Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Maths Symmetry Exercise 14.1
- Class 7 Maths Symmetry Exercise 14.2
- Class 7 Maths Symmetry Exercise 14.3
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry Exercise 14.1
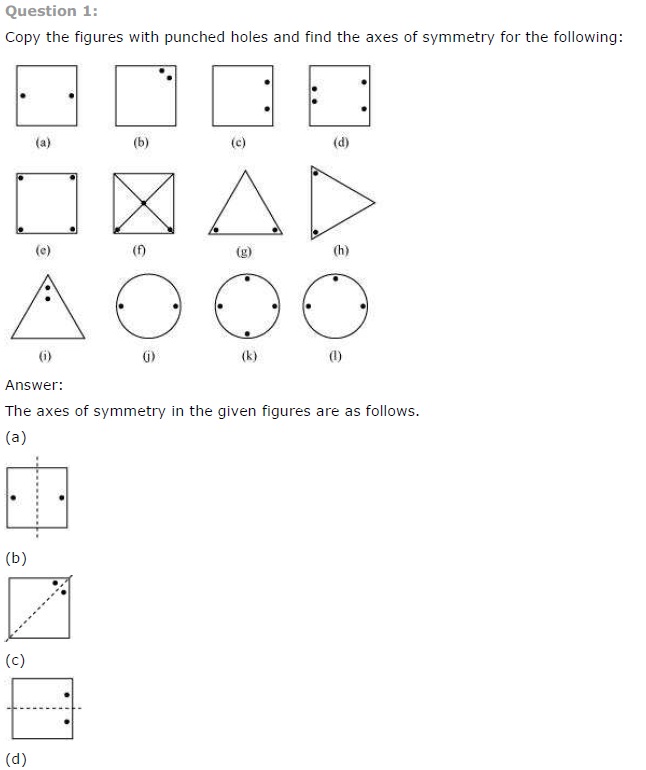
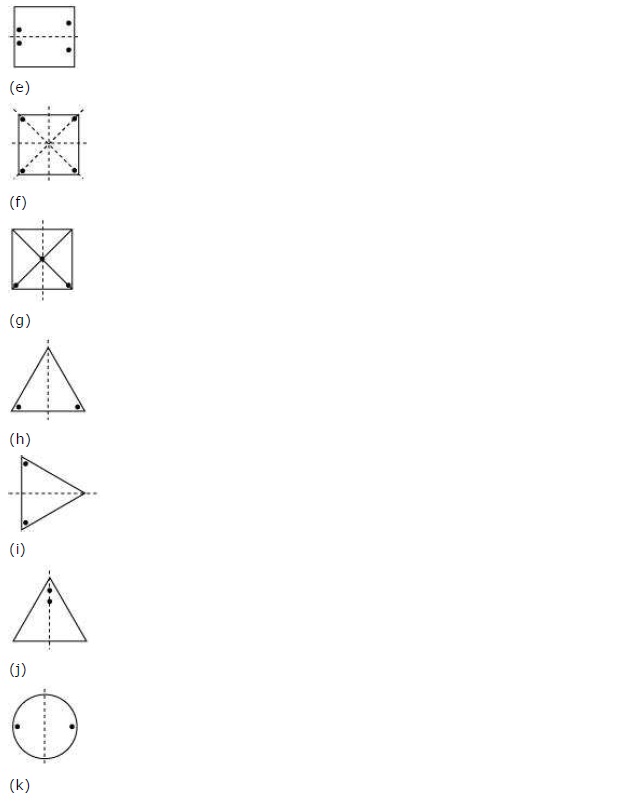
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Copy the figures with punched holes and find the axis of symmetry for the following: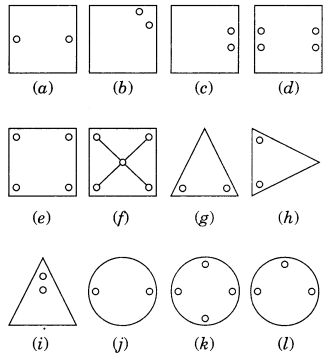
Solution:
The axis of symmetry is shown by following line.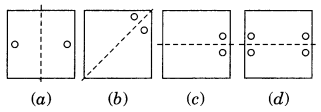
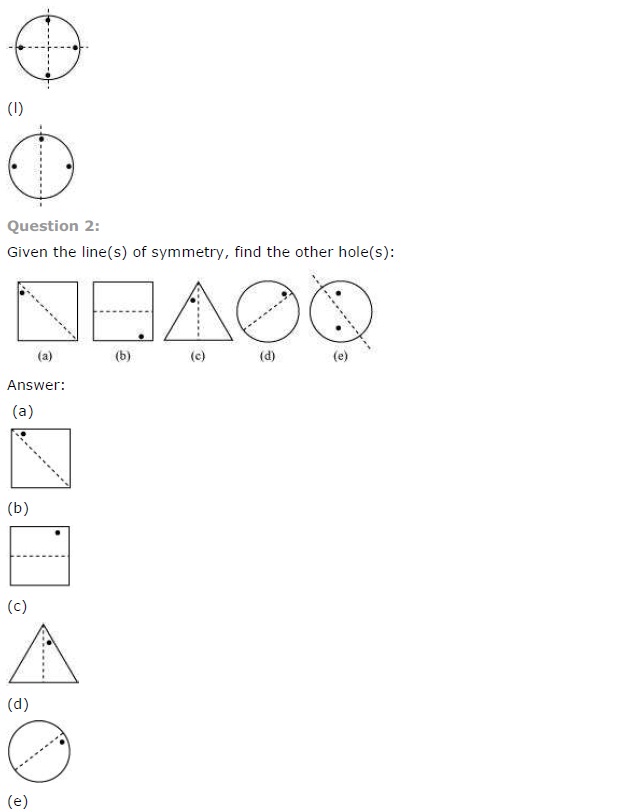
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Give the line(s) of symmetry, find the other hole(s):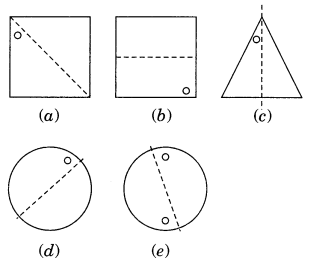
Solution: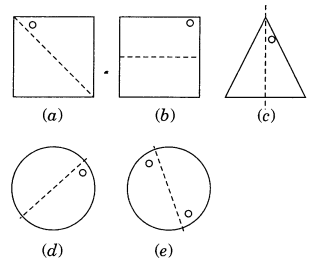
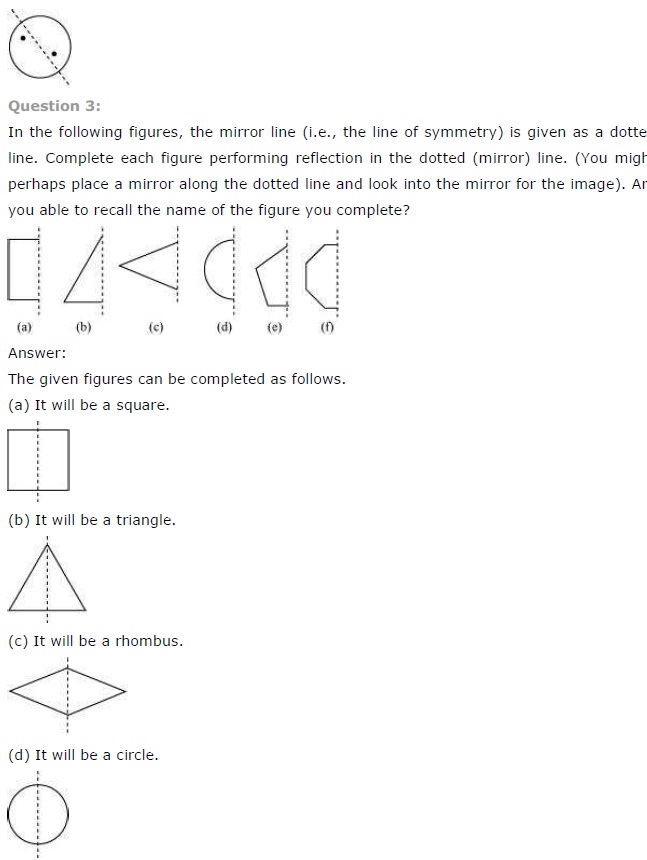
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
