Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources NCERT Solutions
Before getting into the details of management of natural resources class 10 exercise solutions, let us have an overview of topics and sub topics under the management of natural resources class 10 notes:
- Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources
- Why Do We Need To Manage Our Resources?
- Forests And Wildlife
- Water For All
- Coal And Petroleum
- An Overview Of Natural Resource Management
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management Of Natural Resources PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
- प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का प्रबंधन कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Management of Natural Resources Important Questions
- Management of Natural Resources Class 10 Notes
- Management of Natural Resources NCERT Exemplar Solutions
- Class 10 Science Management of Natural Resources Mind Map
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Intext Questions
Page Number: 271
Question 1
What changes can you make in your habits to become more environment friendly ?
Answer:
(i) Segregate waste into recyclable and non-recyclable parts.
(ii) Switch off the lights, fans, television and other electrical appliances when not used.
(iii) Use energy efficient electrical appliances.
(iv) Walk for nearby shops instead of using vehicles.
(v) Reuse paper, plastic and glass bottles.
(vi) Reuse water from washing machines for cleaning purposes.
Question 2
What would be the advantages of exploiting resources with short term aims?
Answer:
The advantage of exploiting resources with short term aim would be self-centred satisfaction. They provide immediate advantages.
Question 3
How would these advantages differ from the advantages of using a long term perspective in managing our resources ?
Answer:
This way the resources can be used for the benefit of the present generation and also conserved for the benefit of generations to come. This ensures uniform distribution of resources among the people.
Question 4
Why do you think there should be equitable distribution of resources ? What forces would be working against an equitable distribution of our resources ?
Answer:
There should be equitable distribution of resources so that all, rich, powerful and poor people get benefit from the development of these resources. Rich, greedy and powerful people could work against an equitable distribution of our resources.
Page Number: 275
Question 1
Why should we conserve forest and wild life ?
Answer:
We should conserve forest and wildlife because of the following reasons.
- They help in maintaining the ecological balance at a place.
- They provide us with useful things like rubber, wood, dyes, gum, resin, oil, fibres, medicines, catachu, wax, honey, fruits, seeds, leaves of bidi etc.
- They purify the air, control flood and prevent soil erosion and maintain its fertility.
- Forests conserve biodiversity and hereditary resources. Ecological stability gets imbalanced due to damage in diversity.
Question 2
Suggest some approaches towards the conservation of forests.
Answer:
Some methods for forest conservation are as follow :
- Only except some trees, there should be ban on cutting of forest. Forests stop soil erosion.
- Forests should be saved from fires. Many forests get destroyed due to fires.
- Forests should be saved from pests and insects. Pesticides, insecticides should be sprayed in forests.
- Overgrazing should be prohibited.
- National rules and laws should be strictly enforced.
Page Number: 278
Question 1
Find out about the traditional systems of water harvesting management in your region.
Answer:
Many of us live in cities, where water is supplied by the municipal authorities. In the houses, systems of rainwater harvesting are installed which collect the water running off and channel it into a special pit created for the purpose. This helps to recharge ground water.
Efforts are being made to collect run off rain water in soak pits. This water enriches underground water and can cause rise in water table.
Run off water from roof tops can also be collected in trenches, specially made to enrich underground water table.
Question 2
Compare the above systems with the probable systems in hilly/mountainous areas or plains or plateau regions.
Answer:
Drinking water system in hilly areas :
- Kuhls were a traditional irrigation system in hilly areas such as Himachal Pradesh. In this system, the water flowing through falls, comes to villages located at lower regions through small human made drains.
- • In Meghalaya, the water is brought down to the lower areas of hills through bamboo drains.
Drinking water system in plains :
- Jhalaras were made in Rajasthan and Gujarat, essentially meant for community use and for religious rites.
- In some places bawaries etc. were made to supply water.
Drinking water system in plateau regions :
- Bandharas are check dams or diversion which were build across rivers. Such a traditional system was found in Maharashtra.
- In some regions, small pits were dug to collect water.
Question 3
Find out the source of water in your regions/locality. Is water from this source available to all people living in that area ?
Answer:
The main source of water in our region (Delhi) is river Yamuna, upper Ganga canal, Bhakra storage and ground water. Water after being treated is supplied to the residents through a system of water pipes.
The water is available to all the people living in the area.
(Note : Students should write about the locality (region around them.)
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Question 1
What changes would you suggest in your home in order to be environment friendly?
Answer:
We would suggest following changes in our home to make it environment friendly.
- Separate wastes into recyclable and non-recyclable.
- Use electricity judiciously.
- Follow three R’s (Reduce, Recycle and Reuse).
- Eat as much as you require but do not waste food.
- Use water judiciously.
- Reuse newspapers and use less plastic.
- Have more windows in the house for natural light.
- T.V., fans, lights etc should be turned off while going outside the room. Less use of heaters. Try wearing sweaters instead.
- Public transport should be used instead of private vehicles.
Question 2
Can you suggest some changes in your school which would make it environment friendly ?
Answer:
Following changes can be made in schools to make it environment friendly.
- Plant enough trees in the school.
- Leaking taps should be repaired so that water is not wasted.
- Bring food in reusable boxes, not in plastic bags or in aluminium foil.
- Teachers can educate students about environmental conservation.
- There should be more windows in school for natural light.
Question 3
We saw in this chapter that thue are four main stakeholders when it comes to forests and wild life. Which among these should have the authority to decide the management of forest produce ? Why do you think so ?
Answer:
The people living in and around the forests and the forest department of The Government could be given the authority to manage the forests because the forest department of the Government has sufficient power and resources that can manage the forest resources well. The people living in and around forests know about the forest products and use them only according to their needs. In addition to this, they would not damage the forests and use forests sustainably.
Question 4
How can you as an individual contribute or make a difference to the management of (a) forests and wild life (b) water resources and (c) and petroleum ?
Answer:
(a) As an individual we can contribute the following to conserve forest and wildlife.
- Trees should not be cut. If trees needed to be cut, then new trees should be planted in their place.
- Trees should be saved from fire.
- Forest animals should be protected and their illegal hunting should be prohibited. Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
(b) As an individual we can contribute the following in the management of water resources.
- Tap should be closed when water is not in use while brushing, shaving, washing hands.
- Protect water sources from getting polluted.
- If there is any leak in water distribution system, then repair it or inform concerned agency.
(c) As an individual we can contribute the following in the management of coal and petroleum.
- Public transport should be used instead of private vehicle. It saves petrol.
- Do not use electricity in vain.
- Switch off the vehicle at the red light if you have to wait for too long.
- Wear extra sweater instead of using heaters.
- Use LPG or CNG.
Question 5
What can you as an individual do to reduce your consumption of the various natural resources ?
Answer:
We can do the following as an individual to reduce our consumption of the various natural resources.
- Follow the principle of three R’s i.e., Reduce, Recycle and Reuse.
- Plastic bags should be reused for the storage of food and small things.
- Food should be taken as per requirement.
- Reusable bottles should be used to store water everyday.
- The devices based on renewable sources of energy like solar cell, solar heater, etc. should be used.
Question 6
List five things you have done over the last one week to
(a) conserve our natural resources.
(b) increase the pressure on our natural resources.
Answer:
(a) To conserve our natural resources :
- Saved electricity by switching off the lights, fans, television and other electrical appliances when not needed.
- Used energy efficient electrical appliances. This is done by using compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) and fluorescent tube lights instead of traditional filament type electric bulbs.
- Used public transport for school instead of parent’s car.
- Took bath with less water than before and did not waste water.
- Took part in community awareness meetings regarding environmental conservation.
(b) To increase the pressure on natural resources :
- Used more paper than required for printing on my computer.
- Kept the fan on even when I was not in the room.
- Wasted food.
- Burnt crackers.
- Wasted petrol by unnecessarily starting the motorbike.
Question 7
On the basis of the issues raised in this chapter, what changes would you incorporate in your life-style in a move towards sustainable use of our resources ?
Answer:
We would bring following changes in our lifestyle so that sustainable use of our natural resources can be encouraged.
- We should limit our personal and collective needs beyond laws, rules and regulation so that the benefit of development can be made available to all and future generations.
- Close the tap when not in use.
- Turn off the lights, fans etc. in home, school or office when not in use.
- Make least use of polythene bags and these should not be thrown in garbage.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Management of natural resources: Conservation and judicious use of natural resources. Forest and wildlife; Coal and Petroleum conservation. Examples of people’s participation for conservation of natural resources. Big dams: advantages and limitations; alternatives, if any. Water harvesting. Sustainability of natural resources.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 16 |
| Chapter Name | Management of Natural Resources |
| Number of Questions Solved | 16 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Question 1.
