Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NCERT Solutions
Before getting into the details of NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction, let’s have an overview of topics and subtopics under NCERT class 10 science book activities solutions chapter 10:
- Light – Reflection And Refraction
- Reflection Of Light
- Spherical Mirrors
- Refraction Of Light
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Intext Questions
Page Number: 168
Question 1
Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Answer:
The principal focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principal axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge after reflection from the concave mirror.
Question 2
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Answer:
Focal length =
Question 3
Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer:
Concave mirror.
Question 4
Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles ?
Answer:
We prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because of two reasons :
- A convex mirror always produces an erect image of the objects.
- The image formed in a convex mirror is highly diminished or much smaller than the object, due to which a convex mirror gives a wide field of view of the traffic behind. A convex mirror enables the driver to view such larger area of the traffic behind him.
Page Number: 171
Question 1
Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Solution:
R = +32 cm and
Question 2
A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located ?
Solution:
Because the image is real, so magnification m must be negative.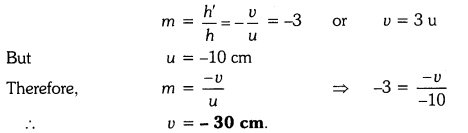
Thus the image is located at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror on the object side of the mirror.
Page Number: 176
Question 1
A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal ? Why ?
Answer:
The light-ray bends towards the normal because the ray of light goes from a rarer medium to a denser medium.
Question 2
Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass ? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 ms-1.
Solution:
Refractive index of glass, n8 = 1.50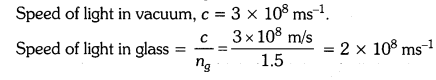
Question 3
Find out, from Table 10.3, the medium having highest optical density. Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
Answer:
From table 10.3, diamond has highest refractive index (= 2.42), so it has highest optical density.
Air has lowest refractive index (= 1.0003),
so it has lowest optical density.
Question 4
You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest ? Use the information given in Table 10.3.
Answer:
For kerosene, n = 1.44
For turpentine, n = 1.47
For water, n = 1.33
Because water has the lowest refractive index, therefore light travels fastest in this optically rarer medium than kerosene and turpentine oil.
Question 5
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer:
By saying that the refractive index of diamond is 2.42, we mean that the speed of light in diamond is lower by a factor of 2.42 relative to that in vacuum.
Page Number: 184
Question 1
Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
Answer:
One dioptre is the power of a lens whose focal length is 1 metre.
Question 2
A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object ? Also, find the power of the lens. , Sol. Here, u — +50 cm ..
Solution:
Here ν = +50cm
Because the real image is of the same size as the object,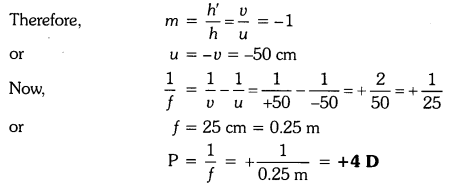
Question 3
Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Solution:
Because the focal length of a concave lens is negative,
therefore f = -2 m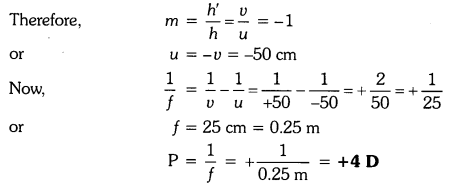
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens ?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer:
(d) Clay
Question 2
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object ?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Answer:
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Question 3
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens (b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
Answer:
(b) At twice the focal length.
Question 4
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of -15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be :
(a) Both concave.
(b) Both convex.
(c) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex.
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave.
Answer:
(a) Both concave
Question 5
No matter how far you stand from mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) either plane or convex.
Answer:
(d) Either plane or convex.
Question 6
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary ?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm.
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm.
Answer:
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
Question 7
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror ? What is the nature of the image ? Is the image larger or smaller than the object ? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer:
A concave mirror gives an erect image when the object is placed between the focus F and the pole P of the concave mirror, i.e., between 0 and 15 cm from the mirror. The image thus formed will be virtual, erect and larger than the object.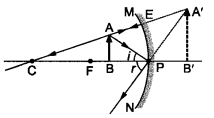
Question 8
Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car.
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle.
(c) Solar furnace.
Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
(a) Concave mirrors are used as reflectors in headlights of cars. When a bulb is located at the focus of the concave mirror, the light rays after reflection from the mirror travel over a large distance as a parallel beam of high intensity.
(b) A convex mirror is used as a side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle because
- A convex mirror always forms an erect, virtual and diminished image of an object placed anywhere in front it.
- A convex mirror has a wider field of view than a plane mirror of the same size.
(c) Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Question 9
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object ? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Answer:
A convex lens forms complete image of an object, even if its one half is covered with black paper. It can be explained by considering following two cases.
Case I : When the upper half of the lens is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object will be refracted by the lower half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the following figure.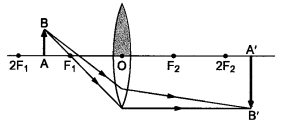
Case II: When the lower half of the lens Is covered
In this case, a ray of light coming from the object is refracted by the upper half of the lens. These rays meet at the other side of the lens to form the image of the given object, as shown in the given figure.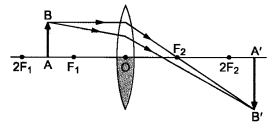
Question 10
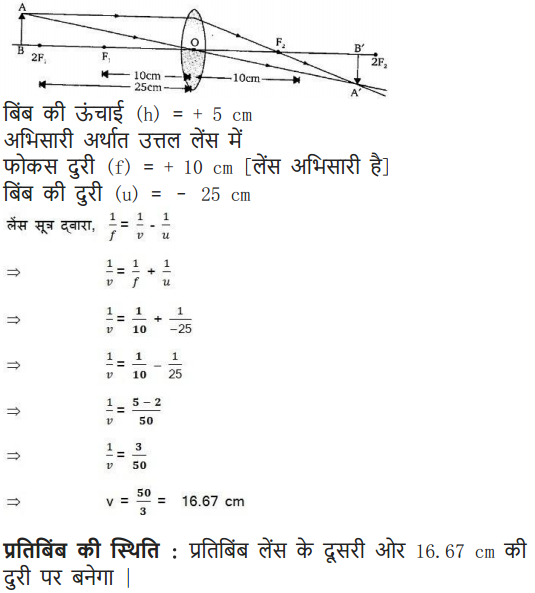
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer:
Here : Object distance, u= -25 cm,
Object height, h = 5 cm,
Focal length, f = +10 cm
According to the lens formula,
⇒
The positive value of v shows that the image is formed at the other side of the lens.
The negative value of image height indicates that the image formed is inverted.
The position, size, and nature of image are shown alongside in the ray diagram.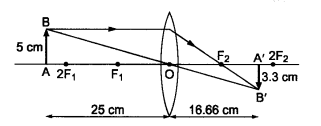
Question 11
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens ? Draw the ray diagram.
Solution:
Focal length, f = -15 cm, Image distance, ν = -10 cm (as concave lens forms the image on the same side of the lens)
From the lens formula 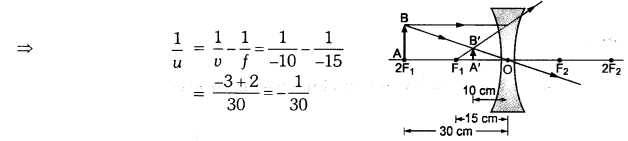
Object distance, u = -30 cm
The negative value of u indicates that the object is placed in front of the lens.
Question 12
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
Solution:
Object distance, u = -10 cm, Focal length, f = +15 cm, Image distance, ν = ?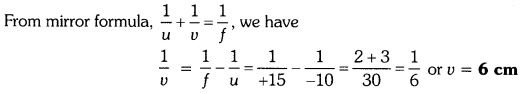
Thus, image distance, ν = + 6 cm
Because ν is +ve, so a virtual image is formed at a distance of 6 cm behind the mirror.
Magnification,
The positive value of m shows that image erect and its value, which is less than 1, shows that image is smaller than the object. Thus, image is virtual, erect and diminished.
Question 13
The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean ?
Answer:
Since magnification,
(i) m = 1 indicates the size of image is same as that of object.
(ii) positive sign of m indicates that an erect image is formed.
The opposite signs of ν and u indicate that image is formed on the other side of the mirror from where the object is placed i.e., image is formed behind the mirror and thus image formed is virtual.
Question 14
An object 5.0 cm in length is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image, its nature and size.
Solution:
Since object size, h = +5 cm,
object distance, u = -20 cm
and radius of curvature, R = +30 cm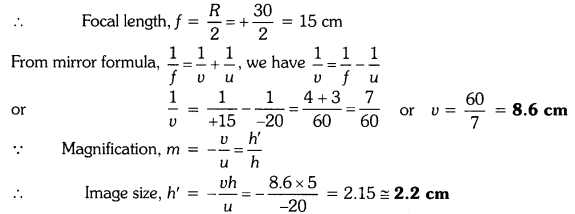
A virtual, erect image of height 2.2 cm is formed behind the mirror at a distance of 8.6 cm from the mirror.
Question 15
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focussed image can be obtained ? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Answer:
Here, object size, h = +7.0 cm,
object distance, u = -27 cm
and focal length, f = -18 cm
Image distance, ν = ?
and image size, h’ = ?
From the mirror formula, 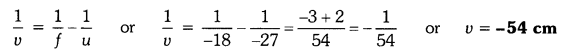
The screen should be placed at a distance of 54 cm on the object side of the mirror to obtain a sharp image.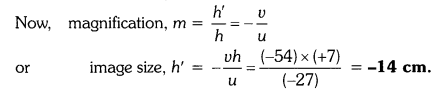
The image is real, inverted and enlarged in size.
Question 16
Find the focal length of a lens of power -2.0 D. What type of lens is this ?
Answer:
Here, P = -2.0 D
The type of lens is concave because the focal length is negative.![]()
Question 17
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging ?
Answer:
Here, P = +1.5 D![]()
Because the focal length is positive, the prescribed lens is converging.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Reflection of light by curved surfaces; Images formed by spherical mirrors, center of curvature, principal axis, principal focus, focal length, mirror formula (Derivation not required), magnification.
Refraction; laws of refraction, refractive index.
Refraction of light by spherical lens; Image formed by spherical lenses; Lens formula (Derivation not required); Magnification. Power of a lens;
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 10 |
| Chapter Name | Light Reflection and Refraction |
| Number of Questions Solved | 31 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Page 168
Question 1.
Define the principal focus of a concave mirror?
Answer:
Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is known as the principal focus of the concave mirror.
Question 2.
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
Answer:
Radius of curvature, R = 20 cm
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror = 2 x Focal length (f)
f = R/2 = 20/2 =10cm
Question 3.
Name the mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer:
When an object is placed between the pole and the principal focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect, and enlarged.
Question 4.
Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Answer:
Convex mirrors give a virtual, erect, and diminished image of the objects placed in front of them. They are preferred as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because they give a wider field of view, which allows the driver to see most of the traffic behind him.
Page 171
Question 1. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Answer: Radius of curvature, R = 32 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 x Focal length (f)
R = 2f
f = R/2 = 32/2 = 16cm
Hence, the focal length of the given convex mirror is 16 cm.
Question 2.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Where is the image located?
Answer:
Given, u = – 10 cm
Since image is real inverted so, m = -3
m = -v / u
⇒ -3 = -v/ -10
v= – 30 cm
Negative sign indicates the image will be real and image is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror.
Page: 176
Question 1.
A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
Answer:
The light ray bends towards the normal. When a ray of light travels from an optically rarer medium to an optically denser medium, it gets bent towards the normal. Since water is optically denser than air, a ray of light travelling from air into the water will bend towards the normal.
Question 2.
Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m/s.
Answer:
Refractive index of a medium nm is given by,
Question 3.
Find out, from Table, the medium having highest optical density. Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
Answer:
Highest optical density = Diamond
Lowest optical density = Air
Optical density of a medium is directly related with the refractive index of that medium. A medium which has the highest refractive index will have the highest optical density and vice-versa.
It can be observed from table 10.3 that diamond and air respectively have the highest and lowest refractive index. Therefore, diamond has the highest optical density and air has the lowest optical density
Question 4.
You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest?
Answer:
The light can travel fast through water.
Question 5.
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer:
Refractive index of a medium nm is related to the speed of light in that medium v by the relation:
Where, c is the speed of light in vacuum/air
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. This suggests that the speed of light in diamond will reduce by a factor 2.42 compared to its speed in air.
Page 184
Question 1.
Define one dioptre of power of a lens?
Answer:
One dioptre is the power Of a lens Of focal length 1m.
Power of lens is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length. If P is the power of a lens of focal length F in metres, then
P = 1/ f (in meters)
The S.I. unit of power of a lens is Dioptre. It is denoted by D.
1 dioptre is defined as the power of a lens of focal length 1 metre.
1 D = 1 m−1
Question 2.
A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also find the power of the lens.
Answer:
v = + 50 cm
Since image is real and of same size. The position of image should be double the focal length.
Hence, the object should be at 2f.
V = 2f = 50, f = 25 cm.
Power = 1/f = 100/25 = 4D
Question 3.
Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Answer:
Question 1.
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(a) Water (b) Glass
(c) Plastic (d) Clay
Answer: (d) Clay
Question 2.
The ¡mage formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of Curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and Its principal focus.
Answer: (d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Question 3.
Where should an object b. placed In front of a convex lens to get a real
image of the size of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus
Answer:
(b) At twice the focal length
Question 4.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of 15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be:
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) the mirror is concave, but the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Answer:
(a) Both concave.
Question 5.
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your Image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) Either plane or convex
Answer:
(d) Either plane or convex.
Question 6.
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found ¡n a dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm.
Answer:
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
Question 7.
We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. what should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this
case.
Answer:
We are given the focal length cf the concave mirror as f = -15cm.
For getting an erect image using a concave mirror, the object should be placed at a distance less than the focal length.
i.e. 15 cm from the pole. The image formed will be virtual, enlarged and erect.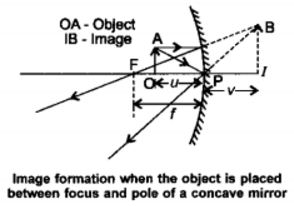
Question 8.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car
(b) Side/rear-view mirror of a vehicle
(c) Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
(a) Concave mirror, to get powerful and parallel beams of light.
