores to collect the water which comes during a high tide. When the water runs back to the ocean, the flow of water can be utilized to generate electricity.
Wave Energy: Waves can also be a good source of energy. Many devices are being designed and tested to produce wave energy. For example; a hollow tower is built near the seashore. When water gushes in the tube because of wave, it forces the air upwards. The kinetic energy of air in the tube is used to run a turbine. When the wave goes down; air from up goes down the tube which is also used in running the turbine.
Ocean Thermal Energy: The water at sea surface is hot during the daytime, while the water at a lower level is cold. The temperature differential in water levels can be utilized to generate energy. If the temperature differential is more than 20°C, then ocean thermal energy can be utilized from that place. For this, a volatile liquid; like ammonia; is boiled using the heat from the hot water at the surface. The steam of the volatile liquid is utilized to run the turbine to generate electricity. Colder water from the surface below is utilized to condense ammonia vapour which is then channelized to the surface to repeat the cycle.
Geothermal Energy: Heat energy from molten rocks present inside the earth created under certain favourable conditions by natural processes is called geothermal energy. It is the only type of energy which does not use solar energy.
Nuclear Energy: Nuclear fission is the process during which a bigger nucleus breaks to produce two smaller nuclei. The process generates a huge amount of energy. This phenomenon is utilized in nuclear power plants. Nuclear power is safest for the environment but the risk of damage due to accidental leaks of radiation is pretty high. Further, the storage of nuclear waste is a big problem because of the potential risk of radiation involved.
Advantages of nuclear energy.
- A very large amount of energy can be produced by a nuclear process on using very small amount of nuclear fuel in a nuclear reactor.
- The energy so produced can be easily transformed into electrical energy.
- It does not produce harmful gases.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
Short Answer Type Questions
1 Why is there a need to harness non-conventional sources of energy? Give two main reasons.
Answer. There is a need to harness non-conventional sources of energy because:
(i) fossil fuels are limited sources and are depleting fast.
(ii) burning of fossil fuels causes a lot of pollution.
2. Write two different ways of harnessing energy from ocean.
Answer. Ocean thermal energy and tidal energy can be harnessed from ocean.
Long Answer Type Questions
3. What are the environmental consequences of using fossil fuels? Suggest the steps to minimise the pollution caused by various sources of energy including non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer. Environmental consequences of using fossil fuels are:
(i) They are the largest emitters of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.
(ii) Extraction of conventional fuels threatens the ecological balance in many
areas.
(iii) These fuels cause environmental problems due to pollution.
Steps to minimize the pollution are:
(i) The dependency on fossil fuels should be reduced by switching to alternate sources of energy.
(ii) The judicious use of energy by avoiding wastage can reduce environmental problems. –
(iii) Regular servicing of energy conversion devices should be done in order to maintain their efficiency.
(iv) We should focus on developing technology that could make the energy conversion devices much more efficient and cleaner.
(v) Research should be continued to produce long lasting devices so that the environmental damage caused by assembly of devices gets minimized.
4.Energy from various sources is considered to have been derived from the sun. Do you agree? Justify your answer.
Answer.Yes, sun is the ultimate source of energy. Directly or indirectly, all the forms of energy are derived from solar energy. Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas are formed due to burial of large plants and ancient creatures whose ultimate source of energy is sun. They are indirectly derived from solar energy such as
(i) – Clouds are formed when water in lakes, rivers, seas etc. evaporates due to solar energy. They bring rainfall and snowfall. The rain and melting snow feed rivers, streams etc. This flowing water can be used for getting hydroelectricity.
(ii) – Wind energy arises due to uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun rays at two different adjoining places. Due to this, wind possesses kinetic energy.
(iii) – Plants in the process of photosynthesis converts the solar
energy into food (chemical energy). This food is consumed by animals. Thus, the animal wastes and remains of the plants constitute biomass which can be utilised as a source of energy.
(iv) – The waves are generated by strong winds (due to solar energy) blowing across the sea.
(v) – Sun is responsible for the temperature difference between the water at the surface and water at depth in seas and oceans.
Thus the energy from various sources is considered to have been derived from
the sun.
Extra Questions – Sources of Energy – CBSE Class 10 Science
Question-1
Explain why only a part of the solar energy that strikes the upper regions of atmosphere, reaches the surface of the earth.
Solution:
The ultra-violet rays and the gamma rays present in the solar energy is absorbed by the atmosphere as it comes down towards the surface of the earth, hence we say that only a part of solar energy reaches the surface of the earth.
Question-2
Exposure to which component of solar-radiation could be a health hazard?
Solution:
Ultra-violet rays and gamma rays are the components of solar radiation which could a health hazard.
Question-3
With the help of a diagram, explain the construction and working of a box type solar cooker.
