Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals NCERT Solutions
Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals, is derived from the NCERT textbook of Class 10 Science as prescribed in CBSE Schools of India. These CBSE NCERT Solutions will not only help in your Class 10 exam preparation but also in clearing other competitive exams. Read further to find out everything about NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals And Non Metals.
Metals and nonmetals Class 10
Before going through NCERT Solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 answers, let’s have a look at the list of topics and subtopics under NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Notes for Metals and Non-Metals:
- Physical Properties of Metals And Non-Metals
- Chemical Properties Of Metals
- What happens when metals are burnt in air?
- What happens when metals react with water?
- What happens when metals react with acids?
- How do metals react with solutions of other Metal Salts
- The Reactivity Series
- How do Metals and Non-Metals react?
- Properties of Ionic Compounds
- Occurrence of metals
- Extraction of metals
- Enrichment of Ores
- Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series
- Extracting Metals in the Middle of the activities Series
- Extracting Metals towards the top of the Activity Series
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion
- Prevention of Corrosion
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
- Metals and Non-metals
- धातु और अधातु कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Metals and Non-metals Important Questions
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Notes
- Metals and Non-metals NCERT Exemplar Solutions
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals Mind Map
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Intext Questions
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 40
Question 1
Give an example of a metal which :
(i) is a liquid at room temperature.
(ii) can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) is the best conductor of heat.
(iv) is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
(i) Mercury
(ii) Sodium
(iii) Silver
(iv) Lead
Question 2
Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Malleable : A metal that can be beaten into thin sheets on hammering is called malleable.
Ductile : A metal which can be drawn into thin wires is called ductile.
Malleable Meaning in Hindi
कुछ धातुओ को पीटकर पतली चादर बनाया जा सकता है | इस गुणधर्म को आघातवर्ध्य कहते है | कुछ धातुओ के पतले तार के रूप में खीचने कि क्षमता को तन्यता कहते है |
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 46
Question 1
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil ?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive. So it is kept immersed in kerosene oil to prevent its reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air to prevent accidental fires.
Question 2
Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with steam.
(ii) calcium and potassium with water.
Answer: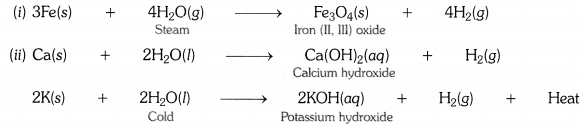
Question 3
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one.
The results obtained have been tabulated as follows :
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(i) Which is the most reactive metal ?
(ii) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
(i) B is the most reactive metal because it gives displacement reaction with iron (II) sulphate.
(ii) When metal B is added to copper (II) sulphate solution, a displacement reaction will take place due to which the blue colour of copper (II) sulphate solution will fade and a red-brown deposit of copper will be formed on metal B.
(iii) Metal B is the most reactive because it displaces iron from its salt solution. Metal A is less reactive because it displaces copper from its salt solution. Metal C is still less reactive because it can displace only silver from its salt solution and metal D is the least reactive because it cannot displace any metal from its salt solution. Hence, the decreasing order of reactivity of the metals is B > A > C > D.
Question 4
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal ? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal.
Chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4 :
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Question 5
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate ? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate, then the greenish colour of iron (II) sulphate solution fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and iron metal is deposited on zinc.
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 49
Question 1
(i) Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer: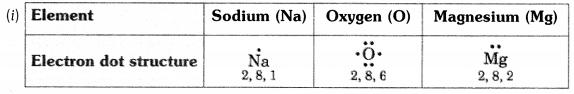
(ii) Formation of Na2O and MgO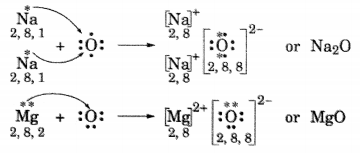
(iii) In Na2O, ions present are Na+ and O2-.
In MgO, ions present are Mg2+ and O2-.
Question 2
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points ?
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer:
The ionic compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compound. Due to this, ionic compounds have high melting points.
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 53
Question 1
Define the following terms : (i) Mineral, (ii) Ore and (iii) Gangue.
Answer:
(i) Mineral : The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals.
(ii) Ore : Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(iii) Gangue : The unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earth particles, lime stone, mica, etc in an ore are called gangue.
Question 2
Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer:
Gold and platinum
Question 3
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
Answer:
Reduction process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
For example, zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc by heating with carbon.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Besides carbon, highly reactive metals like sodium, calcium, aluminium etc. are used as reducing agents. These displace metals of low reactivity from their oxides.
For example,
Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al2O3(s) + Heat
Gold is Metal or Nonmetal ?
Gold is a metal found in nature in the free state
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 55
Question 1
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | |||
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | |||
| 3. | Copper oxide |
In which cases will you find displacement reactions taking place ?
Answer:
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide. But out of zinc, magnesium, and copper metals, magnesium is the most reactive, zinc is less reactive whereas copper is the least reactive metal.
The displacement will take place in the following cases :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | – | Displacement | – |
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | – | – | – |
| 3. | Copper oxide | Displacement | Displacement | – |
Question 2
Which metals do not corrode easily ?
Answer:
Gold and Platinum.
Question 3
What are alloys ?
Answer:
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. For example, bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Metals and Nonmetals Class 10 Question 1.
Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions ?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal.
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal.
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal.
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Answer:
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal.
Question 2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting ?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint.
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) Applying a coating of zinc.
Question 3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer:
(a) Calcium.
Question 4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
(c) zinc is less reactive than tin
(d) zinc is more reactive than tin.
Answer:
(d) Zinc is more reactive than tin.
Metals and Non metals Class 10 Question 5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Answer:
(a) Metals can be beaten into thin sheets with a hammer without breaking. Non-metals cannot be beaten with a hammer to form thin sheets. Non-metals break into pieces when hammered. Metals are malleable, while non-metals are non-melleable. When metals are connected into circuit using a battery, bulb, wires and switch, current passes through the circuit and the bulb glows. When non-metals (like sulphur) are connected, the bulb does not light up at all. Metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) Because of malleability, metals can be casted into sheets. Metals are good conductors of electricity so these can be used for electrical cables.
Question 6.
What are amphoteric oxides ? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides ?
OR
Write chemical equations that show aluminium oxide reacts with acid as well as base. [CBSE2011]
Answer:
Those metal oxides which show basic as well as acidic behaviour are known as amphoteric oxides. In other words, metal oxides that react wtih both acids and bases to form salt and water are called amphoteric oxides. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature.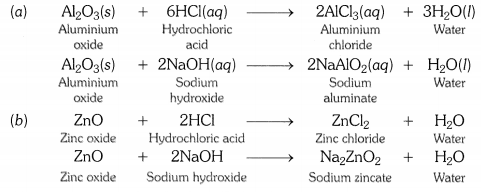
Question 7.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not.
Answer:
(i) Metals above hydrogen in the activity series like sodium and magnesium displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
(ii) Metals below hydrogen in the activity series like copper, silver do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 8.
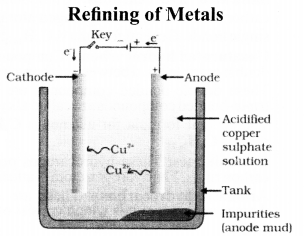
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte ?
Answer:
Cathode – Pure metal
Anode – Impure metal
Electrolyte – Metal salt solution
Question 9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in the figure.
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper ?
(ii) moist litmus paper ?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.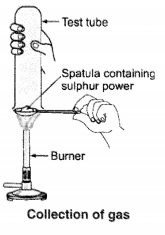
Answer:
(i) Dry litmus paper – no action.
(ii) Moist litmus paper – becomes red.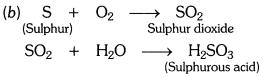
Question 10.
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
Ways to prevent rusting of iron are :
(a) By painting
(b) By galvanizing
Question 11.
What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen ?
Answer:
Non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.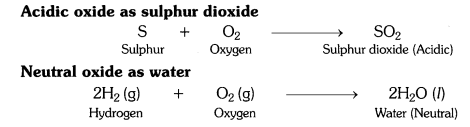
Question 12.
Give reasons :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery because these are malleable and ductile. These are highly resistant to corrosion.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are very reactive and catch fire when exposed to air. This is due to their low ignition temperature and high reactivity.
(c) Aluminium forms a non-reactive layer of aluminium oxide on its surface. This layer prevents aluminium to react with other substances. That’s why aluminium is used to make cooking utensils.
(d) It is easier to reduce a metal oxide into free metal. Since it is easier to obtain metals from their oxides than from their carbonates or sulphides directly, therefore, the carbonate and sulphide ores are first converted to oxides for extracting the metals.
Question 13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Answer:
The sour substances such as lemon or tamarind juice contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and makes them shining red-brown again.
Question 14.
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties. [CBSE 2017 (Delhi)]
Answer:
Difference between metals and non-metals
| Metals | Non-metals |
| (i) Metals form basic oxides or amphoteric oxides. | (i) Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| (ii) Metals replace hydrogen from acids and form salts. | (ii) Non-metals do not replace hydrogen from acids. |
| (iii) With chlorine, metals form chlorides which are electrovalent. | (iii) With chlorine, non-metals form chlorides which are covalent. |
| (iv) With hydrogen few metals form hydrides which are electrovalent. | (iv) With hydrogen, non-metals form many stable hydrides which are covalent. |
Question 15.
A man went door-to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty repeat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he has used ?
Answer:
The dishonest goldsmith dipped the gold bangles in aqua-regia (which contains 1 part of concentrated nitric acid and 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid, by volume). Aqua-regia dissolved a considerable amount of gold from gold bangles and hence reduced their weight drastically. The dishonest goldsmith can recover the dissolved gold from aqua-regia by a suitable treatment.
Question 16.
Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (analloy of iron).
Answer:
(i) Copper is a better conductor of heat than steel.
(ii) Copper does not corrode easily. But steel corrodes easily.
(iii) Copper does not react with water at any temperature, whereas iron reacts with water on heating.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Metals and Non-metals |
| Number of Questions Solved | 31 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Metals and non metals: Properties of metals and non-metals, reactivity series, Formation and properties of ionic compounds, Basic metallurgical processes, corrosion and its prevention.
Question 1
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Solution:
Amphoteric oxides are the oxides, which react with both acids and bases to form salt and water. E.g. ZnO and Al2O3.
Question 2
Name two metals, which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Solution:
Very reactive metals like Zn and Mg displace hydrogen from dilute acids. On the other hand less reactive metals like Cu, Ag, etc. do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 3
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Solution:
Anode is impure, thick block of metal M.
Cathode is a thin strip/wire of pure metal M.
Electrolyte is a suitable salt solution of metal M.
Metals and nonmetals Class 10 PDF
Question 4
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Solution:
By coating the surface of iron by rust proof paints.
By applying oil or grease to the surface of iron objects so that supply of air consisting of moisture is cut off form the surface.
Question 5
What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Solution:
When non-metals combine with oxygen it forms either neutral or acidic oxides. CO is a neutral oxide; N2O5 or N2O3 is an acidic oxide.
extraction of metals from ores class 10 Question 6
Give reason
i. Metals replace hydrogen from dilute acids, where as non-metals do not.
ii. Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Solution:
i. Metals are electropositive in nature. They readily lose electrons. These electrons reduce the protons liberated from the acid to liberate hydrogen gas, where as non-metals possess a tendency to gain electrons and hence they do not furnish electrons to protons liberated from acids. Hence H2 gas is not liberated.
ii. As it is easier to reduce metal oxides to metal, prior to reduction, metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted to oxides.
Question 7
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Solution: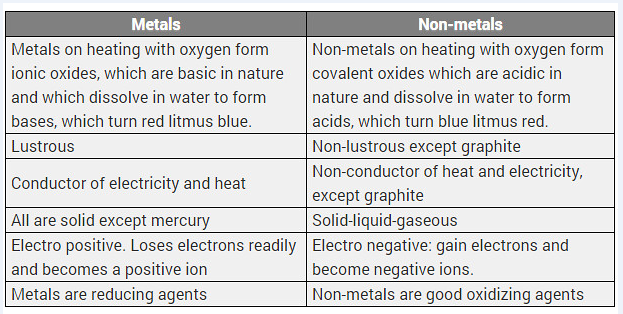
Question 8
Explain why the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Solution:
This is due to the surface oxidation of metals when exposed to moist air. For e.g. copper turns green on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate Cu(OH) 2. CuCO3. Similarly silver becomes black due to the formation of black Ag2S and Aluminium forms a white coating of Al2O3 on its surface.
Question 9
State which of the following metals would give hydrogen when added to dilute hydrochloric acid. i. Iron, ii. Copper iii. Magnesium
Copper does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid at all. This shows that copper is even less reactive than iron.
Question 10
Name a non-metallic element, which conducts electricity.
Solution:
Carbon in the form of graphite conducts electricity, as there is a free electron in each carbon atom, which moves freely in between the hexagonal layers.
Question 11
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Solution:
Gold and platinum and other noble metals do not corrode in air.
Question 12
What are alloys?
Solution:
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.E.g. steel, brass, bronze, etc.
Question 13
Define the following terms.
(i) Minerals
(ii) Ores
(iii) Gangue
Solution:
(i) Minerals
All compounds or elements, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are called minerals. Example: Alums, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3 . 24 H2O, Bauxite Al2O3.2H2O
(ii) Ores
Those minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores. Bauxite (Al2O3.2H2O) is the ore of Al, copper pyrite CuFeS2. All minerals are not ores but all ores are minerals.
(iii) Gangue
When an ore is mined from the earth, it is always found to be contaminated with sand rocky materials. The impurity of sand and rock materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Question 14
Name two metals that are found in nature in the free state.
Solution:
Gold and platinum are found in the free state in nature.
Question 15
What is chemical process used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?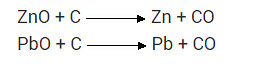
Question 16
Name two metals, which can form hydrides with metals.
Solution:
Sodium and calcium form stable hydrides on reacting with hydrogen.
Question 17
Does every mineral have a definite and a fixed composition? Explain.
Solution:
Yes, every mineral has a definite and a fixed composition. Minerals are widely distributed in the earth’s crust in the form of oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates, nitrates, etc. These minerals are formed as a result of chemical changes taking place during the formation of earth.
Class 10 metals and nonmetals Question 18
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Solution:
Malleable is being able to be beaten/hammered into thin sheets.
Ductile is being able to be drawn into thin wires.
Question 19
i. Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
ii. Show the formation of MgO and Na2O by the transfer of electrons.
iii. What are the ions present in these compounds?
Solution: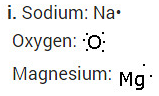
ii. Formation of Magnesium oxide
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing 2 elections, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (Mg2+) and by gaining 2 electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2-).![]()
Formation of Sodium oxide
Two sodium atoms transfer their 2 outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the two sodium atoms form two sodiumions (2Na+). And by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O2-.)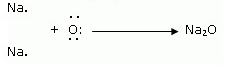
iii. The ions present in sodium oxide compound (Na20) aie sodium ions (2Na+ and oxide ions (O2-).
The ions present in Magnesium oxide compound (MgO) are magnesiumions Mg2+ and oxide ions (O2-).
Question 20
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Solution:
The sour substances such as lemon (or tamarind juice) contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.
Question 21
Give an example of a metal which
i. is a liquid at room temperature.
ii. can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. is the best conductor of heat.
iv. is a poor conductor of heat.