What changes can you make in your habits to become more environment-friendly?
Answer:
We should use the formula of three R’s in our home in order to be environment friendly.
- Reduce, i.e. to use less, and save the water and the electricity by stopping their wastage.
- Recycle, i.e. to segregate the waste so that materials which can be recycled should be dumped in a place for recycling.
- Reuse, i.e. to reuse certain materials like bottles Of jams and pickles for storing other kitchen items, etc.
Question 2.
What would be the advantages of exploiting resources with short-term aims?
Answer:
There would be no advantage of exploiting resources with short-term aims. Their exploitation may appear to be advantageous in the short-term but it is highly disadvantageous in the long- term. By doing so, we may be able to enjoy the comforts Of life but we would damage our environment gradually.
Question 3.
How would these advantages differ from the advantages of using a long-term perspective in managing our resources?
Answer:
The exploitation of natural resources with short-term aims are advantageous for present generation to meet their daily requirements whereas management of natural resources with long-term perspective are aimed to fulfill the needs of future generation and to maintain their sustainability.Question 4.
Why do you think there should be equitable distribution of resources? What forces would be working against an equitable distribution of our resources?
Answer:
Everybody has equal rights over natural resources and also everybody should get the benefits from them. Therefore, equitable distribution of resources is essential to ensure that everybody gets their due benefit. But many forces go against the equitable distribution of natural resources. The geographical factors are the most important factors which do not allow equitable distribution of natural resources. Economy is another factor which prevents equitable distribution Of these resources.
Page 273
Question 1.
Why should we conserve forests and wildlife?
Answer:
We should conserve forests and wildlife for preserving our environment. They together maintain an ecological balance Of nature. We should conserve them for our economic and social growth and to meet our material aspirations.
Question 2.
Suggest some approaches towards the conservation of forests.
Answer:
The principles of three R’s should be followed to conserve the forests. In addition to this, all stakeholders should be made a part of any conservation programmes. Also, the interests of local forest dwellers should always be kept in mind while Organising a conservation programme.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Question 1.
Manu and Dheer goes to same school, but their parents drop and pick them separately. After learning about natural resources and their management, they talked to their parents, who arrived on few decisions. What could be the best possible decisions among those given below.
(a) To walk the small distance to school
(b) Car pool
(c) Use common school bus at nearby stop
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) To save the resources like petrol and diesel used in cars, one can walk to their destination, if it is close, car pooling can be done by people sharing same locations, etc. These practice will save the natural resources and reduce environmental pollution.
Question 2.
The pH of water sample collected from a river . was found to be acidic in the range of 3.5 – 4.5. On the banks of the river were several factories that were discharging effluents into the river. The effluents of which one of the following factories is most likely to cause low pH of river water? [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Soap and detergent factory
(b) Lead battery manufacturing factory
(c) Plastic cup manufacturing factory
(d) Alcohol distillery
Answer:
(b) Lead is a major constituent of lead-acid battery used extensively in car batteries. The discharge from lead battery manufacturing factory can lower the pH of river water by making it acidic.
Question 3.
Varun has read about some national movements associated with conserving environment and its resources. Chipko movement was one tree hugging movement in which the villagers compelled axemen to stop the cutting of trees by embracing and encircling trees. Help him in finding out the person who was not related with this movement?
(a) Rajendera Singh
(b) Gaura Devi
(c) Sunder Lai Bahuguna
(d) Chandi Prasad Bhatt
Answer:
(a) Rajendra Singh was not associated with the Chipko movement. Chipko movement was meant for protection of trees from excessive commercial exploitation and was instigated by Sunder Lai Bahuguna and Chandi Prasad Bhatt.
Question 4.
Due to several human activities, waterbodies are polluted resulting in decreased availability of usable water. Maya was testing the samples of polluted water in lab. The presence of which factor will confirm to her that the water sample is polluted.
Select the correct option.
(a) The presence of coliform bacteria
(b) High BOD
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(c) In polluted water sample, coliform bacteria are present. Biochemical Oxygen Demand is BOD. High BOD indicates that water is polluted.
Coliform bacteria occurs in waterbodies where human excreta and deadbodies are disposed off.
Question 5.
The construction of large dams has faced a lot of oppositions like the Sardar Sarovar Project on river Narmada lead to Narmada Bachao Andolan. Raj has to identify the correct problem that lead to such strong oppositions against construction of such dams.
Choose the correct option.
(a) Large areas of agricultural land and human habitation submerged
(b) Destruction of large ecosystem and loss of biological diversity
(c) Displacement of large number of local population without adequate rehabilitation
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All the given statements are correct. Construction of large dams leads to disappearance of agricultural land, disposal of human habitation.
Thus, disturbing an ecosystem along with its diversity. People are displaced from their homes ” without any recommendation of living space and profession.
Question 6.
Ganga has been considered as a symbol of purity but is grossly polluted by waste dumped in it. Government has been making plans to revive this basin. Which steps should according to you be incorporated in the plan to prevent any further polluting of this river? Choose the correct option.
(a) Renovation of sewage pumps and treatment plants
(b) Extension of sewerage in unsewered areas to bring waste from those areas to treatment plants
(c) Installation of new treatment plants
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All the strategies can be incorporated in the plan of action to make river Ganga pollution free.
Question 7.
Madhur was reading about rainwater harvesting and its benefits. He came to learn about different types of structures that are build in different states to conserve rainwater. Select the correct option which represent such structures.
(a) Bhundhis
(b) Khadins
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Compost pit
Answer:
(c) Khadins and Bhundhis are the traditional rain harvesting systems used in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, respectively.
Question 8.
A student reading an article on sustainable development came across some statements which confused him. Those statements are being given below.
Choose the incorrect statement from therm by selecting an option.
(a) Economic development is linked to environmental conservation
(b) Sustainable development encourages development for current generation and conservation of resources for future generations
(c) Sustainable development does not consider the view points of stakeholders
(d) Sustainable development is a long planned and persistent development
Answer:
(c) Statement (c) is incorrect because sustainable development do consider the interest of stakeholders, i.e. people with dependency on the natural resources and are affected by any project or its outcome directly or indirectly.
Question 9.
A programme called “silviculture” was started to replenish the forest resource, so as to meet the diverse needs of living beings. According to you, which statements from those given below will not be considered an advantage of this initiative.
(a) It maintains a perfect water cycle in nature
(b) It prevents soil erosion.
(c) It encourages plantation of multipurpose trees in open lands of urban area
(d) It produces a large quantity of raw materials for industry
Answer:
(c) Silviculture encourages plantation of multipurpose trees in open lands of urban area is not advantageous because they can be cut down when necessity for more land crops up is required.
Question 10.
Many international treaties and protocols have been developed and signed by different countries to reduce production of greenhouse gases and environment pollution. A treaty/protocol to reduce C02 emission was
(a) Montreal protocol (1987)
(b) Kyoto protocol (1997)
(c) Helesinki declaration (1989)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) The Kyoto protocol was signed by various countries pledging to regulate the emissions of CO2. India signed this protocol in Aug. 2002 and has reduced its CO2 emission by 5.2% till now.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources (Hindi Medium)





Class 10 Science Management of Natural Resources Mind Map
MANAGEMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Natural resources are resources that exist without actions of humankind. They can be abiotic (such as air, water, land, mineral, ores, etc) or biotic (such as plants, animals, fossil fuels as they are obtained from decaying organic matter).
Natural resource management is an interdisciplinary field of study that considers the physical, biological, economic and social aspects of handling natural resources. It involves putting resources to their best use for human purposes in addition to preserving natural systems.
Why Do We Need To Manage Our Resources?
- All the things we use or consume such as food, clothes, books, toys, furniture, tools and vehicles are obtained from resources on this earth.
- A majority of natural resources is limited.
- Human population is increasing at a tremendous rate.
- Utilization of natural resources is increasing at an exponential rate.
- Need to conserve resources for future generations.
- Equal distribution of resources for equal benefit.
- Need to reduce the damage caused to the environment while these resources are either extracted or used.
Forests And Wild Life
Forests are ‘biodiversity hot spots’. Biodiversity hotspots are the regions with very high levels of species richness & high degree of endemism. It is very important to preserve biodiversity we have inherited as loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ecological stability.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are:
- The people who live in or around forests are dependent on forest produce for various aspects of their life.
- The Forest Department of the Government which owns the land and controls the resources from forests.