Solution:
The heat absorbing property of black surfaces and the green house effect are utilised in making solar cookers. There are various types of solar cooker out of which, the box type solar cooker is one. The box of the solar cooker is made from non-conducting materials like plastics or fiberglass, with its inner walls painted in black. The walls of the box are made thick with a lining of non-conducting material to prevent loss of heat. Usually, a plane mirror is hinged on the top of the box. The mirror is adjusted in such a manner that it reflects sunlight into the box. The main purpose of the mirror is to increase the effective area for the collection of solar energy. The box is covered with a glass sheet that facilitates retention of heat inside due to green house effect. The temperature inside this type of solar cookers can go from 100 ºC to 140 ºC when they are kept in the sun for two to three hours. This type of cookers can be used to prepare food items that require slow heating, for example, for boiling rice, vegetables or dal. The solar cookers are provided with small containers with their outer surfaces painted in black. Two or three items could be prepared simultaneously by using these containers.
Question-4
Mention any two differences between a box type and a concentrator type solar heater.
Solution:
Box-type solar heater:
In this type of heater, a plane reflector is used which does not concentrate solar energy at a point.
It produces comparatively low temperature.
Concentrator type solar heater:
In this type of heater a concave reflector or a parabolic reflector is used which concentrates the solar energy in a small region called focus.
It produces high temperature.
Question-5
Why is it not possible to make use of solar cells to meet all our energy needs? State atleast two reasons to support your answer.
Solution:
(i) The electricity generated by solar cells during the day is stored by using it to change storage batteries. These storage batteries give us direct current, but to operate the various devices, alternating current is required.
(ii) The usage of solar cells becomes expensive, since the direct current given by the storage batteries has to be changed into alternating current using suitable appliances.
Question-6
Mention any four areas where solar cells are being used as a source of energy.
Solution:
Solar cells are used for street-lighting, for traffic signals, for operating water-pumps and for running radio and television sets in remote areas.
Question-7
Why can wind energy farms be established only at specific locations? Give reasons to support your answer.
Solution:
Wind energy farms can be established over a big area of land, where sufficient wind is blowing always, because electricity generated by a single wind turbine is quite small, so in order to generate a large amount of electricity, a large number of wind turbines are erected over a big area of land.
Question-8
It is difficult to use hydrogen as a source of energy, although its calorific value is quite high. Explain.
Solution:
(i) When hydrogen gas is lighted, it burns with an explosion which is very unsafe.
(ii) It is very expensive to produce hydrogen gas by the electrolysis of water because it requires a lot of electricity.
(iii) It is very difficult to store and transport hydrogen gas as it is explosively inflammable.
Hence it is difficult to use hydrogen as a source of energy, though it has high calorific value.
Question-9
State the forms in which energy stored in the oceans manifests itself. Which one of these is utilized in OTEC systems?
Solution:
The energy from oceans is obtained in three forms:
(i) Tidal energy
(ii) Ocean waves energy and
(iii) Ocean thermal energy
Ocean thermal energy is used in OTEC system.
Question-10
With the help of a diagram, explain the process of destructive distillation of wood.
Solution:
Let us take two glass tubes. In one tube we put some small pieces of soft wood and in other tube, we put some water. These two tubes are then arranged as shown in the figure. When we heat the tube with a burner, we can find that a gas goes out through the open end of the delivery tube. If we a light a match stick near this gas, it starts burning showing that it is a combustile gas. This combustile gas obtained from wood is called wood gas and it is used as a fuel. In another tube we can find that there are drops of deep black liquid at the bottom of the tube, under water. This deep black liquid is called tar. The black residue left behind the other tube is called charcoal. When this tube is cooled we can remove the charcoal from it.
Question-11
Why is charcoal considered a better fuel than wood? What are the disadvantages of converting wood into charcoal?
Solution:
Charcoal is a better fuel than wood because of the following reasons:
(i) Charcoal has better calorific value than wood, i.e., charcoal produces more heat on burning than an equal mass of wood.
(ii) Charcoal does not produce smoke while burning whereas wood produces a lot of smoke on burning and pollutes the air.
(iii) Charcoal is a compact fuel which is easy to handle and convenient to use.
Disadvantages of converting wood into charcoal:
Cutting down of trees in the forests has created the shortage of wood to prepare sufficient charcoal. As a result of this, charcoal has now become expensive fuel. Hence the use of charcoal as a fuel is discouraged so as to prevent deforestation and hence to conserve the ecosystem from the ill effects of deforestation.
Question-12
Describe the steps involved in obtaining biogas and explain what is meant by anaerobic decomposition.
Solution:
Two types of biogas plants are being used in our country; they are
1. The fixed-dome type
2. The floating gas-holder type
the main raw material used in these plants is animal dung (cow-dung, dung of horse, elephant, goat, etc). Plant wastes like vegetable skins, fruit pulp and human excreta may be added to the animal dung.
Biogas is produced by the anaerobic decomposition of animal wastes like animal dung in the presence of water. The decomposition which takes place in the absence of oxygen is called anaerobic decomposition. This decomposition is carried out by anaerobic micro-organisms called anaerobic bacteria in the presence of water but in the absence of oxygen. Animal dung and plant wastes contain a lot of carbon compounds like carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The anaerobic bacteria decomposes these carbon compounds to form methane gas, which is the main constituent of bio-gas. Some other gases like carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide are also formed.