Solution:
i. Mercury is in liquid state at room temperature.
ii. Sodium and potassium are soft metals which can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. Silver is the best conductor of electricity.
iv. Mercury is a poor conductor of heat.
Question 22
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene?
Solution:
Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
Question 23
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Solution:
These compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the oppositively charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compounds. This is why ionic compounds have high melting points.
Question 24
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Solution:
Aqua regia (By volume, this contains 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid) is the solution, which is used to sparkle the bangles like new, but their weight will be reduced drastically.
Question 25
Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with water
(ii) calcium and potassium with water
Solution:
Question 26
What would you observe when zinc is added to a sodium of iron(II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place?
Solution:
Zinc is more reactive (more electro positive) than iron. Therefore it displaces iron from its salt solution. The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green which becomes colourless.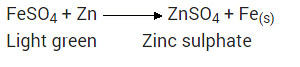
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 27
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test-tube over the burning sulphur.
What will be the action of this gas on:
Dry litmus paper?
Moist litmus paper?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Solution:
a) When sulphur is brunt in air then sulphur dioxide gas is formed.
(i) Sulphur dioxide gas has no action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas turns moist blue litmus paper to red.
(b) S(s) + O2(g) —> SO2(g)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 1.
What is the colour of aqueous solution of CuSO4 and FeSO4 as observed in the laboratory?
(a) CuSO4 – blue; FeSO4 – light green
(b) CuSO4 – blue; FeSO4 – dark green
(c) CuSO4 – green; FeSO4 – blue
(d) CuSO4 – green; FeSO4 – colourless
Answer:
(a) Colour of CuSO4 solution is blue and FeSO4 solution is light green.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 2.
A student took four test tubes I, II, III and IV containing aluminium sulphate, copper sulphate? ferrous sulphate and zinc sulphate solutions respectively. He placed an iron strip in each of them.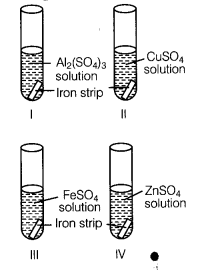
In which test tube, he found a brown deposit?
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(b) In test tube II, because Fe is more reactive than copper but less reactive than Al arid Zn.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 3.
Aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate solutions were taken in two test tubes I and II respectively. A few pieces of iron filings were then added to both the solutions. The four students A, B, C and D recorded their observations in the form of a table as given below:
| Student | Al2(SO4)3 solution (I) | CuSO4 solution (II) |
| A | Colourless solution -> Light green | Blue colour is retained |
| B | Colourless solution -> No change | Blue colour solution -> Green |
| C | Colourless solution -> Light blue | Blue colour solution -> Green |
| D | No change in colour | Blue colour of solution fades |
Which student has recorded the correct observation?
(a) D
(b) C
(c) B
(d) A
Answer:
(c) Student B
Iron does not react with Al2(SO4)3 solution because iron is less reactive than aluminium. But Fe being more reactive than Cu displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution.![]()
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 4.
Aqueous solutions of zinc sulphate and iron sulphate were taken in test tubes I and II by four students A, B, C and D. Metal pieces of iron and zinc were dropped in the two solutions and observations made after several hours were recorded in the form of table as given below:
| Student Solution | Metal | Solution | Colour change Deposit/coating of solution | Deposit/coating obtained |
| A | Fe | ZnSO4 | Turned green | Silvery grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | No change | No change | |
| B | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | Black deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | Colour faded | Grey coating | |
| C | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | No change |
| Zn | FeSO4 | Turned colourless | Black deposit | |
| D | Fe | ZnSO4 | No change | Grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO4 | No change. | Black deposit |
Which student has given the correct report?
(a) B
(b) D
(c) A
(d) C
Answer:
(d) Student C
(i) Fe is less reactive than zinc. So,![]()
(ii) Zn is more reactive than Fe, so it displaces iron as follows: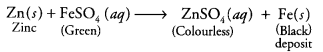
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 5.
2 mL each of cone. HCl, cone. HNO3 and a mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A’and Bbut the metal got dissolved in test tube C. The metal could be [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Answer:
(b, d) A mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO3 in the ratio of 3 : 1 is known as aqua-regia. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) dissolve only in aqua-regia as these metals are very less reactive.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 6.
When an aluminium strip is kept (a) Green solution of FeSO4 slowly turns brown
(b) Green solution of FeSO4 rapidly turns brown
(c) No change in colour of FeSO4
(d) Green solution of FeSO4 slowly turns colourless
Answer:
(a) The green solution of ferrous sulphate slowly turns brown. As aluminium is more reactive than iron, it displaces iron from ferrous sulphate solution.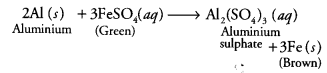
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 7.
Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
(i) Good thermal conductivity
(ii) Good electrical conductivity
(iii) Ductility
(iv) Fligh melting point [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) Good thermal conductivity, malleability, light weight and high melting point are the properties/of aluminium due to which it-is used for making cooking utensils.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 8.
If copper is kept open in air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) CuSO4
(b) CuCO3
(c) CU(NO3)2
(d) CuO
Answer:
(b) Copper reacts with CO2 present in air and forms a green coating on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(OH)2] as: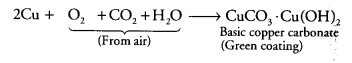
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals (Hindi Medium)

































Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Mind Maps
Metals and Non-Metals
There 92 well known naturally occurring minerals of which 70 are metals and rest 20 are the non-metals.
Physical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
| Property | Metals | Non-Metals |
| Luster | They have shining surface. | They do not have shining surface except iodine. |
| Hardness | Generally hard except sodium, lithium & potassium .These are soft and can be cut with knife. | Generally soft except diamond (hardest natural substance) |
| State | Exist as solids except mercury. | Exist as solids or gases except bromine. |
| Malleability | Can be beaten into thin sheets. Gold & silver are the most malleable metals. | Non-malleable |
| Ductility | Can be drawn into thin wires. | Non-ductile |
| Conductor of heat & electricity | Good conductors of heat and electricity. Ag & Cu are best conductors of heat and Pb & Hg are poor conductor of heat. | Poor conductor of heat and electricity except graphite. |
| Density | High density & high melting point except Na & K. | Low density & melting point. |
| Sonorous | Produce sound on striking a hard surface. | Not sonorous |
| Oxides | Metallic oxides are basic in nature. | Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. |
Reaction between Metals and Non Metals
- Reactivity of an element can be explained as tendency to attain a completely filled outermost shell.
- Metals have 1, 2 or 3 e- in outermost shell and thus it is easier for them to loss e- rather than to gain. They loss e- & gains positive charge & are tenned as cation.
- In contrast, non-metals have 4-8 e- in outermost shell & thus they gain e- to achieve their octet. They gain e- as well as negative charge & tenned as anion.
- Cations & anions attract each other & are held by strong electrostatic force of attraction.
- The compounds fonned by the transfer of electrons from metal to non-non-metal are known as ionic compounds or electrovalent compound.
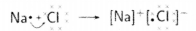
| Chemical Properties of Metals | ||
| Reaction with oxygen | Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide (basic) 2Cu + O2 → 2CuO 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3 Zn & Al form amphoteric oxides i.e., they react with both acids & bases to produce salt & water Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O Al2O3 + 2NaoH → 2NaAlO2 + H2OMetal oxides are insoluble in water but some of them dissolve in water to form alkalis. Na2O(s) + H2O (l) → 2NaOH(aq) | Na & K are vigorous elements & are kept immersed in kerosene oil. Protective metal oxide layer prevents the metal from further oxidation such as found in Al, Zn, Pb etc. Cu doesn’t bum but hot metal coated with CuQ black colored layer. Ag & Au do not react with O2
|
| Reaction with Water | Metals + Water → Metal Oxides + H2 Metal Oxides + H2O → Metal Hydroxide 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + E2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + E | Na & K: react violently with cold water. Ca: reacts less violently. Mg: reacts with hot water. Al, Fe, Zn react with steam to from metal hydroxide & H2.
|
| Reaction with dilute Acids | Metal + Dilute Acid → Salt + H2 Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Metal + HNO3 → H2 not evolved Reason- HNO3 is strong oxidizing agent & oxidized H2 to water. | Mg & Mn react with very dil. HC1 to evolve H2 gas. The reactivity decreases in the order Mg > Al > Zn > Fe. Cu doesn’t react with dil. HCl. |
| Reaction with Solutions of other Metal Salts
| Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution or molten state. Metals A+ Salt solution of B → salt of A+ Metal B CuS04(aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) | Reactivity Series: List of metals in order of their decreasing activities. K > Na> Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au. |
Occurrence of Metals
The elements or compounds, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are known as minerals.
At some places, minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it. These minerals arc called ores.
Corrosion
Corrosion is the deterioration of materials by chemical interaction with their environment for e.g. darkening of silver articles when exposed to air, gaining of green coat on copper, rusting of iron.
Prevention: The rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, chrome plating, anodising or making alloys.
• Galvanisation is a method of protecting steel and iron from rusting by coating them with a thin layer of zinc.
• Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal & nonmetal. For e.g. stainless steel (alloy of Fe. Ni, & Cr), amalgam (alloy of Hg), brass (alloy of Cu & Zn) etc. The electrical conductivity & melting point of an alloy is less than that of pure metals.
Enrichment of Ores
Ores mined from the earth are usually contaminated with large amounts of impurities such as soil, sand, etc., called gangue. The impurities must be removed from the ore prior to the extraction of the metal.
The processes used for removing the gangue from the ore are based on the differences between physical or chemical properties of the gangue and the ore.
Extraction of Metals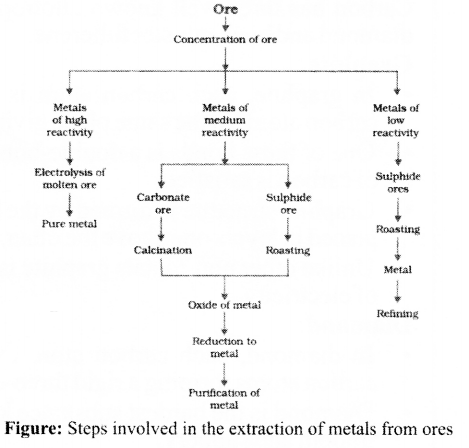
Extracting Metals towards the Top of the Activity Series
These metals are highly reactive & are obtained by electrolytic reduction. For e.g. Na, Mg, & Ca are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides.
The metals are deposited at the cathode whereas chlorine is liberated at anode.
At cathode Na+ + e– →Na
At anode 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Similarly, aluminium is obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide.
Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series
- These metals are the least reactive & are often found in a free state for e.g. An, Ag. Pt & Cu are found in the free state.
- However, Cu & Ag are also found in the combined state as their sulphide or oxide ores.
- The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heating alone. For e.g. cinnabar (HgS), ore of mercury it is heated in air to converted it in mercuric oxide (HgO) which is then reduced to mercury by further heating.
- 2HgS(s) + 3O2(g) Heat 2HgO(s) + 2SO2(g)
- 2HgO(s)Heat 2Hg(l) + O(g)
- Another instance is reduction of Cu2S (ore of copper) to copper by heating.
- 2Cu2S + 3O2(g)Heat 2Cu2O(s) + 2SO2(g)
- 2CU2O + Cu2S Heat 6Cu(s) + SO2
Extracting Metals Middle in the Activity Series
- These metals such as Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, etc are moderately reactive & are usually present as sulphides or carbonates in nature.
- The sulphide ores are converted into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of excess air which is known as roasting.
- The carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air which is known as calcination.
- The metal oxides are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using suitable reducing agents such as carbon.
- For e.g. extraction of Zn
- Roasting: 2ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) Heat . 2ZnO(s) + 2SO2(g)
- Calcination: ZnCO3(s) Heat ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
- Reduction: ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
- Sometimes displacement reactions can also be used in place of reduction & highly reactive metals such as Na, Ca, Al, etc., are used as reducing agents.
- For e.g. 3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(s) + Heat
- Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l)+Al2O3(s) + Heat
- This reaction is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts and is known as the thermit reaction.
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals and we hope this detailed article on metal and nonmetal class 10 notes is helpful. If you find any doubts regarding this article or NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals, leave your comments in the comment section below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Important Questions of Metals and Non-Metals Class 10 Science Chapter 3
Question 1.
Reverse of the following chemical reaction is not possible:
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Justify this statement with reason. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
If a strip of zinc metal is put in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and reddish-brown copper metal is deposited on zinc strip.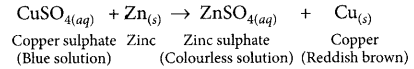
In this reaction, zinc metal being more reactive than copper displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. If however, a strip of copper metal is placed in zinc sulphate solution, then no reaction occurs. This is because copper metal is less reactive than zinc metal and hence, cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.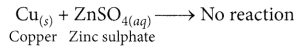
Question 2.
Name a metal which:
(a) is the best conductor of heat.
(b) has a very low melting point.
(c) does not react with oxygen even at high temperature.
(d) is most ductile. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Metal which is the best conductor of heat is silver.
(b) Gallium has a very low melting point.
(c) Silver and gold do not react with oxygen even at high temperature.
(d) Gold is the most ductile metal.
Question 3.
What is meant by amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxides from the following :
Na2O, ZnO, CO2, Al2O3, H2O (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Amphoteric oxides are those which show acidic as well as basic character, i.e., they react with bases as well as acids. ZnO and Al2O3 are amphoteric oxides.
Question 4.
Complete the following equation with balancing: (Board Term I, 2013)
(i) Al + HCl →
(ii) Mg + HNO3 →
Answer: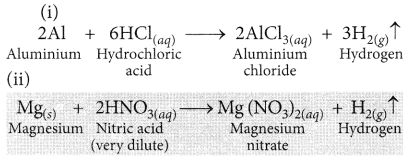
Question 5.
Compare in tabular form the reactivities of the following metals with cold and hot water: (2020)
(a) Sodium
(b) Calcium
(c) Magnesium
Answer: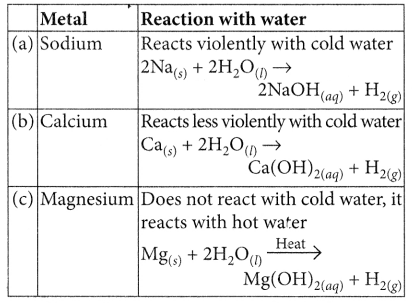
Question 6.
Give reason for the following:
(i) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most of the metals react with nitric acid.
(ii) Zinc oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(iii) Metals conduct electricity. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(i) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when most metals react with nitric acid. It is because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced to water and itself gets reduced to any of the nitrogen oxides (N2O, NO, NO2).
(ii) ZnO reacts both with acids as well as bases to form salt and water. Thus, ZnO is an amphoteric oxide.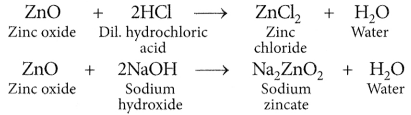
(iii) Metals conduct electricity due to the flow of free electrons present in them.
Question 7.
(a) Why does calcium start floating when it reacts with water? Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
(b) Name two metals which do not react with water. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Calcium reacts with cold water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.![]()
The bubbles of hydrogen gas produced stick to the surface of calcium and hence, it starts floating on the surface of water.
(b) Gold and silver do not react with water.
Question 8.
State what would happen if:
(i) some zinc pieces are placed in blue copper sulphate solution.