- The industrialists who use various forests’ produce, but are not dependent on the forests in any one area.
- The wild life and nature enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
When we consider the conservation of forests, we need to look at the stakeholders.
Let us look at an example for this:
The local people depend on forests for their firewood, timber, thatch, food, fruits, nuts, as well as medicine. In addition, their cattle also graze in forest areas or feed on other fodder which is collected from forests.
However, when vast tracts of forests have been converted to monocultures of pine, teak or eucalyptus for industrial use, a large amount of biodiversity in the area was destroyed. In addition, the varied needs of the local people (fodder, herbs, fruits & nuts for food) can no longer be met from such forests.
Hence, conserv ation of forests resources must be done at the broader level and should consider each and every group of stakeholder associated with forests resources.
In other words, while the environment is preserved, the benefits of the controlled exploitation should go to the local people, a process in which decentralised economic growth and ecological conservation go hand in hand.
Example of People’s Participation in the Management of Forests
Amrita Devi Bishnoi, in 1731 sacrificed her life along with 363 others for the protection of’khejri’ trees in Khejrali village near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
The Chipko Andolan, result of a grass-root level effort to end the alienation of people from their forests. The movement was originated in a remote village called Reni in Garhwal during the early 1970s.
In 1972, the West Bengal Forest Department failed in reviving the degraded Sal forests in the southwestern districts of the state.
With the active and willing participation of the local community, the sal forests of Arabari underwent a remarkable recovery by 1983, a previously worthless forest w’as valued Rs 12.5 crores.
Pollution Of The Ganga
Ganga Action Plan, a multi-crore project came about in 1985 because the quality of the water in the Ganga was very poor. Several factors responsible for this poor condition of the river are:
- Hundred of towns & cities pour their garbage and excreta into it.
- Large amount of untreated sewage is dumped into the Ganges every day.
- In addition, human activities like bathing, washing of clothes & immersion of ashes or un-burnt corpses also lead to the huge amount of pollution in the river.
- Lastly, industries contribute chemical effluents to the Ganga’s pollution load which kills fish in large sections of the river.
Three R’s
Reduce: This means that you use less. For e.g. saving electricity by switching off unnecessary lights & fans, save water by repairing leaky taps etc.
Recycle: This means that you collect plastic, paper, glass & metal items & recycle these materials to make required things instead of synthesising or extracting fresh material. It requires proper segregation of wastes to prevent the dumping of recyclable materials along with other wastes.
Reuse: In this strategy, one simply use things again & again for e.g. plastic or glass bottles used for packaging of food can be used for storing things in the kitchen.
Coal And Petroleum
Coal and petroleum were formed from the degradation of bio-mass millions of years ago & hence they will be exhausted in the future no matter how carefully we use them i.e. they are exhaustible resources.
The management of these resources includes sustainable use of these resources, finding the alternative in forms of renewable energy such as solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy etc, and increasing the efficiency of our machines or automobiles.
Water Conservation
Dams: Large dams can ensure the storage of adequate water for irrigation as well as for generating electricity.
Canal systems leading from these dams can transfer large amounts of water to greater distances. For e.g. Indira Gandhi Canal has brought greenery to considerable areas of Rajasthan.
However, constructions of large dams address three problems in particular:
- Social problems as they displace large no. of peasants & tribals without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
- Economic problems, they invest huge amounts of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
- Environmental problems, they contribute enormously to deforestation & loss of biological diversity.
- Water Harvesting: Watershed management emphasises scientific soil and water conservation in order to increase the biomass production.
- Various organisations have been working on rejuvenating ancient systems of water harvesting as an alternative to the ‘mega-projects’ like dams.
- These communities have used hundreds of indigenous water saving methods such as dug small pits & lakes, put in place simple watershed systems, built small earthen dams, constructed dykes, sand & limestone reservoirs, and set up rooftop water-collecting units. This has recharged groundwater levels & even brought rivers back to life.
- Water harvesting is an age-old concept in India for e.g. khadins, tanks & nadis in Rajasthan, bandharas & tals in Maharashtra, bundhis in Madhya Pradesh & Uttar Pradesh, altars & pyncs in Bihar, kulhs in Himachal Pradesh, ponds in the Kandi belt of Jammu region, eris (tanks) in Tamil Nadu, surangams in Kerala, and kattas in Karnataka.
- Their main purpose of water harvesting is not to hold surface water but to recharge the ground water beneath. The advantages of storing ground water are:
- It does not evaporate, but spreads out to recharge wells & provides moisture for vegetation over a wide area.
- It does not provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Ground-water is also relatively protected from contamination by

Important Questions of Management of Natural Resources Class 10 Science Chapter 16
Question 1.
Switching off unnecessary lights and fans and repairing leaking taps correctly defines which terms of 5R’s?
(a) Recycle
(b) Reuse
(c) Repurpose
(d) Reduce (2020)
Answer:
(d) Reduce
Question 2.
“We need to manage our resources.” List two reasons to justify this statement. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
We need to manage our natural resources because (i) the resources of the earth are limited and (ii) the proper management of our resources ensures their equitable distribution.
Question 3.
List two items which can be easily recycled, but we generally throw them in the dust-bins. (AI 2014)
Answer:
Newspapers and tin cans are the two items that can be easily recycled.
Question 4.
How do advantages of exploiting natural resources with short term gains in mind differ from the advantages of managing our resources with a long-term perspective? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
The advantages of exploiting resources with short term aim is to meet the immediate basic human needs. Short term exploitation of natural resources meets the current demand. It is beneficial for the present generation only whereas management of resources with long term perspective is aimed to fulfil the needs of future generations. Long term use of resources can be achieved through their sustainable use.
Question 5.
Why is an equitable distribution of resources essential in a society? List two forces which are against such distribution. (AI 2017)
Answer:
Equitable distribution of natural resources is necessary so that all and not just a handful of rich and powerful people use them. Two forces against equitable distribution of resources are :
- Industrialisation
- Profit makers who want to make profit from these resources.
Question 6.
“Reuse is better than recycling of materials”. Give reason to justify this statement. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Reuse is better than recycling because the process of reuse does not require any energy as in the case of recycling. I lie reuse strategy comprises using things again and again. For example, used envelopes can be used again to make notes.
Question 7.
What is sustainable development? State its two main objectives. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Sustainable development can be defined as management of available resources and development of new techniques for use ol natural resources to meet the changing basic human needs, at the same time preserving the resources for the need of future generations. The two main objectives of sustainable development are:
- To reduce the dependence on the conventional sources and adopt non-conventional sources of energy.
- Evolving new technology and conserving natural resources.
Question 8.
(a) Why do we need to manage our resources carefully?
(b) Why management of natural resources requires a long term perspective? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(a) The resources of earth are limited and their demand is increasing day by day with ever growing population. So, we have to avoid their wastage and should properly manage, conserve and replenish our natural resources.
(b) Management of natural resources requires a long term perspective so that they can last for generations to come and may not be merely exploited for short term gains.
Question 9.
What is meant by “sustainable management”?
Why is reuse considered better than recycling? (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Sustainable management means managing the use of natural resources in a way that they fulfill the needs of present generation and are also conserved for future generations.
Reuse is considered better than recycling because reusing products reduces the amount of waste and saves energy needed to recycle it.
Question 10.
Everyone of us can do something to reduce our personal consumption of various natural resources. List four such activities based on 3R approach. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Activities which can reduce consumption of natural resources are as follows:
- If we take public transport instead of private transport to travel to our destinations then we can help reduce the use of fossil fuels.
- Reusing the water used for washing vegetables, to water plants in the garden can help in saving water.
- Repairing and reusing old mobiles, televisions, etc., help reduce consumption of natural resources.
- Promoting the use of furniture made of metals, fabrics, etc., instead of wood can help to reduce the cutting of trees for making such items.
Question 11.
Why is sustainable management of natural resources necessary? Out of the two-reuse and recycle-which, in your opinion is better to practise? Give reason. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Sustainable management of natural resources is necessary because:
(i) The resources of the earth are limited and because of the rapid increase in human population, the demand for resources is increasing day by day. Proper management can ensure that the natural resources are used judiciously so that they fulfill the needs of present generation and also last for the generations to come.
(ii) It also takes into consideration long-term perspective and prevents exploitation of natural resources for short-term gains.
The process of ‘reuse’ is better than that of ‘recycling’ because some energy is used to recycle old objects but no energy is required during reuse.
Question 12.