Question-13
State the advantages of obtaining biogas from animal dung and bio-wastes.
Solution:
(i) The bio-gas obtained from animal dung and bio-wastes can be used as a smokeless fuel.
(ii) It gives us a clean fuel.
(iii) The spent dung can be used as a manure.
Question-14
Why are fossils fuels classified as non-renewable sources of energy? What steps should be taken to conserve these sources?
Solution:
Fossil fuels are non-renewable source of energy, because if they are exhausted, it cannot be regenerated in a short time. This is because of the fact that, the fossil fuels which we use today, took millions of years to be formed. The fossil fuels are being fast depleted. To overcome this depletion, we have to conserve energy. We can follow the following simple rules to conserve energy:
(i) Switch off lights and fans when not in use.
(ii) Use solar cookers, heaters, dryers wherever possible.
(iii) Use tube lights which consumes less energy instead of incandescent lamp wherever possible.
(vi) Use efficient home appliances and fuel efficient stove.
Question-15
The heat produced on complete combustion of 10 g of a fuel could raise the temperature of 2 kg of water from 20° C to 70° C. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel, if the specific heat capacity of water was 4.2 J/g ° C. Assume that the heat taken by the container is negligible.
Solution:
Mass of water = 2 kg = 2000 g
Specific heat of water = 4.2 J/g ° C
Rise in temperature, t = 70 ° C – 20 ° C = 50° C
We know that heat produced Q = m × s × t
= 2000 × 4.2 × 50
= 420000 joules
This heat of 420000 joules has been produced by burning 10 g of fuel.
Let us calculate the heat produced by burning 1 g of fuel, hence
10 g of fuel produce heat = 420000 joules
and 1 g of fuel produce heat = 420000 /10 = 42000 joule.
Thus, the calorific value of the fuel is 42000 joules per gram.
To convert it into kilojoules per gram, we have to divide by 1000, hence
Calorific value of fuel = 42000/1000 kJ/g = 42 kJ/g.
Question-16
How much energy will 1 kg mass of wood yield on complete combustion if its calorific value were 15 kJ/g?
Solution:
Calorific value of wood = 15 kJ/g = 15000 J/g
Mass of wood = 1 kg = 1000 g
Therefore heat produced by 1 kg of wood = 15000 × 1000 = 15 × 105 J.
Question-17
Suppose the average solar energy incident on the green canopy (leaves) of a tree is 108 J per day. The calorific value of the wood obtained from the tree could convert 1% of incident solar energy as wood, how many days will it take to produce 10 kg of wood?
Solution:
Calorific value of wood = 15KJ/g
Conversely the same energy (15KJ) is required to form 1g of wood.
Energy required to form 10Kg of wood = 10 × 1000 × 15 = 15 × 104 KJ of energy
The average solar energy received per day = 108J day-1
But 1% of incident energy that is useful for the formation of wood = (108) / 100 = 106 J day-1
No of days required to form 10kg of wood = (15 x 104 x 103) / 106 = 15 × 10 = 150 days.
Question-18
State the conditions essential for combustion to take place.
Solution:
The conditions for combustion to take place are:
(i) Presence of a combustible substance.
(ii) Presence of a supporter of combustion like air or oxygen.
(iii) Presence of a combustible substance to its ignition temperature.
Question-19
Explain how knowledge of the conditions of combustion could help in fire fighting.
Solution:
(i) The combustible substance like furniture, clothes and books, etc., are removed first when fire starts in a room, so that the fire may not spread due to the presence of a large number of combustible substance.
(ii) When the burning clothes of a person are covered with a blanket, the supply of air is cut off and burning stops.
(iii) A wet cloth does not burn because water present in it keeps the temperature of the cloth below its ignition temperature.
Question-20
What constitutes a source of energy?
Solution:
A resource which can provide adequate amount of energy in a convenient form over a long period of time constitutes a source of energy.
Question-21
State the two forms in which energy is mainly utilized at our homes.
Solution:
Electrical energy is used for lighting bulbs, tubes and to run household appliances. Heat energy obtained by burning wood, coal, kerosene or cooking gas are used for cooking our food.
Question-22
Explain why fossils fuels are classified as non-renewable sources of energy.
Solution:
Fossil fuels are present in limited amounts in the earth and they cannot be replaced quickly when exhausted. Hence they are called non-renewable sources.
Question-23
Name any two renewable sources of energy.
Solution:
(i) Solar energy
(ii) Wind energy.
Question-24
Why is the use of wood as a fuel not advised although forests can be replenished?
Solution:
Wood produces a lot of smoke on burning and pollutes the air. Hence it is advised not to use it as a fuel.
Question-25
How much solar energy will be received by 1m2 area in one hour, if the solar constant were 1.4 kilowatt per square metre?
Solution:
One hour = 60 × 60 = 3600 s
Solar constant = 1.4 kW/m2 = 1.4 kJ/s/m2
i.e., in 1s, 1m2 area receives energy = 1.4 kJ
So, in 1 hour, i.e., in 3600 s, 1 m2 area receive energy = 1.4 × 3600 kJ = 5040 kJ.