In the following figures, the mirror line (i.e., the line of symmetry) is given as dotted line. Complete each figure performing reflection in the dotted (mirror) line. (You might perhaps place a mirror along the dotted line and look into the mirror for the image). Are you able to recall the name of the figure you complete?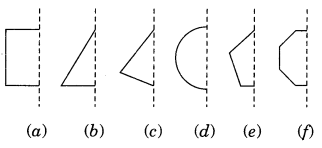
Solution:
Following are the complete figures.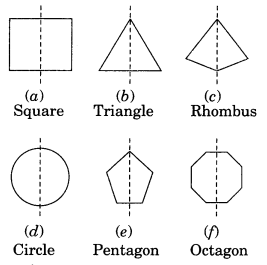
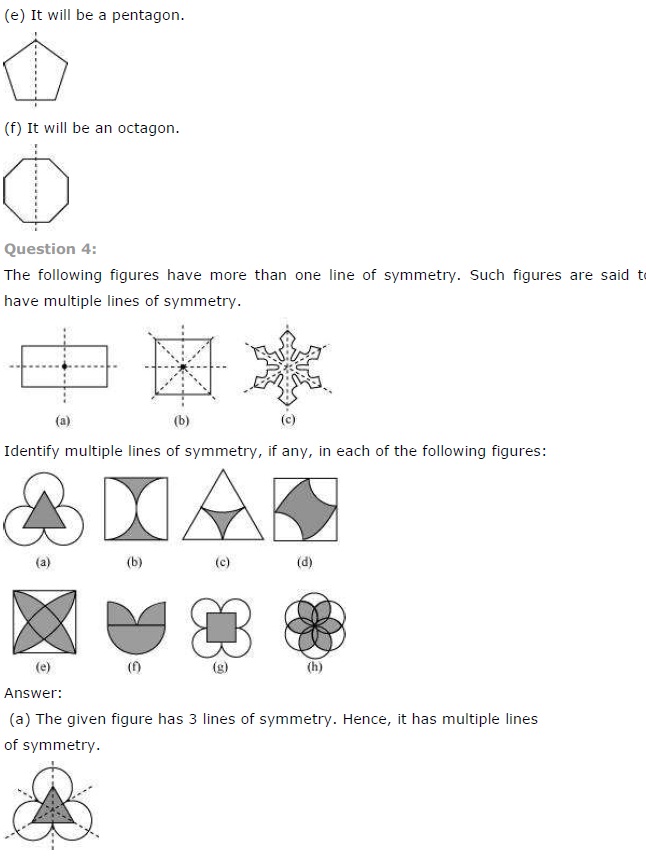
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 4.
The following figures have more than one line of symmetry. Such figures are said to have multiple lines of symmetry.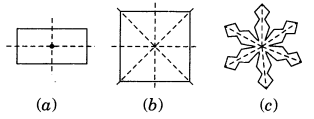
Identify multiple lines of symmetry, if any, in each of the following figures: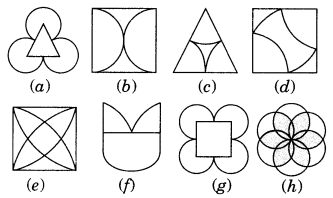
Solution:
Here, figure (6), (d), (e), (g) and (h) are the multiple lines of symmetry.