(ii) some’copper pieces are placed in green ferrous sulphate solution.
(iii) an iron nail is dipped in a solution of copper sulphate for some time. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(i) Refer to answer 1.
(ii) Cu + FeSO4 No Reaction
Cu is less reactive than Fe, thus, it cannot displace Fe from FeSO4 solution.
(iii) When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution, then the blue colour of copper sulphate fades gradually and a reddish brown coating is formed on the iron nail.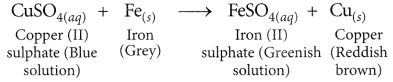
As iron is more reactive than copper, it displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.
Question 9.
Give reason:
(a) Aluminium is a reactive metal but is still used for packing food articles.
(b) Calcium starts floating when water is added to it. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Aluminium is a strong and cheap metal. It is also a good conductor of heat. But it is highly reactive. When it is exposed to moist air, its surface is covered with a thin impervious layer of aluminium oxide (Al2O3). This layer does not allow moist air to come in contact with the fresh metal and hence, protects the metal underneath from further damage or corrosion. Thus, after the formation of this protective layer of Al2O3, aluminium becomes resistant to corrosion. It is because of this reason that although aluminium is a highly reactive metal, it is still used in food packaging.
(b) Refer to answer 7(a).
Question 10.
(a) Complete and balance the following chemical equations:
(i) Al2O3 + HCl →
(ii) K2O + H2O →
(iii) Fe + H2O →
(b) An element ‘X’ displaces iron from the aqueous solution of iron sulphate. List your observations if the element ‘X’ is treated with the aqueous solutions of copper sulphate, zinc sulphate and silver nitrate. Based on the observations arrange X, Zn, Cu and Ag in increasing order of their reactivities. (2020)
Answer:
(a) (i) Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
(ii) K2O + H2O → 2KOH
(iii) 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2
(b) As X displaces iron from its salt solution hence X is more reactive than iron. It will also displace copper from copper sulphate and silver from silver nitrate as both are less reactive than iron. As zinc is more reactive than iron hence, X can be more or less reactive than zinc. Then the order of their reactivities can be
Ag < Cu < Fe < Zn < X or Ag < Cu < Fe < X < Zn.
Question 11.
A metal ‘X’ combines with a non-metal ‘Y’ by the transfer of electrons to form a compound Z.
(i) State the type of bond in compound Z.
(ii) What can you say about the melting point and boiling point of compound Z?
(iii) Will this compound dissolve in kerosene or petrol?
(iv) Will this compound be a good conductor of electricity? (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
X being a metal loses electrons and Y being a non-metal gains electrons to form Z.
(i) The chemical bond formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as an ionic bond. Hence, Z is an ionic compound.
(ii) Compound Z is an ionic compound thus, it has high melting and boiling points.
(iii) Ionic compounds are insoluble in non-polar solvents such as kerosene or petrol.
(iv) As Z is an ionic compound, it does not conduct electricity in the solid state because movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure. But it conducts electricity in the molten state or in aqueous solution due to the movement of ions freely.
Question 12.
(i) By the transfer of electrons, illustrate the formation of bond in magnesium chloride and identify the ions present in this compound.
(ii) Ionic compounds are solids. Give reasons.
(iii) With the help of a labelled diagram show the experimental set up of action of steam on a metal. (2020)
Answer: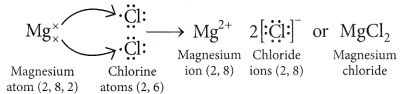
(ii) Ionic compounds are solids because the particles which make up ionic compounds are held together by strong electrostatic bonds.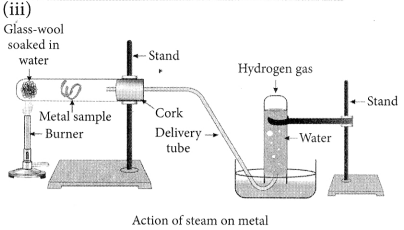
Question 13.
(a) (i) Write two properties of gold which make it the most suitable metal for ornaments.
(ii) Name two metals which are the best conductors of heat.
(iii) Name two metals which melt when you keep them on your palm.
(b) Explain the formation of ionic compound CaO with electron-dot structure. Atomic numbers of calcium and oxygen are 20 and 8 respectively. (2020)
Answer:
(a) (i) The malleability and ductility properties of gold make it suitable for ornaments.
(ii) Silver and gold.
(iii) Gallium and caesium have so low melting points that they melt even on keeping them on palm.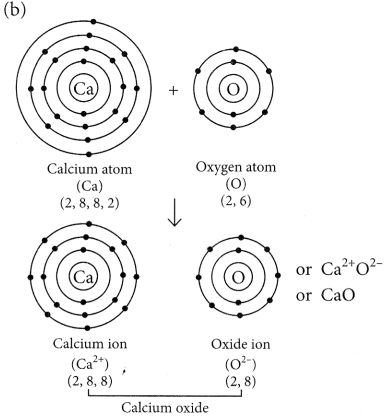
Question 14.
(i) Write down the electronic configuration
of magnesium and oxygen.
(ii) Give two general properties of the compound formed by combination of magnesium and oxygen.
(iii) Show the formation of this compound by the transfer of electrons. (Board Term 1,2014)
Answer:
(i) Atomic number of magnesium (Mg) = 12
∴ Its electronic configuration = 2, 8, 2
Atomic number of oxygen = 8
Electronic configuration of oxygen = 2, 6
(ii) Magnesium (Mg) reacts with oxygen (O2) to form magnesium oxide (MgO).
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Properties of MgO are :
(a) It involves ionic bonding.
(b) It has high melting point due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between Mg2+ and O2- ions.
(iii) In the formation of magnesium oxide, two electrons are transferred from magnesium atom to oxygen atom as represented :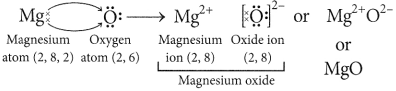
Question 15.
An ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence. Name the type of ore with one example. What steps will be required to obtain metal from the enriched ore? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved in the process. (AI 2019)
Answer:
The ore on treatment with dilute hydrochloric acid produces brisk effervescence hence, it must be a carbonate ore. Calamine (ZnCO3) is an important carbonate ore of zinc.
Steps required to obtain metal from the enriched carbonate Are:
(a) Conversion of the carbonate ore into metal oxide : This is done by calcination (for carbonate ores).
Calcination is the process of heating the ore strongly in the absence or limited supply of air. The zinc carbonate on heating decomposes to form zinc oxide as shown :
(b) Reduction of the metal oxide to metal : As zinc is moderately reactive, zinc oxide cannot be reduced by heating alone. Hence, it is reduced to zinc by using a reducing agent such as carbon.
The reduction of metal oxides by heating with coke is called smelting.
Question 16.
(i) Carbonate of metal ‘2T is abundant in earth crust and its hydroxide is used in ‘white washing’. Identify metal ‘XI
(ii) How will you convert this carbonate into its oxide? Name the process and write its equation. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(i) Calcium carbonate is abundant in earth’s crust and calcium hydroxide is used in white washing. Hence, metal X is calcium (Ca).
(ii) CaCO3 is strongly heated in the absence of air to get the metal oxide. This process is called calcination.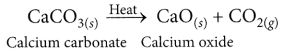
Question 17.
Zinc is a metal found in the middle of the activity series of metals. In nature, it is found as a carbonate ore, ZnCO3. Mention the steps carried out for its extraction from the ore. Support with equations. (Board Term 1,2013)
Answer:
Refer to answer 15.
Question 18.
Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium to their respective metals. Why? Where are these metals placed in the reactivity series? How are these metals obtained form their ores? Take an example to explain the process of extraction along with chemical equations. (2020)
Answer:
Sodium, magnesium and aluminium have higher affinity towards oxygen than that of carbon because these are highly reactive metals. Hence, carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium to their respective metals. These metals are placed at the top of the reactivity series. The highly reactive metals like Na, Mg, Al, etc. are extracted by electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides or oxides. Electrolytic reduction is brought about by passing electric current through the molten state. Metal gets deposited at the cathode.
NaCl ⇌ Na+ + Cl–
At cathode : Na+ + e– → Na
At anode : 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Question 19.
Write balanced chemical equations to explain what happens, when
(i) Mercuric oxide is heated.
(ii) Mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous sulphide is heated.
(iii) Aluminium is reacted with manganese dioxide.
(iv) Ferric oxide is reduced with aluminium.
(v) Zinc carbonate undergoes calcination. (2020)
Answer:
(i) On heating, mercuric oxide decomposes to give mercury .and oxygen.![]()
(ii) On heating mixture of cuprous oxide and cuprous sulphide, copper and sulphur dioxide are produced.![]()
(iii) When aluminium is heated with manganese dioxide, manganese and aluminium oxide are formed.![]()
(iv) Ferric oxide reacts with aluminium to produce aluminium oxide and iron.![]()
(v) On calcination, zinc carbonate produces zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.![]()
Question 20.
(a) List in tabular form three chemical properties on the basis of which we can differentiate between a metal and a non¬metal.
(b) Give reasons for the following :
(i) Most metals conduct electricity well.
(ii) The reaction of iron (III) oxide [Fe2O3] with heated aluminium is used to join cracked machine parts. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
| s.no. | Chemical property | Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. | Nature of oxides | Metals generally form basic oxides. | Non-metals generally form acidic oxides. |
| 2. | Reaction with water | Metals which lie above hydrogen in the reactivity series displace hydrogen from water. | Non-metals (except F) do not react with water. |
| 3. | Oxidising or reducing character. | Metals generally behave as reducing agents. | Non-metals generally behave as oxidising agents. |
(b) (i) Refer to answer 6 (iii).
(ii) The reaction of iron (III) oxide, Fe2O3 with aluminium is highly exothermic and the iron produced melts. This molten iron is used to join cracked iron parts of machines and railway tracks.
Question 21.
(a) Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series from their carbonate ores.
(b) How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations. Draw labelled diagram for the electrolytic refining of copper. (2018)
Answer:
(a) Extraction of metals of medium reactivity:
The metals in the middle of the reactivity series are zinc, iron, lead, etc. The carbonate ores first need to get converted to oxides as it is easier to get metal from their oxides.
Refer to answer 15.
(b) Copper glance (Cu2S) when heated in air gets partially oxidised to copper oxide which further reacts with the remaining copper glance to give copper metal.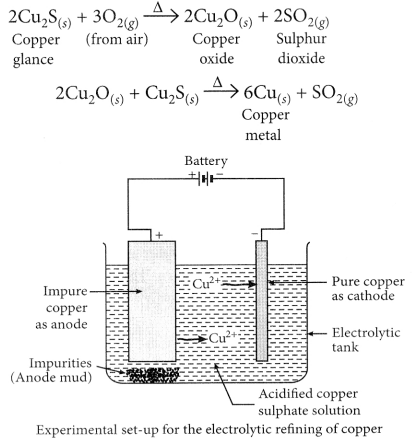
Question 22.
Draw a schematic diagram of the various steps involved in the extraction of metals from ores for metals of medium reactivity and for metals of low reactivity. (Board Term I, 2018)
Answer:
Various steps involved in the extraction of a metal from its ore followed by refining of the metal is called ‘metallurgy’. The steps involved are summarised as follows :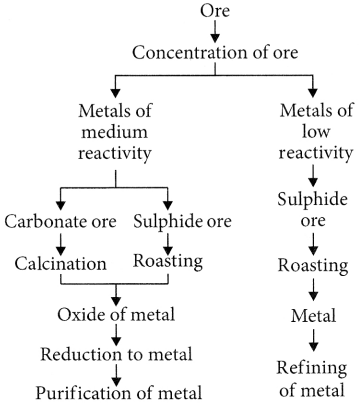
Question 23.
(a) Describe an activity to show that metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) Account for the following :
(i) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when a metal reacts with nitric acid.
(ii) For storing sodium metal, it is kept immersed in kerosene.
(iii) The reaction of iron (III) oxide with aluminium is used to join cracked iron parts of machines. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Activity : (i) Set up an electric circuit as shown in the figure.
(ii) Place the metal to be tested (Cu, Al, Ag, Fe, etc.) in the circuit, between the terminal A and B.
(iii) Switch on the battery.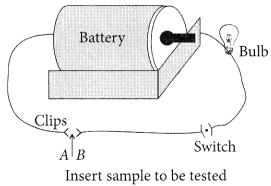
Observations : Bulb begins to glow.
Conclusion : This indicates that the current is flowing through the metal wire. Hence, metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) (i) Refer to answer 6(i).
(ii) Sodium reacts vigorously with air and catches fire. Also, sodium reacts with water and the hydrogen gas is evolved which catches fire. Therefore, sodium is kept under kerosene.
(iii) Refer to answer 20(b) (ii).
Question 24.
How is copper obtained from its ore (Cu2S)?
Write only the chemical equations. How is copper thus obtained refined? Name and explain the process along with a labelled diagram. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 21(b).
Copper obtained is refined by electrolytic refining.
Electrolytic refining of crude copper :
Thick block of impure metal acts as anode and a thin strip of pure copper metal acts as cathode. The electrolyse used is aqueous solution of copper sulphate containing a small amount of sulphuric acid. On passing electric current through the electrolyte, the metal from the anode dissolves into the electrolyte. An equivalent amount of copper metal from copper sulphate solution gets deposited on cathode.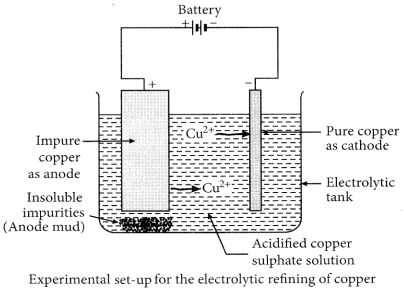
Question 25.
(a) Copper produced by heating the ore in air is not very pure. Describe the method used for refining impure copper. Draw labelled diagram of the process.
(b) Write chemical equations for the reactions taking place when :
(i) zinc sulphide is heated in air.
(ii) zinc carbonate is calcined. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 24.
Question 26.
Assertion (A) : The metals and alloys are good conductors of electricity.
Reason (R) : Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin and it is not a good conductor of electricity.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer:
(c) : Metals and alloys have free electrons in them which can move freely inside them, so they conduct electricity very easily. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin and it is a very good conductor of electricity.
Question 27.
Name first discovered alloy. Give its composition also. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Bronze is the first discovered alloy. Its composition is copper (90%) and tin (10%).
Question 28.
List three differentiating features between the processes of galvanisation and alloying.
Answer:
| Galvanisation | Alloying |
| 1. It is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron, to prevent rusting. | 1. It is the process of combining two or more metals or a metal and a non-mental. |
| 2. It is done through electrolysis. | 2. It is done by heating the primary metal and adding other elements in definite proportions and then cooling it down to room temperature. |
| 3. The properties of inner metal are not changed. | 3. The properties like strength, conductivity etc. are changed. |
Question 29.
Describe an activity to find out the conditions under which iron rusts. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Activity:
(i) Take three test tubes and put clean nails in each of the three tubes. Label them as A, B and C.
(ii) Pour some water in test tube A and cork it.
(iii) In tube B, pour some boiled distilled water along with some turpentine oil and cork it.
(iv) In test tube C, add some anhydrous calcium chloride and cork it.
(v) Look these test tubes properly and keep them undisturbed for a few days.
Observation : Only in test tube A, iron nails get rusted since the nails in this test tube are exposed to both air and water.