Question-26
What is the range of the wavelength of electromagnetic waves that constitutes visible radiation?
Solution:
The wavelength range for the visible radiation is 400 nm in violet to 700 nm in red.
Question-27
Name the component of sunlight that mainly carries heat with it.
Solution:
Infrared rays carries the sensation of heat in sunlight.
Question-28
Name any two components of solar radiation that are not visible to us.
Solution:
Ultraviolet rays and infrared rays.
Question-29
Name the type of radiation emitted by a hot electric iron?
Solution:
Infrared radiation.
Question-30
State any two activities from our daily life in which solar energy is utilized.
Solution:
(i) Solar energy is used for drying clothes.
(ii) Solar energy is used for the preservation of fruits, vegetables and fish, etc., by the process of sun-drying.
Question-31
Wavelength of radiation incident on a surface is 850 nm. Will the surface become visible when exposed to this radiation?
Solution:
The surface is not visible since the radiation incident is more than visible range, i.e., the incident radiation is an infrared radiation which is invisible.
Question-32
Name any two materials that are used for making solar cells.
Solution:
Solar cells are made from semiconductor materials like silicon and gallium.
Question-33
What prevents us in making use of solar cell panels to meet all our domestic needs of electricity?
Solution:
The electricity generated by solar cell panels during the day is stored by using it to charge storage batteries. These storage batteries give us direct current. But to operate the various devices, alternating current is required. So, the direct current given by storage batteries has to be changed into alternating current by using suitable appliances before it can be used to run various devices. This increases the cost of using solar panels as the source of electricity.
Question-34
Explain the principle behind the working of a windmill.
Solution:
When the blowing wind strikes across the blades of wind-mill, it exerts a force on them due to which the blades of the wind-mill start rotating. As long as the wind is blowing, the blades of wind-mill keep on rotating continuously. The rotational motion of the blades of the wind-mill can be used to drive a large number of machines like water-pumps, flour mills and electric generators.
Question-35
What is the minimum wind velocity required for obtaining useful energy with a windmill?
Solution:
The minimum wind velocity required for obtaining useful energy is 15 km/h.
Question-36
Explain how the energy of flowing water is related to solar energy.
Solution:
The energy of flowing water is an indirect source of solar energy. The heat of solar energy evaporates water from the oceans and the surface of earth. The water vapour thus formed rise high in the atmosphere, get cooled and fall back to the earth in the form of rain and snow. This rain water and the water formed by the melting of snow then flows rapidly in the rivers and provides us energy.
Question-37
Mention any two advantages and disadvantages of producing hydroelectricity by building dams on rivers.
Solution:
Advantages
(i) The use of water energy does not cause any pollution.
(ii) It is a cheap and renewable source of electricity, which will never get exhausted.
Disadvantages
(i) The construction of dams on rivers results in to a variety of ecological changes in the downstream area of the river.
(ii) The soil in the downstream area becomes poor in quality because of the lack of annual floods to deposit nutrient rich slit on the banks of the river.
Question-38
Name the process that converts solar energy into chemical energy in nature.
Solution:
Photosynthesis.
Question-39
Mention any two situations where muscular energy of animals is utilized to do mechanical work.
Solution:
(i) To burn the dry bio-mass, like cattle dung, directly to produce heat.
(ii) To convert the bio-mass into more useful fuels and then use these fuels for heating purposes.
Question-40
Why is burning firewood in traditional chulhas considered disadvantageous?
Solution:
(i) Most of the heat produced by burning the fuels in traditional chulhas is lost to the surroundings, only 8% of the heat is utilized in cooking food, etc.
(ii) It produces lot of smoke due to the incomplete combustion of wood, etc.
Question-41
Name the main constituent of biogas.
Solution:
Methane is the main constituent of biogas.
Question-42
Give two examples of fossil fuels.
Solution:
Coal and Petroleum.
Question-43
Name any three varieties of coal found in nature.
Solution:
Anthracite, Bituminous and Lignite.
Question-44
How is petroleum gas obtained? Name the gas that is its main constituent.
Solution:
Petroleum gas is obtained as a by-product in oil refineries from the fractional distillation of petroleum. It is also produced by the cracking of petrol. The main constituent of petroleum gas is butane.
Question-45
Name any two components obtained by fractional distillation of petroleum that are not used as a fuel.
Solution:
Asphalt and lubricating oil.
Question-46
Write the full name for LPG and CNG.
Solution:
LPG – Liquefied Petroleum Gas
CNG – Compressed Natural Gas.
Question-47
Name three characteristics of a fuel that determines its quality.
Solution:
The three characteristics of a fuel that determines its quality are:
(i) It should burn easily.
(ii) It should cause least pollution in air.
(iii) It should be easy to store and should not produce any hazards during transportation.
Question-48
The heat produced by burning of cow dung cake of mass 210 g raised the temperature of 50 g of water by 2° C. Assuming that all the heat was utilized for heating water whose specific heat capacity is 4.2 J/g ° C, calculate the calorific value of the dung cake.