What is meant by three types of ‘R’ (3Rs) to save the environment? Explain with examples how would you follow the 3Rs in your school to save the environment. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
3Rs to save tire environment are reduce, recycle and reuse. For sustainable use of resources, the three Rs can be practised in school in following ways:
Reduce : Switching off unnecessary lights and fans when not in use, avoiding wastage of food, closing of over flowing taps.
Recycle : Students should segregate the wastes generated in classroom and should discard them in separate dustbins for their proper disposal. Reuse : Certain items can be reused like old books should not be thrown instead can be given to junior students for their use.
Question 13.
Write two advantages of sustainable management of natural resources. Out of the two – reuse and recycle – which is better and why? (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Two advantages of sustainable management of natural resources are :
(i) It avoids wasteful use of natural resources.
(ii) Benefits of the resources are conserved for present as well as future generations.
Of the two, reuse and recycle, reuse is better because reusing an item helps to conserve energy that may be required to recycle it.
Question 14.
Why is sustainable management of natural resources necessary? Out of the two methods – reuse and recycle – which one would you suggest to practise and why? (AI 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 11.
Question 15.
State the meaning of “sustainable management”. Reuse is better than recycling. How? (Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 9.
Question 16.
How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Suggest any three methods. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
In our daily lives, we generate a lot of useless materials and discard them. The useless left over or discarded materials are termed as wastes. Disposal of waste materials is a global problem of high magnitude. Waste disposal literally means getting rid of wastes. We can help in reducing the problem of waste disposal by adopting following approaches:
(i) Reduce : This means that we can use less of the things or resources. For example, we can reduce the use of electricity by switching off unnecessary lights and fans or the use of water by turning off the tap while brushing or shaving. We can use both sides of paper, for writing, do not waste food or take only that much food which we can finish, etc. Thus, by adopting such methods, we can reduce the problem of waste disposal to a larger extent.
(ii) Recycle : There are certain items such as plastic, clothes, paper, glass, metal, etc., in our houses which are usually thrown in the garbage when not of any use. This should not be practiced and we should try the practice of recycling. We should segregate wastes into biodegradable (domestic sewage, livestock wastes, etc.) and non- biodegradable (plastics, glass, metals, etc.). The biodegradable wastes should be dumped into preplanned site to be converted into manure or landfilling. The non-biodegradable wastes should be sent to respective recycling units where these are remoulded and again put to use.
(iii) Reuse : The reuse strategy comprises using things again and again. For example, instead of throwing away used plastic bottles in which we buy various food items like jam or pickle, tea leaves, sweets, etc., we can use them for storing things in the kitchen. Mobile phones, camera, TV sets should be repaired when required instead of throwing them and getting new ones. Newspapers and magazines can be used to make envelopes and paper bags, etc.
Question 17.
Consider the following criticisms that are generally addressed when a new project is launched:
I. Displacement of peasants and local tribals without compensation.
II. Swallowing up large amount of public money without any benefits.
III. Deforestation and loss of biodiversity. The criticisms about large dams in particular are
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) I and III
(d) I, II and III. (2020)
Answer:
(d) I, II and III.
Question 18.
The Reni village of Garhwal is famous for
(a) monocultures of pine, teak and Eucalyptus
(b) Chipko movement
(c) extensive biodiversity
(d) participation of local people in efficient management of forests. (2020)
Answer:
(b) Chipko movement
Question 19.
The major ill effect of monoculture practice in forests is on the
(a) biodiversity which faces large destruction
(b) local people whose basic needs can no longer be met from such forests
(c) industries
(d) forest department. (2020)
Answer:
(a) biodiversity which faces large destruction
Question 20.
What is meant by wildlife? How is it important for us? (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Life in any form (plants or animals), which
exists in its natural hahiLaL is called wildlife. Wildlife is very important for us, as it provides ecological stability by maintaining the food chain. Wildlife is important to us in following ways:
- Wildlife is a renewable source of large variety of commercial products like food, fur, lac, musk, leather, feather, ivory, timber, fibre, fodder, fuel, medicines, etc., which can be used from time to time.
- Wildlife is considered as gene bank, which can be used for producing high yielding plants and animals through the process of selection and hybridisation.
- The wildlife can be used commercially to earn money through tourism (jungle safari, etc.) as it provides best means of sports and recreation.
Question 21.
Management of forest and wild life resources is a very challenging task. Why? Give any two reasons. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Management of the forest and wildlife resources is considered as a challenging task as there are many stakeholders of forest. These stakeholders are directly or indirectly involved in forest and wildlife resources. These stakeholders are :
- The people who live in or around forests and are dependent on forest products for various aspects of their lives.
- The industrialists who use various forest products and the wildlife enthusiasts who want to conserve the forest and wildlife.
- The Forest Department of the Government which owns the land and controls the resources from forests.
Maintaining the interest of all the stakeholders is a challenging task as:
- Due to industrialisation and urbanisation forest resources are depleting.
- There are profit makers who want to make money from this resource.
Question 22.
Why must we conserve our forests? List two factors responsible for causing deforestation. (AI 2017)
Answer:
We must conserve our forests as they are useful resources. Forests are useful to us in many ways:
- They provide living places (natural habitats), shelter, protection and food to our wildlife.
- They provide timber for making furniture, houses, boats and other useful things of daily use.
- They provide raw materials for paper, rayon and many other industries,
- They are the rich source of many other things like honey, lac, medicines, dyes, katha, sandalwood, spices, etc.
- They help in maintaining a balance of gases like CO2 and O2 in the atmosphere, etc.
Two main reasons for deforestation are as follows:
- Indiscriminate felling of trees for the purpose of timber, fuel and industrial demand of wood, building dams, etc.
- Over-grazing by a large livestock population.
Question 23.
State two advantages of conserving (i) forests, and (ii) wildlife. (Al 2017)
Answer:
Two advantages of conserving forests and wildlife are:
(i) Forests
(a) Forests provide us a number of valuable goods i.e., wood, spices, rubber, etc.
(b) Forests help to reduce atmospheric pollution. They absorb CO2, collect suspended particles and reduce noise.
(ii) Wildlife
(a) Wildlife helps to maintain ecological balance of nature.
(b) Wild animals are a source of valuable products like ivory, honey, musk, etc.
Question 24.
Explain giving example where active involvement of local people lead to efficient management of forest. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Active participation of public and their support must be generated in order to conserve our forests and wildlife to achieve the real goal of eco- developmenl. An example of public participation in conservation of forest and wildlife is the case of the Bishnoi Community in Rajasthan. In 1731, Amrita Devi Bishnoi sacrificed her life along with 363 others for the protection of’Kheiri’ trees in Khejarli village near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Question 25.
“What was Chipko Andolan”? How did this Andolan ultimately benefit the local people and the environment? (AI 2016)
Answer:
The Chipko Andolan (tree hugging movement) is an example of the contribution of common people towards the conservation of forests. The Chipko Andolan originated from an incidence in a remote village of Garhwal, high up in the Himalayas in the early 1970s. A logging contractor had been allowed to cut down trees in a forest close to a village. The people of the village did not want this forest to be cleared because it would spoil their healthy environment. One day, when the men folk of the village were out for work, the contractor’s workers came in the forest to cut down the trees.
In the absence of men, the women of the village reached the forest quickly and clasped the tree trunks with their arms, preventing the workers from cutting them down. The forest trees were thus saved. The Chipko movement quickly spread across all the communities and helped in the conservation of forests thereby contributing to the service of mankind. Both local people and environment were benefitted due to conservation of food, fodder, fuel, fibre and fertiliser trees.
Question 26.
Forests are “biodiversity hotspots”. Justify this statement. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Forests are reservoirs of diversity. They contain different species of plants, animals and all sorts of living organisms. Forests are also under severe threat due to ‘habitat loss, climate change and extensive species loss. Hence, they are considered as biodiversity hotspots.
Question 27.
List four stakeholders which may be helpful in the conservation of forests. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Major stakeholders of forest resources are:
- Local people
- The Forest department of the Government
- The Industrialists
- The nature and wildlife enthusiasts
Question 28.
List four causes of damage to forests. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Four causes of damage to forests are:
- Increasing human population necessitates the expansion of human habilitation which requires clearing of forests to make more land available for residential purposes.
- Rapid industrialisation also mandates setting up of new factories. Land for factory set up is also made available by clearing forests.
- Ever increasing human population increases the demand of fresh supply of wooden furniture and other items for which trees are cut.
- Forest fires resulting from mishandling of inflammable objects, left unattended campfire, negligently discarded cigarettes etc., by humans causes damage to forests on a large scale.
Question 29.