Conclusion : Both air and water are required for rusting of iron.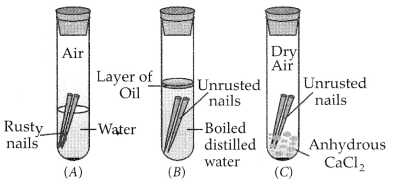
Question 30.
Why some metal surfaces acquire a dull appearance when they are exposed to moist air? Write colour acquired by the surfaces of copper and silver in such situation and also write the chemical names of the substances due to which it happens. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
When a metal has been kept exposed to air for a long time, then it gets a dull appearance. The metals lose their shine or brightness due to the formation of a thin layer of oxide, carbonate or sulphide on their surface and thus, the metal surface gets corroded. The surface of copper gets coated with a green layer in moist air due to the formation of basic copper carbonate, silver articles acquire a blackish tinge due to the formation of silver sulphide.
Question 31.
(a) Name the following :
(i) Metal that can be cut by knife
(ii) Lustrous non-metal
(iii) Metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature
(iv) Most malleable and ductile metal
(v) Metal that is best conductor of electricity
(vi) Non-metal that can exist in different forms
(b) How are alloys better than metals? Give composition of solder and amalgam.
Answer:
(a) (i) Sodium
(ii) Iodine
(iii) Mercury
(iv) Gold
(v) Silver
(vi) Carbon
(b) Alloys are stronger than the metals from which they are made, more resistant to corrosion, have lower melting point, have lower electrical conductivity. Solder is an alloy of lead and tin. An amalgam is an alloy of mercury with another metal.
Question 32.
(a) Define corrosion.
(b) What is corrosion of iron called?
(c) How will you recognise the corrosion of silver?
(d) Why corrosion of iron is a serious problem?
(e) How can we prevent corrosion of iron? (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(a) The process of slowly eating up of metals due to their conversion into oxides, carbonates, sulphides, etc., by the action of atmospheric gases and moisture is called corrosion.
(b) The corrosion of iron is called rusting.
(c) Silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air. This is due to formation of a coating of black silver sulphide (Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S gas present in the air.
(d) Corrosion of iron is a serious problem. Every year large amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron articles. Corrosion causes damage to car bodies, bridges and iron railings, ships and to all objects made of metals specially those of iron.
(e) Corrosion of iron is prevented by coating it with a layer of oil. The reason being that the layer of oil does not allow air and water to react the surface of iron. Corrosion of iron can also be prevented by painting, greasing, galvanising, anodising, electroplating or making alloys.
Question 33.
Give reason for the following :
(a) Ionic compounds have higher melting point and higher boiling point.
(b) Sodium is kept immersed in kerosene.
(c) Reaction of calcium with water is less violent.
(d) Silver articles become black after some time when exposed to air.
(e) Prior to reduction the metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted into metal oxides for extracting metals. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
(a) Due to strong forces of attraction, the ions are bound to each other very firmly. As a result, the electrovalent or ionic solids have high melting and boiling points.
(b) Refer to answer 23(b) (ii).
(c) Calcium reacts with cold water but the reaction is less violent. The heat evolved is not sufficient for the hydrogen to catch fire.![]()
(d) Refer to answer 32(c).
(e) The reduction of metal oxides to metal is easier than the reduction of metal sulphides and metal carbonates. Hence, these are first reduced to their corresponding metal oxides.
Question 34.
(a) Metals like iron, silver and copper get corroded on exposure to air. Write the chemical name of the substance deposited on their surface respectively with it’s colour, in each case.
(b) List four ways by which rusting can be prevented. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Iron gets corroded and forms ferric oxide which is rust, it is reddish brown in colour. For silver and copper, refer to answer 30.
(b) The various methods used for preventing the rusting of iron are given below:
(i) By applying paint : Materials like railings, iron gates, iron bridges, bodies of cars, buses and trucks, etc. are all painted to protect them from rusting. Painting the metal surface does not allow them to come in contact with the moist air and thus, prevents rusting.
(ii) Greasing and oiling : When some grease or oil is applied on the surface of an iron object, then moisture and air cannot come in contact with it and hence, rusting is prevented.
(iii) Galvanization : It is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating them with a thin layer of zinc. The iron coated with zinc is called galvanized iron.
(iv) Electroplating : It is another technique used to prevent articles from rusting. In this process, metals like tin, nickel and chromium which do not corrode are electroplated on iron.
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks]-Year 2015
35.Write one example of each of
(i) a metal which is so soft that, it can be cut with knife and a non-metal which is the hardest sustance.
(ii) a metal and a non-metal which exist as liquid at room temperature.
Answer.
(i) Sodium, carbon (diamond).
(ii)Mercury is liquid metal, bromine is liquid non-metal.
36.Mention the names of the metals for the following:
(i) Two metals which are alloyed with iron to make stainless steel.
(ii) Two metals which are used to make jewellary.
Answer.
(i) Nickel and chromium.
(ii) Gold and platinum.
Short Answer Type Question[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2013
37.Give reason for the following:
(a) School bells are made up of metals.
(b) Electric wires are made up of copper.
Answer.
(a) It is because metals are sonorous, i.e. they produce sound when struk with a hard substance.
(b) It-is because copper is good conductor of electricity.
Short Answer Type Question[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2013
38. Suggest a method of reduction for the following metals during their metallurgical processes:
(i) metal ‘A’ which is one of the last, second or third position in the reactivity.
(ii) metal ‘B’ which gives vigorous reaction even with water and air.
(iii) metal ‘C’ which is kept in the middle df activity series.
Answer.
(i) ‘A’ can be obtained by chemical reduction using carbon or carbon monoxide as reducing agent.
(ii) ‘B’ can be obtained by electrolytic reduction.
(iii) ‘C’ can be reduced by reducing agent like ‘Al’.
Very Short Answer Type Question [1 Mark] -Year 2012
39.A green layer is gradually formed on a copper plate left exposed to air for a week in a bathroom. What could this green substance be?
Answer. It is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuC03.Cu(0H)2].
Short Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2012
40.Name the following:
(a) A metal, which is preserved in kerosene.
(b) A lustrous coloured non-metal.
(c) A metal, which can melt while kept on palm.
(d) A metal, which is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer.
(a) Sodium is preserved in kerosene.
(b) Iodine is lustrous coloured non-metal.
(c) Gallium. ‘
(d) Lead.
41. Give reason for the following:
(a) Aluminium oxide is considered as an amphoteric oxide.
(b) Ionic compounds conduct electricity in molten state.
Answer.
(a) It is because it reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water.’Al’ is less electropositive metal. So, it forms amphoteric oxide which can react with acid as well as base.
(b) Ionic compounds can conduct electricity in molten state because ions ’ become free to move in molten state.
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2012
42. A metal ‘X’ acquires a green colour coating on its surface on exposure to air.
(i) Identify the metal ‘X’ and name the process responsible for this change.
(ii)Name and write chemical formula of the green coating formed on the metal.
(iii) List two important methods to prevent the process.
Answer.
(i) Metal is copper. The process is corrosion.
(ii)Basic copper carbonate [CuCO3.Cu(0H)2].
(iii)
• It should be coated with tin
• It should be mixed with other metals to form alloys.
43.What are amphoteric oxides? Choose the amphoteric oxides from amongst the following oxides:
Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O
Answer.Those oxides which reacts with acids as well as bases to produce salts and water are called amphoteric oxides, e.g. Na2O, ZnO, are amphoteric oxides among given oxides.
44.Define the terms:
(i) mineral
(ii) ore, and
(iii) gangue.
Answer.
(i) Mineral: It is a naturally occurring substance from which metal may or may not be extracted profitably or economically, e.g. A1 cannot be extracted profitably from mica.
(ii)Ore: It is a rocky material which contains sufficient quantity of mineral so that metal can be extracted profitably, e.g. zinc blende is an ore of zinc from which zinc can be extracted profitably.
(iii) Gangue: It is a rocky material which is present along with the mineral in the ore, e.g. FeO is gangue in extraction of copper.
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2012
45. (a) Write the chemical name of the coating that forms on silver and copper articles when these are left exposed to moist air.
(b) Explain what is galvanisation. What purpose is served by it?
(c) Define an alloy. How are alloys prepared? How do the properties of iron change when:
(i) small quantity of carbon,
(ii) nickel and chromium are mixed with it.
Answer.
(a) Ag2S (silver sulphide) is formed on silver, basic copper carbonate CuCO3. CU(OH)2 is formed on copper.
(b) The process of coating zinc over iron is called galvanisation. It is used to prevent rusting of iron.
(c) Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals. One of them can be non-metal. Alloys are prepared by melting two or more metals together.
(?) Iron does not rust on adding small,quantity of carbon.
(ii) When we form alloy of iron with nickel and chromium, we get stainless steel which is malleable and does not get rusted.
46.(a) Carbon cannot be used as reducing agent to obtain Mg from MgO. Why?
(b) How is sodium obtained from molten sodium chloride? Give equation of the reactions.
(c) How is copper obtained from its sulphide ore? Give equations of the reactions.
Answer.
(a) It is because ‘Mg’ is stronger reducing agent than carbon.
(b) Sodium is obtained from molten NaCl by electrolysis.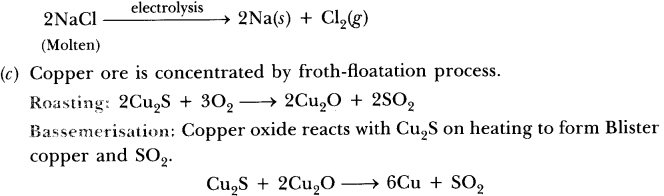
Blister Copper is purified by electrolytic refining.
47.Give reasons for the following:
(i) Silver and copper lose their shine when they are exposed to air. Name the substance formed on their surface in each case.
(ii) Tarnished copper vessels are cleaned with tamarind juice.
(iii) Aluminium is more reactive than iron yet there is less corrosion of aluminium as compared to iron when both are exposed to air.
Answer.
(i) These metals get corroded. Silver forms black Ag2S (silver sulphide) and copper form greenish layer of basic copper carbonate CuCO3. CU(OH)2 .
(ii) Tamarind contains acid which reacts with basic copper carbonate and product gets dissolved and removed from copper vessel.
(in) Aluminium forms oxide layer on its surface which does not further react with air.
48. What are alloys? How are they made? Name the constituents and uses of brass, bronze and solder.
Answer. Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals. One of them can be a non-metal also. They are made by melting a metal which is in large amount first and then adding the other metal. ,
Brass contains copper and zinc. It is used for making decorative articles. Bronze contains copper and tin. It is used for making statues and medals. Solder contains lead and tin. It is used for soldering purposes.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2011
49. A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer. ‘X’ is carbon, ‘Y’ is diamond as it is the hardest natural substance and ‘Z’ is graphite as it is good conductor of electricity.
50. Why does calcium float in water?
Answer. It is because hydrogen gas is formed which sticks to surface of calcium, therefore it floats. –
51.Name a non-metal which is lustrous and a metal which is non-lustrous. Iodine is a non-metal which is lustrous,
Answer.lead is a non-lustrous metal.
52.Which gas is liberated when a metal reacts with an acid? How will you test the presence of this gas?
Answer. Hydrogen gas is formed. Bring a burning matchstick near to it, H2 will burn explosively with ‘pop’ sound.
53.Name the metal which reacts with a very dilute HNOs to evolve hydrogen gas.
Answer. Magnesium
54.Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer.(i) Gold (ii) Silver
Answer Type Questions[l] [2 Marks] -Year 2011
55.The way, metals like sodium, magnesium and iron react with air and water is an indication of their relative positions in the ‘reactivity series’. Is this statement true ? Justify your answer with examples.
Answer.Yes, sodium reacts explosively even with cold water, it is most reactive. Magnesium reacts with hot water, it is less reactive than Na. Iron reacts only with steam which shows it is least reactive among the three.
56. X + YSO4——-> XSO4+ Y
Y + XSO4 ——–> No reaction
Out of the two elements, ‘X’ and ‘Y’, which is more reactive and why?
Answer. ‘X’ is more reactive than ‘Y’ because it displaces ‘Y’ from its salt solution.
57.What is an alloy? State the constituents of solder. Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Answer. Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals. One of them can be a non-metal also. Solder consists of lead and tin. It has low melting point which makes it suitable for welding electrical wires.
58. Write chemical equations that shows aluminium oxide reacts with acid as well as base.
Answer.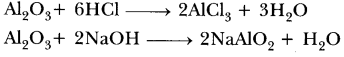
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2011
59.(a) How can the metals at the top of the reactivity series be extracted from their ores? Explain with an example.
(b) Name any one alloy made from
(i) a metal and a non-metal, and
(ii) two metals.
Answer.
(a) These metals are extracted by electrolytic reduction, e.g. aluminium is obtained from bauxite by electrolytic reduction.
(b) (i) Steel is made up of iron and carbon.
(ii) Brass is made up of copper and zinc.
Very Short Answer Type Questions [1 Mark] -Year 2010
60.What is the valency of silicon with atomic number 14?
Answer. Its valency is equal to 4.
61.What is the valency of phosphorus with atomic number 15?
Answer. Phosphorus has valency 3.
62.What is the valency of an element with atomic number 35?
Answer. Its valency is 1.
Short Answer Type Question[I] [2 Marks] -Year 2010
63.Elements magnesium and oxygen respectively belong to group 2 and group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table. If the atomic numbers of magnesium and oxygen are 12 and 8 respectively, draw their electronic configurations and show the process of formation of their compound by transfer of electrons.
Answer.(Mg)=2,8,2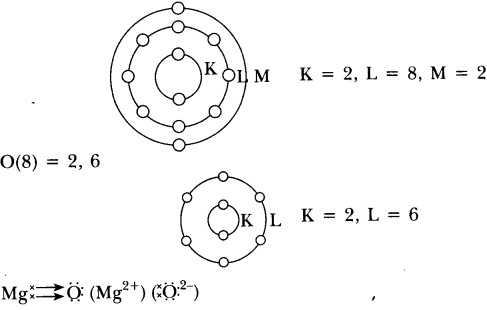
Very Short Answer Type Question [1 Mark] -Year 2009
64. Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of reactivity: Na, K, Cu, Ag.
Answer. K > Na > Cu > Ag
Short Answer Type Questions[ll] [3 Marks] -Year 2009
65. Give reasons for the following observations:
(i) Ionic compounds in general have high melting and boiling points.
(ii) Highly reactive metals cannot be obtained from their oxides by heating
them with carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels get a green coat when left exposed to air in the rainy season.
Answer. (i) Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
(ii) It is because these metals themselves are strong reducing agents. Therefore, cannot be reduced by reducing agent like carbon.
(iii) Copper vessels react with CO2, O2 and moisture to form green-coloured basic copper carbonate
[CuCO3.Cu(OH)2].
66. State reasons for the following observations:
(i) The shining surface of some metals becomes dull when exposed to air for a long time.
(ii) Zinc fails to evolve hydrogen gas on reacting with dilute nitric acid.
(iii) Metal sulphides occur mainly in rocks but metal halides occur mostly in sea and lake waters.
Answer.
(i) It is because metal reacts with substances present in atmosphere to form surface compounds which make it dull.
(ii) It is because dil. HNOs is an oxidising agent therefore zinc gives NO and notH2 with dil. HNOs.
(iii) It is because sea water contains sodium chloride due to which metal halides are formed, whereas sulphur is found below rocks. Therefore, metal – sulphides are formed in rocks.
67. State reasons for the following:
(i) Electric wires are covered with rubber like material.