Solution:
Mass of cow dung = 210 g
Mass of water, m = 50 g
Specific heat of water, s = 4.2 J/g/° C
Rise in temperature, t = 2 ° C
Heat produced Q = m × s × t = 50 × 4.2 × 2 = 420 Joules
Calorific value of cow dung = 420/210 = 2 J/g.
Question-49
Explain why is it difficult to burn a wet piece of wood.
Solution:
It is difficult to burn a wet piece of wood because water present in it keeps the temperature of wood below its ignition temperature.
Question-50
Pouring dry sand over fire helps to contain it. Explain why?
Solution:
When sand is poured over fire, the supply of air is cut off and the fire stops. When the supporter of combustion is cut off, then the combustion also stops. Hence we say that pouring dry sand over fire helps to contain it.
Question-51
What is the ultimate source of almost all our sources of energy?
Solution:
The energy that the earth receives from the sun, in the form of heat and light, is the ultimate source of almost all our source of energy.
Question-52
Define net energy or useful energy with an example.
Solution:
The difference between the output energy and the input energy is usually referred to as the net energy or useful energy. For example, when we use fuel, say coal or wood or kerosene, we have to provide some initial heat to ignite it, which in this case, is the input. The difference between the heat given off by the burning fuel i.e. the output and the input, will be the useful energy in this case.
Question-53
How does technology help in the transformation of energy?
Solution:
Technology provides the means to transform the energy of different sources into either a fuel or electricity
Question-54
How is bio gas produced?
Solution:
Bio-gas is produced by the anaerobic degradation of bio-mass in the presence of water but in the absence of air.
Question-55
Why is sun called the ultimate source of fossil fuels?
Solution:
Fossil fuels are formed by plants and animals in the course of millions of years. Fossil fuels are the energy rich compounds of carbon which were originally made by plants with the help of sun’s energy (by photosynthesis) when they (plants) were alive millions of years ago.
Question-56
Why can a match-stick light a splinter of wood but not a log of wood?
Solution:
The ignition temperature of a splinter of wood is much lower than that of a log of wood. Thus, a match-stick can produce sufficient heat to reach the ignition temperature of a splinter of wood and make it burn while a match-stick cannot produce sufficient heat to reach the ignition temperature of log of wood and thus cannot cause it burning.
Question-57
What is combustion? Give the conditions necessary for combustion.
Solution:
The process of burning of a substance in the presence of air (oxygen) to produce heat and light is known as combustion.
Conditions required for combustion are:
(i) presence of a combustible substance.
(ii) presence of a supporter of combustion (oxygen).
(iii) heating the combustible substance to its ignition temperature.
Question-58
Give the uses of Natural gas.
Solution:
Natural gas is used
(i) as a domestic and industrial fuel.
(ii) in thermal power plants to generate electricity.
(iii) as a fuel in vehicles like buses, cars, autos etc.
(iv) in the fertilizer industry as a source of hydrogen gas.
(v) in the tyre industry as a source of carbon
Question-59
Wood is a renewable source of energy, but the use of wood as a fuel is not a wise decision. Explain.
Solution:
Wood is a renewable source of energy. It is obtained by cutting trees. A newly planted sapling usually takes more than 15 years to grow and mature into a tree. Therefore replenishment of cut down trees takes a very long time. Cutting down of trees causes the depletion of forests leading to an imbalance in nature. Due to unsuitable air and the above reasons, usage of wood as a source of energy is not a wise decision.
Question-60
What is meant by solar heating device?
Solution:
A device, which utilises sun’s energy, is called a solar heating device.
Example: Solar Cooker, Solar Heater, etc.
Question-61
Solar energy can be harnessed directly as well as indirectly. Give two examples of each type.
Solution:
(i) Direct utilization of solar energy
The direct utilization of solar energy can be done either by collecting it as heat or by converting it directly into electricity.
Examples: Solar cooker and solar water heater uses this type of utilization of solar energy.
(ii) Indirect utilization of solar energy
The indirect utilization of solar energy can be done by converting it into chemical energy like the bio-mass of plants. The other indirect ways of utilizing the solar energy are: Harnessing the energy of the wind and utilization of energy of the sea-waves.
Question-62
Explain why a solar cooker box is painted black from the inside?
Solution:
A black coloured surface absorbs much more heat when compared to a white coloured surface. Hence in the designing of solar heating devices, black painted surfaces are used so that they may absorb the maximum amount of heat from the sunlight or sunshine. In a box-type solar cooker, the inner walls and the bottom of the cooker are painted black to maximize absorption of heat and to minimize heat loss due to reflection. A metal sheet, which is painted black, can be considered as the simplest solar heating device because on keeping in sunshine, it absorbs a lot of sunrays and becomes quite hot. However, after becoming hot, a black surface itself starts radiating the absorbed heat. So, after some time its temperature starts decreasing and tends to become equal to the temperature of its surroundings.
Question-63
Explain why the property of glass in trapping heat is called greenhouse effect?