How did ‘Chipko Andolan ultimately benefit the local people? Explain briefly. (Foreign 2016)
Answer:
Refer to answer 25.
Question 30.
List four measures that can be taken to conserve forests. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Measures to conserve forests are :
- Afforestation – Plantation of trees to meet basic needs.
- Instead of cutting trees for fuel wood we should use alternative sources of energy such as biogas.
- By adopting agro and urban forestry methods.
- By limiting human interference such as settlement, cropping, recreation, etc.
Question 31.
Why are forests considered “biodiversity hot¬spots”? List two ways in which an individual can contribute effectively to the management of forests and wildlife. (Delhi 2015, Foreign 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 26.
Two ways in which individuals can contribute effectively to the management of forests and wildlife are:
- By protecting the natural habitats of wild animals by identification, breeding, nursing habitats of each species.
- By planting trees and by maintaining the wildlife protected areas.
Question 32.
What is biodiversity? What will happen if biodiversity of an area is not preserved? Mention one effect of it. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of living organisms on earth or in a particular habitat. Biodiversity forms the foundation of the vast array of ecosystem services (pollination, food, timber, spices, etc.) that critically contribute to human well being. Biodiversity boosts ecosystem productivity where each species, no matter how small, has an important role to play. Hence, biodiversity is required for maintaining ecological balance. Loss of biodiversity will disturb ecological balance and create an ecological imbalance. Moreover it will deprive humans of some important ecological services.
Question 33.
What is meant by biodiversity? List two advantages of conserving forests and wildlife. (AI 2015, Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answers 32 and 23.
Question 34.
List two problems that may arise by planting trees of single variety over vast tracts of forest. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Two major problems that may arise by planting trees of single variety over a vast tract of forest are:
- Loss of biodiversity
- Varied need of the local people will not be fulfilled.
Question 35.
List two criteria of measuring the biodiversity of an area. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
The basic criteria of measuring the biodiversity of an area are:
- The presence of varied number of organisms and the type of ecosystem present in the area.
- Indicator organisms are also a measure of biodiversity.
Question 36.
Monoculture of a particular type of tree is no substitute for natural forests. List two reasons to justify this statement. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Monoculture of few plants is useful for few industries. It is a source of earning for the forest department only but leads to loss of biodiversity and also varied needs of villagers and local people cannot he met. Hence, it cannot he a substitute of natural forest.
Question 37.
(a) Why should National Parks be allowed to remain in their pristine form?
(b) Why is reuse of materials better than recycling? (AI 2019)
Answer:
(a) National parks are the areas maintained by government and reserved for betterment of wildlife. It is a place where cultivation, grazing, forestry, habitat manipulation and other activities are restricted. They are allowed to remain in their pristine form because they contain highest biological diversity, natural habitats for many wild animals, flora and fauna. National parks are essential for stability of ecosystem and having influence on health and social prosperity. If these parks will not remain in their pristine form then the sustainable benefits for the present as well as future strategies will not obtained. We can easily harvest useful genes to develop high yielding plants and animals to remain them in their pristine form because population recovers in natural habitat.
(b) Reuse is better than recycling because the process of reuse does not require any energy as in the case of recycling. The reuse strategy comprises using things again and again. For example, newspapers and magazines can be used to make envelopes.
Question 38.
Which one of the following is responsible for the sustenance of underground water?
(a) Loss of vegetation cover
(b) Diversion for high water demanding crops
(c) Pollution from urban wastes
(d) Afforestation (2020)
Answer:
(d) Afforestation
Question 39.
A diagram of traditional water harvesting system is given below:
The statement which defines the system and its parts is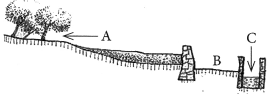
(a) This is an ideal setting of the Khadin system and A = Catchment area; B = Saline area and C = Shallow dugwell.
(b) This is an ideal setting of the Shallow dugwell system and A = Catchment area; B = Saline area and C = Khadin.
(c) This is an ideal setting of Catchment area and A = Khadin, B = Saline area and C = Shallow dugwell.
(d) This is showing Saline area and A = Catchment area; B = Khadin and C = Shallow dugwell. (2020)
Answer:
(a) This is an ideal setting of the Khadin system and A = Catchment area; B = Saline area and C = Shallow dugwell.
Question 40.
Bandharas and Tals are age old water harvesting concepts/structures found in
(a) Bihar
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Rajasthan. (2020)
Answer:
(b) Maharashtra
Question 41.
Which of the following are water intensive crops?
(a) Wheat and rice
(b) Wheat and sugarcane
(c) Sugarcane and rice
(d) Wheat and gram (2020)
Answer:
(c) Sugarcane and rice
Question 42.
Water is a valuable resource. List two ways that you would suggest every family member to save this resource. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Water is a valuable resource and to save this resource two suggestive methods are :
- Preventing wastage of water, in household by turning off tap when not in use while brushing, shaving, etc., and in public places.
- Promoting reusing water like water used for washing vegetables can be reused for watering garden plants.
Question 43.
List two measures that you would suggest for the better management of water resources. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 42.
Question 44.
What is watershed management system? List two benefits derived by the communities that participate’ in this system. (AI2014)
Answer:
Watershed management emphasises scientific soil and water conservation in order to increase the biomass production. The aim is to develop primary resources of land and water so that they can be used to produce secondary resources of plants and animals without causing the ecological imbalance. Benefits derived from watershed management are:
- It identifies degraded area of land and emphasises the need of the improvement of quality and quantity of clean water to the local community and thus ensures their participation.
- Construction of a series of long trenches and mounds to hold rain water and allow it to percolate into the ground, thus increasing the groundwater.
Question 45.
List two advantages of building dams. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Two advantages of building dams are :
- It helps in irrigation.
- It helps to generate electricity.
Question 46.
List two causes of pollution of river Ganga. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
The two causes of pollution of river Ganga are:
- Increasing human activities like bathing, washing clothes, bathing of animals, in river water.
- Dumping of industrial wastes and ashes of corpses which are cremated in the water of river Ganga.
Question 47.
Explain two main advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level. (AI 2017)
Answer:
Two advantages of water harvesting at community level are:
- Water can be used for irrigation.
- Water can be used to recharge wells and to raise the water table.
Question 48.
List four advantages of properly managed watershed management. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Four advantages of properly managed watershed management are:
- It increases the crop production.
- It increases the income of the watershed community.
- It reduces the menace of drought and floods.
- It enhances the life of downstream dams and reservoirs.
Question 49.
What is water harvesting? How can this technique help in the conservation of water? (AI 2016, AI 2014)
Answer:
Water harvesting is the technique used to capture and store rainwater for future use by making special water harvesting structures. Properly stored rainwater can be used for human consumption, irrigation and can be used to raise the water table. Hence, it helps in the conservation of water.
Question 50.
The construction of large dams leads to social and environmental problems. List two problems of each category. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Social and environmental problems that arise due to building of dams are:
(a) Social problems :
- People residing in the area where dam is being built are rendered homeless.
- Unequal distribution of water is another social problem.
(b) Environmental problems :
- Deforestation
- Loss of biodiversity
Question 51.
List two advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level. (Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 47.
Question 52.
List two main causes of the pollution of water of the river Ganga. State how pollution and contamination of the river water prove harmful for the health of the people of neighbouring areas. (AI 2015)
Answer:
Two main causes of pollution of water of river Ganga are:
- Human activities like bathing, washing clothes and cleaning of animals in the river water makes the water dirty.
- Dumping of materials used in religious rituals like objects of worship (idols, sticks, flowers, sweets, plates made of banana leaves, etc.) as well as dumping ashes generated after cremation of dead bodies also pollutes river water.
Such contaminated and polluted river water poses various health hazards to the people living nearby. It contains various pathogenic microbes that cause diseases like typhoid, cholera, jaundice, etc., in the people who consume it. Bathing in such water can cause various skin diseases in humans.
Question 53.
List four advantages of water stored in the ground as “groundwater”. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Four advantages of conserving water in the form of groundwater are :
- It does not evaporate hence can be used for longer time.
- It provides moisture for vegetation over a large area.
- It remains protected from contamination and hence is fit for human consumption.
- Groundwater does not become a breeding site for mosquitoes.
Question 54.
Building of big dams gives rise to some problems. List three main problems that may arise. Suggest a solution to any one of these problems. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
The three problems which arise due to construction of big dams are :
- Social problems : Building of dams cause displacement of large number of local people without sufficient compensation and rehabilitation.
- Economic problems : Large amount of money is used for construction of dams.