(b) Convex mirror because it always gives an erect image and enables the driver to view much larger area.
(c) Concave or parabolic mirror because it can concentrate sunlight at the focus to produce heat in the solar furnace.
Question 9.
One half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Answer:
Yes, even when one half of the lens is covered with a black paper, complete image of the object will be formed. Take a convex lens and focus the light from a distant object onto a screen. As expected an image (sharp) is formed at a distance equal to the focal length Cover the lower or the upper half of the lens and focus the light from the same object onto the same screen. You will be able to get a sharp image again; however the brightness of the image will be less in the second case. The same effect w,ll be seen even if the lens is half covered with black strips.
Question 10.
An object 5cm in length is held 25cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer: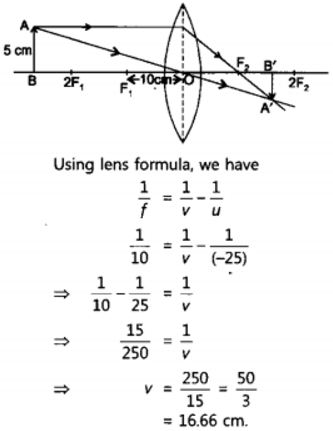
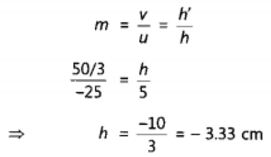
Therefore, the mage ¡s formed between F2 and 2F2 on the other side of the lens. It is real and inverted, and smaller in size than the object.
Question 11.
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an ¡mage 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the Pens? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer: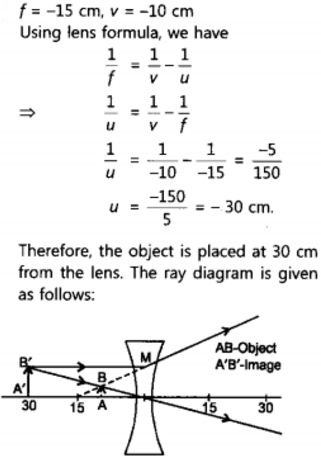
Question 12.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the ¡mage.
Answer:
f = +15 cm. u = -1o cm
For mirror, we have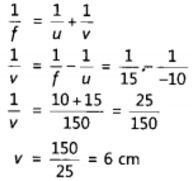
The image must be virtual and erect.
Question 13.
The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. What does this mean?
Answer:
This means that size of the image is equal to the size of the object.
Question 14.
An object 5.0 cm in length Is placedat a distanc, of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position of the image nature and size.
Answer:
Question 15.
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
Answer:
Question 16.
Find the focal length of a lens of power -2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
Answer:
Question 17.
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
Answer:
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 mark each]
Question 1.
Hold a highly polished steel spoon curved inwards close to your face and move it slowly away from your face. What will you observe?
(a) Enlarged and erect image of your face
(b) Smaller and inverted image of your face
(c) Smaller and erect image of your face
(d) Enlarged and inverted image of your face
Answer:
(b) The inner curved surface of a highly polished steel spoon acts as a concave mirror. When the spoon is at a small distance from the face such that, the object lies between pole and focus of concave mirror, so an enlarged and erect image of your face will be observed but as the spoon is slowly moved away from the face, the image becomes smaller and appears inverted.
Question 2.
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens? [NCERT]
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer:
(d) Clay can never be transparent, so it cannot be used to make lens.
Question 3.
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be [NCERT]
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) either plane or convex
Answer:
(d) Plane mirrors and convex mirrors always form the erect images.
Question 4.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object? [NCERT]
(a) Between principal focus and centre of curvature
(b) At centre of curvature
(c) Beyond centre of curvature
(d) Between pole of the mirror and its principal focus
Answer:
(d)
Question 5.
An object AB is placed in front of a convex lens at its centre of curvature as shown in figure below.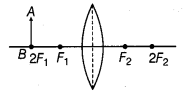
Four students traced the path of light ray after refraction through the lens. Which one of them is correct?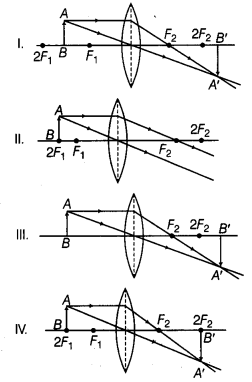
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Only III
(d) Only IV
Answer:
(d) When the object is placed at centre of curvature (2Fx) of convex lens, the same sized image is formed at 2F2. The image formed is real and inverted.
Question 6.
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each of a focal length -15 cm. The mirror and lens are likely to be [NCERT]
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) mirror is concave and lens is convex
(d) mirror is convex and lens is concave
Answer:
(a) The focal length is taken as negative for both concave mirror and concave lens.
Question 7.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
(b) Convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
(d) Concave mirror as well as concave lens
Answer:
(a) A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror or convex lens, after reflection/refraction, will emerge parallel to the principal axis.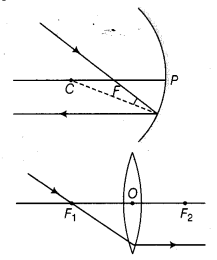
Question 8.
Under which of the following conditions, a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) When an object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
(b) When an object is kept at a distance less than its focal length
(c) When an object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
(d) When an object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
Answer:
(c) A concave mirror can form an image enlarged, real and inverted than the actual object, beyond centre of curvature (C) when object is placed between the focus (F) and centre of curvature.
Question 9.
A light ray enters from medium A to medium Bas shown in the figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be [NCERT Exemplar]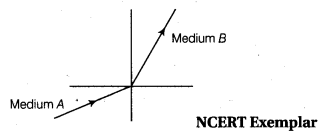
(a) greater than unity
(b) less than unity
(c) equal to unity
(d) zero
Answer:
(a) Since, light rays in the medium B goes towards normal. So, it has greater refractive index and lesser velocity of light w.r.t. medium A. So, refractive index of medium B w.r.t. medium A is greater than unity.
Question 10.
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is
Answer:
(a) Given, angle of incidence, i = 60°, angle of refraction, r = 45°
Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A,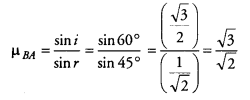
Question 11.
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C – and D respectively, as Box shown in the figure.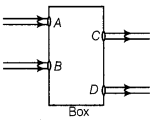
Which of the following could be inside the box? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) A rectangular glass slab
(b) A convex lens
(c) A concave lens
(d) A prism
Answer:
(a) Here, the emergent rays are parallel to the direction of the incident ray. Therefore, a rectangular glass slab could be inside the box as the extent of bending of light ray at the opposite parallel faces AB (air-glass interface) and CD (glass-air interface) of the rectangular glass slab are equal and opposite. This is why the ray emerges parallel to the incident ray.
Question 12.
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box? [NCERT Exemplar]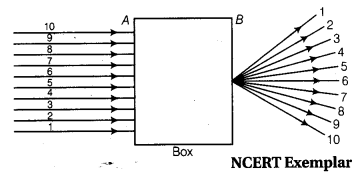
(a) Concave lens
(b) Rectangular glass slab
(c) Prism
(d) Convex lens
Answer:
(d) Since, in the figure all the parallel rays converge at a point. So, inside the box there must be a convex lens.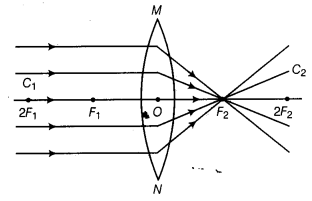
Question 13.
Which of the following statement is true? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) A convex lens has 4D power having a focal length 0.25 m
(b) A convex lens has 4D power having a focal length -0.25 m
(c) A concave lens has 4D power having a focal length 0.25 m
(d) A concave lens has 4D power having a focal length -0.25 m
Answer:
(a) The power P of a lens of focal length f is given by
P = 1/f, where f is the focal length in metre and P is the power in dioptre.
P= 1/f or f = 1/P = 1/4 = 0.25 m
Question 14.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) is less than one
(b) is more than one
(c) is equal to one
(d) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front of it.
Answer:
(a) The convex mirror forms virtual, erect and diminished image of the object and rear view mirror also form same type of image. Therefore, magnification (m) produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles is less than one, i.e. m < 1.
Question 15.
Rays from the Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed, so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer:
(b) The rays from the Sun, i.e. from infinity, are parallel to principal axis after reflection converge at a point is known as focus. Therefore, focal length if) of concave mirror is 15 cm. And we know that, same size, real and inverted image is formed by concave mirror when object is placed at focus 2 A or centre of curvature, so to form same size of image, object will be placed at 15 x 2 =30 cm.
Question 16.
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students shown as I, II, III and IV in the figure. Which one of them is correct? [NCERT Exemplar]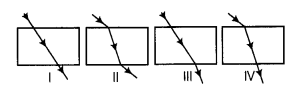
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Only III
(d) Only IV
Answer:
(b) In a rectangular glass slab, the emergent rays are parallel to the direction of the incident ray, because the lateral deviation of bending of the ray of light at the opposite parallel faces (air-glass interface) and (glass-air interface) of the rectangular glass slab are equal and opposite. This is why the ray emerges are parallel to the incident ray.
Question 17.
You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Kerosene
(b) Water
(c) Mustard oil
(d) Glycerine
Answer:
(d) The given material having their refractive index as kerosene is 1.44, water is 1.33, mustard oil is 1.46 and glycerine is 1.74. Thus, glycerine is most optically denser and hence have the largest refractive index. Therefore, ray of light bend most in glycerine.
Question 18.
A student placed a light bulb in midway between the two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 60°. How many images will be observed by him?
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) Number of images formed by two plane mirrors inclined at an angle 60° when a light bulb is placed in midway between them is
N = 360°/60° – 1 = 6 – 1 = 5
Question 19.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object? [NCERT]
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus
Answer:
(b) To set the real image of the size of the object, it should be placed at twice the focal length of a convex lens.
Question 20.
Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in dictionary? [NCERT]
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Answer:
(c) Convex lens is used as magnifying glass. For better performance its focal length should be small.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction (Hindi Medium)





























Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction Mind Map
LIGHT REFLECTION & REFRACTION
Form of energy produces the sensation of vision in eyes. Light (EM waves wave-length 400 nm to 750 nm).
The path of light (always travel in straight line) is ray of light
Characteristics of light
- Rectilinear propagation of light
- Light travels with a speed of 3 × 108 m/s in air/vaccum.
- Speed of light depends on the medium
- Light shows behaviour such as reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, polarisation etc.
Law of Refraction
Refraction of light: Bending of light ray while passing from one medium to another medium
- A ray of light bends towards the normal, while going from rarer to denser medium
- And bends away from the normal while going from denser to rarer medium
- Refraction of light takes place because the speed of light is different in the two media
Total internal Reflection : Ray totally reflected back to denser medium
Phenomena based on TIR
- Mirage – optical illusion in deserts
- Looming – optical illusion in cold countries
- Optical fibre
- Brilliance of diamond
Necessary conditions for TIR
(i ) Ray of light must travel from denser to rarer medium
(ii) ∠i > ∠c for two media
Critical angle (c) Angle i in denser medium for which angle of refraction in rarer medium is 90° μ =
Snell’s law
μ =
For two media
1μ2 =
Reflection of light: Turning back of light in the same medium after striking the reflecting surface or mirror
- After reflection, velocity, frequency and wavelength of light remains same but intensity decreases
- If reflection takes place from denser medium then phase change ‘π’
Regular Reflection
Reflection on smooth surface.
Diffuse Reflection
Reflection on rough surface.
Laws of Reflection
The incident ray the normal and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane The angle of incidence (i) is always equal to angle of reflection (r) i.e., ∠i = ∠r
Mirror formula
When two plane mirrors are held at an angle 9 with their reflecting surfaces facing each other and an object is placed between them, images are formed by successive reflections. .
fconcave = negative
fconvex = positive
and fplane = ∞
Relation between focal length (f) and radius of curvature, R
f =
Magnification
m =
m =
The incident ray, the normal and the refracted ray all lie in the same plane
Refractive index,
μ =
Plane Mirror
Is a looking glass, highly polished on one surface.
- Forms virtual and erect image
- Distance of object from mirror = distance of image from mirror.
- The size of the image is same as object.
- Image is laterally inverted.
- Used in kaleidoscope periscope, etc.
Concave Mirror
Spherical glass polished on the outside. It is also known as a converging mirror.
- Images produced are always real, inverted, can be enlarged based on the position except when object is placed between pole and focus.
- Uses: Make-up and shaving mirrors, dentist mirror, in floodlight etc.
Image formation by a convex mirror for different positions of the object
| ‘‘Position of the object” | “Position of the image” | “Size of the image” | “Nature of the image” |
| Anywhere between Between Pole(P) and infinity (∞) | Between P and F back of the mirror | Small | Virtual and erect |
| At infinity | At F | Very small in size | Virtual and erect |
Convex Mirror
Spherical glass polished inside. It is also known as diverging mirror.
- It forms virtual, upright and small images.
- Uses: for security’ purposes, in vehicles as rear- view mirror and street lighting.
Image formation by a concave mirror for different positions of the object
| “Position of the object” | “Position of the image” | “Size of the image” | “Nature of the image” |
| At infinity | At the focus F | Highly -diminished, point-sized | Real and inverted |
| BeyondC | Between F and C’ | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At C | At C | Same size | Real and inverted |
| B/W C and F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real and inverted |
| At F | At infinity | Highly enlarged | Real and inverted |
| B/W P and F | Behind the mirror | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |
Atmospheric Refraction
Earth’s atmosphere is thin at the top and dense at the bottom, thus leads to refraction of light,
μ = c/v
- Twinkling of stars
- Rainbow
- Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset
Refraction Through a Glass Slab
x =
∴ x ∝ μ
Power of a lens
P =
Unit of power of lens is diopter (D)
Pconvex → Positive
Pconcave → Negative
and Pplane → Zero
Lens
Piece of transparent material with two refracting surfaces, at least one is curved and refractive index should different as that of the surrounding.
Lens formula
fconvex → negative
fconcave → positive
and fplane → ∞
Concave Lens
Cental portion of lens is thinner than marginal. It as also known as diverging lens.
Convex Lens
Central portion of lens is thicker than marginal. It is also known us converging lens.