(ii)From dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc can liberate hydrogen gas but copper cannot.
(iii) Sulphide ore of a metal is first converted to its oxide to extract the metal from it.
Answer.
(i) It is because rubber is an insulator and does not allow current to flow through it.
(ii) Zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. Therefore, it can displace hydrogen from dilute HCl whereas copper cannot, because it is less reactive than hydrogen. ,
(iii) It is because it is easier to reduce oxide ore as compared to sulphide ore.
Long Answer Type Questions [5 Marks] -Year 2009
68.(a) What is meant by corrosion? Name any two methods used for the prevention
of corrosion.
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series, write various steps used in extracting this metal.
Answer. (a) Corrosion is a process in which metal reacts with substances present in the environment to form surface compounds.
Prevention:
(i) Galvanisation is a process to prevent corrosion of iron.
(ii)Electroplating is also used to prevent corrosion.
(b)(i) Concentration of ores: Sulphide ore will be concentrated by froth- floatation process. Sulphide ore will be collected in froth whereas gangue will be left behind.
(ii) Roasslng: Sulphide ore is heated strongly in the presence of O2 to form metal oxide and sulphur dioxide.
2MS + 3O2 ————- ► 2MO + 2SO2
(iii) Reduction: MO reacts with carbon (acts as reducing agent) to form metal and CO.
MO + C —-> M + CO
(iv) Electrolytic refining: Impure metal ‘M’ is purified by electrolytic refining. Impure metal is taken as anode, pure metal is taken as cathode, soluble salt of metal is taken as electrolyte. Impure metal forms metal ions which gain electrons and form pure metal at cathode.
Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Science Notes
Metals: Physical properties of metals, chemical properties of metals and non-metal oxide.
Metals are the elements that conduct heat and electricity and are malleable and ductile. Examples are Iron (Fe), Aluminium (Al), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), Gold (Au), Platinum (Pt), Lead (Pb), Potassium (K), Sodium (Na), Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) etc.
Metals are the elements which form positive ions by losing electrons. Thus, metals are known as Electropositive Elements.
Physical Properties of Metals
- Hardness: Most of the metals are hard, except alkali metals, such as sodium, potassium, lithium, etc. are very soft metals. These can be cut by using a knife.
- Strength: Most of the metals are strong and have high tensile strength. Because of this, big structures are made using metals, such as copper (Cu) and iron (Fe). (Except Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) which are soft metals).
- State: Metals are solid at room temperature except for mercury (Hg).
- Sound: Metals produce ringing sound, so, metals are called Sonorous. Sound of metals is also known as Metallic sound. This is the cause that metal wires are used in making musical instruments.
- Conduction: Metals are a good conductor of heat and electricity. This is the cause that electric wires are made of metals like copper and aluminium.
- Malleability: Metals are malleable. This means metals can be beaten into a thin sheet. Because of this property, iron is used in making big ships.
- Ductility: Metals are ductile. This means metals can be drawn into thin wire. Because of this property, a wire is made of metals.
- Melting and Boiling Point: Metals have generally high melting and boiling points. (Except sodium and potassium metals which have low melting and boiling point.)
- Density: Most of the metals have a high density.
- Colour: Most of the metals are grey in colour. But gold and copper are exceptions.
Chemical Properties of Metals
1. Reaction with oxygen: Most of the metals form respective metal oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide
Examples:
Reaction of Potassium with Oxygen: Potassium metal forms potassium oxide when reacts with oxygen.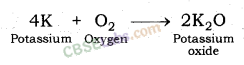
Reaction of Sodium with Oxygen: Sodium metal forms sodium oxide when reacts with oxygen.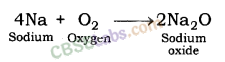
Lithium, potassium, sodium, etc. are known as Alkali-metals. Alkali metals react vigorously with oxygen.
Reaction of Copper metal with Oxygen: Copper does not react with oxygen at room temperature but when burnt in air, it gives oxide.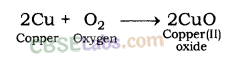
Silver, gold and platinum do not combine with the oxygen of air even at high temperature. They are the least reactive.
2. Reaction of metals with water: Metals form respective hydroxide and hydrogen gas when reacting with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
Most of the metals do not react with water. However, alkali metals react vigorously with water.
Reaction of Sodium metal with Water: Sodium metal forms sodium hydroxide and liberates hydrogen gas along with lot of heat when reacting with water.
Reaction of Calcium metal with Water: Calcium forms calcium hydroxide along with hydrogen gas and heat when react with water.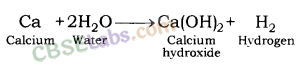
Reaction of Magnesium metal with Water: Magnesium metal reacts with water slowly and forms magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.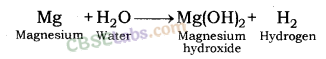
When steam is passed over magnesium metal, magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas are formed.
Reaction of Aluminium metal with Water: Reaction of aluminium metal with cold water is too slow to come into notice. But when steam is passed over aluminium metal, aluminium oxide and hydrogen gas are produced.
2Al + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 2H2
Reaction of Zinc metal with Water: Zinc metal produces zinc oxide and hydrogen gas when steam is passed over it. Zinc does not react with cold water.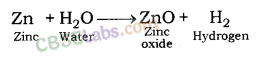
Reaction of Iron with Water: Reaction of iron with cold water is very slow and comes into notice after a long time. Iron forms rust (iron oxide) when reacts with moisture present in the atmosphere. Iron oxide and hydrogen gas are formed by passing of steam over iron metal.
Both calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) are heavier than water but still float over it: Both calcium and magnesium float over water surface because hydrogen gas is evolved when these metals react with water. It is in the form of bubbles which stick on the metal surface. Therefore, they float over it.
Other metals usually do not react with water or react very slowly. Lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with steam. Thus, the order of reactivity of different metals towards water may be written as :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Ae > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag > Au
3. Reaction of metals with dilute acid: Metals form respective salts when reacting with dilute acid.
Metal + dil. acid → Metal salt + Hydrogen
Reaction of Sodium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Sodium metal gives sodium chloride and hydrogen gas when react with dilute hydrochloric acid.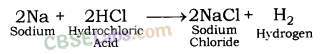
Reaction of Magnesium metal with dilute hydrochloric acid: Magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed when magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Reaction of Zinc with dilute sulphuric acid: Zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed when zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid. This method is used in the laboratory to produce hydrogen gas.
Hydrogen (H2) gas is not evolved when metal is treated with nitric acid (HNO3):
Nitric acid is strong oxidising agent and it oxidises the hydrogen gas (H2) liberated into water (H2O) and itself get reduced to some oxide of nitrogen like nitrous oxide (N2O)3 nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
Copper, gold, silver are known as noble metals. These do not react with water or dilute acids.
The order of reactivity of metal towards dilute hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid is in the order;
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu > Hg > Ag
Metal Oxides
Chemical Properties: Metal oxides are basic in nature. The aqueous solution of metal oxides turns red litmus blue.
Reaction of Metal oxides with Water: Most of the metal oxides are insoluble in water. Alkali metal oxides are soluble in water. Alkali metal oxides give strong base when dissolved in water.
Reaction of Sodium oxide with Water: Sodium oxide gives sodium hydroxide when reacts with water.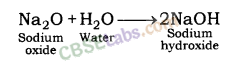
Reaction of Potassium oxide with Water: Potassium oxide gives potassium hydroxide when reacts with water.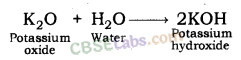
Reaction of Zinc oxide and Aluminium oxide: Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are insoluble in water. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature. An amphoteric substance shows both acidic and basic characters. It reacts with base like acid and reacts with an acid like a base.
When zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it behaves like an acid. In this reaction, sodium zincate and water are formed.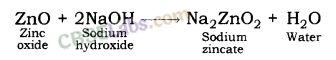
Zinc oxide behaves like a base when reacts with acid. Zinc oxide gives zinc chloride and water on reaction with hydrochloric acid.
In a similar way, aluminium oxide behaves like a base when reacts with acid and behaves like acid when reacts with a base.
Aluminium oxide gives sodium aluminate along with water when reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Aluminium oxide gives aluminium chloride along with water when it reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Reactivity Series of Metals: The order of intensity or reactivity of metal is known as Reactivity Series. Reactivity of elements decreases on moving from top to bottom in the given reactivity series.
In the reactivity series, copper, gold, and silver are at the bottom and hence, least reactive. These metals are known as Noble metals. Potassium is at the top of the series and hence, most reactive.
Reactivity of some metals are given in descending order :
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu
4. Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts: Reaction of metals with the solution of other metal salt is displacement reaction. In this reaction, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its salt.
Metal A + Salt of metal B → Salt of metal A + Metal B
Examples :
Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.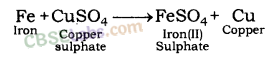
Similarly, aluminium and zinc displace copper from the solution of copper sulphate.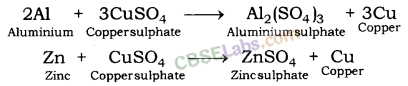
In all the above examples, iron, aluminium and zinc are more reactive than copper. This is why they displace copper from its salt solution.
When copper is dipped in the solution of silver nitrate, it displaces silver and forms copper nitrate.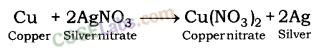
In the reaction, copper is more reactive than silver and hence, displaces silver from silver nitrate solution.
Silver metal does not react with copper sulphate solution because silver is less reactive than copper and not able to displace copper from its salt solution.
Similarly, when gold is dipped in the solution of copper nitrate, no reaction takes place because copper is more reactive than gold.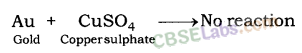
In similar way, no reaction takes place when copper is dipped in the solution of aluminium nitrate because copper is less reactive than aluminium.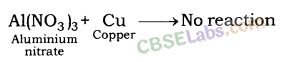
Non-Metals: Physical Properties of non-metals, chemical properties of non-metals, non¬metal oxides, Reaction of metal and Non-metal, Ionic bonds and formation of an ionic bond. Non-metals are the elements that do not conduct electricity and are neither malleable nor ductile.
Examples: Carbon (C), Sulphur (S), Phosphorous (P), Silicon (Si), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Neon (Ne) and Argon (Ar) etc.
Non-metals are the elements which form negative ions by gaining an electron. Thus, non¬metals are also known as Electronegative Elements.
Physical properties of non-metals
- Hardness: Non-metals are not hard rather they are generally soft. But the diamond is an exception; it is the hardest naturally occurring substance.
- State: Non-metals may be solid, liquid or gas.
- Lustre: Non-metals have a dull appearance. Diamond and iodine are exceptions.
- Sonority: Non-metals are not sonorous, i.e., they do not produce a typical sound on being hit.
- Conduction: Non-metals are a bad conductor of heat and electricity. Graphite which is allotrope of carbon is a good conductor of electricity and is an exception.
- Malleability and ductility: Non-metals are brittle.
- Melting and boiling point: Non-metals have generally low melting and boiling points.
- Density: Most of the non-metals have low density.
- Colour: Non-metals are in many colours.
Carbon in the form of graphite is non-metal which conduct electricity.
Iodine is non-metal which is lustrous having a shining surface.
Carbon in the form of diamond is a non-metal which is extremely hard.
Diamond is a non-metal which has a very high melting point and boiling point.
Chemical properties of Non-metals
1. Reaction of Non-metals with Oxygen: Non-metals form respective oxide when reacting with oxygen.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metallic oxide
When carbon reacts with oxygen, carbon dioxide is formed along with the production of heat.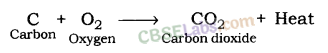
When carbon is burnt in an insufficient supply of air, it forms carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is a toxic substance. Inhaling of carbon monoxide may prove fatal.![]()
Sulphur gives sulphur dioxide when reacting with oxygen. Sulphur catches fire when exposed to air.![]()
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen it gives water.![]()
Non-metallic Oxide: Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. The solution of non-metal oxides turns blue litmus red.
Carbon dioxide gives carbonic acid when dissolved in water.![]()
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphurous acid when dissolved in water.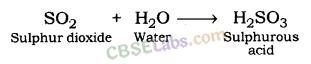
Sulphur dioxide gives sulphuric acid when reacts with oxygen.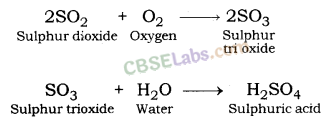
2. Reaction of Non-metal with Chlorine: Non-metal gives respective chloride when they react with chlorine gas.
Non-metal + Chlorine → Non-metal chloride
Hydrogen gives hydrogen chloride and phosphorous gives phosphorous trichloride when reacting with chlorine.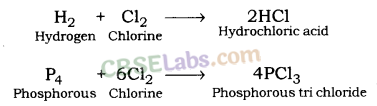
3. Reaction of Non-metals with Hydrogen: Non-metals reactive with hydrogen to form covalent hydrides.
Non-metal + Hydrogen → Covalent Hydride
Sulphur combines with hydrogen to form a covalent hydride is called Hydrogen sulphide.
Nitrogen combines with hydrogen in presence of an iron catalyst to form covalent hydride ammonia.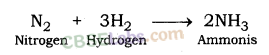
Non-metals do not react with water (or steam) to evolve Hydrogen gas.
Non-metals do not react with dilute acids.
4. Reaction of Metal and Non-metal: Many metals form ionic bonds when they react with non-metals. Compounds so formed are known as Ionic Compounds.
Ions: Positive or negative charged atoms are known as ions. Ions are formed because of loss or gain of electrons. Atoms form ions obtain by the electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas.
Positive ion: A positive ion is formed because of the loss of electrons by an atom.
Following are some examples of positive ions:
Sodium forms sodium ion because of the loss of one electron. Because of the loss of one electron, one positive charge comes over sodium.![]()
Magnesium forms positive ion because of the loss of two electrons. Two positive charges come over magnesium because of loss of two electrons.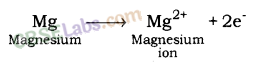
Negative ion: A negative ion is formed because of the gain of an electron.
Some examples are given below :
Chlorine gains one electron in order to achieve a stable configuration. After the loss of one electron, chlorine gets one negative charge over it forming chlorine ion.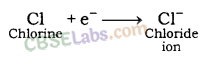
Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are formed because of transfer of electrons from metal to non¬metal. In this course, metals get positive charge because of transfer of electrons and non-metal gets negative charge because of acceptance of electrons. In other words, bond formed between positive and negative ion is called Ionic Bond.
Since, a compound is electrically neutral, so to form an ionic compound, negative and positive both ions must be combined.
Some examples are given below:
Formation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl): In sodium chloride, sodium is a metal (alkali metal) and chlorine is a non-metal.
Atomic number of sodium = 11
Electronic configuration of sodium : 2, 8, 1
Number of electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Valence electrons = Electrons in outermost orbit = 1
Atomic number of chlorine = 17
Electronic configuration of chlorine : 2, 8, 7
Electrons in outermost orbit = 7
Therefore, valence electrons = ?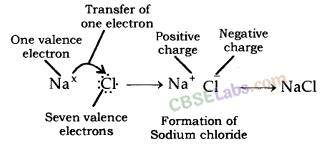
Sodium has one valence electron and chlorine has seven valence electrons. Sodium requires losing one electron to obtain stable configuration and chlorine requires gaining one electron in order to obtain stable electronic configuration. Thus, in order to obtain stable configuration, sodium transfers one electron to chlorine. After loss of one electron, sodium gets one positive charge (+) and chlorine gets one negative charge after gain of one electron. Sodium chloride is formed because of transfer of electrons. Thus, ionic bond is formed between sodium and chlorine. Since, sodium chloride is formed because of ionic bond, thus, it is called Ionic compound. In similar way, potassium chloride (KCl) is formed.