- Environmental problems : Construction of dams leads to enormous deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
A proper compensation must be given to the local people who are rendered homeless due to building of the dam.
Question 55.
List four advantages of conserving water in the form of groundwater. (Foreign 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 53.
Question 56.
List four advantages of water stored in the ground. (Foreign 2014, Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 53.
Question 57.
List and explain any two advantages associated with water harvesting at community level. (Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Refer to answer 47.
Question 58.
List three problems which arise due to construction of big dams. Suggest a solution for these problems. (AI 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 54.
Question 59.
What is water harvesting? List two main advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level. Write two causes for the failure of sustained availability of ground- water. (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Refer to answers 49 and 47.
Two causes for the failure of sustained availability of groundwater are:
- Loss of vegetation cover
- Pollution from industrial effluents and wastes.
Question 60.
What is dam? Why do we seek to build large dams? While building large dams, which three main problems should particularly be addressed to maintain peace among local people? Mention them. (2018)
Answer:
Dams are large water storing bodies usually built across the river to hold and regulate the flow of water. After independence, emphasis was laid on construction of large dams because large dams served dual purpose-storage of huge amount of water and helped in generation of electricity. From the dams, bigger canals and smaller canals are connected to supply water to the needy areas.
The three problems which arise due to construction of big dams are as follows :
- Building of dams causes displacement of large number of local people without sufficient compensation and rehabilitation. A proper compensation must be given to the local people who are rendered homeless due to building of the dam.
- Mismanagement and no equitable distribution of water from canals leads to discontentment of local people who live farther downstream from the dam.
- Construction of dams leads to enormous deforestation and loss of biodiversity directly or indirectly effecting the local people who depend mainly on the forests and its products for their livelihood.
Question 61.
(a) Water is an elixir of life, a very important natural resource. Your science teacher wants you to prepare a plan for a formative assessment activity. “How to save water, the vital natural resource?” Write any two ways that you will suggest to bring awareness in your neighbourhood on ‘how to save water’.
(b) Name and explain any one way by which the underground water table does not go down further. (Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(a) Water is an important vital natural resource. Freshwater constitutes only a small proportion of total quantity of water present on Earth. However, proper management can lead to conservation of this important renewable resource. It can be preserved by the following ways:
- Taps must be closed after use.
- Water used for washing clothes, etc., can be reused to wash car and for other purposes.
- Water discarded from RO purifier can be used to wash vegetables.
(b) By use of water harvesting technique, underground water can be recharged. It includes digging small pits and lakes, building small
earthen dams, constructing sand and limestone reservoirs and setting up roof top water collecting units. The water from trenches and pits seeps into deeper layer recharging groundwater levels.
Question 62.
The most poisonous product formed by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels is
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) nitrogen dioxide
(c) carbon monoxide
(d) sulphur dioxide. (2020)
Answer:
(c) carbon monoxide
Question 63.
Incomplete combustion of coal and petroleum
(A) Increases air pollution
(B) Increases efficiency of machines
(C) Reduces global warming
(D) Produces poisonous gases.
The correct option is
(a) (A) and (B)
(b) (A) and (D)
(c) (B) and (C)
(d) (C) and (D). (2020)
Answer:
(b) (A) and (D)
Question 64.
“Burning of fossil fuels results in global warming”. Give reasons to justify this statement. (AI 2016)
Answer:
Burning of fossil fuels releases gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen and sulphur. Of these gases, carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, because it traps sun’s heat and keeps earth warm and hospitable. Excess of this gas results in enhanced greenhouse effect causing increase in mean annual temperature of earth (global warming).
Question 65.
List two products of combustion of fossil fuels other than carbon dioxide. What happens when combustion takes place in insufficient air? Name a greenhouse gas. (Foreign 2014)
Answer:
Two products of combustion of fossil fuels other than carbon dioxide are sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
In insufficient air, combustion of fossil fuel produces carbon monoxide.
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas.
Question 66.
Burning of fossil fuels is a cause of global warming. Justify this statement. (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Refer to answer 64.
Question 67.
List the products of combustion of fossil fuels. What are their adverse effects on the environment? (AI 2012)
Answer:
The products of combustion of fossil fuels are carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Following are their adverse effects on the environment:
(i) Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with rain water and make it acidic. It falls on earth as acid rain and damages trees, plants, buildings and metal structures.
(ii) Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. Increase in amount of carbon dioxide in atmosphere causes enhanced greenhouse effect that leads to global warming.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Anything in the environment which can be used is called a natural resource.
Natural Resources includes total natural environment that support human life and contribute to the production of necessities and comforts to mankind. So natural resources are the coihponents of atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere.
Types of Natural Resources: On the basis of abundance and availability, the natural resources are of two types
- Inexhaustible.
- Exhaustible.
(a) Inexhaustible: These are in plenty and cannot be exhausted by man’s consumption. For example; air, sand, clay etc. It gets affected by the over-population of mankind.
(b) Exhaustible: These are limited and can get exhausted over a period of time, i.e., coal, petroleum etc.
Management of Natural Resources: A system of controlling the use of natural resources in such a way, as to avoid their wastage and to use them in the most effective way is called management of natural resources.
Why do we Need to Manage Our Natural Resources: We need to manage our natural resources because of the following reasons :
- The resources of the earth are limited. Because of the rapid increase in human population,
the demand for resources is increasing day-by-day. The proper management can ensure that the natural resources are used judiciously, so that they fulfill the needs of present generation and also last for the generations to come. – - The proper management of natural resources takes into consideration long-term perspective (or view) and prevents their exploitation to hilt for short-term gains.
- The proper management can ensure equitable distribution of natural resources so that all the people can benefit from the development of these resources.
- The proper management will take into consideration the damage caused to the environment during the ‘extraction’ or ‘use’ of the natural resources and find ways and means to minimise this damage.
Conservation of Wildlife: It is very important to conserve wild-life to maintain the ecological balance in nature and to preserve the gene pool. Some of the measures (or steps) to be taken for the conservation of wildlife are given below:
- Laws should be made to impose a total ban on the poaching (killing) or capturing of any animal or bird belonging to an endangered species.
- The natural habitats of wild animals and birds should be preserved by establishing National Parks and Sanctuaries throughout the country.
- The Government Department connected with the conservation of wildlife should conduct a periodic survey in all the forests, National parks and Sanctuaries to have knowledge of the population of all species of wild animals and birds.
- Special attention should be paid to the conservation of endangered species of wild animals and birds to prevent their extinction altogether.
- The unauthorized felling (cutting) of forest trees for timber trade and fuel-wood should be curbed (stopped) immediately.
Forest and wild life conservation: Forests are biodiversity hot spots. Biodiversity of an area is the number of species of different life forms like bacteria, fungi, powering plants insects, birds, etc.
Hotspot means an area full of biological diversity.
loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ecological stability/ecological imbalance.
Stake holders: A person having interest or concern for something is called as a stakeholder.
Sustainable Management: Management of forest resources wisely to make it available for future generations.
To consider the conservation of forests, we need to look at the stakeholders who are :
- The people who live in or around forests are dependent on forest products for various aspects of their life.
- The Forest Department of the Government which owns the land and controls the resources from forests.
- The industrialists—from those who use ‘tendu’ leaves to make bidis to the ones with papermills who use various forest produce.
- The wild life and nature enthusiasts who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
A major program called silviculture has been started to replenish the forests by growing more trees and plants.
Conservation of forests: It is carried out by the following methods
- Afforestation: It is growing of forests on unprotected barren lands. Van Mahotsava is a tree plantation movement carried out twice a year (February and July) by both government and voluntary agencies.
- Reforestation: It is developing forest cover in the area which has been damaged or cleared during exploitation.
- Separation of Commercial Forestry: Useful plants required by industry should be planted separately preferably on waste land. Growing industry required plants is called production plantation.
- Grazing: Grazing should be regulated according to the availability of pasturage.
Deforestation: Removal, decreases or deterioration of forest cover of an area is called deforestation.
Effects of Deforestation
- Soil Erosion: Removal of plant cover exposes the fertile soil to wind and water. The latter remove the top soil and make the area infertile.
- Desertification: Removal of forest cover in the plains makes the area dry. In hot season, the soil becomes loose. Air currents take away the fine soil particles leaving behind sand.
- Floods: In rainy season many temporary rivulets are formed due to loss of absorption capacity by unprotected soil. The rivulets produce floods in low land causing loss to agriculture, property and life.
- Destruction of wildlife: Deforestation leads to destruction of natural habitats of wild animals and plants. Wildlife is, therefore, destroyed.