Magnification
Ratio of distance of image to the distance of object from the optical centre. Also equal to height of image to the height of object
m =
Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a concave lens for various position of the object
| ‘‘Position of the object” | “Position of the image” | Relative Size of the image” | “Nature of the image” |
| At infinity | At focus F1 | Highly-diminished, point-sized | Virtual and erect |
| Between infinity and Optical centre O of the lens | Between F1 and Optical centre O | Diminished | Virtual and erect |
Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for various positions of the object
| Position of the object | Position of the image | Relative size of the image | Nature of the image |
| At infinity | At focus F2 | Highly -diminished, point-sized | Real and inverted |
| Beyond 2F1 | Between F2 and 2F2 | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At 2F1 | At 2F2 | Same size | Real and inverted |
| Between F1 and 2F1 | Beyond 2F2 | Enlarged | Rea! and inverted |
| At Focus F1 | At infinity | Infinitely large or highly enlarged | Real and inverted |
| Between F1 and Optical centre O | On the same side of the lens as the object | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |
Important Questions of Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Science Chapter 10
Question 1.
The laws of reflection hold true for
(a) plane mirrors only
(b) concave mirrors only
(c) convex mirrors only
(d) all reflecting surface
Answer:
(d) The laws of reflection holds true for all reflecting surface.
Question 2.
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors. (Delhi 2015, AI2011)
Answer:
Characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror are
(i) imagedistanceissameasthatofobjectdistance
(ii) image formed is virtual and erect
(iii) image formed is of the same size as that of the object
(iv) image formed is laterally inverted (left appears right and right appears left).
Question 3.
State the two laws of reflection of light. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Laws of reflection of light states that
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Question 4.
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is
(a) real
(b) inverted
(c) virtual and inverted
(d) virtual and erect (2020)
Answer:
(d) When an object is placed between the principal focus and pole of a concave mirror, an enlarged virtual and erect image is formed behind the mirror.
Question 5.
What is the magnification of the images formed by plane mirrors and why? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Magnification of images formed by plane mirrors is unity because for plane mirrors, the size of the image formed is equal to that of the object.
Question 6.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it. (AI 2019)
Answer: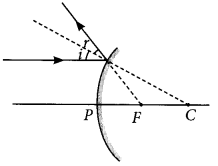
Question 7.
If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished , what type of mirror is it? Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer. (2018)
Answer:
If the image formed by a spherical mirror is always erect and diminished then it is convex mirror.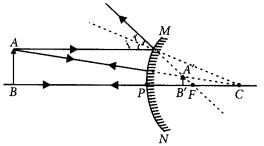
Question 8.
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Write four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Four characteristics of the image formed by the given convex mirror are :
(i) Virtual
(ii) Erect
(iii) Diminished
(iv) Image is always formed behind the mirror between pole and focus.
Question 9.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror. Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are:
(i) Virtual
(ii) Erect
(iii) Enlarged
(iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Question 10.
A ray of light is incident on a convex mirror as shown. Redraw the diagram and complete the path of this ray after reflection from the mirror. Mark angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it. (Delhi 2016)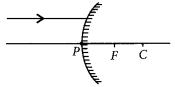
Answer: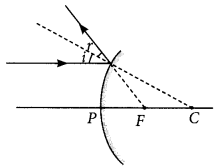
Question 11.
Name the type of mirrors used in the design of solar furnaces. Explain how high temperature is achieved by this device. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Concave mirrors are used in the designing of solar furnaces.
When a solar furnace is placed at the focus of a large concave mirror, it focuses a parallel beam of light on the furnace. Therefore, a high temperature is attained at the point after some time.
Question 12.
“The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -3”. List four informations you obtain from this statement about the mirror/ image. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Negative sign of magnification indicates that the image is real and inverted. Since the image is real and inverted, the mirror is concave and magnification of -3 indicates that the image is magnified.
Question 13.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why? (Foreign 2016)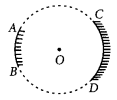
Answer:
Focal length of a mirror is given by
Focal length = \(\frac { Radius of curvature }{ 2 }\)
Since both the mirrors have same radius of curvature, therefore focal length of the two mirrors will be same, i.e.,
\(\frac { f_1 }{ f_2 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 1 }\)
Since virtual image is always formed by convex mirror. The mirror AB will always form virtual image.
Question 14.
List two properties of the images formed by convex mirrors. Draw ray diagram in support of your answer. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Convex mirrors always form diminished, virtual and erect images.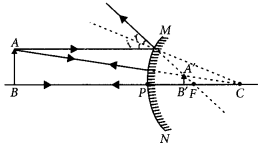
Question 15.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +3. Analyse this value and state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Positive value of the magnification indicates that image is virtual and erect.
(i) Since the image is magnified, the mirror is concave.
(ii) The object is between pole and focus of the mirror as shown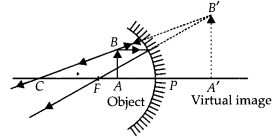
The image produced in second case will be real and inverted.
Question 16.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 8
Question 17.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed towards the principal focus of a convex mirror. Mark on it the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. (Delhi 2014)
Answer: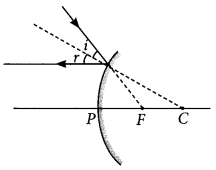
Question 18.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror, Mark on it the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 6
Question 19.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it. (Delhi 2014)
Answer: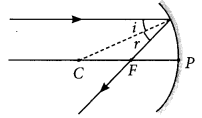
Question 20.
List two possible ways in which a concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. State the difference if any between these two images. (AI2014)
Answer:
A concave mirror can produce a magnified image of an object when object is placed:
(1) In between its pole and its focus
(2) In between its focus and its centre of curvature.
Difference,between these two images:
The image produced in first case will be virtual and erect.
The image produced in second case will be real and inverted.
Question 21.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should the position of the object be relative to the mirror? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer. (AI 2014)
Answer:
The position of the object should be between P and F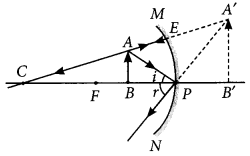
Question 22.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is +1/3. Analysing this value state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw any diagram to justify your answer. (AI 2014, Foreign 2014)
Answer:
(i) Convex mirror
(ii) Between infinity and the pole of the mirror.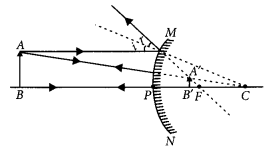
Question 23.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -1. Analysing this value state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw any diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
(i) Concave mirror because the image is real, inverted.
(ii) Object is placed at C.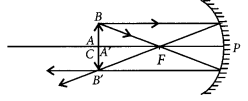
Question 24.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -1/5. Analysing this value state the (i) type of spherical mirror and (ii) the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw ray diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
(i) Concave mirror
(ii) Object is placed beyond C.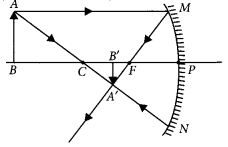
Question 25.
Draw ray diagrams for the following cases when a ray of light:
(i) passing through centre of curvature of a concave mirror is incident on it.
(ii) parallel to principal axis is incident on convex mirror.
(iii) is passing through focus of a concave mirror incident on it. (2020)
Answer:
(i) Ray of light passing through centre of curvature of concave mirror, after reflection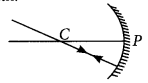
(ii) Ray of light parallel to the principal axis is incident on a convex mirror after reflection appear to diverge from the principal focus of a convex mirror.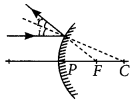
(iii) Ray of light passing through focus of a concave mirror after reflection will emerge parallel
Question 26.
A concave mirror is used for image formation for different positions of an object. What inferences can be drawn about the following when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm?
(a) Position of the image
(b) Size of the image
(c) Nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to justify your inferences. (2020)
Answer:
Given, f = -15 cm, u = -10 cm.
Thus the object is placed between the principal focus and pole of the mirror.
(a) The position of the image will be behind the mirror.
(b) The size of the image will be highly enlarged.
(c) The nature of the image will be virtual and erect.
Question 27.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed. (AI 2019)
Answer:
Given f = -20 cm v = -30 cm u = ?
Using \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -20 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { -3+2 }{ 60 }\)
⇒ u = -60 cm
∴ Object placed at 60 cm from the mirror.
Also magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\)
⇒ h’ = \(\frac { -(-30) }{ -60 }\) × 4 = -2 cm
∴ The size of the image is 2 cm.
Question 28.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from its pole. What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image. State whether the image formed is erect or inverted. (Delhi 2017)
Given:
Object distance, u = – 30 cm, image size, h’ = ?
Image distance, v = – 60 cm,
Object size ,h = 2.4 cm,
Focal length, f = ?
Using mirror formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \quad \text { or } \quad \frac{1}{f}=\frac{-1-2}{60}=\frac{-3}{60}=-\frac{1}{20}\)
or f = – 20 cm
Hence, focal length is 20 cm
Also, magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\)
or, m = \(\frac { (-60)}{ (-30) }\) = -2 or \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = -2
h’ = – 2 × 2.4 = – 4.8 cm
As the image formed is real, therefore the mirror is concave.
The height of the image is 4.8 cm.
The image formed is enlarged and inverted.
Question 29.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Given : object distance, u = -15 cm,
object height, h = 4 cm, focal length f = -10 cm;
Image distance, v = ?
Using mirror formula,
\(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{(-15)}=\frac{1}{-10} \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{10}\)
or \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{10-15}{150}=\frac{-5}{150}=\frac{-1}{30}\) or v = -30
In order to obtain a sharp image of the object on the screen, screen should be placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror.
Also, magnification, m = \(\frac{h^{\prime}}{h}=\frac{-v}{u}\)
or \(\frac{h^{\prime}}{4}=-\frac{(-30)}{(-15)}\) or h’ = \(\frac { -(30)×4 }{ (15) }\) = -2 × 4
or h’ = -8 cm
Thus, the height of the image is 8 cm.
Question 30.
Draw the following diagram in which a ray of light is incident on a concave/convex mirror, on your answer sheet. Show the path of this ray, after reflection, in each case.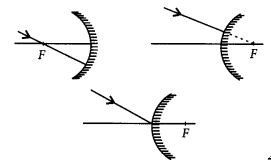
Answer:
The path of the rays are shown in figure.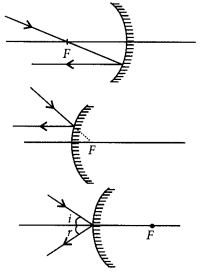
Question 31.
The image of an object formed by a mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -1. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Where would the image be if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror? State reason and also draw ray diagram for the new position of the object to justify your answer. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Since the image formed by the mirror is real and inverted, therefore the mirror is concave and magnification of the mirror will be
m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ v = u
i.e., object and image both are formed at the centre of curvature, i.e., 40 cm from the mirror.
Now, if the object is moved 20 cm towards the mirror, the object will be at the focus of the mirror and therefore the image will be formed at infinity.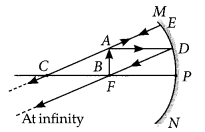
Question 32.
The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and its magnification is -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Since the image formed is real and inverted, the mirror is concave.
Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ -2 = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ v = 2u
Now, if v = – 30 cm then u = – 15 cm
As focal length of the mirror is
f = \(\frac{u v}{u+v}=\frac{-15 \times-30}{-15-30}=f=\frac{450}{-45}\) = -10 cm
If the object is shifted 10 cm towards the mirror, then the object is between principal focus and the optical centre and the image formed will be virtual and erect.
Question 33.
If the image formed by mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual and diminished, state the type of the mirror. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. Where are such mirrors commonly used and why? (Foreign 2016, AI 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 7.
Convex mirrors are widely used as rear view mirrors in cars, motorcycles etc. It produces an erect image that is smaller in size than the object hence giving a wide view.
Question 34.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. (Delhi 2015, AI 2012)
Answer:
We use two rays of light, one passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, and another is parallel to the principal axis. After reflection, the ray passing through the centre of a concave mirror is reflected back along the same path and the ray parallel to the principal axis will pass through the principal focus.
u = -15 cm, f= -10 cm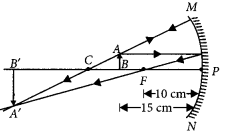
From ray diagram, v = -30 cm, i.e., beyond C Nature of image is real, inverted and magnified.
Question 35.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray in each of the following cases. A ray of light incident on a convex mirror :
(a) strikes at its pole making an angle 0 from the principal axis.
(b) is directed towards its principle focus.
(c) is pardllel to its principal axis. (Foreign 2015)
Answer: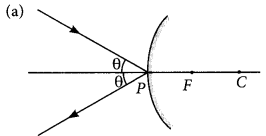
(b) Refer to answer 17.
(c) Refer to answer 6.
Question 36.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror.
(a) Write the type of mirror.
(b) Find the distance of the image from the object.
(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014, AI 2014)
Answer:
(a) Concave mirror
(b) Magnification, m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) or v = u
∴ Distance of the image from the object is, v – u = 0
(c) As the image is formed at centre of curvature i.e., v = R.
∴ focal length of the mirror, f = \(\frac { -50 }{ 2 }\) = -25 cm
(d) Refer to answer 23(ii).
Question 37.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror.
(i) Write type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) This is a concave mirror.
(ii) The image is real and inverted and of same size.
(iii) As m = – 1
∴ m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) ⇒ u = v
Hence, object is located at centre of curvature i.e., at distance of 40 cm from the pole of the mirror,
(iv) Refer to answer 23(ii).
Question 38.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(iii) What is the nature of the images formed?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) The mirror is concave mirror.
(ii) Distance the image from the mirror = – 30 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\)
Here m = – 1 and v = – 30 cm
-1 = –\(\frac { (-30) }{ u }\)
∴ u = – 30 cm
As v = u, object is placed at centre of curvature. Therefore, focal length of the mirror,
f = \(\frac { -30 }{ 2 }\) = – 15 cm
(iii) Image formed is real and inverted and of the same size of the object.
(iv) Refer to answer 23(ii).
Question 39.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) How far is the image from its object?
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (AI 2014)
Answer:
(a) Concave mirror
(b) Linear magnification,
m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -(-48) }{ -12 }\) = -4
(c) The distance between the image and the object
= 48 – 12 = 36 cm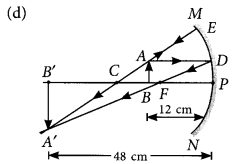
Question 40.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 12 cm focal length. What should be the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
To obtain an erect image, the object is placed in between pole and the focus of the concave mirror. So range of distance of the candle llame from the mirror is in between 12 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect.