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 5.
Copy the figure given here.
Take any one diagonal as a line of symmetry and shade a few more squares to make the figure symmetric about a diagonal. Is there more than one way to do that? Will the figure be symmetric about both the diagonals?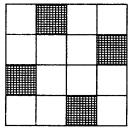
Solution:
(i) Let us take a diagonal as the axis of symmetry and shade the square as shown in the figure.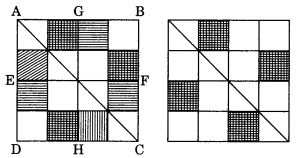
(ii) Yes, there are more than the line of symmetry i.e. BD, EF and GH.
(iii) Yes, the figure is symmetric about both the diagonals.
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 6.
Copy the diagram and complete each shape to be symmetric about the mirror line(s).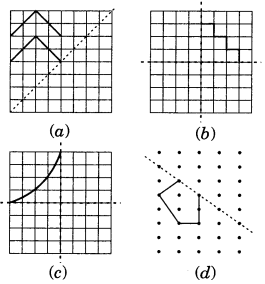
Solution: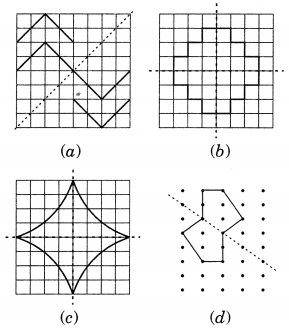
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 7.