Solution:
The property of glass is made use of in constructing green-houses used for protecting green plants in very cold climate. A greenhouse is a house-like structure made entirely of glass. The plants to be protected from the cold weather are placed inside this glass house. The glass roof and glass walls of the green-house allow the heat and light of the sun to pass through them and go inside it. They do not allow the inside heat to go out. In this way, heat gets trapped in the glass house due to which it becomes quite warm inside.
Question-64
How are solar cells made?
Solution:
Solar cells are made from semi-conductor materials like silicon and gallium. To make solar cells, the wafers of semiconductor materials containing impurities are arranged in such a way that when light falls on them, a potential difference is produced between the two regions of the semi-conductor wafers. This potential difference then produces electric current. The potential difference produced by a single solar cell of 4 square centimeter size is about 0.4 volt to 0.5 volt and generates a current of 60 milliamperes.
Question-65
What causes the wind to blow?
Solution:
Solar energy is responsible for the blowing of the wind. The sunrays fall on the whole earth. But the intensity of sunrays is much more stronger near the equator of the earth than in the polar regions. Due to more intense sun-heat, the air near the surface of the earth in equatorial regions becomes quite hot. This hot air, being lighter, rises upwards. The cooler air from the polar regions of the earth starts flowing towards the equatorial regions of the earth to fill the space vacated by the hot rising air. In this way, air flows from the higher pressure regions to the low pressure regions of the earth. This flow of air from one place to another constitutes wind.
Question-66
Explain the transformation of energy taking place in the generation of hydroelectricity.
Solution:
The water stored in a high dam has potential energy in it. When the dam water is allowed to fall down, the potential energy of stored water is converted into the kinetic energy of flowing water. When this fast moving water falls on the water turbine, its kinetic energy is transferred to the water turbine. By gaining the kinetic energy, the water turbine starts rotating rapidly and also rotates the armature of the generator fixed on its shaft. The armature then converts the kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Question-67
Explain how tidal energy can be used for generating electricity.
Solution:
The rise of ocean water due to the attraction of the moon is called ‘high tide’ whereas the fall of ocean water is called ‘low tide’. The tidal water in the oceans builds up and recedes twice a day. The enormous movement of water between the high tides and low tides provides a very large source of energy in the coastal areas of the world. The tidal energy can be harnessed by constructing a tidal barrage or tidal dam. During high tide,when the level of water in the sea is high, sea-water flows into the reservoir of the barrage and turns the turbines. The turbines then turn the generators to produce electricity. During the low tide, when the level of seawater is low, the seawater stored in the barrage reservoir is allowed to flow out into the sea. This flowing water also turns the turbines and generates electricity. Thus, as seawater flows in and out of the tidal barrage during high and low tides, it turns the turbines to generate electricity.
Question-68
State two advantages and two disadvantages of geothermal energy.
Solution:
Advantages
(i) It is economical to use because the cost of electricity produced by using geothermal energy is almost half of that produced from conventional energy sources.
(ii) It does not cause any pollution.
Disadvantages
(i) It is not available everywhere, it is available only in those areas where there are hot rocks near the earth’s surface.
(ii) Deep drilling in the earth to obtain geothermal energy is technically very difficult and expensive.
Question-69
Why is it not good to burn animal dung directly as a fuel?
Solution:
It is not good to burn animal dung directly as a fuel because
(i) Animal dung contains important elements like nitrogen and phosphorus which are required by the soil to support crops. So, burning of dung in the form of dung cakes, destroys the useful nutrients which can otherwise be use as a manure in agriculture.
(ii) They produce a lot of smoke on burning which causes air pollution.
(iii) They do not burn completely, they produce a lot of ash as residue.
(iv) They have a low calorific value.
Question-70
Name the substance from which alcohol is manufactured on a large scale. What is this process known as?
Solution:
Alcohol is made from sugar. It is manufactured in large quantities by fermentation of sugar.
Question-71
What are the drawbacks of wind energy?
Solution:
The power which is generated using wind energy is not much efficient and also we cant get the power generation all the times.
Question-72
How is tidal energy harnessed?
Solution:
High tides of sea, which can be used to generate power by using the turbine. A turbine converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Question-73
Why is charcoal a better fuel than wood?
Solution:
Charcoal is a better fuel than wood, because it has high thermal capacity than wood.
Question-74
How is biogas prepared?
Solution:
When wood is compressed for a number of years inside the earth, it becomes charcoal. By using the charcoal, we can produce the biogas. Methane is the known biogas.
Question-75
Explain the function of turbine.
Solution:
Turbine is one which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Hydroelectric power is generated using turbines which converts air pressure into electrical energy using rotation of turbines and also flow of water through turbines converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Question-76
Give some examples for renewable and non-renewable sources?
Solution:
Solar energy, wind energy are the examples of renewable sources. Coal, petroleum, fuel are the examples of non-renewable sources.
Question-77
Which is the known biogas?
Solution:
Methane is the known biogas.
Question-78
Heat produced on burning 5gm of a fuel raises the temperature of 1 kg of H2O from 20oC – 60oC. If the specific heat of H2O is 4.2J/goC, calculate the calorific value of the fuel?