Size of the image = Enlarged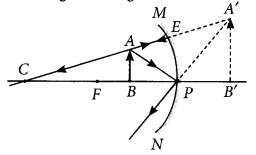
Question 41.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of a candle flame using a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. What should be the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror?
State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
To obtain an erect image of an object, the object should be placed in between pole and focus. Range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror is in between 15 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect
Size of the image = Enlarged
For ray diagram, refer to answer 40.
Question 42.
A student has a concave mirror of 20 cm focal length and he wants to see an erect image of his face in the mirror. What should be the range of distance of the mirror from his face? State the nature and size of the image he is likely to observe. Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Focal length of a concave mirror = 20 cm Range will be in between 20 cm.
Nature of the image = Virtual and erect
Size of the image = Enlarged
For ray diagram, refer to answer 40.
Question 43.
Mention the types of mirrors used as (i) rear view mirrors, (ii) shaving mirrors. List two reasons to justify your answer in each case. (Delhi 2013, Delhi 2012)
Answer:
(i) Convex mirror is used as rear view mirror because
(a) it gives erect image.
(b) it gives diminished image thus provides wider view of traffic behind the vehicle.
(ii) Concave mirror is used as shaving mirror because
(a) it gives erect image when mirror is close to the face.
(b) it gives enlarged image of the face so that a person can shave safely.
Question 44.
Calculate the magnification of the image of an object placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm. The object is at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Given, focal length of concave mirror,
f = -15 cm
Object distance, u = -20 cm
Image distance, v = ?
Using mirror formula,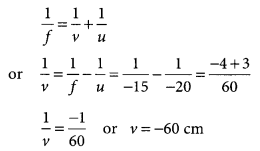
Using magnification formula,
m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\) = -(\(\frac { -60 }{ -20 }\)) or m = -3
So, the magnification, m = -3.
Question 45.
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror. (AI2012)
Answer:
A ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of a convex mirror.
A ray passing through the centre of a curvature of a concave mirror or directed in the direction of the centre of curvature of a convex mirror, after reflection, is reflected back along the same path. The light rays come back along the same path because the incident rays fall on the mirror along the normal to the reflecting surface.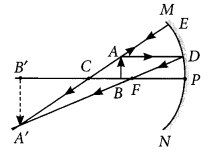
Question 46.
State the types of mirrors used for (i) headlights and (ii) rear view mirrors, in motorcycles. Give reason to justify your answer in each case. (AI 2012)
Answer:
(i) Concave mirrors are used in headlights of cars to get powerful beams of light.
(ii) Convex mirrors are used as rear-view mirrors of vehicle to get a wider field of view and and erect image of traffic behind.
Question 47.
An object is placed between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. Draw a ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of the image formed. (AI 2011)
Answer: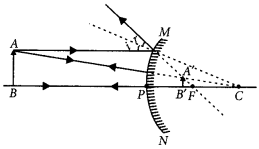
Position: Image is formed between pole and principal focus of the mirror.
Relative size : Image formed is diminished.
Nature : Image formed is virtual and erect.
Question 48.
With the help of a ray diagram explain why a convex mirror is preferred for rear view mirrors in the motor cars. (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
Convex mirror is preferred for rear view mirrors in motor cars because no matter where the object is located in front of convex mirror, it always gives erect and diminished image of the object, so that driver is able to see the large traffic view in small area and the image is erect. This can be interpreted from the following diagram.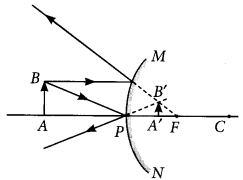
Question 49.
An object 4.0 cm in size, is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (2020)
Answer:
(i) Given, h = 4 cm,
u = -25 cm (concave mirror), f = -15 cm
Using mirror formula,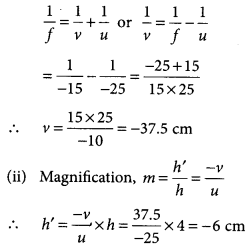
Thus, the image is real and inverted.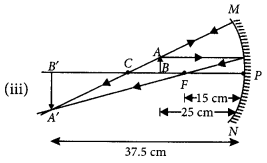
Question 50.
(a) A concave mirror of focal length 10 cm can produce a magnified real as well as virtual image of an object placed in front of it. Draw ray diagrams to justify this statement,
(b) An object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. The distance of the object from the pole of the mirror is 10 cm. Find the position of the image formed. (2020)
Answer:
(a) A magnified real image is produced in a concave mirror when the object is placed between principal focus and centre of curvature.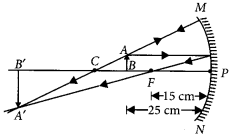
A magnified virtual image is produced in a concave mirror when the object is placed between the pole and the principle focus of the mirror.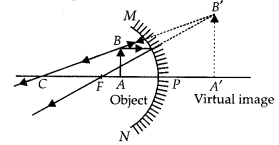
(b) Given, f = +10 cm (convex mirror) and u = -10 cm
From mirror formula,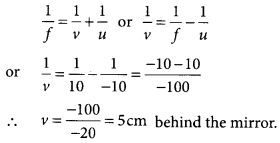
Question 51.
(a) A security mirror used in a big showroom has radius of curvature 5 m. If a customer is standing at a distance of 20 m from the cash counter, find the position, nature and size of the image formed in the security mirror.
(b) Neha visited a dentist in his clinic. She observed that the dentist was holding an instrument fitted with a mirror. State the nature of this mirror and reason for its use in the instrument used by dentist. (2020)
Answer:
(a) Given radius of curvature of the mirror,
R = 5 m
∴ Focal length, f = R/2 = 2.5 m (convex mirror) and u = -20 m
From mirror formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u} \text { or } \frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2.5}-\frac{1}{-20}=\frac{-20-2.5}{-20 \times 2.5}\)
∴ v = 2.22 m
Thus, the image is formed 2.22 m behind the mirror. The image is diminished, virtual and erect.
(b) Concave mirrors are used by dentist. Dentist use it as it is a converging mirror and when used at close range forms a highly enlarged, virtual and erect image of the object.
Question 52.
(a) To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
(b) A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the objects placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(a) Two lights rays whose path of reflection are priorly known are :
(i) When the incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, it gets reflected in the same path.
(ii) When the ray is incident obliquely to the principal axis, towards the pole of mirror, it gets reflected back by making equal angles with the principal axis (laws of reflections).
Suppose an object is placed between focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then by using the above two rays, the image of the object can be located as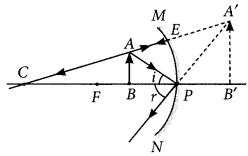
Image formed is virtual, erect, magnified and it is formed behind the mirror.
(b) Given : Magnification, m = – 3
Object distance, u = – 20 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\) or -3 = \(\frac { -v }{ -20 }\)
or v = -60 cm
The screen is placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 60 cm from the pole.
Thus, the screen is placed 40 cm (= 60 cm – 20 cm) away from the object.
Question 53.
(a) If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always diminished, erect and virtual, state the type of the mirror and also draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Write one use such mirrors are put to and why?
(b) Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirrors. Find the nature and focal length of a spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm. (AI2017)
Answer:
(a) If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always diminished, erect and virtual then the mirror is convex mirror.
The ray diagrams for the formation of image by a convex mirror for the first position when the object is at infinity and the second position when the object is at a finite distance from the mirror are shown.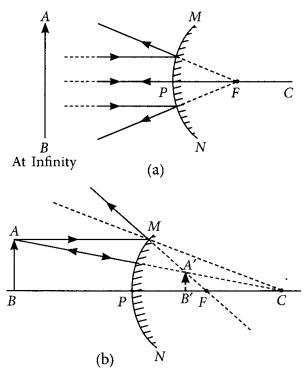
Use of Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors are commonly used as rear-view (wing) mirrors in vehicles because they always give an erect, though diminished image. Also, they have a wider field of view as they are curved outwards. Thus, convex mirrors enable the driver to view a large area.
(b) Radius of Curvature: The radius of the sphere of which the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror forms a part, is called the radius of curvature of the mirror. It is represented by the letter R.
∵ The radius of curvature is equal to twice the focal length.
∴ R = 2f
If R = +24 cm ∴ f = \(\frac { R }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 2 }\) = 12 cm
Since the radius of curvature is positive, the mirror is convex mirror. Hence the nature of the image is virtual and erect.
Question 54.
(a) Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors:
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principal axis
(iv) Principal focus
(b) Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a
(i) Concave mirror (ii) Convex mirror
(c) Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.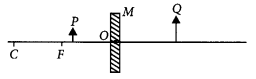
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) (i) Pole : The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a point called the pole. It lies in the surface of the mirror and its represented by the letter P.
(ii) Centre of curvature: The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a part of a sphere which has a centre. This point is called the centre of curvature of spherical mirror and is represented by the letter C.
(iii) Principal axis : An imaginary line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror and normal to the mirror at its pole is called principal axis.
(iv) Principal focus : Incident rays parallel to principal axis, after reflection either converge to as appear to diverge from a fixed point on the principal axis known as principal focus of the spherical mirror.
(c) The object is placed between focus and pole of the mirror and a magnified image is formed behind the mirror.
∴ The mirror is concave and image formed is virtual and erect.
Question 55.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
(i) What should be the range of distance of a , object placed in front of the mirror?
(ii) Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
(iii) Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also to justify your answer.
Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams. (AI2016)
Answer:
Given : focal length of the concave mirror f = 12 cm
(i) If the object is placed between the pole and focus of the concave mirror, then the image formed is virtual and erect. Iheretore, the range of distance of the object should be 0 < u <. 12 cm.
(ii) The image formed will be enlarged as shown below.
(iii) If the object is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror i.e., at the centre of the curvature then the image will also be formed at the centre of the curvature.
Question 56.
Suppose you have three concave mirrors A, B and C of focal lengths 10 cm, 15 cm and 20 cm. For each concave mirror you perform the experiment of image formation for three values of object distances of 10 cm, 20 cm and 30 cm. By giving reason, answer the following:
(a) For the three object distances, identify the mirror/mirrors which will form an image of magnification -1.
(b) Out of the three mirrors, identify the mirror which would be preferred to be used for shaving purposes/make up.
(c) For the mirror B draw ray diagram for image formation for object distances 10 cm and 20 cm. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Given fa = 10 cm, fb = 15 cm, fc = 20 cm
ua = 10 cm, ub = 20 cm, uc = 30 cm
(a) Magnification of -1 implies that size of image is same as that of object or image is formed at the same distance as of the object. This is the case when the object distance, u = 2f, i.e., when the object is at the centre of the curvature.
For fa, ub and for fb, uc, we get magnification – 1.
(b) Concave mirror forms virtual, erect and magnified image when the object is between focus and pole of the mirror, i.e., direct distance should be less than the focal length of the mirror.
For object distance 10 cm, mirrors of focal length fb = 15 cm and fc = 20 cm can be used.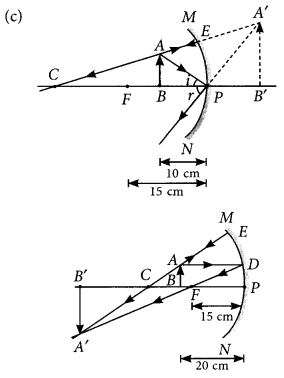
Question 57.
A student has focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a concave mirror. The situation is a given below:
Length of fhe flame = 1.5 cm
Focal length of the mirror = 12 cm
Distance of flame from the mirror = 18 cm
If the flame is perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror, then calculate the following:
(a) Distance of the image from the mirror
(b) Length of the image
If the distance between the mirror and the flame is reduced to 10 cm, then what would be observed on the screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer from this situation. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Given: focal length of the concave mirror, f = – 12 cm
Length of the flame, h = 1.5 cm
Distance of flame from the mirror, u = -18 cm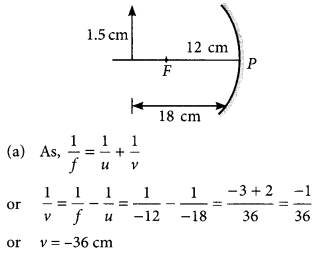
(b) Let h’ be the length of the image.
∵ Magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\)
∴ h’ = \(\frac{-v \times h}{u}=\frac{-(-36) \times 1.5}{-18}\) = -3 cm
If the distance between the mirror and the flame is reduced to 10 cm, then
\(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{-12}-\frac{1}{-10}=\frac{1}{60}\)
∴ v = 60 cm
Hence, image is formed behind the mirror.
Question 58.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a mirror.
(a) Which type of mirror should he use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length ‘f’ of the mirror should he place the candle flame so as to get the magnified image on the wall?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
(d) Can he use this mirror to project a diminished image of the candle flame on the same wall? State ‘how’ if your answer is ‘yes’ and ‘why not’ if your answer is ‘no’ (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) He should use concave mirror to get image of candle flame on the walls of school laboratory. Because concave mirror is a converging mirror and produce real image.
(b) He should place the candle flame in between centre of curvature C and principal focus F of the mirror to get the magnified image on the wall.
(d) Yes, he can use concave mirror to project a diminished image of the candle flame on the same wall. He has to place the candle flame beyond centre of curvature to get diminished image.
Question 59.
Define the following terms in case of a concave mirror:
(a) Pole
(b) Radius of curvature
(c) Principal axis
(d) Principal focus
Suppose you want to observe an erect image of a candle flame using a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. State the range of distance of the candle flame from the mirror. List two other characteristics of the observed image. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 54(a) (i).
(b) Refer to answer 53(b).
(c) Refer to answer 54(a) (iii).
(d) Refer to answer 54(a) (iv).
If we want to get an erect image of a candle flame using concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, then we must place the object between a pole and focus of the mirror. If u is the image distance, then 0 < u < 20 cm
Other two characteristics of the observed image are
(i) Image is virtual and erect
(ii) Image is enlarged
The ray diagram for this situation can be drawn as follows: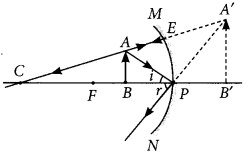
Question 60.