Properties of Ionic compound
- Ionic compounds are solid. Ionic bond has a greater force of attraction because of which ions attract each other strongly. This makes ionic compounds solid.
- Ionic compounds are brittle.
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points because force of attraction between ions of ionic compounds is very strong.
- Ionic compounds generally dissolve in water.
- Ionic compounds are generally insoluble in organic solvents; like kerosene, petrol, etc.
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in the solid state.
- The solution of ionic compounds in water conduct electricity. This happens because ions present in the solution of ionic compound facilitate the passage of electricity by moving towards opposite electrodes.
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals: Minerals, ores, extraction of metals of least reactivity, extraction of metals of middle reactivity, extraction of metals of high reactivity, refining or purification of metals and corrosion.
Occurrence and Extraction of Metals:
Source of metal: Metals occur in Earth’s crust and in seawater; in the form of ores. Earth’s crust is the major source of metal. Seawater contains many salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium chloride, etc.
Mineral: Minerals are naturally occurring substances which have a uniform composition.
Ores: The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called Ores.
Metals found at the bottom of reactivity series are least reactive and they are often found in nature in free-state; such as gold, silver, copper, etc. Copper and silver are also found in the form of sulphide and oxide ores.
Metals found in the middle of reactivity series, such as Zn, Fe, Pb, etc. are usually found in the form of oxides, sulphides or carbonates.
Metals found at the top of the reactivity series are never found in free-state as they are very reactive, example; K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al, etc.
Many metals are found in the form of oxides because oxygen is abundant in nature and is very reactive.
Extraction of Metals: Metals can be categorised into three parts on the basis of their reactivity: Most reactive, medium reactive and least reactive.
The three major steps involved in the extraction of a metal from its ore are
- Concentration or enrichment of ores.
- Conversion of concentrated ore into crude metal and,
- Refining of impure or crude metal.
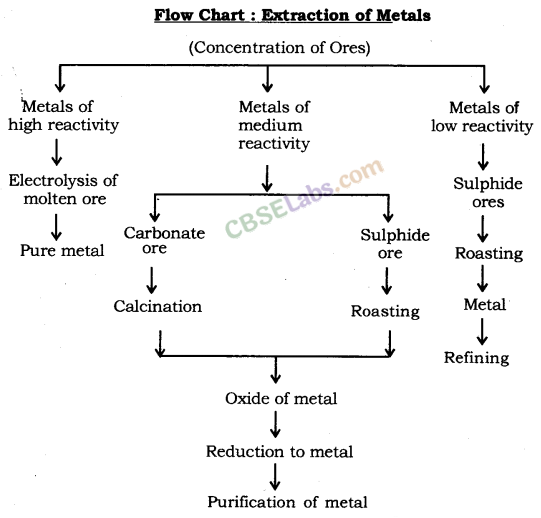
1. Concentration of Ores: Removal of impurities, such as soil, sand, stone, silicates, etc. from mines ore is known as Concentration of Ores.
Ores which are mined often contain many impurities. These impurities are called gangue. First of all, concentration is done to remove impurities from ores. The concentration of ores is also known as enrichment of ores. Process of concentration depends upon physical and chemical properties of ores. Gravity separation, electromagnetic separation, froth flotation process, etc. are some examples of the processes which are applied for concentration of ores.
2. Conversion of Concentrated Ore into Crude Metal
Conversion of metals ores into oxides: It is easy to obtain metals from their oxides. So, ores found in the form of sulphide and carbonates are first converted to their oxides by the process of roasting and calcination. Oxides of metals so obtained are converted into metals by the process of reduction.
Roasting: Heating of sulphide ores in the presence of excess air to convert them into oxides is known as Roasting.![]()
Calcination: Heating of carbonate ores in the limited supply of air to convert them into oxides is known as Calcination.![]()
| Calcination | Roasting |
| (i) It is done for carbonate ores. | (i) It is done for sulphide ores. |
| (ii) Carbonates ores heated in the absence of oxygen. | (ii) Sulphide ores are heated in the Presence of oxygen. |
| (iii) The CO2 gas is released and Metal oxide is obtained. ZnCO3(s) | (iii) SO2 gas is released and Metal oxide is obtained. 2ZnS(s) + 3O2(g) |
3. Reduction: Heating of oxides of metals to turn them into metal is known as Reduction.
(i) Extraction of Metals of Least Reactivity: Mercury and copper, which belong to the least reactivity series, are often found in the form of their sulphide ores. Cinnabar (HgS) is the ore of mercury. Copper glance (Cu2S) is the ore of copper.
Extraction of Mercury Metal: Cinnabar (HgS) is first heated in air. This turns HgS (mercury sulphide or cinnabar) into HgO (mercury oxide) by liberation of sulphur dioxide. Mercury oxide so obtained is again heated strongly. This reduces mercury oxide to mercury metal.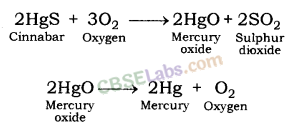
Extraction of Copper Metal: Copper glance (Cu2S) is roasted in the presence of air. Roasting turns copper glance (ore of copper) into copper (l) oxide. Copper oxide is then heated in the absence of air. This reduces copper (l) oxide into copper metal.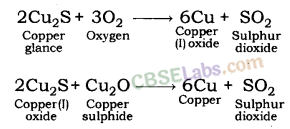
(ii) Extraction of Metals of Middle Reactivity: Iron, zinc, lead, etc. are found in the form of carbonate or sulphide ores. Carbonate or sulphide ores of metals are first converted into respective oxides and then oxides are reduced to respective metals.
Extraction of Zinc: Zinc blende (ZnS: zinc sulphide) and smithsonite or zinc spar or calamine (ZnCO3: zinc carbonate) are ores of zinc. Zinc blende is roasted to be converted into zinc oxide. Zinc spar is put under calcination to be converted into zinc oxide.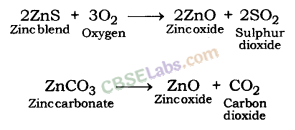
Zinc oxide so obtained is reduced to zinc metal by heating with carbon (a reducing agent).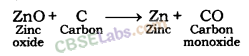
Extraction of Iron from Haematite (Fe2O3): Haematite ore is heated with carbon to be reduced to iron metal.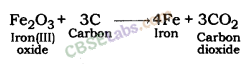
Extraction of Lead from Lead oxide: Lead oxide is heated with carbon to be reduced to lead metal.
Reduction of Metal oxide by Heating with Aluminium: Metal oxides are heated with aluminium (a reducing agent) to be reduced to metal. Following is an example: Manganese dioxide and copper oxide are reduced to respective metals when heated with aluminium.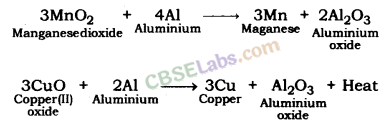
Thermite Reaction: Ferric oxide; when heated with aluminium; is reduced to iron metal. In this reaction, a lot of heat is produced. The thermite reaction is used in the welding of electric conductors, iron joints, etc. such as joints in railway tracks. This is also known as Thermite Welding (TW).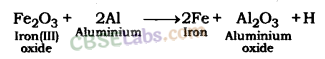
(iii) Extraction of Metals of High Reactivity: Metals of high reactivity; such as sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, etc. are extracted from their ores by electrolytic reduction. These metals cannot be reduced using carbon because carbon is less reactive than them.
Electrolytic Reduction: Electric current is passed through the molten state of metal ores. Metal being positively charged is deposited over the cathode.
Example: When an electric current is passed through molten state or solution of sodium chloride, sodium metal gets deposited over the cathode.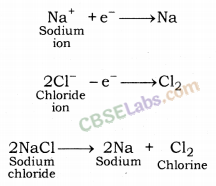
Metals obtained from the process of electrolytic reduction are pure in form.
4. Refining or purification of metals: Metals extracted from various methods contains some impurities, thus, they are required to be refined. Most of the metals are refined using electrolytic refining.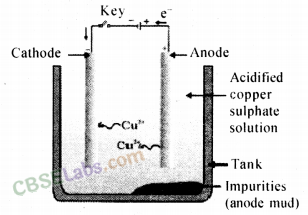
Electrolytic Refining: In the process of electrolytic refining, a lump of impure metal and a thin strip of pure metal are dipped in the salt solution of metal to be refined. When an electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal is deposited over a thin strip of pure metal
from a lump of impure metal. In this, impure metal is used as anode and pure metal is used as a cathode.
Electrolytic Refining of Copper: A lump of impure copper metal and a thin strip of pure copper are dipped in the solution of copper sulphate. Impure lump of metal is connected with the positive pole and thin strip of pure metal is connected with negative pole. When electric current is passed through the solution, pure metal from anode moves towards cathode and is deposited over it. Impurities present in metal are settled near the bottom of anode in the solution. Settled impurities in the solution are called Anode Mud.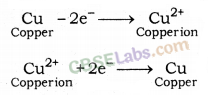
5. Corrosion: Most of the metals keep on reacting with the atmospheric air. This leads to the formation of a layer over the metal. In the long run, the underlying layer of metal keeps on getting lost due to conversion into oxides or sulphides or carbonate, etc. As a result, the metal gets eaten up. The process is called Corrosion.
Rusting of Iron: Rusting of iron is the most common form of corrosion. When iron articles like the gate, grill, fencing, etc. come in contact with moisture present in the air, the upper layer of iron turns into iron oxide. Iron oxide is brown-red in colour and is known as Rust. The phenomenon is called Rusting of Iron.
If rusting is not prevented in time, the whole iron article would turn into iron oxide. This is also known as Corrosion of Iron. Rusting of iron gives a huge loss every year.
Prevention of Rusting: For rusting, iron must come in contact with oxygen and water. Rusting is prevented by preventing the reaction between atmospheric moisture and the iron article. This can be done by:
- Painting
- Greasing
- Galvanization
- Electroplating
- Alloying
6. Alloys: The homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal is called Alloy.
Types of alloys :
- Ferrous alloys: An alloy in which iron (Fe) is present. For example : manganese steel (Fe = 86% ; Mn = 13% ; C = 1%) and Nickle steel (Fe = 98% ; Ni = 2%).
- Non-ferrous alloys: An alloy does not contain iron. For example : Brass (Cu = 80% ; Zn = 20%), and Bronze (Cu = 90% ; Sn = 10%).
- Amalgams: An alloy in which mercury (Hg) is present. For example Sodium amalgams [Na(Hg)] and Zinc amalgams [Zn(Hg)].
Properties of an Alloy
- Alloys are stronger than the metal from which they are obtained.
- It is harder than the constituent metals.
- More resistance to corrosion.
- The melting point of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
Example: Solder [Sn(80%) + Pb(50%)] has lower m. p. than Pb and Sn. - The electrical conductivity of alloys is lower than the constituent metals.
Some examples of Alloys:
- Brass: [80% Cu + 20% Zn ]
- Bronze: [90% Cu + 20% Sn]
- Solder: [50% Pb + 50% Sn]
- Duralumin: [95% Al + 4% Cu + 0.5% Mg + 0.5 Mn]
- Steel: [99.95% Fe + 0.05% C]
- Stainless steel: [74% Fe + 18% Cr + 8% Ni]
- Magnesium: [95% Al + 5% Mg]
- German Silver: [60% Cu + 20% Zn + 20% Ni]
- Alloys of Gold: Pure gold is said to be of 24 carats. Gold is alloyed with a small amount of silver or copper to make it hard.
Metals and Non-metals:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Metals generally occur as hard solid substances. | 1. Non-metals generally occur in all the three forms of matter- solid, liquid and gases. |
| 2. Metals are malleable and ductile. | 2. Non-metals are non-malleable and non-ductile. |
| 3. Metals produce ringing sound on striking which is called their sonorous property. | 3. Non-metals do not show this sonorous property. |
| 4. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. | 4. Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity with the exception of graphite which is a good conductor of heat and electricity. |
Chemical Properties of Metals and Non-metals.
The reaction of metals with oxygen. Metals form their oxides when reacting with oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
Metal oxides are basic in nature. Example, Reaction of Iron metal with oxygen When iron reacts with moist air, it forms rust.
Rust is iron oxide. Articles made of iron, such as grills, fencing, etc. are getting rusted because of reaction with moist air.
Iron (Fe) + Water (H2O) + Oxygen (O2) → Fe3O4n.H2O (Iron II, III) Oxide (Rust)
Rust is reddish brown in colour and is iron oxide. Iron oxide is basic in nature. It turns red litmus blue.
Rusting of iron can be prevented:
- by galvanizing the iron articles with zinc coating.
- by painting and applying grease on the articles.
The reaction of Magnesium metal with oxygen: When magnesium is burnt in air, it forms magnesium oxide. Burning in the air means reaction with oxygen.
Magnesium + Oxygen (O2) → MgO (Magnesium oxide)
Magnesium oxide forms magnesium hydroxide with water. The solution of Magnesium oxide turns red litmus paper blue. This means magnesium oxide is basic in nature.
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2 (Magnesium Hydroxide)
The reaction of Non-metals with oxygen: Non-metals form their oxides when they react with oxygen.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metal oxide
Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature.
Example., Reaction of sulphur with oxygen.
When sulphur is burnt in air, it forms sulphur dioxide.
Sulphur + Oxygen (O2) → SO2 (Sulphur dioxide)
The solution of sulphur dioxide turns blue litmus paper red. Sulphur dioxide forms sulphurous acid when dissolved in water. Thus, sulphur dioxide is acidic in nature.
SO2 + H2O → Sulphurous acid (H2SO3)
The reaction of carbon with oxygen—When carbon is burnt in air, it forms carbon dioxide.
Carbon + Oxygen (O2) → CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
You can observe that when coal (carbon) is burnt it forms smoke, which contains carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is acidic in nature. The solution of carbon dioxide in water turns blue litmus paper red.
CO2 + H2O → Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
The reaction of Metals and Non-metals with water: Generally, metals form respective hydroxides when they react with water.
Metal + Water → Metal hydroxide
The reaction of sodium metal with water: Sodium metal vigorously reacts with water and forms sodium hydroxide along with a lot of heat.
Na + H2O → NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) + H2 (Hydrogen) + Heat
Non-metals generally do not react with water. Rather some non-metals which react with air vigorously are stored in water. The reaction of metals and non-metals with dilute acid. Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with dilute acid.
Metal + Acid → Hydrogen gas + Salt
The reaction of zinc with dilute acid. Zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc chloride when it reacts with hydrochloric acid. Similarly, zinc gives hydrogen gas along with zinc sulphate when it reacts with sulphuric acid. This method is used to produce hydrogen gas in the laboratory.
Zn + H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid) → ZnSO4 (Zinc sulphate) + H2 (Hydrogen)
The reaction of Aluminium with dilute acid. Aluminium gives hydrogen gas along with aluminium chloride when it reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
2Al + 6HCl (Hydrochloric acid) → 2AlCl3 (Aluminium Chloride) + 3H2 (Hydrogen)
Copper does not react with dilute sulphuric acid even on heating, but it reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid. Copper, silver and gold are considered as noble metals as do not react with dilute acid.
Generally, non-metals do not react with dilute acid.
The reaction of metals and non-metals with the base. Metals give hydrogen gas when they react with a base.