Solution:
Formula: mst = 5 gm x 4.2 x 40 = 840.
Question-79
Explain greenhouse effect.
Solution:
The phenomenon whereby the earth’s atmosphere traps solar radiation, caused by the presence in the atmosphere of gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the earth’s surface.
Question-80
Why does the interior of a car parked in the sun become hot?
Solution:
The solar radiation which is absorbed by the car is the basis for the green house effect.
Question-81
What is solar constant?
Solution:
The Solar Radiation that falls on an area above the atmosphere at a vertical angle: s = 1.37 kW / m².
In space, solar radiation is practically constant; on earth it varies with the time of day and year as well as with the latitude and weather. The maximum value on earth is between 0.8 and 1.0 kW / m². In Germany, the average annual amount of insolation varies between 950 and 1100 kWh / m², depending on the region.
Question-82
What radiations are converted to electricity in a solar cell? What are they used?
Solution:
Solar radiations are converted into electricity in solar cell which is used in traffic signal lights, etc.
Question-83
Name any two renewable sources of energy.
Solution:
Solar energy and wind energy.
Question-84
Explain about calorific value of fuel.
Solution:
Heat energy is measured in units of joules or calories (1calorie = 4.18 joules). The heat generated by fuels when they burn in joules or calories measures quality of fuels. All fuels do not burn efficiently. Thus there are fuels that produce more heat than the others are. This can be distinguished in terms of number of joules or calories that they generate on burning.
Question-85
Define ignition temp. Which has lower ignition temperature, kerosene or LPG. Why?
Solution:
When any substance tends to burn for a particular temperature it is called the ignition temperature for that particular substance.
Question-86
Explain about solar collector.
Solution:
Solar collector is a form of collector which collects solar energy and transforms the solar energy to the form which can be utilized according to the system.
Question-87
What are the characteristics of source of energy?
Solution:
Characteristics are generally classified in to renewable sources of energy and non-renewable sources of energy, which is used in heating, producing power, etc.
Question-88
How is electricity produced from thermal power plants?
Solution:
In thermal power plants, heat is converted into steam energy which runs the turbine to get electrical energy.
Question-89
Give the peculiar property of glass sheet?
Solution:
A glass sheet transmits solar radiation into it as a semiconductor.
Question-90
What are the important factors/parts in constructing a solar cooker? Give its importance.
Solution:
Black coated sheets, glass plates, vessel, etc.
Question-91
Give one main difference between solar cooker and solar concentrator.
Solution:
In solar cooker, solar radiation spreads at all the points, whereas in solar concentrator it is concentrated at a particular point.
Question-92
Explain the construction of a solar cell. Give the uses of solar cell.
Solution:
Solar cell consists of a black plate, which absorbs the solar radiation and converts this solar radiation in to electrical energy by the process of photoelectric effect. It is used in traffic signals, etc.
Question-93
How is harnessing hydroelectric energy done on a small scale?
Solution:
By using the flow of water in rivers and dams, hydroelectricity is demonstrated and power is generated.
Question-94
Explain about hydroelectricity.
Solution:
It is the conversion of flow of water in to electric power. The basic process is electromagnetic induction, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Question-95
How is biogas energy better than any energy?
Solution:
Biogas energy is better than any other energy, because it is not harmful at any cause and it is pollution free.
Question-96
Why are hydrogen and alcohol not commercial fuel?
Solution:
When alcohol is used as a fuel, then the byproduct is carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. This is the reason that hydrogen and alcohol are not commercial fuel.
Question-97
Explain wind energy.
Solution:
Wind energy is the conversion of air pressure into electric power. The high pressure wind runs the wind mill, which in turn produces electric power.
Question-98
What are the qualities in choosing a good fuel?
Solution:
Must be highly efficient, low in cost and durable.
Question-99
What are the limitations of harnessing wind energy? Where is the largest wind energy farm in India?
Solution:
Windmill gives high efficiency only in wind seasons. Wind energy is the conversion of air pressure into electric power. The high-pressure wind runs the windmill, which in turn produces electric power. We have the wind mills in northern part of our country which produces high power.
Question-100
Draw a neat diagram of the box type solar cooker. Label it and explain the function of each part.
Solution:
A solar cooker is like a hot box, in which we can cook our food without any cooking gas or kerosene, electricity, coal or wood. We do not need to spend even a single paisa on fuel. This cooker works with the solar energy, which is available free. In a solar cooker we can boil, bake and roast, and in a cooker for domestic use, we can cook food for four to five persons. Bigger size solar cookers are also available for cooking food upto 15 persons.
Insulating Box
A solar cooker consists of a well-insulated box for storing energy. To increase the absorption of solar radiation, the inside of the box is painted back.
Glass Lid
The insulated box has a glazing glass surface for collecting energy. The solar cooker absorbs the Sun’s radiant energy through this glass lid.
Reflector
The insulated box has a reflector, which is an ordinary mirror used to reflect sunlight into the box. This reflector helps to track the movement of the sun, focusing sunlight and therefore concentrating the heat energy inside the box.