List the sign conventions for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in the determination of focal length of a spherical mirror which forms a three times magnified real image of an object placed 16 cm infront of it. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Sign Convention for Reflection by Spherical Mirrors : While dealing with the reflection of light by spherical mirrors, we shall follow a set of sign conventions called the New Cartesian Sign Convention, the conventions are as follows:
(i) The object is always placed to the left of the mirror. This implies that the light from the object falls on the mirror from the left-hand side.
(ii) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
(iii) All the distances measured to the right of the origin (along + x-axis) are taken as positive while those measured to the left of the origin (along – x-axis) are taken as negative.
(iv) Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +y-axis) are taken as positive.
(v) Distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis (along-y-axis) are taken as negative.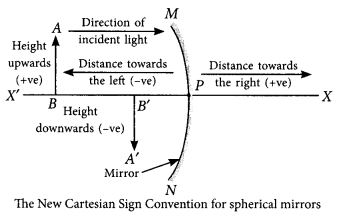
Given that m = -3 (real image), u = -16 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac { -v }{ u }\)
Question 61.
List the new Cartesian sign convention for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions for calculating the focal length and nature of a spherical mirror which forms a 1/3 times magnified virtual image of an object placed 18 cm in front of it. (AI 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 60.
Given that m = +\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) (virtual image), u = -18 cm
Magnification, m = –\(\frac { v }{ u }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -18 }\) ⇒ v = 6 cm
mirror formula \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 3-1 }{ 18 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ⇒ f = 9 cm
As the value of focal length is positive, the mirror used is convex mirror.
Question 62.
Name the type of mirror used in the following situations
(i) Headlights of a car
(ii) Rear-view mirror of vehicle
(iii) Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason. (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
(i) Refer to answer 46(i).
(ii) Refer to answer 46(ii).
(iii) Concave mirrors are used in solar furnaces to concentrate sunlight to produce heat.
Question 63.
What is meant by power of a lens? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Power is the degree of convergence or divergence of light rays achieved by a lens.
It is defined as the reciprocal of its focal length.
i.e., P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
Question 64.
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens. (AI2017)
Answer:
Given : Object distance, u = – 15 cm
Focal length, f = + 20 cm
Using lens formula, As |u| < |f|
The object is placed between F and optical centre of lens.
Thus, the four characteristics of the image formed by the convex lens are:
(i) Erect
(ii) Virtual
(iii) Enlarged image,
(iv) Image is formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Question 65.
What is meant by power of a lens? What does its sign (+ve or -ve) indicate? State its S.I. unit related to focal length of a lens. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Refer to answer 63.
Positive sign (+) of power indicates that lens is convex and negative sign (-) of power indicates that lens is concave.
If focal length (f) is expressed in metres, then, power is expressed in dioptres. The SI unit of power is dioptre. Thus, 1 dioptre is the power of lens whose focal length is 1 metre. 1 D = 1 m-1
Question 66.
The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, find the speed of light in water. (AI 2016)
Answer: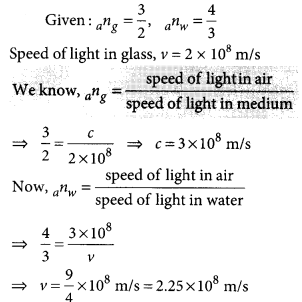
Question 67.
The absolute refractive indices of glass and water are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, calculate the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Given that: ng = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\), nw = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\), vg = 2 × 108 m/s
Absolute refractive index of a medium, nm = \(\frac { c }{ v }\)
where, c is the speed of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in medium.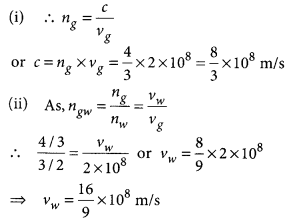
Note: The values given in question are not correct as the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m/s
Question 68.
“A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself.” Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement”. (Delhi 2013)
Answer: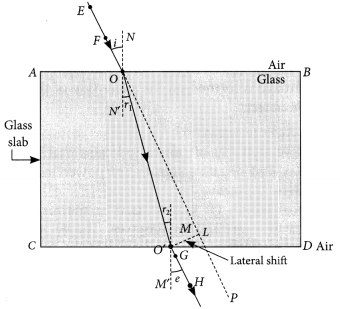
Question 69.
The absolute refractive indices of glass and water are 1.5 and 1.33 respectively. In which medium does light travel faster? Calculate the ratio of speeds of light in the two media. (Delhi 2013 C)
Answer:
Given : refractive index of glass, ng = 1.5
Refractive index of water, nw = 1.33
Since, refractive index of medium,
For glass ng = \(\frac { c }{ v_g }\) ……… (i)
For water nw = \(\frac { c }{ v_w }\) ……… (ii)
Since velocity of light in medium is inversely proportional to its refractive index, the light will travel faster in optically rarer medium i.e., water.
Dividing (i) by (ii),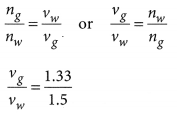
So, the ratio of vg and vw is 1.33 : 1.5.
Question 70.
To construct a ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after refraction from the lens. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after refraction. Use these two rays to locate the image of an object placed between ‘f’ and ‘2f’ of a convex lens. (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
The two rays are :
(i) A ray of light from the object, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction from a convex lens, passes through the principal focus on the other side of the leps and in case of concave lens, a ray appears to diverge from the principal focus located on the same side of the lens.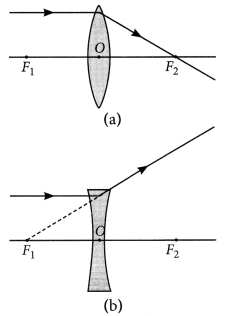
(ii) A ray of light passing through the optical centre of a lens will emerge without any deviation.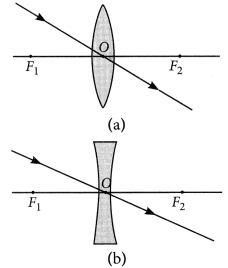
When object is placed between F and 2F.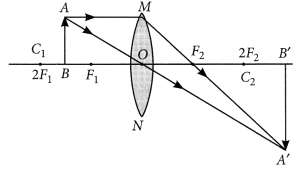
Question 71.
(a) Water has refractive index 1.33 and alcohol has refractive index 1.36. Which of the two medium is optically denser? Give reason for your answer.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light passing obliquely from water to alcohol.
(c) State the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction in the above case. (2020)
Answer:
(a) Here, alcohol is optically denser medium as its refractive index is higher than that of water. When we compare the two media, the one with larger refractive index is called the optically denser medium than the other as the speed of light is lower in this medium.
(b) Since light is travelling from water (rarer medium) to alcohol (denser medium), it slows down and bends towards the normal.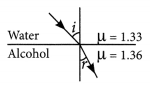
where i = angle of incidence and r = angle of refraction.
(c) According to Snell’s law,
\(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\frac{\mu_{\text {alcohol }}}{\mu_{\text {water }}}=\frac{1.36}{1.33}\) = 1.0225
∴ sin i = 1.0225 × sin r
Question 72.
The refractive index of a medium V with respect to a medium ‘y’ is 2/3 and the refractive index of medium ‘y’ with respect to medium ‘z’ is 4/3. Find the refractive index of medium ‘z with respect to medium V. If the speed of light in medium ‘x’ is 3 × 108 m s-1, calculate the speed of light in medium ‘y’. (2020)
Answer:
Given, refractive index of medium x with respect to y,
yµx = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Refractive index of medium y with respect to z,
zµy = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)
∴ Refractive index of medium x with respect to z,
zµx = yµx . zµy = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) × \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 9 }\)
∴ Refractive index of medium z with respect to x,
xµy = \(\frac { 1 }{ ^zµ_x }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 8 }\)
Now speed of light in x = 3 × 108 m/s
Speed of light in y, vy = ?
⇒ vy = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) × 3 × 108 = 2 × 108 m/s
Question 73.
A real image 2/3rd of the size of an object is formed by a convex lens when the object is at a distance of 12 cm from it. Find the focal length of the lens. (AI 2019)
Answer:
Given, h’ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)h, u = -12 cm
∴ Focal length of the convex lens = 4.8 cm
Question 74.
State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vaccum. (2018)
Answer:
(a) Laws of refraction of light:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media.
This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
\(\frac { sin i }{ sin r }\) = constant,
where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
This constant value is called refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first when the light travels from first medium to second medium.
⇒ constant = n21 = \(\frac { v_1 }{ v_2 }\) ∴\(\frac { sin i }{ sin r }\) = \(\frac { v_1 }{ v_2 }\)
If n is the absolute refractive index of the medium, c is the velocity of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in a given medium, then n = cl v.
Question 75.
What is meant by power of a lens? Write its SI unit. A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of -20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens. (2018)
Answer:
Refer to answer 65.
Given that: Focal length of lens A, fA = +40 cm
Focal length of lens B, fB = -20 cm
Lens A is converging. Lens B is diverging.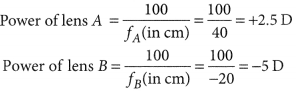
Question 76.
Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of three times magnified (a) real, and (b) virtual image of an object by a converging lens. Mark the positions of O, F and 2F in each diagram. (AI 2017)
Answer: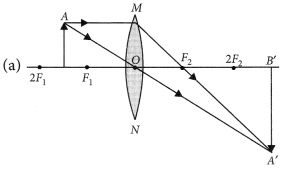
(b) Ray diagrams of an object placed between F1 and optical centre O of lens can be drawn as follows: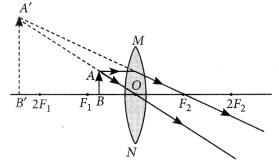
(i) The image formed is virtual and erect.
(ii) Image is formed in front of the lens.
(iii) Image formed is enlarged.
Question 77.
(a) Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by a ray of light while passing through the slab.
(b) If the refractive index of glass for light going from air to glass is 3/2, find the refractive index of air for light going from glass to air. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 68.
(b) Refractive index of glass w.r.t air is 3
gna = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
Now, refractive index of air w.r.t glass will be
ang = \(\frac { 1 }{ _gn_a }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ (3/2) }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Question 78.
The image of an object formed by a lens is of magnification -1. If the distance between the object and its image is 60 cm, what is the focal length of the lens? If the object is moved 20 cm towards the lens, where would the image be formed? State reason and also draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. (AI2016)
Answer:
Magnification of -1 indicates that the image is real and inverted and is of the same size as of the object. The object must be at 2f and image also at 2f on the other side.
Total distance between image and object
Also 4f = 60 cm ⇒ f = 15 cm
If object is moved 20 cm towards the lens, then the object will be between focus and optical centre of the lens and image formed will be virtual and erect and on the same side of the lens.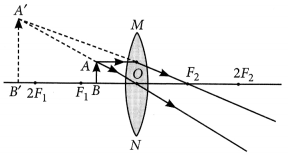
Question 79.
(a) Define focal length of a spherical lens.
(b) A divergent lens has a focal length of 30 cm. At what distance should an object of height 5 cm from the optical centre of the lens be placed so that its image is formed 15 cm away from the lens? Find the size of the image also.
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) Distance between the optical centre and the focus of the lens is known as the focal length of the lens.
(b) Given f = -30 cm, v = -15 cm, h = 5 cm From the lens formula,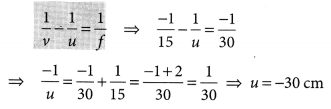
Object should be placed 30 cm from the optical centre.
Also m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ h’ = h(\(\frac { v }{ u }\))
or h’ = 5 × \(\frac { -15 }{ -30 }\) = 2.5 cm
Size of image formed is 2.5 cm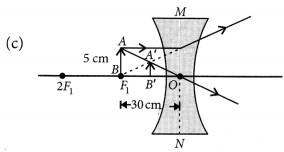
Question 80.
If the image formed by a lens for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual, erect and diminished, state the type of the lens. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. If the numerical value of focal length of such a lens is 20 cm, find its power in new cartesian sign conventions. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Concave lens always forms virtual, erect and diminished image for all positions of the object.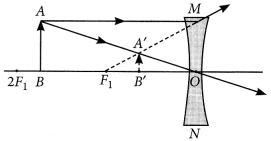
Focal length of the concave lens
f = -20 cm = \(\frac { -20 }{ 100 }\) m
Power of the lens, P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f(in m) }\) = \(\frac { -100 }{ 20 m }\) = -5D
Question 81.
State the laws of refraction of light. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m/s, find the absolute refractive index of a medium in which light travels with a speed of 1.4 × 108 m/s. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Laws of refraction: Refer to answer 74.
The speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m/s
The speed of light in a medium = 1.4 × 108 m/s
∴ Absolute refractive index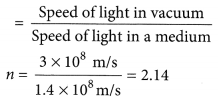
Question 82.
State the laws of refraction of light. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m s-1, find the speed of light in a medium of absolute refractive index 1.5. (Delhi 2014, AI 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 74.
The speed of light in vacuum = 3 × 108 m/s
Absolute refractive index =1.5
∴ The speed of light in a medium
Question 83.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 40 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed on the other side of the lens at a distance of 40 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and write its focal length. What will be the nature of the image formed if the candle flame is shifted 25 cm towards the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Given : u = -40 cm, v = 40 cm
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{40}+\frac{1}{40}=\frac{2}{40}\) ⇒ f = 20 cm
Type of lens : Convex lens
Focal length = 20 cm
Nature of the image will be virtual and erect if the candle flame is shifted 25 cm towards the lens.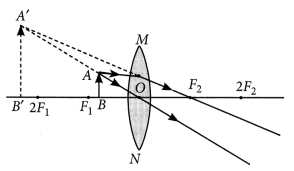
Question 84.
An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Focal length of given concave lens, f= – 5 cm
Distance, u = -10 cm, object size, h = 6 cm
Image distance, v = ?
Using lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
\(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{-5}+\frac{1}{-10}=\frac{-3}{10}\)
v = –\(\frac { 10 }{ u }\) = -3.33 cm
So, the image is located 3.33 cm from the lens. Magnification (m) of lens is given by
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac{-\frac{10}{3}}{-10}=\frac{1}{3}\) = 0.33
m is positive implies that image is virtual and erect. Also, magnitude of m is less than one implies that image is diminished.
Since m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) ⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ 6 }\) or h’ = 2 cm
Question 85.
Draw ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases. A ray of light incident on a concave lens
(i) is parallel to its principal axis, (ii) is passing through its optical centre and (iii) is directed towards its principal focus. (Delhi 2013 C)
Answer:
(i) A ray of light incident on a concave lens is parallel to its principal axis, the diagram can be drawn as follows:
The refracted ray appears to pass through focus on the same side of the lens.