Metal + Base → Hydrogen gas + Salt
The reaction of aluminium metal with sodium hydroxide.
Al + NaOH (Sodium hydroxide) → NaAlO2 (Sodium aluminate) + H2 (Hydrogen)
Aluminium metal forms hydrogen gas and sodium aluminate when it reacts with sodium hydroxide. Similarly, zinc gives sodium zincate and hydrogen gas when it reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Displacement Reaction: When a more reactive metal reacts with the salt solution of less reactive metal, more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal from its solution.
Metal A + Salt Solution of metal B → Salt Solution of metal A + metal B
In the above equation, metal A is more reactive than metal B.
Example., When aluminium metal is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate, it forms aluminium sulphate and copper.
Al + CuSO4 (Copper sulphate) → Al2(SO4)3 (Aluminium Sulphate) + Cu (Copper)
In the above reaction, aluminium is more reactive than copper, that is why it replaces copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
When copper metal is dipped in the solution of aluminium nitrate, no reaction takes place. Because copper is less reactive than aluminium.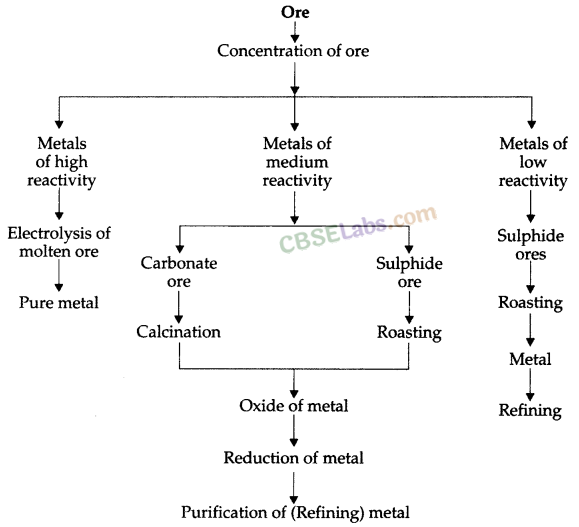
Roasting and Calcination:
| Roasting | Calcination |
| 1. It is done in case of sulphide ores. | 1. It is done in case of carbonate ores. |
| 2. In this, the ore is heated in the presence of air to convert it into oxide compound. | 2. The carbonate ore is heated in the absence of air to convert into oxide. |
| 3. The gas given out is SO2 (sulphur dioxide) gas. | 3. The gas given out is CO2 (carbon dioxide) gas. |
4. Example: 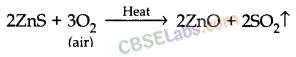 | 4. Example: |
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals And Non-Metals
Short Answer Type Questions
1.Iqbal treated a lustrous, divalent element M with sodium hydroxide. He observed the formation of bubbles in reaction mixture. He made the same observations when this element was treated with hydrochloric acid. Suggest how can he identify the produced gas. Write chemical equations for both the reactions.
Answer:
M + 2NaOH —>Na2M02 + H2(g)
M + 2HCl —> MCl2 + H2(g)
Bring a burning candle near the gas. If it burns with pop sound, the gas is hydrogen and the element is a metal.
2 During extraction of metals, electolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals.
(a) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process?
(b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also.
(c) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current?
Answer:
(a) Pure silver rod will be used as cathode and impure silver rod will be used as anode.
(b) Ag NO3 (aq) can be used as electrolyte.
(c) Pure silver will be formed at cathode.
At anode : Ag —> Ag+ +e–
At cathode : Ag+ +e–—> Ag
3.Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated but when metals (except Mn and Mg), treated with HNOs, hydrogen is not liberated. Why?
Answer.It is because HNO3 is an oxidising agent and it gets reduced to NO if it is dilute and NO2if HNOs is concentrated, it oxidises H2 to H2O.
4.Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks.
(a) Identify the compound X.
(b) Name the reaction.
(c) Write down its reaction.
Answer.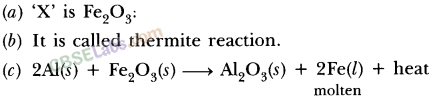
5.What are the constituents of solder alloy? Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Answer. Solder is made up of lead and tin. It has low melting point, therefore, it is used for soldering (welding) electrical wires.
6.A metal A, which is used in thermite process, when heated with oxygen gives
an oxide B, which is amphoteric in nature? Identify A and B. Write down the reactions of oxide B with HC1 and NaOH.
Answer: ‘A’ is aluminium.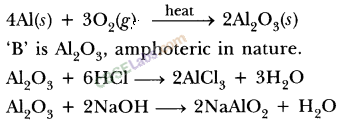
7.What happens when
(a) ZnCOs is heated in the absence of oxygen?
(b) a mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S is heated?
Answer: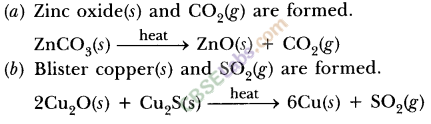
8.A non-metal A is an important constituent of our food and forms two oxides B and C. Oxide B is toxic whereas oxide C causes global warming.
(a) Identify A, B and C.
(b) To which group of periodic table does A belong?
Answer:
(a) A is carbon. It forms two oxides: CO (B) is toxic whereas CO2 (C) causes
global warming as it absorbs heat radiations from atmosphere.
(b) A belongs to group 14 of periodic table.
9.An element A reacts with water to form a compound B which is used in white washing. The compound B on heating forms an oxide C which on treatment with water gives back B. Identify A, B and C and give the reactions involved.
‘A’ is calcium metal, ‘B’ is calcium hydroxide, ‘C’ is calcium oxide.
Answer:
10. A metal M does not liberate hydrogen from acids but reacts reacts with oxygen to give a black colour product. Identify M and black coloured product and also explain the reaction of M with oxygen.
Answer:
M is ‘Cu’. It does not liberate hydrogen with dilute acid as it is less reactive than hydrogen gas.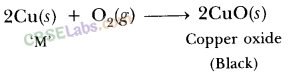
11. A solution of CuS04 was kept in an iron pot. After few days, the iron pot was found to have a number of holes in it. Explain the reason in terms of reactivity. Write the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer: Iron is more reactive than copper. Therefore, it displaces copper from copper sulphate solution.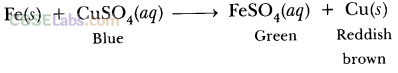
12. When a metal ‘X’ is treated with cold water, It gives base salt ‘X’ with molecular formula XOH (Molecular mass = 40) and liberate a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z and also write the reaction involved.
Answer.
‘X’ is Na ‘Y’ is NaOH ‘Z’ is H2 gas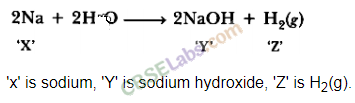
13. A non-metal ‘X’ exists in two different forms ‘Y’ and ‘Z\ ‘Y’ is hardest natural substance, whereas ‘Z’ is good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Answer: ‘X’ is carbon ‘Y’ is diamond ‘Z’ is graphite.
‘Y’ (diamond) is hardest natural substance.
‘Z’ (graphite) is good conductor of electricity.
14. The following reaction takes place when aluminium powder is heated with MnO2 :
3MnO2(s) + 4Al(s)—–> 3Mn(l) + 2Al2O3(l) + Heat
Molten Molten
(a) Is aluminium getting reduced ?
(b) Is MnO2 getting oxidised ?
Answer:
(a) No, aluminium is getting oxidised.
(b) No, MnO2 is getting reduced.
15. A metal that exists as liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide in the presence of air. Identify the metal and its ore and give the reaction involved.
Answer: The metal is mercury.
2HgS(s) + 3O2(g)—–> 2HgO(s) + 2SO2(g)
HgS(s) + 2HgO(s)—–> 3Hg(l) + SO2(g)
16. Give the formulae of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of following pairs of elements :
(a) Mg and N2 (b) Li and 02
(c) A1 and Cl2 (d) K and O2
Answer:
(a) 3Mg + N2—–> Mg3N2
(b) 4Li + O2—–> 2Li20
(c) 2Al + 3Cl2—–> 2AlCl3
(d) 4K + O2 —–> 2K2O
17.Give two examples each of the metals that are good conductors and poor conductors of heat respectively.
Answer: Good conductors of heat are copper and silver. Poor conductors of heat are lead and mercury.
18. Name-one metal and one non-metal that exist in liquid state at room temperature. Also name two metals having melting point less than 310 K (37 °C).
Answer: Metal in liquid state is mercury, non-metal in liquid state is bromine.
Gallium (Ga) and Cesium (Cs) have melting point below 310 K.
19. An alkali metal A gives a compound B (molecular mass = 40) on reacting with water. The compound B gives a soluble compound C on treatment with aluminium oxide. Identify A, B and C and give the reaction involved.
Answer: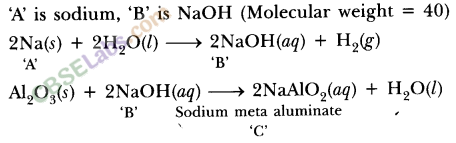
‘C’ is sodium meta aluminate, soluble in water.
20. Give the reaction involved during extraction of zinc from its ore by
(a) roasting of zinc ore.
(b) calcination of zinc ore.
Answer: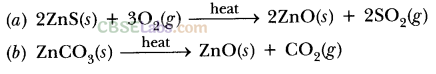
21. An element forms an oxide, A2Os which is acidic in nature. Identify A as a metal or non-metal.
Answer: A is non-metal as non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature.
Long Answer Type Questions
22. A non-metal A which is the largest constituent of air, when heated with H2 in 1 : 3 ratio in the presence of catalyst (Fe) gives a gas B. On heating with O2, it gives an oxide C. If this oxide is passed into water in the presence of air, it gives an acid D which acts as a strong oxidising agent.
(a) Identify A, B, C and D.
(b) To which group of periodic table does this non-metal belong?
Answer:
(a) N2 is largest constituent of air, when heated with H2 in the ratio of 1 : 3 .
in the presence of catalyst (Fe) gives a gas NH3(B).
Nitrogen reacts with oxygen on heating to form nitrogen monoxide ‘C’, which gets oxidised in the presence of O2 to nitrogen dioxide. Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water in the presence of oxygen to form nitric acid which is an oxidising agent.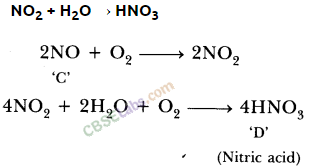
‘A’ is N2, ‘B’ is NH3, ‘C’ is NO and ‘D’ is HNO3.
(b) Group 15
23. Explain the following:
(a) Reactivity of A1 decreases if it is dipped in HNO3.
(b) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg.
(c) NaCl is not a conductor of electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in aqueous solution as well as in molten state.
(d) Iron articles are galvanised.
(e) Metals like Na, K, Ca and Mg are never found in their free state in nature.
Answer:
(a) It is due to the formation of oxide layer on its surface.
(b) It is because Na or Mg are strong reducing agents, therefore, carbon cannot reduce their oxides.
(c) NaCl does not conduct electricity in solid state as it does not have free ions to move in solid state but in aqueous solution and in molten states ions are free to move.
(d) Iron articles are galvanised to protect them from rusting.
(e) It is because these metals are highly reactive and occur in the form of their compounds.
24.An element A burns with golden flame in air. It reacts with another element B, atomic number 17 to give a product C. An aqueous solution of product C on electrolysis gives a compound D and liberates hydrogen. Identify A, B, C and D. Also write down the equations for the reactions involved, HOTS;
Answer: A is sodium as it burns with golden flame in air.
‘B’ (17) has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7 so ‘B’ is chlorine
A is Na, ‘B’ is Cl2 , ‘C’ is NaCl and ‘D’ is NaOH.
25.Give the steps involved in the extraction of metals of low and medium reactivity from their respective sulphide ores.
Answer: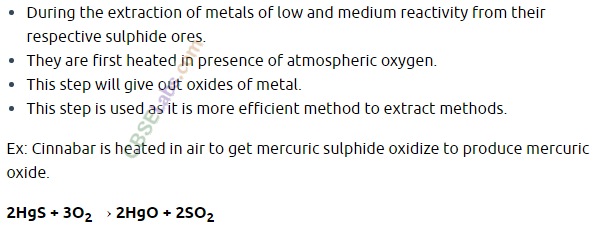
Metal sulphide like HgS reacts with 02 to form mercuric oxide and sulphur dioxide. Mercuric oxide is unstable changes to Hg(l) which can be refined by distillation.
2HgS 4- 3O2 —–> 2HgO + 2SO2
HgS + 2HgO —–> 3Hg + SO2
Sulphide ore like Zn, on roasting (in presence of O2 ) gives metal oxide which on reduction with metal sulphide (ZnS) or suitable reducing agent gives metal which is refined by electrolyte refining.
2ZnS + 3O2 —–> 2ZnO + 2SO2
2ZnO + ZnS —–> 3Zn + SO2
Alternative method of reduction :
ZnO + C —–> Zn + CO
Pure zinc is obtained by electrolytic refining.
26.Of the three metals X, Y and Z, X reacts with cold water, Y with hot water and Z with steam only. Identify X, Y and Z and also arrange them in order of increasing reactivity.
Answer: X’ is sodium or potassium metal.
2Na(s) + 2HsO(l) —–> 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
‘X’ ‘cold’
Or
2K(s) + 2H2O(l) —–> 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
‘X’ ‘cold’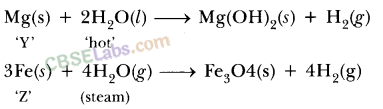
Fe < Mg < Na < K is an increasing order of reactivity.
27.Two ores A and B were taken. On heating, ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2 . What steps will you take to convert them into metals ?
Answer:Since ore ‘A’ gives CO2 and ore ‘B’ gives SO2 . Therefore, A is metal carbonate ore and ‘B’ is metal sulphide ore.
Metal carbonate on heating gives ‘MO’.
‘MO’, on reduction with coke gives metal and carbon monoxide.![]()
Metal ‘M’ is obtained which can be purified by electrolytic refining.
Metal sulphide is heated in presence of oxygen to form metal oxide and S02.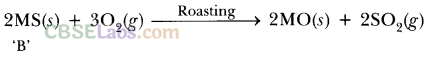
Metal sulphide reacts with metal oxide to form impure metal and S02.![]()
MO can also be reduced with carbon to form metal. The metal ‘M’ from ore ‘B’ is obtained.![]()
28.Impure metal is purified by electrolytic refining
(i) Given below are steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (I) sulphide
(b) Reduction of copper (I) oxide with copper (I) sulphide
(c) Electrolytic refining
(ii) Draw the neat and labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper.
Answer:
(i)
(a) 2CU2S(S) + 3O2(g) ——–> 2Cu2O(s) + 2SO2(g)
(b) 2CU2O(S) + Cu2S(s) ——–> 6CU(s) + SO2(g)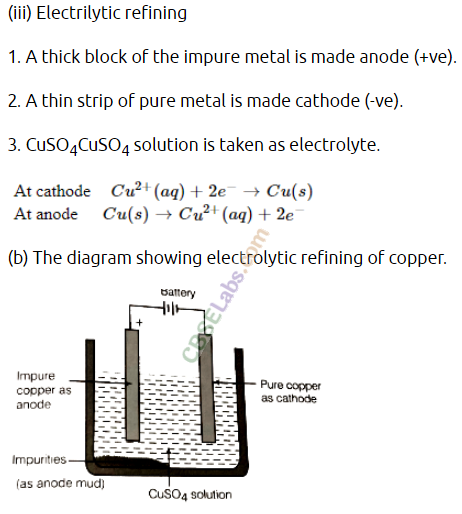
Metals and Nonmetals Class 10 Science Extra Questions
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 3 | Metals And Non-Metals |
| 3.1 | Physical Properties |
| 3.2 | Chemical Properties Of Metals |
| 3.3 | How Do Metals And Non-Metals Rea Als React? |
| 3.4 | Occurrence Of Metals |
| 3.5 | Corrosion |
Question-1
a) Due to which property of metals are metallic foils prepared?
b) Write uses of aluminium foils
Solution:
a) Metallic foils are prepared, making use of the malleable property of metals.
b) Aluminium foils are used for
(i) wrapping chocolates and food stuff
(ii) to prepare hydrogen.