Black Pots
Solar absorption is also increased by using dark-coloured pots for cooking. The vessels that are painted in black are placed inside the box with the food to be cooked.
Question-101
Why is the sun very hot than any other hot body and how does it continously emit solar energy? Justify.
Solution:
Due to nuclear fusion, there is a continuous emission of solar energy.
Question-102
Give the purpose of mirror and glass sheet in solar cooker.
Solution:
In solar cooker glass sheet acts as a transparent medium which allows light into the medium. Mirror reflects the light which emerges from the cooker.
Question-103
Why are solar cells not used effectively?
Solution:
High expensive, not re-usable. Hence it is not used effectively.
Question-104
Give the limitations in using commercially wood as fuel, over windmills.
Solution:
Basic commercial fuel used is wood, because of its abundance in existence. Another fact is it is non-renewable but windmill energy is a renewable source of energy.
Question-105
A student constructed a box type solar cooker. He found that it is not working efficiently. What could this be due to? Give any four possible mistakes that he could have made?
Solution:
The transparency of the glass plate must be checked.
The reflectance of the mirror is to be checked.
The black coating must be coated effectively.
The solar cooker must be placed in a way such that it faces the sun’s radiation.
Question-106
What are the advantages of using solar water heater? Draw a labeled schematic diagram for a solar water heater.
Solution:
A Solar Water Heater (SWH) is a device that uses solar energy to heat water. Solar Water Heater have several advantages over conventional water heating systems. For consumers, they save electrical energy, save interior space (because they are usually located on rooftops,) and eliminate the risk of accidents in bathrooms due to electrical water heating equipment, They require little or no care and attention while providing hot water for about 300 days in a year in most parts of India. For society at large, they reduce the need for fossil fuels for electrical generation and for fuels such as firewood, coal, furnace oil, etc, that are used in domestic, commercial and industrial boilers. Thereby, they also reduce degradation of the environment
Solar water heater
Question-107
Define solar constant.
Solution:
The amount of solar energy form the sun which incident on the earth per square metre is called solar constant.
Question-108
What is the main basic cause for winds to blow? Compare wind power and power of water flow in respect of generating mechanical and electrical energies.
Solution:
The main basic cause for the winds to blow is the difference in temperature of the atmosphere, which makes the air to get high dense and low dense and in turn flow from one part to other. When comparing wind power and hydroelectricity, it seems that hydroelectricity is better when compared with wind energy.
Question-109
Write two limitations of wind mill.
Solution:
An estimated 1% to 3% of energy from the Sun that hits the earth is converted into wind energy. This is about 50 to 100 times more energy than is converted into biomass by all the plants on Earth through photosynthesis. Most of this wind energy can be found at high altitudes where continuous wind speeds of over 160 km/h (100 mph) occur. Eventually, the wind energy is converted through friction into diffuse heat throughout the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
The origin of wind is simple. The Earth is unevenly heated by the sun resulting in the poles receiving less energy from the sun than the equator does. Also the dry land heats up (and cools down) more quickly than the seas do. The differential heating powers a global atmospheric convection system reaching from the Earth’s surface to the stratosphere which acts as a virtual ceiling.
Question-110
Explain wind power, the principle behind wind mill and its uses.
Solution:
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into more useful forms, usually electricity using wind turbines. In 2005, worldwide capacity of wind-powered generators was 58,982 megawatts; although it currently produces less than 1% of world-wide electricity use, it accounts for approximately 25% of electricity use in Denmark, 9% in Spain, and 6% in Germany. Globally, wind power generation more than quadrupled between 1999 and 2005.
Most modern wind power is generated in the form of electricity by converting the rotation of turbine blades into electrical current by means of an electrical generator. In windmills (a much older technology) wind energy is used to turn mechanical machinery to do physical work, like crushing grain or pumping water.
Wind power is used in large scale wind farms for national electrical grids as well as in small individual turbines for providing electricity to rural residences or grid-isolated locations. Wind energy is ample, renewable, widely distributed, clean, and mitigates the greenhouse effect if used to replace fossil-fuel-derived electricity.
Question-111
(a) What is a solar water heater?
(b) Mention one advantage and one disadvantage of harnessing solar energy.
Solution:
(a) A Solar Water Heater (SWH) is a device that uses solar energy to heat water.
(b) Solar Water Heater have several advantages over conventional water heating systems. For consumers, they save electrical energy, save interior space (because they are usually located on rooftops) and eliminate the risk of accidents in bathrooms due to electrical water heating equipment, They require little or no care and attention while providing hot water for about 300 days in a year in most parts of India. For society at large, they reduce the need for fossil fuels for electrical generation and for fuels such as firewood, coal, furnace oil, etc, that are used in domestic, commercial and industrial boilers. Thereby, they also reduce degradation of the environment.
Question-112
Draw the two common designs of solar cookers.
Solution:
Box type solar heater and Spherical type solar heater
Question-113
What is the meaning for gobar?
Solution:
Gobar means animal dung in Hindi.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Subject NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
.png)
.png)