(ii) If a ray of light incident on a concave lens is passing through its optical centre then the refracted ray will go without deviation.
(iii) If a ray of light incident on a concave lens is directed towards its principal axis then it will go parallel to principal axis.
Question 86.
What is the principle of reversibility of light? Show that the incident of light is parallel to the emergent ray of light when light falls obliquely on a side of a rectangular glass slab. (AI 2011)
Answer:
Principle of reversibility of light states that the light will follow exactly the same path if the direction is reversed.
Using Snell’s law of refraction, \(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r_{1}}=\frac{\sin e}{\sin r_{2}}\)
Since r1 = r2, so i = e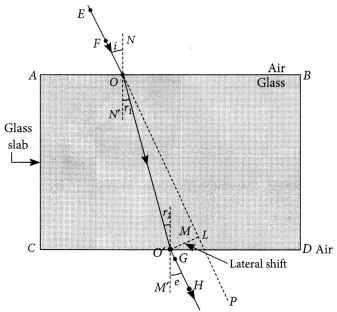
so PQ is parallel to RS.
So, we conclude that incident ray is parallel to the emergent ray.
Question 87.
What is understood by lateral displacement of light? Illustrate it with the help of a diagram. List any two factors on which the lateral displacement in a particular substance depends. (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
When a ray of light is incident obliquely on a parallel sided glass slab, the emergent ray shifts laterally. The perpendicular distance between the direction of the incident ray and emergent ray is called lateral shift.
Diagram : Refer to answer 68.
Tire factors on which the lateral displacement depends are:
(i) thickness of the refracting material.
(ii) the refractive index of the material.
Question 88.
Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of image, when the object is placed:
(i) between optical centre and principal focus of a convex lens.
(ii) anywhere in front of a concave lens.
(iii) at 2F of a convex lens.
State the signs and values of magnifications in the above mentioned cases (i) and (ii). (2020)
Answer:
(i) When an object is placed between Fj and optical centre, O of a convex lens, it forms a virtual and erect image. The ray diagram for this situation can be drawn as follows: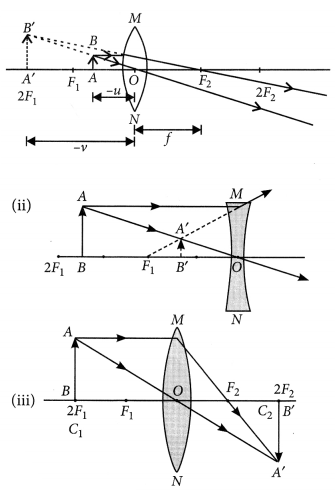
In case (i), the magnification, m is given by,
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -u }\) = positive
i.e., the image formed virtual and erect.
In case (ii), the magnification,
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -v }{ -u }\) = positive
i.e., the image formed is virtual and erect.
Question 89.
(a) Define the following terms :
(i) Power of lens
(ii) Principal focus of a concave mirror
(b) Write the relationship among the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f) of a
(i) Spherical lens
(ii) Spherical mirror
(c) An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from optical centre of a convex lens of focal length 15 cm. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case. (2020)
Answer:
(a) (i) Refer to answer 63.
(ii) Refer to answer 54(a)(iv).
(b) (i) for a spherical lens, according to lens formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
where f is the focal length of the lens, v is the image distance and u is the object distance.
(ii) For a spherical mirror, according to mirror formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
where f is the focal length of the mirror, v is the image distance and u is the object distance.
(c) Given focal length, f = +15 cm (convex lens) and u = -10 cm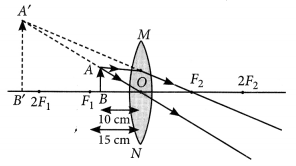
Question 90.
Rishi went to a palmist to show his palm. The palmist used a special lens for this purpose.
(i) State the nature of the lens and reason for its use.
(ii) Where should the palmist place/hold the lens so as to have a real and magnified image of an object?
(iii) If the focal length of this lens is 10 cm, the lens is held at a distance of 5 cm from the palm, use lens formula to find the position and size of the image. (2020)
Answer:
(i) The lens used here is a convex lens and it is used as a magnifying glass because at close range, i.e., when the object is placed between optic centre and principal focus it forms an enlarged, virtual and erect image of the object.
(ii) When this lens is placed such that the object is between the centre of curvature and the principal focus, the palmist obtain a real and magnified image.
(iii) Given focal length, f = 10 cm and u = -5 cm According to lens formula,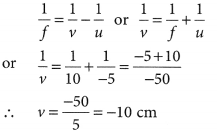
Thus, the image will be formed at 10 cm on the same side of the palm and the size of the image will be enlarged.
Question 91.
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case
(iii) Draw ray diagram to justify your answer of pair (ii) . (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Given, f = -30 cm, u = -60 cm, v = ?
Using lens formula,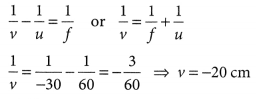
(ii) (a) The image is virtual in nature.
(b) The image is formed at a distance of 20 cm on the left from the concave lens.
(c) Magnification, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\)
Here, v = – 20 cm; u = – 60 cm
So, m = \(\frac { 20 }{ 60 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = + 0.3
Since value of magnification is less than 1, therefore, the image is diminished.
(d) The plus sign for the magnification shows that the image is erect.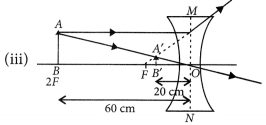
Question 92.
(a) A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image formed.
(b) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing object distance, image distance and focal length in the above case. (AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) Given, h = 5 cm, f = 20 cm, u = -30 cm
Using lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
\(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{-30}+\frac{1}{20}=\frac{-2+3}{60}=\frac{1}{60}\)
⇒ v = 60 cm
Now, magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { v }{ u }\)
⇒ h’ = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) × h = \(\frac {60 }{ -30 }\) × 5 = -10 cm
Hence, the image formed at 60 cm, which is real and magnified.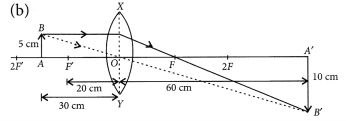
Question 93.
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follows, without doing any calculations :
| S. No. | Object distance u (cm) | Image distance v (cm) |
| 1 | -90 | + 18 |
| 2 | -60 | + 20 |
| 3 | -30 | + 30 |
| 4 | -20 | + 60 |
| 5 | – 18 | + 90 |
| 6 | – 10 | + 100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Take an appropriate scale to draw ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and the approximate value of magnification. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(a) When an object placed at 2F from a convex lens, then its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. Thus from S. No.(3) we can say that.
f = v/2 ⇒ f = \(\frac {30}{ 2 }\) = + 15 cm
Thus, the focal length is + 15 cm.
(b) In this case S.No. (6) is incorrect as the object distance is between focus and pole, for such case, the image formed is virtual and on the same side as the object, hence image distance is negative.
(c) The approximate value of magnification for object distance -20 cm and image distance +60 cm is -3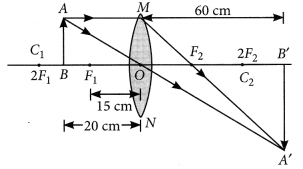
Question 94.
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations.
| S. No. | Object Distance w(cm) | Image Distance v(cm) |
| 1 | -100 | +25 |
| 2 | -60 | +30 |
| 3 | -40 | +40 |
| 4 | -30 | +60 |
| 5 | -25 | +100 |
| 6 | -15 | +120 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of the observation which is not correct. On what basis have you arrived at this conclusion?
(c) Select an appropriate scale and draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 2. Also find the approximate value of magnification. (AI 2017)
Answer:
(a) When an object is placed at 2F from the convex lens, then its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. Thus from S.No. (3), we can say that
∴ f = \(\frac {v}{ 2 }\) = \(\frac {40}{ 2 }\) = 20 cm
(b) In this case, S. No. (6) is incorrect as the object distance is between focus and optical centre for such cases, the image formed is virtual and image distance is negative.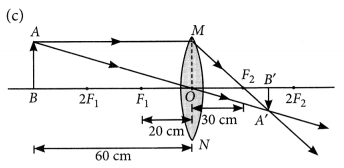
The approximate value of magnification for object distance -60 cm and image distance +30 cm is -1/2.
Question 95.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a convex lens when an object is placed in front of the lens between its optical centre and principal focus.
(b) In the above ray diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper sign (+ve or -ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (f) of the convex lens in this case.
(c) Find the power of a convex lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification -1 of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm from its optical centre. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 88(i).
(b) The lens formula is given as
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
(c) Magnification of the lens is given by
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = \(\frac { -v }{ 20 }\) [u = -20 cm]
∴ v = 20 cm
As v = u then
∴ f = \(\frac { 20 }{ 2 }\) cm = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Power of the lens, P = \(\frac { 1 }{ f(in m) }\) D = \(\frac { 1}{ 0.1 }\) D = 10 D
Question 96.
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image by a concave lens when an object is placed in front of it.
(b) In the above diagram mark the object distance (u) and the image distance (v) with their proper sign (+ve or -ve as per the new Cartesian sign convention) and state how these distances are related to the focal length (/) of the concave lens in this case.
(c) Find the nature and power of a lens which forms a real and inverted image of magnification -1 at a distance of 40 cm from its optical centre. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 88(ii).
(b) The lens formula is given by
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
(c) Since, the nature of the image is real and inverted therefore the lens is convex.
Now magnification of the lens is
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ -1 = \(\frac { v }{ u}\) ⇒ v = -u
Now, from lens formula,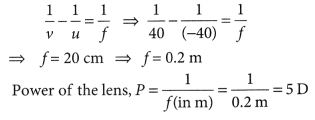
Question 97.
(a) Define optical centre of a spherical lens.
(b) A divergent lens has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance should an object of height 4 cm from the optical centre of the lens be placed so that its image is formed 10 cm away from the lens. Find the size of the image also.
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in above situation. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) Optical centre is the central part of the lens through which a ray of light passes without suffering any deviation. It is usually represented by the letter O.
(b) Given f = – 20 cm, h = 4 cm, v = – 10 cm
From lens formula,
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -1 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) ⇒ u = -20 cm
Also, magnification of the lens,
m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) ⇒ h’ = \(\frac { 10 }{ 20 }\) × 4 ⇒ h’ = 2 cm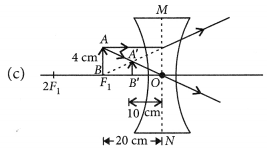
Question 98.
(a) Define focal length of a divergent lens.
(b) A divergent lens has a focal length of 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre. Use lens formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation. (AI 2016)
Answer:
(a) Distance between the principal focus and the optical centre is known as the focal length of the lens.
(b) Given, f = -30 cm, v = -15 cm, h = 6 cm
Now, from lens formula,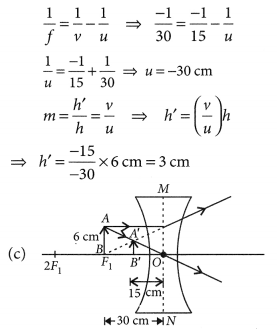
Question 99.
At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm a 6 cm tall object be placed so as to obtain its image at 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed. Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Focal length of concave lens, f = -20
cm Height of the object, h = 6 cm
Image distance, v = -15 cm
From lens formula,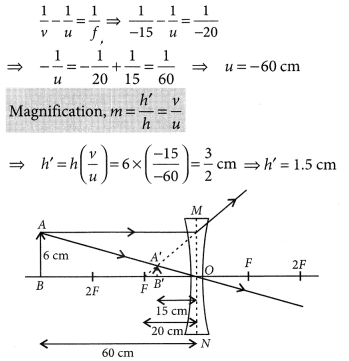
Question 100.
At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 25 cm a 10 cm tall object be placed so as to obtain its image at 20 cm from the lens. Also calculate the size of the image formed. Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer for the above situation and label it. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Focal length of concave lens f = – 25 cm
Image distance, v = -20 cm
Height of the object, h = 10 cm
Now, from lens formula,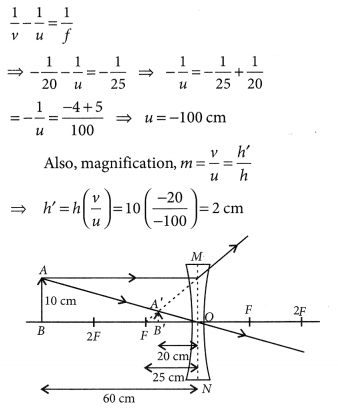
Question 101.
“A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it”. Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case. An object of height 4 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position of the image formed. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Magnified erect image: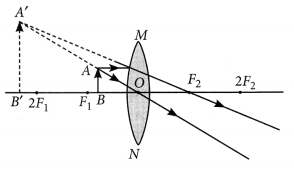
Magnified inverted image: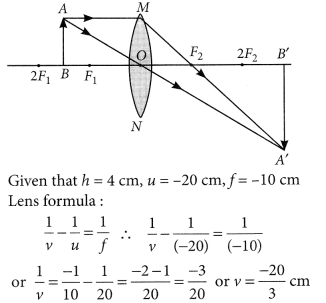
Given that h = 4 cm, u = -20 cm, f = -10 cm
Lens formula:
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ (-20) }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ (-10) }\)
or \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{-1}{10}-\frac{1}{20}=\frac{-2-1}{20}=\frac{-3}{20}\) or v = \(\frac { -20 }{ 3 }\) cm
Question 102.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed on the other side of the lens at a distance of 60 cm from the optical centre of the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 3 cm, find the height of its image. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Given that u = -30 cm, v = 60 cm, h = 3 cm
Lens Formula:
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) ∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ 60 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ (-30) }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
⇒ \(\frac{1+2}{60}=\frac{1}{f}=\frac{3}{60}=\frac{1}{20}\) or f = 20 cm
As focal length is positive, hence lens is convex lens.
Magnification, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\)
∴ \(\frac { 60 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { h’ }{ 3 }\) or h’ = \(\frac { -60×3 }{ 30 }\) = -6 cm
⇒ The height of image is 6 cm and negative sign shows that the image is real and inverted.
Question 103.
(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
(b) The absolute refractive indices of two media A and B are 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. If the speed of light in medium B is 2 × 108 m/s, calculate the speed of light in
(i) vacuum
(ii) medium A (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 74.