- Climatic Changes: In the absence of forest cover, the summer becomes hotter while the winters become extra cool. The frequency of rainfall decreases.
National Award for Wildlife Conservation: The Govt, of India, has recently instituted an ‘Amrita Devi Bishnoi National Award for wildlife conservation in the memory of Amrita Devi, who in 1931 sacrificed her life along with 363 other for the protection ‘Khejri Trees’ in Kherali Village near Jodhpur in Rajasthan.
Chipko Andolan: Movement originated in Garhwal in early 1970’s that was the result of a grassroot level effort to end the alienation of people from their forest.
Thus, Chipko Movement (i.e., chipko Andolan) is the tree hugging movement, in which the villagers compel the axeman to stop tree felling by embracing and forming ring (circle) around the marked trees. Example : Protection of Sal Forest in West Bengal in 1972.
Re-use is better than recycling as it saves energy.
Water as a Resource
- Water is a basic necessity for all terrestrial forms of life. Regions of water scarcity are closely
related to the regions of acute poverty. - Failure to sustain water availability has resulted in loss of vegetation cover, diversion for high water demanding crops and pollution from industries and, urban wastes and less rain.
- Irrigation methods like dams, tanks should be used in various part of India.
Advantages of Dams
- Water from a dam is used for irrigation in fields through a network of canals. Dams ensure round the year water supply to the crop fields and help raise agricultural production.
- Water from a dam is supplied to the people in towns and cities through pipelines after suitable treatment. In this way, construction of dams ensures continuous water supply in the region.
- The falling water (or flowing water) from the dam is used for generating electricity. The water rushing down the dam turns turbines which run electric generators.
Disadvantages of Dams
- Social Problems: Due to the construction of high-rise dams, a large number of human settlements (or villages) are submerged in the water of large reservoir formed by the dam and many people are rendered homeless. This creates a social problem.
- Environmental Problems: The construction of high-rise dams on the rivers contributes to deforestation and loss of biodiversity. This is because a vast variety of flora and fauna (plants and animals) get submerged in the water of large reservoir formed by the dam and disturb the ecological balance.
- Economic Problems: Some people say that the construction of high-rise dams involves the spending of a huge amount of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
Forests: Forests are important renewable natural resources dominated mainly by trees forming a sort of canopy, they are essential for the ecological balance of all ecosystems. They maintain the biological ecosystem.
Water Harvesting: Aim is to develop primary resources of land and water and to produce secondary resources of plants and animals for use in a manner which will not cause ecological imbalance.
Various ancient methods of water harvesting
| Methods | State |
| Khadin, tanks, nadis | Rajasthan |
| Banderas, tals | Maharashtra |
| Bundhis | Madhya Pradesh and U.P. |
| Pyhes and Pynes | Bihar |
| Kulhs | Himachal Pradesh |
| Ponds | Jammu Region |
| Eris (tanks) | Tamilnadu |
Baylis – Old method of water harvesting in Delhi and nearby region.
These techniques are local specific to ensure the mismanagement and over-exploitation of these resources.
Advantages of Water Harvesting System
- Water does not evaporate.
- Recharge wells and moisture for vegetation.
- Does not provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
- Ground water is protected from contamination by human and animal waste.
Pollution of Water: The pollution of water is caused by the dumping of untreated sewage and industrial wastes into it.
The contamination of river water can be usually found from two factors :
- the presence of coliform bacteria in river water, and
- measurement of pH of river water.
Gangs Action Plan (GAP): Muticrore project came in 1985 to improve the quality of Ganga. Ganga Action Plan (GAP) was formulated to reduce the pollution load of river Ganga by more than 75%. The water quality has been tested from time-to-time by checking coliform (a group of harmless bacteria in human intestine) number/100 ml.
Accordingly, a survey was conducted and data was collected for total coliform (a group of bacteria found in human intestine) between 1993-1994 which was as below:
MPN – Most Probable Number.
Advantages of Water Stored in the Ground
- The water stored in the ground does not evaporate.
- The water stored in the ground spreads out to recharge wells and provides moisture for crops over a wide area.
- The water stored in the ground does not promote the breeding of mosquitoes (unlike stagnant water collected in ponds or artificial lakes).
- The water stored in the ground is protected from contamination by human and animal waste.
Coal and Petroleum Conservation: Coal and petroleum are fossil fuels found in earth’s
crust. They are non-renewable and exhaustible resources.
1. Coal: Coal is combustible fossilized rock derived from a large accumulation of plant remains that is gradually compressed. Coal is used for cooking, heating, in industry and thermal power plants.
2. Petroleum: Petroleum is another fossil fuel that occurs in the form of liquid oil. It has been formed in the past (about 10 to 20 crore years old) from plant and animal remains and occur in the form of mineral oil in sedimentaiy rocks. Petroleum is mainly used as fuel for transport, agricultural operations, generators and some industries.
Methods of Conservation of Fossil Fuels
- Burning of coal causes air pollution. Thus direct use of coal for the purpose or burning should be avoided. Coal may be converted into liquid fuel and compressed natural gas (CNG) through coal gasification.
- Techniques should be developed to recover maximum fossil fuel that lies in deep mines and wells. Wastage during extraction and transportation should be avoided.
- Both oil wells and coal mines are prone to catch fire. Therefore, these should be well protected from fire to avoid wastage pollution and loss of life and property.
- Over-consumption of oil in automobiles should be checked. We must save oil for future use because only a few years are left for its depletion.
- Alternative sources of energy, such as hydroelectric, nuclear, solar, wind power and biogas plants should be encouraged.
Steps for Conservation of Energy Resources
- Save electricity, water, etc. by not using when not required.
- Use energy efficient electrical appliances to save electricity.
- Use pressure cooker for cooking food.
- Use solar cookers.
- Encourage the use of biogas as domestic fuel.
- Fuel efficient motor vehicle should be designed to reduce consumption of petrol and diesel.
Management of natural resources is needed for the conservation of natural resources.
- There are national and international laws and Acts to protect the environment.
- Ganga Action Plan. Multi Crore Project came in 1985 to improve the quality of Ganga — Accordingly a survey was conducted and a data was collected of total coliform (a group of bacteria found in human intestine) between 1993-1994 National Award for wildlife conservation – In the memory Amrita Devi Bishnoi who lost her life in the protection of Khejri trees in Rajasthan along with 363 other people.
Chipko Movement: Chipko Movement is an example of the contribution of common people towards the conservation of forests. The Chipko Movement also called ‘Hug the tree’ movement originated from an incident in a remote village called ‘Reni’ in Garhwal (Himalayas), where the people of this village clasped the tree trunks with their arms to protect them from being cut down by a contractor’s workers. The people acted this way because they knew that this mass deforestation would spoil their healthy environment. The forest trees were thus saved.
The Chipko Movement quickly spread across all the communities and helped in the conservation of forests and thus helped in safeguarding the environment.
Three R’s to save the environment.
- Reduce: It means we should minimise our use of natural resources, sources of energy and food materials.
- Recycle: It means that we should collect materials like paper, plastics, glass and metal items. These waste materials should be recycled to obtain these materials again for use.
- Reuse: In this strategy, we should be encouraged to use things again and again instead of throwing them away. For example, plastic bottles those we get with jams and pickle can be reused for storing things in the kitchen.
Forest and wildlife conservation: Forests are biodiversity hot spots. Biodiversity of an area is the number of species of different life forms like bacteria, fungi, powering plants insects, birds etc. The main aim of forest conservation is to preserve the biodiversity we have inherited.
Stakeholders: Those persons, who are directly or indirectly involved in using the produce of forests or are interested in the conservation of forests, are called stakeholders.
Hotspot: means an area full of biological diversity. Loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ecological stability/ecological imbalance.
Sustainable management: Management of forest resources wisely to make it available for future generations. Sustainable development is development encourages the judicious use of natural resources to meet the current basic human needs, while preserving the resources for the needs of future generations.
Water as a Resource: Water is a basic necessity for all terrestrial forms of life.
- Regions of water scarcity are closely correlated to the regions of acute poverty.
- Failure to sustain water availability has resulted in the loss of vegetation cover, diversion for high water demanding crops and pollution from industries and urban wastes and less rain.
- Irrigation methods like dams, tanks and coals have been used in various part of India.
Dams: In order to make proper use of river water, dams are constructed across the rivers to regulate the flow of water. A dam has a large reservoir to store huge amounts of water. This stored water is then allowed to flow downstream at the desired rate.
Advantages.