State the number of lines of symmetry for the following figures:
(а) An equilateral triangle
(b) An isosceles triangle
(c) A scalene triangle
(d) A square
(e) A rectangle
(f) A rhombus
(g) A parallelogram
(h) A quadrilateral
(i) A regular hexagon
(j) A circle
Solution:
| Figure | Number of lines of symmetry |
| (a) An equilateral triangle | 3 |
| (6) An isosceles triangle | 1 |
| (c) A scalene triangle | 0 |
| (d) A square | 4 |
| (e) A rectangle | 2 |
| (f) A rhombus | 2 |
| (g) A parallelogram | 0 |
| (h) A quadrilateral | 0 |
| (i) A regular hexagon | 6 |
| (j) A circle | Infinite |
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 8.
What letters of the English alphabet have reflectional symmetry (i.e. symmetry related to mirror reflection) about
(а) a vertical mirror
(b) a horizontal mirror
(c) both horizontal and vertical mirrors.
Solution:
(a) Alphabet of vertical mirror reflection symmetry are
A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, Y
(b) Alphabet of horizontal mirror reflection symmetry are:
B, C, D, E, H, I, K, O, X
(c) Alphabet of both horizontal and vertical mirror reflection symmetry are:
H, I, O, X.
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 9.
Give three examples of shapes with no line of symmetry.
Solution:
Example 1: Scalene triangle has no line of symmetry.
Example 2: Quadrilateral has no line of symmetry.
Example 3: Alphabet R has no line of symmetry.
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 10.
What other name can you give of the line of symmetry of
(a) an isosceles triangle?
(b) a circle?
Solution:
(a) Median of an isosceles triangle is its line of symmetry.
(b) Diameter of a circle is its line of symmetry.

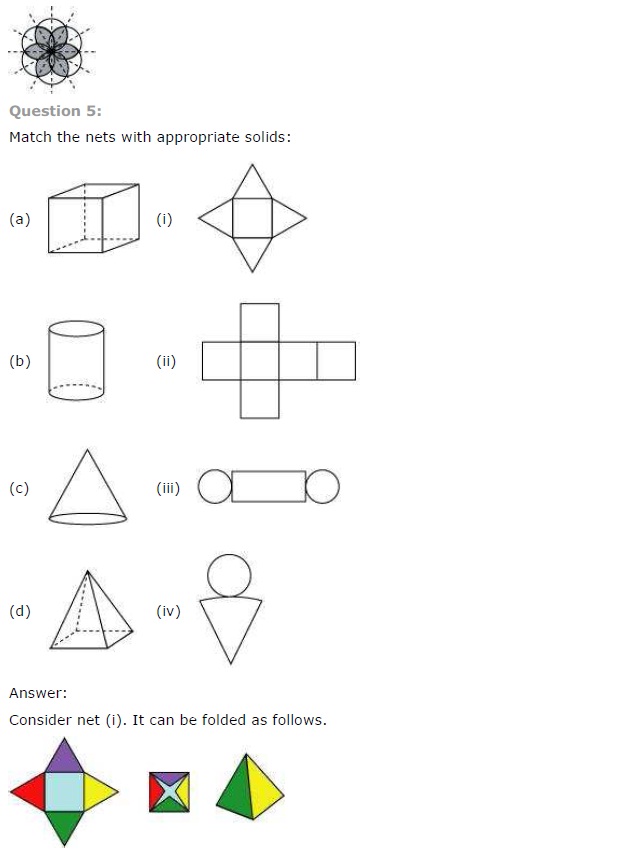
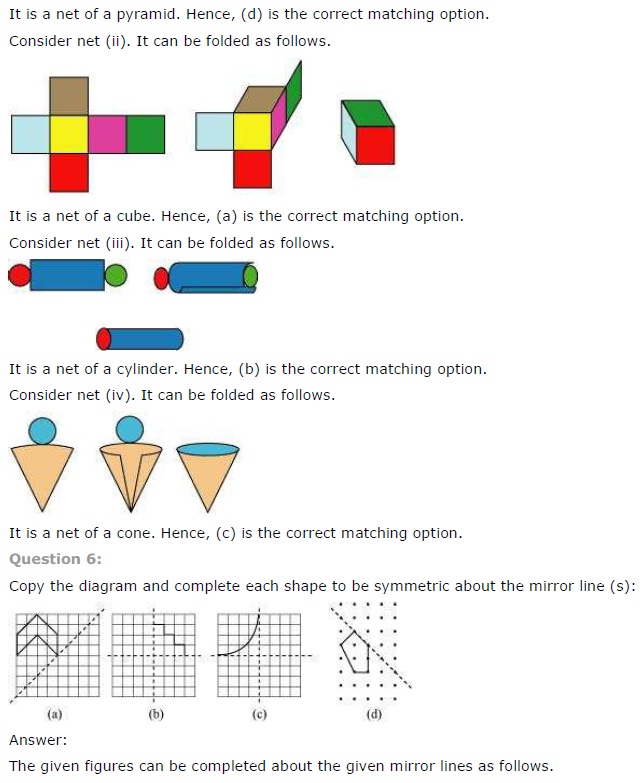



NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry Exercise 14.2
Ex 14.2 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
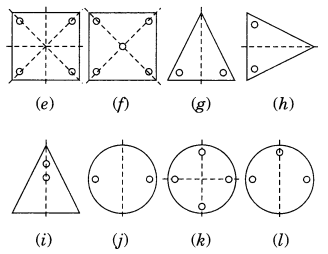
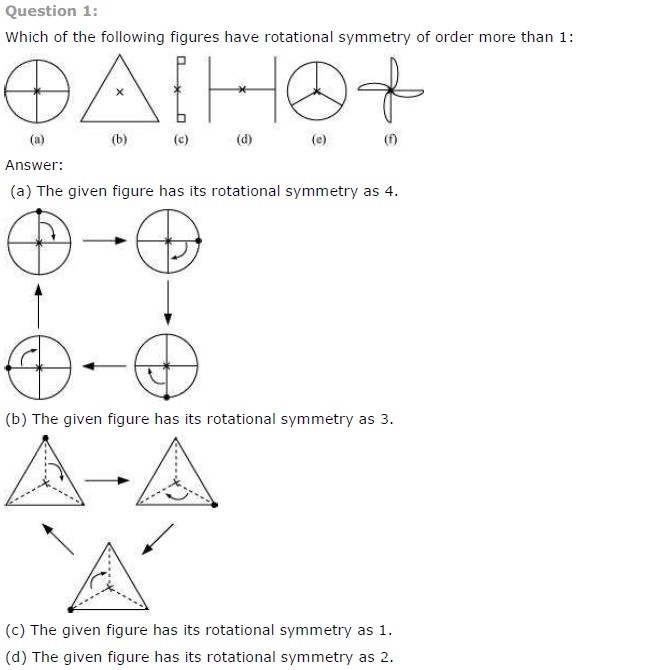
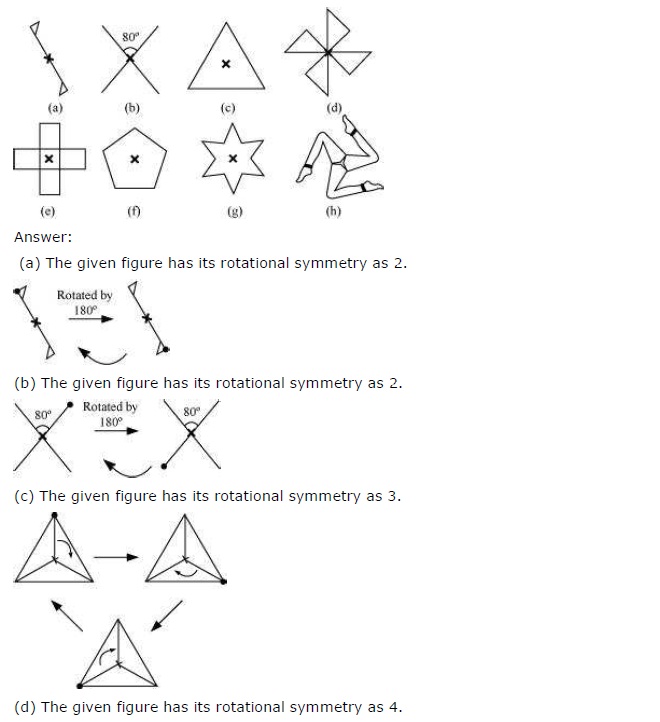
Which of the following figures have rotational symmetry of order more than 1?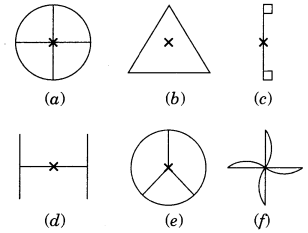
Solution:
The figure (a), (b), (d), (e) and (f) have rotational symmetry more than 1.