(b) Given that nA = 2.0, nA = 1.5, vA = 2 × 108 m/s
(i) nB = \(\frac { c }{ v_B }\), where c is the speed of light in vacuum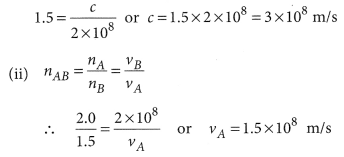
Question 104.
What is meant by power of a lens? Define its S.I. unit.
You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths + 10 and -10 cm respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 65.
Given that:
Focal length of lens A, fA = +10 cm
Focal length of lens B, fB = -10 cm
Lens A is convex lens . Lens B is concave lens,
Power of lens A = \(\frac { 100 }{ f_A(in cm) }\) = \(\frac { 100 }{ 10 }\) = +10 D
Power of lens B = \(\frac { 100 }{ f_B(in cm) }\) = \(\frac { 100 }{ -10 }\) = -10 D
Lens A will form a virtual and magnified image.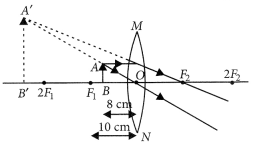
Question 105.
One half of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm is covered with a black paper. Can such a lens produce an image of a complete object placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
A 4 cm tall obj ect is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 15 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Yes, the lens will produce an image of complete object.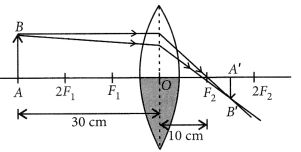
Given that h = 4 cm, f = 20 cm, u = -15 cm
Lens formula: = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ (-15) }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) or \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 20 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac { -1 }{ 60 }\)
⇒ v = -60 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -60 }{ -15 }\) = 4
Nature of image: Virtual, erect and enlarged Position of image : In front of lens 60 cm from the lens
Size of image : Four times of object, i.e.,
(4 × 4) cm = 16 cm
Question 106.
What is meant by the power of a lens ? What is its S.I. unit ? Name the type of lens whose power is positive. The image of an object formed by a lens is real, inverted and of the same size as the object. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the lens, what is the nature and power of the lens? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 65.
Convex lens has positive power. Since the image of an object formed by a lens is real, inverted and of the same size as the object.
Given: Size of object = Size of image and h’ = -h
∴ Magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h}\) = \(\frac { -h }{ h}\) = -1
∴ -1 = \(\frac { v }{ u}\) or v = -u
Focal length of the lens,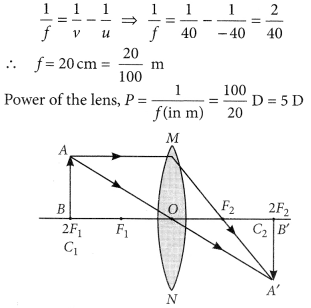
Question 107.
(a) Explain the following terms related to spherical lenses:
(i) optical centre
(ii) centres of curvature
(iii) principal axis (iv) aperture
(v) principal focus (vi) focal length
(b) A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance should the object be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens. (AI 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) Optical centre : The centre point of a lens is known as the optical centre. It always lies inside the lens. A light beam passing through the optical centre without any deviation.
(ii) Centre of curvature : It is defined as the centre of the sphere of which the lens is originally a part of. Because the spherical lens consists of two spherical surfaces, the lens has two centre of curvature.
(iii) Principal axis : A straight line passing through the optical centre and principal focus of a spherical lens. This line is called the principal axis.
(iv) Aperture : The diameter of the reflecting surface of spherical lens is called its aperture.
(v) Principal focus : A number of rays parallel to the principal axis are falling on a lens.
These rays, after refraction from the lens, are appearing to converge to or diverge from a point on the principal axis. This point on the principal axis is called the principal focus of the lens.
(vi) Focal length: The distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of a spherical lens is called the focal length. It is represented by the letter f.
(b) Given f = 12 cm, v = 48 cm, u = ?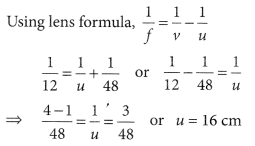
Question 108.
(i) Explain the following terms related to spherical lenses
(a) Centres of curvature (b) Principal axis
(c) Optical centre (d) Principal focus
(ii) At what distance from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm, should a 6 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at 15 cm from the lens? Also determine the size of the image formed. (AI 2014)
Answer:
(i) Refer to answer 107(a).
(ii) Refer to answer 99.
Question 109.
What is meant by power of a lens? Name and define its S.I. unit.
One student uses a lens of focal length +50 cm and another of -50 cm. State the nature and find the power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will always give a virtual and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object? (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 65.
A convex lens has the focal length +50 cm.
∴ power = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { +100 }{ 50 }\) = +2 D
A concave lens has the focal length -50 cm.
∴ power = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { -100 }{ 50 }\) = -2 D
Concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
Question 110.
(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Give an expression to relate the absolute refractive index of a medium with speed of light in vacuum.
(b) The refractive indices of water and glass with respect to air are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m s-1, find the speed of light in (i) air, (ii) water. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 74.
(b) Refer to answer 66.
Question 111.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 45 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 90 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2 cm, find the height of its image. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Given that u = -45 cm, v = +90 cm, h = 2 cm
(as the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and hence image is formed by convex lens on the other side of the lens).
Type of the lens used : Convex lens
Lens formula
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\)
∴ \(\frac{1}{90}-\frac{1}{(-45)}=\frac{1}{f}=\frac{3}{90}\) or f = 30 cm
Focal length, f = 30 cm
Magnification, m = \(\frac { h’ }{ h }\) = \(\frac { v }{ u }\)
∴ \(\frac { h’ }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 90 }{ -45 }\) or h’ = -4 cm
⇒ height of image = 4 cm (inverted)
Question 112.
State the law of refraction of light that defines the refractive index of a medium with respect to the other. Express it mathematically. How is reffactive index of any medium ‘A’ with respect to a medium ‘B’ related to the speed of propagation of light in two media A and A? State the name of this constant when one medium is vacuum or air.
The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to vacuum are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (i) vacuum, (ii) water. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 74 and 66.
Question 113.
A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of convex lens of focal length 24 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 16 cm. Find the position, size and nature of the image formed, using the lens formula. (AI 2012, Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Given that :u = -16 cm, f = 24 cm, h = 4 cm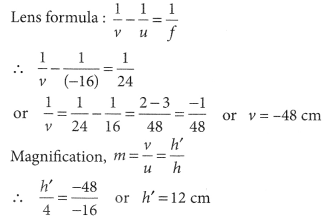
Nature of image : virtual and erect, enlarged
Question 114.
With the help of a ray diagram state what is meant by refraction of light. State Snell’s law for refraction of light and also express it mathematically.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is 2/3 and the refractive index of water with respect to air is 4/3. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (a) air, (b) water. (AI 2012)
Answer:
When travelling obliquely from one medium to another, the direction of propagation of light in the second medium changes. This phenomenon is known as refraction of light.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media. This law is also known as snell’s law of refraction.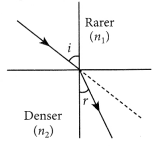
\(\frac { sin i }{ sin r }\) = constant,
Where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
Given that: nag = 2/3, nwa = 4/3, vg = 2 × 108 m/s
(a) Refer to answer 66.
(b) Va = nga × vg
= \(\frac { 1 }{ n_{ag} }\) × Vg = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) × 2 × 108 = 3 × 108 m/s
Question 115.
List the sign conventions that are followed in case of refraction of light through spherical lenses. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in determining the nature and focal length of a spherical lens which forms three times magnified real image of an object placed 16 cm from the lens. (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
For lenses, we follow sign convention, similar to one used for spherical mirrors. We apply the rules for signs of distances, except that all measurements are taken from the optical centre of the lens.
For sign convention of mirror : refer to answer 60.
u = -16 cm, m = -3 (real)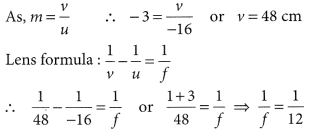
or f = 12 cm
Spherical lens is convex lens or converging lens of focal length 12 cm.
Question 116.
(a) What is meant by ‘power of a lens?’
(b) State and define the S.I unit of power of a lens.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in close contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of this combination. (AI 2011)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 63.
(b) Refer to answer 65.
(c) Power of convex lens of focal length 25 cm is
p1 = \(\frac { 100 }{ 25(in m) }\) = 4 D
Power of concave lens of focal length 10 cm is 100
p2 = \(\frac { 100 }{ -10(in m) }\) = -10 D
∴ Power of the combination = P = P1 + P2
∴ P = 4 – 10 = -6D
Question 117.
(a) Under what condition with a glass lens placed in a transparent liquid become invisible.
(b) Describe and illustrate with a diagram, how we should arrange two converging lenses so that a parallel beam of light entering one lens emerges as a parallel beam after passing through the second lens.
(c) An object is placed at a distance of 3 cm from a concave lens of focal length 12 cm. Find the (i) position and (ii) nature of the image formed. (Foreign 2011)
Answer:
(a) If the refractive index of glass lens is equal to the refractive index of liquid then the glass lens placed in a transparent liquid will become invisible.
(b) Suppose we have two converging lens of focal lengths f1 and f2. We will keep the two converging lens at a distance of f1 +f2 so that a parallel beam of light entering one lens emerges as a parallel beam after passing through the second lens.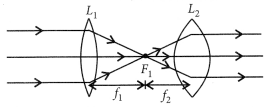
Here the focus of the two lenses should coincide,
(c) (i) Focal length of concave lens, f = -12 cm
Object distance, u = -3 cm Image distance, v = ?
Using lens formula,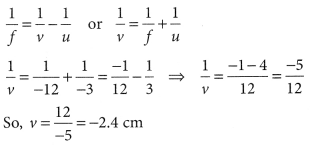
So, the image is formed at 2.4 cm from the concave lens.
(ii) Using magnification formula,
m = \(\frac { v }{ u }\) = \(\frac { -2.4 }{ -3 }\) = + 0.8
Since m is +ve and magnitude of m is less than 1, so the image formed is virtual and diminished.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
REFLECTION
Reflection of Light: The phenomenon of bouncing back of light into the same medium by the smooth surface is called reflection.
Incident light: Light which falls on the surface is called incident light.
Reflected light: Light which goes back after reflection is called reflected light.
The angle of incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal.
An angle of reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Mirror: The surface which can reflect the light is a mirror.
Plane Mirror: If the reflecting surface is a plane then the mirror is plane.
Spherical Mirror: If the reflecting surface is part of the hollow sphere then the mirror is a spherical mirror.
The spherical mirror is of two types:
- Convex mirror: In this mirror reflecting surface is convex. It diverges the light so it is also called a diverging mirror.
- Concave mirror: In this mirror reflecting surface is concave. It converges the light so it is also called converging mirror.
Parameters of Mirror:
- Center of Curvature: The centre of hollow sphere of which mirror is a part.
- The radius of curvature: The radius of hollow sphere of which mirror is a part.
- Pole: The centre of mirror (middle point) is pole.
- Principal axis: The line joining the pole and center of curvature is called principal axis.
- Aperture: Size of mirror is called aperture of mirror.
- Principal Focus: The point on the principal axis, where all the incident rays parallel to principal axis converge or diverge after reflection through mirror.
- Focal Length: The distance between pole and focus point is focal length.
Special Rays for Formation of Image:
- A ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis of a spherical mirror, after reflection converges or diverges from focus.
- A ray of light passing through or appearing from the center of curvature of spherical mirror is reflected back along the same path.
- A ray of light passing through or appearing from the focus of spherical mirror becomes parallel to the principal axis.
- A ray of light which is incident at the pole of a spherical mirror is reflected back making same angle with principal axis.
Use of Concave Mirror: It is used as a makeup mirror, the reflector in torches, in headlights of cars and searchlights, doctor’s head-mirrors, solar furnace, etc.
Sign Conventions of Spherical Mirror
- All the distances are measured from the pole of the mirror as the origin.
- Distances measured in the direction of incident rays are taken as positive.
- Distances measured opposite to the direction of incident rays are taken as negative.
- Distances measured upward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as positive.
- Distances measured downward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as negative.
1f=1v+1u …where f, v and u are focal length, image distance, object distance
Linear Magnification: This is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
Use of Convex Mirror: Convex mirror used as rear view mirror in vehicles, as shop security mirrors, etc.
REFRACTION
Refraction of Light: The bending of light at the interface of two different mediums is called Refraction of light.
- If the velocity of light in medium is more, then medium is called optical rarer.
Example, air or vacuum is more optical rarer. - If the velocity of light in medium is less, then medium is called optical denser.
Example, glass is more denser than air.
Refractive Index: It represents the amount or extent of bending of light when it passes from one medium to another.
There are two types of refractive index
- Relative refractive index and
- Absolute refractive index.
Refractive index of medium with respect to other medium is called Relative Refractive Index.
Refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 =
Refractive index of medium with respect to air or vacuum is called Absolute Refractive Index.
Absolute refractive index of medium (m) =
Incident ray: It is incoming ray on the refracting surface.
Refracted ray: It is an outgoing ray from the refracting surface.
An angle of incidence (i): It is the angle between incident rays and perpendicular line (normal) at the point of incidence.
An angle of refraction (r): It is the angle between refracted rays and perpendicular line (normal) at the point of incidence.
Law of Refraction: According to this law
- “The incident ray, refracted ray and normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.”
- “The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.”
sini = constant (µ)
Lens: The transparent refracting medium bounded by two surfaces in which at least one surface is curved is called lens.
Lenses are mainly two type
- Convex lens and
- Concave lens.
Center of Curvature: The centres of two spheres, of which lens is part is called the centre of curvature.
Radii of Curvature: The radii of spheres, of which lens is part is called radius of curvature.
Principal Axis: The line joining the centres of curvature of two surfaces of lens is called principal axis.
Optical Center: It is a special point on the principal axis. Light incident on the optical centre passes through the lens without deviation.
Principal Focus: The point on the principal axis at which all incident rays parallel to the principal axis converge or appear to diverge after refraction through the lens.
Special Rays for Image Formation by Lens:
- An incident ray, parallel to the principal axis, after refraction passes through (or appears to come from), second focus of the lens.
- An incident ray, passing through the optical center of the lens, goes undeviated from the lens.