- Water from a dam is used for irrigation in fields through a network of canals. Dams ensure round the year water supply to the crop fields and help raise agricultural production.
- The water rushing down the dam turns turbines which run electric generators to generate electricity.
Disadvantages.
Construction of large dams addresses three problems in particular-
- Social problem. A large number of local people have to be displaced which includes farmers and tribals without their adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
- Economic problem. As dams are built up with huge amounts of public money without the generation of proportionate benefits.
- Environmental problem. Because the making of large dams contributes enormously to deforestation and the loss of biological diversity.
Water Harvesting: Collecting rainwater for use in future by storing it in storage reservoirs is called rainwater harvesting.
Various ancient methods of water harvesting. These techniques are locale specific to ensure the mismanagement and over-exploitation of these resources.
Advantages of Khadin System
- Water does not evaporate
- Recharge wells and moisture for vegetation.
- Does not provide a breeding ground for mosquito
- Groundwater is protected from human and animal waste.
Green House Effect: When the reflected back infra-red rays (of longer wave-length) of the Sun are entrapped by C02 gas of atmosphere, the atmosphere gets warmed. This phenomenon is known as ‘Green House Effect’.
1. A coliform is a group of bacteria, found in human intestines, whose presence in water indicates contamination by disease-causing microorganisms.
2. In 1985, our government started a multi-crore project named as ‘Ganga Action Plan’. The main aim of this project is to improve the water quality of Our holy river Ganga.
3. The water of the river Ganga gets polluted because of the following reasons :
- Dumping of untreated sewage.
- Human activities like bathing or washing of clothes.
- Immersion of ashes or unburnt corpses.
- Chemical effluents from industries.
This all pollutes water, increasing the toxicity level which kills fish in large sections of the river.
4. One should keep in mind the three R’s to save the environment:
Reduce: Using less and less of natural resources.
One can help by switching off unnecessary lights and fans, repairing leaky taps, preventing wastage of food.
Recycling: It minimises the faster depletion of natural resources.
Reuse: It is better than recycling because the process of recycling uses some energy.
5. Economic development is linked to environmental conservation.
6. The concept of sustainable development encourages forms of growth that meet current basic human needs, while preserving the resources for the needs of future generation.
7. The sustainable development : It implies a change in all aspects of life. It depends upon the willingness of the people to change their perceptions of the socioeconomic and environmental conditions around them and the readiness of each individual to alter their present use of natural resources.
8. Sustainable natural resource management demands the following:
- Using resources carefully because these are not unlimited.
- A long term perspective so that these resources will last for the generations to come and will not merely be exploited for short-term gains.
- Equitable distribution of resources so that all and not just a handful of rich and powerful people, benefit from the development of these resources.
- Checking the damage caused to the environment while these resources are either extracted or used,
- Planning for the safe disposal of the waste which is generated when natural resources are either extracted or used.
9. Forests are ‘biodiversity hot spots’. One measure of the biodiversity of.an area is the number of different species found there. However, the range of different life forms (such as bacteria, fungi, ferns, flowering plants, nematodes, insects, birds, reptiles and so on) is also important.
10. One of the main aim of conservation is to try and preserve the biodiversity that we have inherited.
11. A loss of diversity may lead to a loss of ecological stability.
12. Forest resources ought to be used in a manner that is both environmentally and developmentally sound.
13. The destruction of forests not only affects the availability of forest products, but also the quality of soil and the sources of water.
14. Despite nature’s monsoon bounty, failure to sustain water availability underground has resulted largely from the loss of vegetation cover, diversion for high water demanding crops and pollution from industrial effluents and urban wastes.
15. Dams are built to ensure the storage of adequate water not only for irrigation but also for generating electricity. However, building of large dams cause social, economic and environmental problem.
16. Watershed Management: Watershed management emphasises scientific soil and water conservation in order to increase the biomass production. The aim is to develop primary resources of land and water, to produce secondary resources of plants and animals for use in a manner which will not cause ecological imbalance. Watershed management not only increase the production and income of the watershed
: community, but also mitigates droughts and floods and increases the life of the downstream dam and reservoirs.
17. The Chipko Andolan (‘Hug the Trees Movement’) :
It started in a remote village called Reni in Garhwal in early 1970s. In this movement, women of the village used to clasp the tree trunks thus preventing the felling of trees.
Role of Chipko Andolan :
- It helped in conservation and preservation of forests, one of the most important natural resources.
- It allowed the village communities to utilise the forest produce and allowing the resource to replenish over time.
- It taught people that, the destruction of forests not only affects the availability of forest products but also the quality of soil and the sources of water.
- It forced government to rethink the priorities of the local people (to whom the forests belong) in the use of forest produce.
- It encouraged the participation of the local people in the efficient management of forests.
18. Stakeholders of forest:
- People living in or around forest: They depend on forest produce for their living.
- The forest Department of the Government : Which owns the land and controls the resources from forests.
- The industrialists : Who use various forest produce as raw material, but are not dependent on the forest in any orie area.
- The wildlife and nature enthusiasts: Who want to conserve nature in its pristine form.
19. Water harvesting : It is an age-old concept in India which involves capturing rainwater in the large structures which can hold this water round the year. The main purpose is not only to hold the surface water but also to recharge the groundwater beneath.
Advantages of water harvesting :
- The water does not evaporate, but spreads out to recharge wells and provides moisture for vegetation over a wide area.
- It does not provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes like stagnant water collected in ponds or artificial lakes.
- The groundwater is also relatively protected . from contamination by human and animal
wastes. - It raises the groundwater level.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Short Answer Questions
1. List two advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level.
Answer. Two advantages of water harvesting at the community level are:
- Water can be stored during rainy season and can be used when required.
- Groundwater level increases due to recharging of wells.
2. In a village in Karnataka, people started cultivating crops all around a lake which was always filled with water. They added fertilisers to their field in order to enhance the yield. Soon they discovered that the water body was completely covered with green floating plants and fishes started dying in large numbers. Analyse the situation and give reasons for excessive growth of plants and death of fish in the lake.
Answer. Because of the excessive use of fertilisers in the fields, they were carried down to the lake during rains. The fertilisers contain phosphates and nitrates, resulting excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants which float on water surface. The submerged plants are killed due to shading and insufficient availability of dissolved oxygen resulted in the death of fish.
3. What measures would you take to conserve electricity in your house?
Answer.
- Switch off lights and fans when not required.
- Use of solar radiation for cooking food and lighting.
- Use of fluorescent tubes or CFL.
- Use of solar water heating system during winters.
4. Although coal and petroleum are produced by degradation of biomass, yet we need to conserve them. Why?
Answer. Coal and petroleum are rich sources of energy and it takes millions of years for their formation. As these resources are being consumed in ever increasing amount in industry, transport, kitchen, etc’ and utilized at a much faster rate than their formation, they will be exhausted. Therefore, they must be conserved.
5. Suggest a few measures for controlling carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere.
Answer.
- Plant more trees.
- Reduce the consumption of petrol and diesel in auto mobiles.
- Use of CNG.
- Instead of burning litter, manure can be prepared.
- Treatment of smoke to remove harmful gases before discharging into atmosphere.
6. (a) Locate and name the water reservoirs in figures (a) and (b).
(b) Which has an advantage over the other and why?
Answer. (a) Water reservoir in Fig (a) is pond while in Fig (b) it is underground water body.
(b) Fig (b), i.e. Groundwater has more advantages than pond water because the advantages of water stored in the ground are many as follows:
- It spreads out to recharge wells,
- It provides moisture for vegetation over a wide area.
- It does not evaporate.
- It does not allow breeding of insects.
- It is protected from contamination by animal and human wastes.
Long Answer Questions
7. In the context of conservation of natural resources, explain the terms reduce, recycle and reuse. From among the materials that we use in daily life, identify two materials for each category.
Answer. Reduce means to use materials in lesser quantity, e.g. electricity and water. Recycle means a material that is used once is collected and sent back to a manufacturer so that they can make some other useful material from it, e.g. plastic cups and buckets, glass tumbler, paper. Reuse means using a thing over and over again instead of throwing it away, e.g. used envelopes, plastic bottles of jam or pickle.
8. Is water conservation necessary? Give reasons.
Answer. Yes, water conservation is necessary because:
- Water distribution is uneven and large tracts are deficient in rain as well as groundwater.
- Requirement of water for urban and industrial areas is higher than availability.
- The demand of water is rising in various fields of agriculture or domestic use.
- At most places, more water is withdrawn from reservoir and underground source than their recharging.
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
.png)
.png)