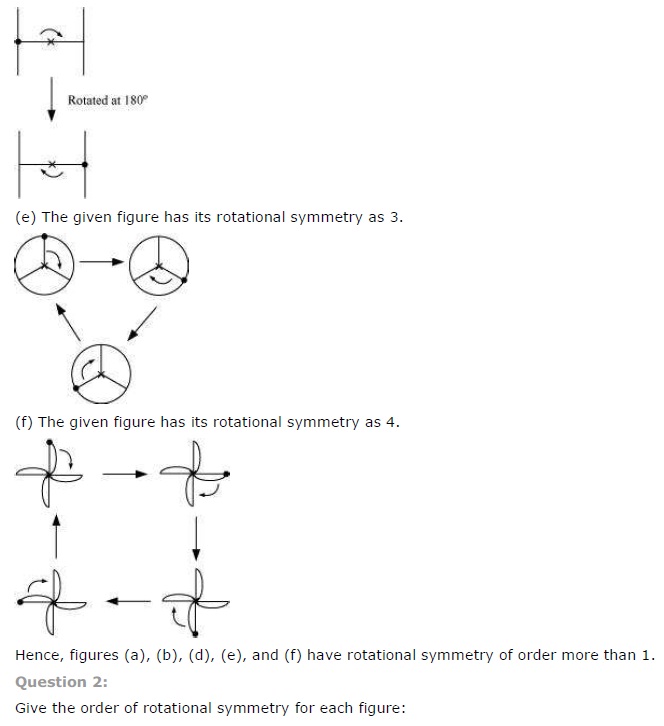
Question 2.
Give the order of rotational symmetry for each figure: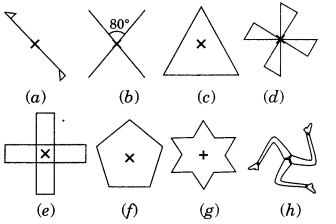
Solution: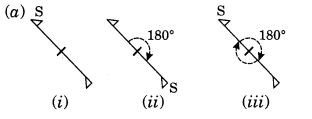
Let us take a point S on one end of the given figure. Rotating by 180°, S comes at other end and then again rotating by 180°, it comes at its original position.
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
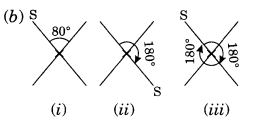
Let us take any point S in figure (1). It takes two rotations to come back to its original position.
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
Let us mark any vertex of the given figure. It takes three rotations to come back to its original shape.
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
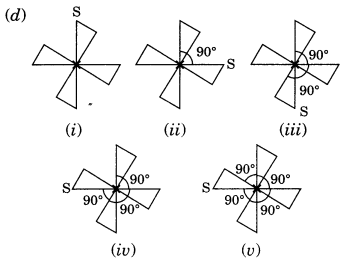
Order of rotational symmetry =
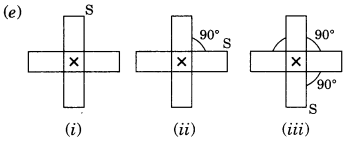
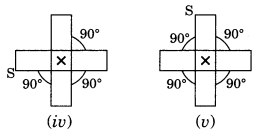
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
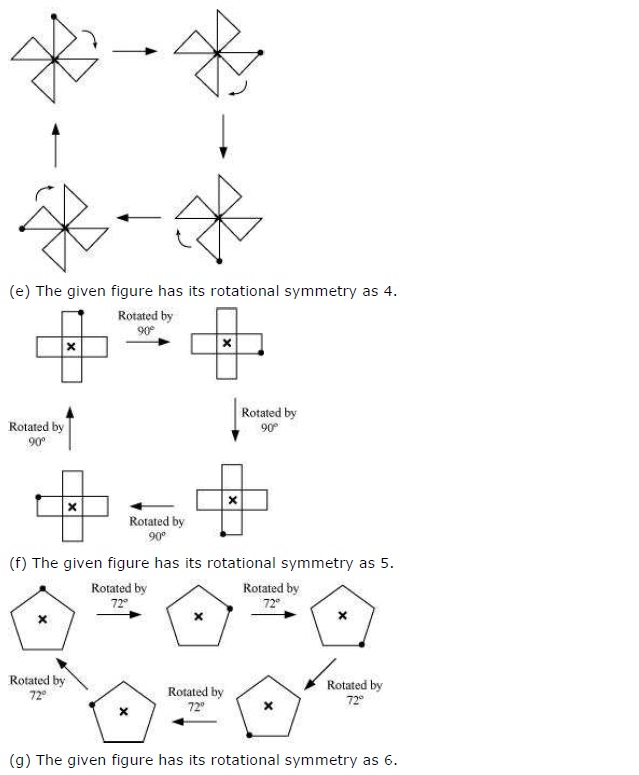
(f) The given figure is a regular pentagon which can take one rotation at an angle of 72°.