- An incident ray, passing through the (first) principal focus of the lens, or directed toward it, becomes parallel to the principal axis after refraction through lens.
Use of Lens: In photographic cameras, magnifying glass, microscope, telescope, the human eye.
1. Light travels in a straight line.
2. Light gets reflected when it falls on polished surfaces; like mirrors.
3. Light suffers refraction when it travels from one medium to another.
4. There is a change in the wavelengths!light when it moves from one medium into another.
5. The bouncing back of light when it strikes a smooth or polished surface is called reflection of light. Reflection is of two types; Specular or regular and Diffuse or irregular reflection.
6. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Mathematically, we have ∠i = ∠r.
7. The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front.
8. The image is unmagnified, virtual and erect.
9. The image has right-left reversal.
10. Focal length of a plane mirror is infinity.
11. Power of a plane mirror is zero.
12. If a plane mirror is turned by an angle, the reflected ray turns by 2θ.
13. The least size of a plane mirror to view an object is equal to half the size of the object.
14. Pole (Vertex): The central point of a mirror is called its pole.
15. Centre of curvature : The centre of the sphere of which the mirror is a part is called the centre of curvature. It is denoted by C.
16. Radius of curvature : The radius of the sphere of which the mirror is a part is called the radius of curvature. It is denoted by R.
17. Principal axis : The straight line passing through the pole and the centre of curvature of the mirror is called the principal axis.
18. Principal focus : It is a point on the principal axis at which the rays parallel to the principal axis meet after reflection or seem to come from. For a concave mirror, the focus lies in front of the mirror and for a convex mirror, it lies behind the mirror. In short, a concave mirror has a real focus while aconvex mirror has a virtual focus.
19. Focal plane : A plane, drawn perpendicular to the principal axis and passing through the principal focus.
20. Focal length : The distance between the pole and the focus is called the focal length. It is represented by f. The focal length is half the radius of curvature.
21. Aperture: The size of the mirror is called its aperture. It is also defined as the effective diameter of the light reflecting area of the mirror.
22. Real image : When the rays of light, after reflection from a mirror, actually meet at a point, then the image formed by these rays is said to be real. Real images can be obtained on a screen.
23. Virtual image: When the rays of light, after reflection from a mirror, appear to meet at a point, then the image formed by these rays is said to be virtual. Virtual images can’t be obtained on a screen.
24. The following rays are used while drawing ray diagrams to find the position of an image :
- A ray of light parallel to the principal axis after reflection passes through the focus. (1)
- A ray of light passing through the focus after reflection becomes parallel to the principal axis. (2)
- A ray of light incident on the centre of curvature retraces its path after reflection form the mirror.
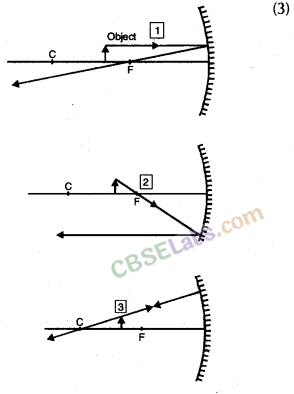
25. For mirrors, the following results hold :
u is – ve, if the object is in front of the mirror.
(Real object)
u is + ve, if the object is behind the mirror.
(Virtual object)
v is – ve, if the image is in front of the mirror.
(Real image)
vis +ve, if the image is behind the mirror.
(Virtual image)
Focal length of a concave mirror is taken as – ve. Focal length of a convex mirror is taken as +ve.
26. When the image formed by a spherical mirror is real, it is also inverted and is on the same side of the mirror as the object. Since both v and u are negative, the magnification is negative.
27. When the image formed by a spherical mirror is virtual, it is also erect and is on the other side of the mirror as the object. In this case, u is – ve and v is + ve , therefore, m is positive.
28. The expression for the mirror formula is 1/u+1/v = 1/f
29. Linear magnification is given by the expression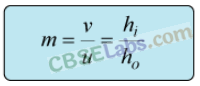
30. If m is positive, the image is erect w.r.t the object and if m is negative, the image is inverted w.r.t. the object.
31.The position of the image for various positions of the object for a concave mirror is as shown in the table below. The table also shows the use of the mirror for different positions of the object.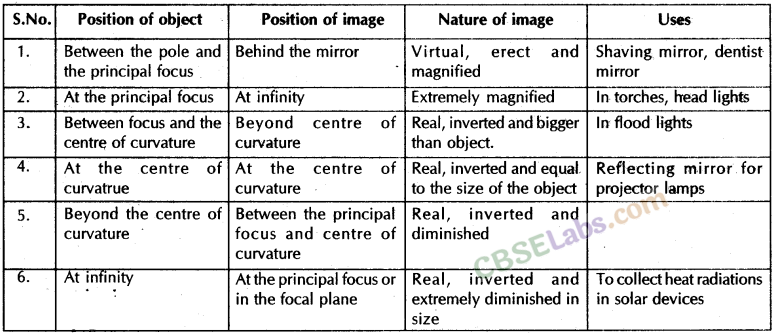
The position of the image for various positions of the object for a convex mirror is as shown in the table below. The table also shows the use of the mirror for different positions of the object.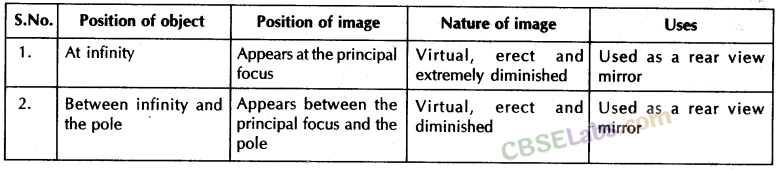
32. The bending of light when it travels from one medium into another is called refraction of light
33.![]()
34. As light travels from ,one medium to another, the frequency of light does not change.
35. Light refracts because it has different speeds in different media.
36. The refraction of light obeys the following two laws :
- The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.This
constant is called the index of refraction or refractive index.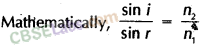
37. If wng is the refractive index of glass w.r.t. water, ang be the refractive index of glass w.r.t. air and anw be the refractive index of water w.r.t. air ,then![]()
38. The most familiar and widely used optical device is the lens. A lens is an optical system with two refracting surfaces. The simplest lens has two spherical surfaces close enough together that we can neglect the distance between them. Such a lens is called a thin lens. The two common types of lenses are Converging lens or Convex lens, Diverging lens or Concave lens.
39. It should be noted that, if the above lenses are surrounded by .a material with a refractive index greater than that of the lens, the convex lens gets converted into a concave lens and vice-versa.
40. Any lens that is thicker at its centre than at its edges is a converging lens with positive f, and any lens that is thicker at its edges than at the centre is a diverging lens with negative f.
41. Optical centre : The central point C in the lens is called the optical centre. If a ray is incident towards the optical centre, it passes undeviated .through the lens.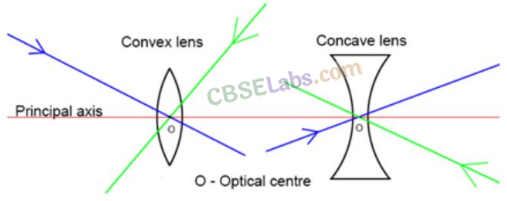
42.Principal axis: Since the lens contains two spherical surfaces, therefore, it has two centres of curvatures.
The line joining these centres and passing through the optical centre is called principal axis.
43. Aperture: The effective width of a lens through which refraction takes place is called the aperture.
44. Focus and Focal Length : If a beam of light moving parallel to the principal axis of a convex lens is incident on it, the rays converge or meet at a point on the principal axis. This point F is called the focus. The distance CF is called the focal length. If a beam of light moving parallel to the principal axis is incident on a concave lens, the beam of light diverges. If these diverged rays are produced backward, they meet at a point F on the principal . axis. The transmitted rays appear to come from this point. This point F is called the focus and distance CF is called the focal length.
45. For drawing the ray diagrams, we note the following :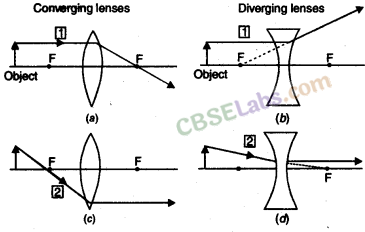
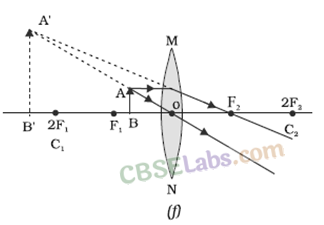
- All rays parallel to the principal axis after refraction pass through the principal focus or seem to come from it.
- A ray of light passing through the focus after refraction becomes parallel to the principal axis.
- A ray of light passing through the optical centre of the lens after refraction passes undeviated.
46. A convex and a concave lens can be supposed to be made-up of prisms.
47. Image formation by a concave lens.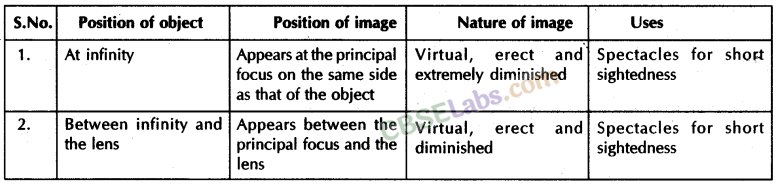
48. Image formation by a convex lens.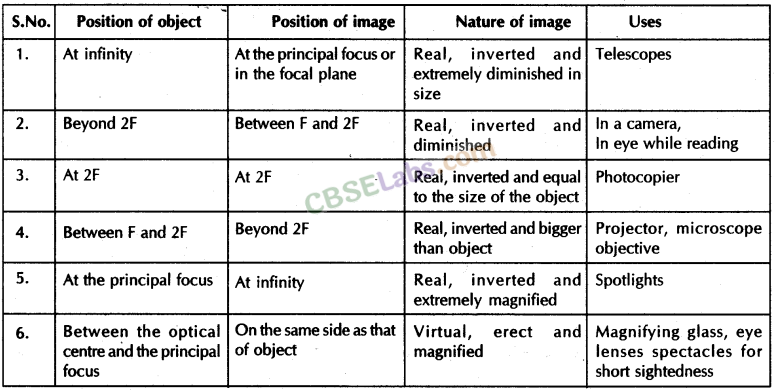
49. New Cartesian sign conventions :
- All distances, object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length f are measured from the optical centre.
- The distances measured in the direction of incident ray are taken as positive and distances measured against the direction of incident ray are taken as negative.
- All distances (heights) of objects and images above principal axis are taken as positive and those below the principal axis are taken as negative.
50. For the two lenses, the sign conventions take the form
- u is- ve, if the object is in front of the lens. (Real object)
- u is +ve, if the object is virtual.
- v is – ve, if the image is on the same side as that of the object. (Virtual image )
- v is +ve, if the image is real.
- Focal length of a concave lens is taken as – ve.
- Focal length of a convex lens is taken as +ve.
51. Lens formula for convex lens 1/v-1/u = 1/f
52. The linear magnification produced by a lens is defined as the ratio of the size of the image (h’) to the size of the object (h). It is represented by m i.e.,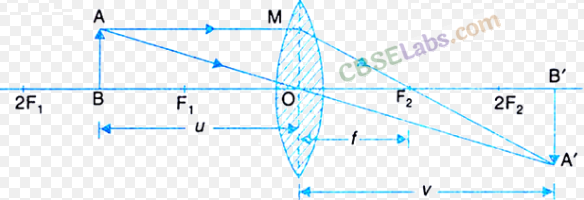
53. If the magnification of a lens is negative, then the image formed is inverted and real.
54. If the magnification of a lens is positive, then the image formed is erect and virtual.
55. Power is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length. Power is measured in dioptre.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Why does a light ray incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself? Explain using a diagram.
Answer. Due to variation in speed of light in different medium, light bends as it moves from One medium to another. Since, there are two surfaces for refraction which are parallel, the light ray should bend in opposite sense in them equally, the emerging light ray is always parallel to the incident ray.
Question 2. A pencil when dipped in water in a glass tumbler appears to be bent at the interface of air and water. Will the pencil appears to be bent to the same extent, if instead of water we use liquids like, kerosene or turpentine. Support your answer with reason.
Answer. No, it will depend on the refractive index of the liquid in which the pencil is dipped. The tip at the bottom will get elevated as per the relation.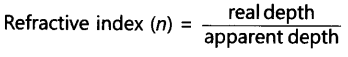
Question 3. Refractive index of diamond with respect to glass is 1.6 and absolute refractive index of glass is 1.5. Find out the absolute refractive index of diamond.
Answer.
Question 4. A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
Answer. Yes, for getting virtual image the object has to be placed between the optical centre and the focus. For real and enlarged image, the object should be placed between F and 2F.
Question 5. Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be angle of incidence. Show the same with the help of diagram.
Answer. When the two mirrors are placed at 90° to each other, the incident and the reflected rays will remain parallel to each other.
Long Answer Questions
Question 6. Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex mirror when an object is placed
(a) at infinity
(b) at finite distance from the mirror
Answer.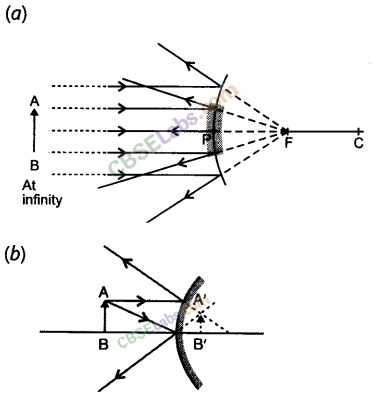
Question 7. The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. If the image is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens? What is the nature of the image at a distance of 80 cm and the lens?
Answer.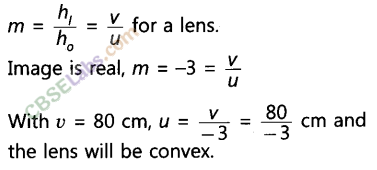
Question 8. Define power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of focal length 50 cm and another of -50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
Answer. Power of a lens: The ability of a lens to converge or diverge the light rays is called power (P) of the lens. It is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length, i.e. f = 1/f .The SI unit of power of a lens is dioptre (D). A lens of focal length 100 cm has a power of 1 dioptre, i.e. 1 dioptre = 1 m-1. The lens of focal length +50 cm has a power of +2 D and is convex while the other is having a power of -2 D and is concave.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Subject NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
.png)
.png)