Question-2
Name one non-metal and one metal, which are in liquid state at room temperature.
Solution:
Bromine is the non–metal and mercury is the metal which are in liquid state at room temperature.
Question-3
Give reasons for the following
i) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide.
ii) Non-metals in general do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
iii) Metals conduct electricity.
Solution:
i) Zinc oxide is considered an amphoteric oxide because it shows both acidic and basic behaviour.
ii) Non-metals do not react with dilute acids hence do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
iii) thatMetals conduct electricity because they contain free electrons which can move easily through the metal and conduct electric current.
Question-4
Identify the following oxides with neutral, acidic, basic and amphoteric oxides.
i) Al2O3 ii) MgO iii) SO2 iv) CO; v) Na2O vi) N2O vii) ZnO viii) CO2 ix) SO3 x) CaO.
Solution:
Neutral oxides: CO; N2O
Acidic oxides: SO2; CO2; SO3
Basic oxides: MgO; Na2O; CaO
Amphoteric oxides: Al2O3 ; ZnO
Question-5
By what processes do you concentrate the following ores:
i) PbS(galena)
ii) Fe2O3(haematite)
iii) Al2O3.2H2O (bauxite).
Solution:
i) PbS (galena) is concentrated by froth floatation method.
ii) Fe2O3 (haematite) is concentrated by magnetic separation.
iii) Al2O3.2H2O (bauxite) is concentrated by leaching process (chemical method).
Question-6
Why is that iron does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth? What are the common compound forms in which iron occurs? Which of these is more often used for extracting iron? Why are carbon and limestone mixed with iron ore before feeding it into the blast furnace? Write the chemical equations for the reduction step and the slag formation step.
Solution:
Iron is quite reactive and so it does not occur as a metal in the crust of the earth. The common compounds formed are its oxide, a carbonate and a sulphide. The oxide ore of iron called haematite is more often used for extracting iron. The carbon and limestone which is mixed with iron ore is called the charge. This charge is responsible for the formation of iron metal. Coke acts the reducing agent and addition of limestone helps to remove the earthy impurities like sand from the blast furnace by forming fusible slag.
Reduction of Iron(III)oxide or haematite to Iron: carbon monoxide reduces iron(III)oxide to iron metal
Question-7
By what chemical processes do you obtain the following metals?
i) Mercury from HgO ii) Iron from Fe2O3 iii) Manganese from MnO2 iv) Sodium form NaCl v) Aluminium from Al2O3.
Question-8
i) What is the composition of molten slag, formed in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace?
ii) What is the use of slag?
Solution:
i) Molten slag in the extraction of iron is calcium silicate(CaSiO3).
ii) Slag is used for constructions of roads.
Question-9
Write the name of the compound, when iron is corroded?
Solution:
When iron is corroded rust is formed which is hydrated iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3.x.H2O)
Question-10
Give reasons for the following
i. Na, K and Ca metals form hydrides by combination with hydrogen gas, but most other metals do not.
ii. Aluminium easily combines with oxygen but still it can be used for making kitchen utensils.
Solution:
i. Metals like Na, K and Ca can force the hydrogen atoms to accept electrons given by them and form hydrides.
ii. Aluminium forms a protective oxide layer when it combines with oxygen and hence it is used for making kitchen utensils.
Question-11
i) Among iron and aluminium which rusts easily?
ii) What are the conditions, necessary for rusting of iron?
Solution:
i) Among iron and aluminium, iron rusts easily. It forms Al2O3. That is why iron pipes are wrapped with aluminium metal to prevent rusting of iron.
ii) 1) Air or oxygen 2) Water, containing dissolved air.
These are necessary conditions for rusting of iron.
Question-12
Name an ore of zinc other than zinc oxide. By what process can this ore be converted to zinc oxide.
Solution:
Zinc blende(ZnS) is an ore of zinc other than zinc oxide. Roasting is the process by which ZnS can be converted into zinc oxide.
Question-13
What property of hydrogen is observed in the following experiments?
i) Balloon, filled with hydrogen, floats.
ii) Pop sound is heard when a burning splint is introduced at the mouth of hydrogen filled jar.
iii) When black cupric oxide is heated in a stream of hydrogen, reddish colour is obtained.
Solution:
i) Hydrogen is light. So hydrogen filled balloons float.
ii) Pop sound is due to the combustible property of hydrogen. Hydrogen burns with oxygen at the mouth of the hydrogen filled jar.
iii) Hydrogen has reducing property. Hence it reduces black cupric oxide to red copper metal.
Question-14
Select the non-metals amongst the following
i) Bismuth ii) Sulphur iii) Arsenic iv) Hydrogen.
Solution:
Hydrogen and Sulphur are the non-metals.
Question-15
How do you test ammonia gas?
Solution:
Ammonia gas is tested, by showing a drop of conc. HCl by means of a glass rod to it, when dense white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed.
Ammonium chloride (dense white fumes).
Question-16
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
i) Cinnabar is heated in air.
ii) Concentrated sulphuric acid and sulphur are heated together. Calcium metal reacts with water.
Solution:
Question-17
What are the uses of ammonia?
Solution:
i) Ammonia is used in the manufacture of fertilizers like ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate.
ii) To manufacture nitric acid by Ostwald’s process.
iii) To prepare dyes, explosives, cellulose acetate etc.
Question-18
Why do some metals like, Na, K, Ca, Mg not occur in nature as free elements?
Solution:
Metals like Na, K, etc (alkali metals) and Ca, Mg etc (alkaline earth metals) are very reactive and hence they react with atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide and also with other non-metals like sulphur present in the earth’s crust to form compounds like oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates and chlorides. So they do not occur in free state, but are found in the form of the above compounds.
Question-19
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when:
i) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
ii) Steam is passed over hot iron.
iii) A mixture of ammonia and oxygen is passed over platinum heated to 1073 K.
Solution:
Question-20
Why are metals like sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium etc. obtained by electrolytic reduction?
Solution:
Metals like Na, Ca, Mg, Al etc, which are high up in the activity series are electropositive elements and possess a high affinity for oxygen. So their oxides are very much stable and cannot be reduced with common reducing agents like carbon. So carbon reduction process cannot be applied to prepare these metals. They can only be prepared by electrolytic reduction of their fused chlorides or oxides.
Question-21
State briefly how you will extract iron from its ore. Draw a neat and labelled diagram. Write all the chemical reactions involved in it.
Solution:
Iron is usually extracted from its chief ore, Haemitite.
The various steps involved in the production of iron metal from haematite are as follows:
1. Concentration of ore
The concentration of haematite or is done by the method of hydraulic washing. The ore is spilt into small pieces and then washed in a stream of water to remove sand, clay. In this way ,a fairly concentrated ore is obtained and usually there is no need of any further concentration.
2. Calcination
The washed iron ore is then strongly heated in the absence of air to expel water sticking to it.
3. Reduction
The washed and dried ore is mixed with weighed quantities of coke and limestone and put into a blast furnace from the top .A blast of hot air is blown into the furnace from near its bottom. This air is to supply for the burning of coke.
The two reactions which take place in the blast furnace leading to the formation of iron metal are: formation of carbon monoxide and reduction of haematite.

Question-22
Write the chemical formula for the following.
a) Alumina b) Silica c) Rust d) Oleum e) Slag f) Sodium amalgam g) Bauxite h) Haematite.
Solution:
| a) Alumina | – Al2O3 |
| b) Silica | – SiO2 |
| c) Rust | – Fe2O3. xH2O |
| d) Oleum | – H2S2O7 (SO3, dissolved in H2SO4) |
| e) Slag | – CaSiO3 |
| f) Sodium amalgam | – Na – Hg (an alloy of sodium with mercury) |
| g) Bauxite | – Al2O3.2H2O |
| h) Haematite | – Fe2O3 |
Question-23
In Frasch process of digging out sulphur from a deep underground, how has it made possible to life sulphur from the bed to surface of each? What is the basic principle on which extraction of sulphur is based? Draw a neat and labelled diagram. Besides elemental form, in what compound forms is sulphur found. Give two physical properties of sulphur.
Solution:
In the Frasch process in order to bring out sulphur from the underground deposits, a hole of about 30 cm diameter is bored up to the sulphur bed. It is based on the principle that sulphur has a comparatively low melting point of 1150 or 3880 due to which it can be melted by introducing super-heated water in the underground sulphur deposits. This mixture of molten sulphur and water is then brought out by the force of hot, compressed air.
Three concentric pipes A, B, C of different diameters are put down in the boring.
The three pipes are arranged one inside the other as shown in the above figure. Super-heated water under pressure is forced down through the outermost pipe A. The heat given out by hot water melts the underground sulphur. A jet of hot, compressed air is then sent down through the innermost pipe C. The force of compressed air brings the mixture of molten sulphur and water through the central pipe B. The sulphur water emulsion is kept in settling tanks when sulphur gets cooled and separates from water in the form of a yellow solid. The sulphur obtained by this method is 99.5% pure.
Question-24
The copper vessels used in homes are found to be coated with green colour. Answer the following.
a) What is the chemical composition of the green coating?
b) Why do copper vessels form such a green coating?
c) What is the name of the phenomenon, responsible for the green coating?
d) Copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon juice, but not with soap. Why?
Solution:
a) Green coloured coating on copper is due to the formation of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2.
b) Copper forms green coating of basic copper carbonate as it reacts with water, atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide.
c) Corrosion phenomenon is responsible for the formation of basic copper carbonate (green).
d) Since basic copper carbonate is basic in nature, it can be removed by tartaric acid present in tamarind or citric acid, present in lemon. Soap is basic in nature. So copper vessels are best cleaned with tamarind or lemon.
Question-25
Give reasons for the following
i. Silicon counts among metalloids
ii. Carbon is not used for making aluminium from aluminium oxide.
iii. For making hydrogen by reaction with hydrochloric acid, granulated zinc is preferred to a block of zinc.
Solution:
i. Silicon shows properties of both metals and non-metals and hence silicon counts among metalloids.
ii. Carbon has less affinity for oxygen than Aluminium and hence it cannot eliminate oxygen from Aluminium oxide.
iii. Zinc granules are preferred to a block of zinc because it offers a large surface area for the reaction with the acid.
Question-26
Explain
i) Why sugar chars (turns black) when conc. H2SO4 is added to it?
ii) What is the blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate due to?![]()
ii) Blue colour of crystalline copper sulphate is due to five water molecules of hydration in CuSO4 5H2O.
Question-27
Write chemical equations for reactions taking place when
i. Zinc carbonate is calcined.
ii. Ammonia gas is passed over heated copper (II) oxide.
Solution:
Question-28
(i) What is the colour of potassium dichromate solution?
(ii) What is the colour of Cr3+ ion?
(iii) What property of SO2 is responsible for bringing change of colour of potassium dichromate?
Solution:
(i) Potassium dichromate solution is orange yellow colour.
(ii) The colour of Cr3+ ion is green.
(iii) Reducing property of sulphur dioxide is responsible to change the orange yellow colour of K2Cr2O7 to green colour.
Question-29
How is chloride of lime chemically different from calcium chloride? Why does chloride of lime gradually lose its chlorine when kept exposed to air?
Solution:
Chemically, chloride of lime is calcium oxy chloride, CaOCl2, also called bleaching powder. When exposed to air it gradually lose its chlorine because it reacts with carbon dioxide present in air to produce calcium carbonate and chlorine gas.
Question-30
Write short notes on the bleaching action of sulphur dioxide.
Solution:
a) Sulphur dioxide bleaches the vegetable colours in the presence of moisture.
b) It bleaches the vegetable colours by reduction. It removes oxygen from coloured material.
c) Its bleaching action is temporary, because atmospheric oxygen again oxidises the bleached article back to its original colour.
d) SO2 is used to bleach delicate fabrics like wool, silk etc.
Question-31
(a) What is the atomicity of sulphur?
(b) How do you bring the change of rhombic sulphur to monoclinic sulphur and vice versa?
(c) What is the action of conc. HNO3 on sulphur?
Solution:
(a) Atomicity of sulphur is 8. Its formula is S8.
Question-32
Name two metals used in making fuse wires.
Solution:
Copper and Aluminium are the two metals used in making fuse wires.
Question-33
(i) How can ammonia be converted to NO2 and nitric acid?
(ii) What is liquor ammonia?
Solution:
Question-34
Complete the following reactions
Question-35
Define the following terms
i) Mineral
ii) Ore
iii) gangue.
Solution:
i) The inorganic elements or compounds which occur naturally in the earth’s crust are known as minerals.
ii) The minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores.
iii) The impurity of sand and rocky materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Question-36
a) State why hydrogen is said to be a clean fuel?
b) What property of hydrogen is involved in being a good fuel?
c) What is hydrogenation of oils? Write one application.
Solution:
a) Hydrogen is a clean fuel because its reaction with oxygen produces only water. It does not form gases like CO2, NO2 etc, which pollute air.
b) Hydrogen, on combustion with oxygen, produces water and a lot of heat. This is an exothermic reaction.
c) Oils are unsaturated molecules, containing double bond. So hydrogen atoms are added at the double bonds of the molecules of oil. The reaction of hydrogen with oils is known as hydrogenation.
The hydrogenation reaction takes place at 473 K and in the presence of nickel catalyst.
Vanaspati or dalda ghee is prepared by hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
Question-37
What is the formula of Ammonia? Write the flow diagram for the manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process. State any two of its physical properties. Write the equation for its reaction with HCl.
Solution:
The formula of Ammonia is NH3.
The flow diagram of the manufacture of ammonia by Haber’s process is given below:
Physical Properties
1. Ammonia is a colourless gas having a characteristic pungent smell.
2. Ammonia is highly soluble in water.
Question-38
How do metals react with hydrogen? Explain with an example.
Solution:
Only very few reactive metals like sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium react with hydrogen to form metal hydrides. Example when hydrogen gas is passed overheated sodium, sodium hydride is formed.
Question-39
Name a metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Solution:
Sodium is a metal which is stored in kerosene oil.
Question-40
Metals are electropositive in nature. Explain.
Solution:
Metals are electropositive in nature because they can form positive ions by the loss of electrons.
Question-41
Explain the displacement of hydrogen by a metal from an acid with an example. Give the equation to support the same.
Solution:
Question-42
Why is sodium kept in kerosene?
Solution:
Sodium reacts so vigorously that they catch fir if it is kept in the open air and hence sodium is kept in kerosene.
Question-43
Name the element or compound which is associated with Hall’s process.
Solution:
Aluminium is associated with Hall’s process.
Question-44
Which metal is used in nuclear reactors and aerospace projects?
Solution:
Aluminium is used in nuclear reactors and aerospace projects.
.png)
.png)