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
(g) The given figure requires six rotations each through an angle of 60°
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
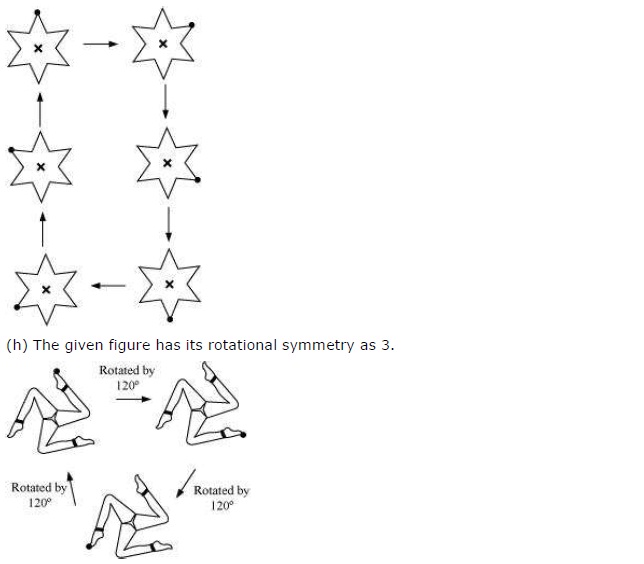
(h) The given figure requires three rotations, each through an angle of 120°.
∴ Order of rotational symmetry =
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry Exercise 14.3
Ex 14.1 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Name any two figures that have both line symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Solution:
English alphabet H and O both have line symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Draw, wherever possible, a rough sketch of
(i) a triangle with both line and rotational symmetries of order more than 1.
(ii) a triangle with only line symmetry and no rotational symmetry of order more than 1.
(iii) a quadrilateral with a rotational symmetry of order more than 1 but not a line symmetry.
(iv) a quadrilateral with line symmetry but not a rotational symmetry of order more than 1.
Solution:
(i) Equilateral triangle has 3 rotational symmetries.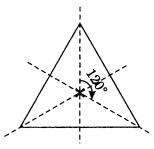
(ii) Not possible.
(iii) 
(iv) Not possible.
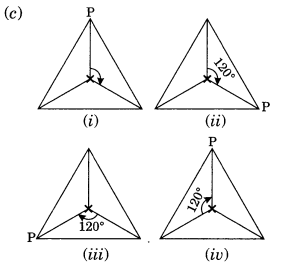
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
If a figure has two or more lines of symmetry, should it have rotational symmetry of order more than 1?
Solution: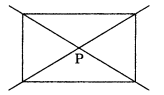
Yes. The above figure has two lines of symmetry and also rotational symmetry of order 2.
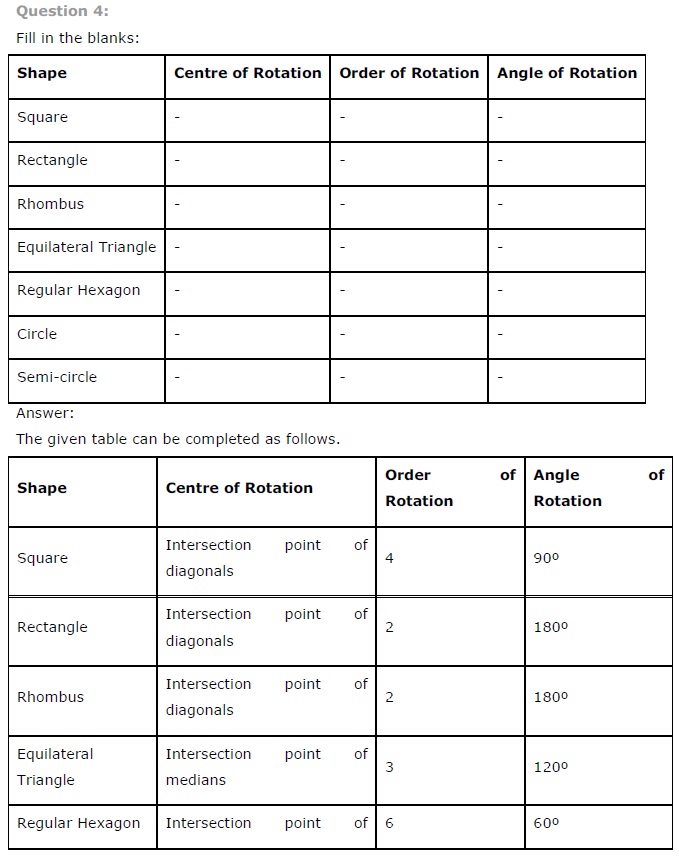
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 4.
Fill in the blanks:
| Shape | Centre of rotation | Order of rotation | Angle of rotation |
| Square | |||
| Rectangle | |||
| Rhombus | |||
| Equilateral triangle | |||
| Regular hexagon | |||
| Circle | |||
| Semicircle |
Solution:
| Shape | Centre of rotation | Order of rotation | Angle of rotation |
| Square | Point of intersection of diagonals | 4 | 90° |
| Rectangle | Point of intersection of diagonals | 4 | 90° |
| Rhombus | Point of intersection of diagonals | 4 | 90° |
| Equilateral triangle | Point of intersection of medians | 3 | 120° |
| Regular hexagon | Point of intersection of diagonals | 6 | 60° |
| Circle | Centre | Infinite | Every angle |
| Semicircle | Centre | 4 | 90° |
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 5.
Name the quadrilaterals which have both line and rotational symmetry of order more than 1.
Solution:
Square, rectangles and rhombus are such quadrilateral which have both line and rotational symmetry.
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 6.
After rotating by 60° about a centre, a figure looks exactly the same as its original position. At what other angles will this happen for the figure?
Solution:
If a figure is rotated through the angles 120°, 180°, 240°, 300° and 360°, it looks exactly the same.
Ex 14.3 Class 7 Maths Question 7.
Can we have a rotational symmetry of order more than 1 whose angle of rotation is
(i) 45°?
(ii) 17°?
Solution:
(i) Yes
(ii) No

Symmetry Class 7 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 14
Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry
Symmetry Class 7 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Draw any two English alphabets having an only a vertical line of symmetry.
Solution:
Question 2.
Draw any two English alphabets having a horizontal line of symmetry.
Solution:
Question 3.
Draw any two English alphabets having both horizontal and vertical line of symmetry.
Solution:
Question 4.
Dray any two English alphabets which has no line of symmetry.
Solution:
Question 5.
Draw any two figures which have the order of rotational symmetry 4.
Solution:
Question 6.
Draw any two figures which have the order of rotational symmetry 2.
Solution:
Question 7.
State the order of rotational symmetry of the following figures.
Solution:
(i) Order of equilateral triangle = 3
(ii) Order of regular pentagon = 5.
Question 8.
Draw a figure having an infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Solution:
A circle has the infinite number of lines of symmetry.
Question 9.
Draw any two figure having no lines of symmetry.
Solution:
English alphabet R and P have no lines of symmetry.
Question 10.
State the English alphabet which has only the horizontal line of symmetry.
Solution:
B, C, D, E, H, I, O, X and K are the English alphabets having an only horizontal line of symmetry.
Symmetry Class 7 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 11.
Give the order of rotational symmetry of each of the following figures:
Solution:
(a) Order of rotational symmetry = 4
(b) Order of rotational symmetry = 5
(c) Order of rotational symmetry = 3
(d) Order of rotational symmetry = 6
(e) Order of rotational symmetry = 3
(f) Order of rotational symmetry = 4
Question 12.
How many lines of symmetry do the following have:
(a) a parallelogram
(b) an equilateral triangle
(c) a right angle with equal legs
(d) an angle with equal arms
(e) a semicircle
(f) a rhombus
(g) a square
(h) scalene triangle
Solution:

Question 13.
What letters of the English alphabet have reflectional symmetry about
(а) a vertical mirror
(b) a horizontal mirror
(c) both horizontal and vertical mirrors
Solution:
(a) The letters of English alphabet having reflectional symmetry about a vertical mirror are:
A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W, X, Y
(b) Letters of the English alphabets having reflectional symmetry about a horizontal mirror are:
B, C, D, E, H, I, O, X
(c) Letters of the English alphabet having reflectional of symmetry about vertical and horizontal mirror are:
O, X, I, H.
.png)
.png)