Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry
- Class 7 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 10.1
- Class 7 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 10.2
- Class 7 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 10.3
- Class 7 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 10.4
- Class 7 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 10.5
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.1
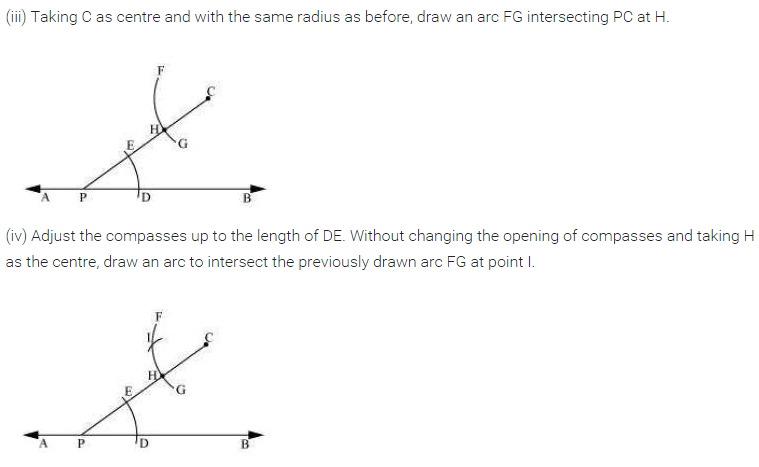
Ex 10.1 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Draw a line, say AB, take a point C outside it. Through C draw a line parallel to AB using ruler and compasses only.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line AB.
(ii) Take any point D on it.
(iii) Join the given point C to D and mark ∠1 to ∠CDB.
(iv) Mark ∠1 = ∠2 at C and produce to both side.
(v) MN is the required line.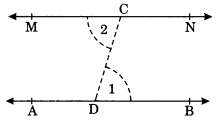
Using the Property of Alternate Angles
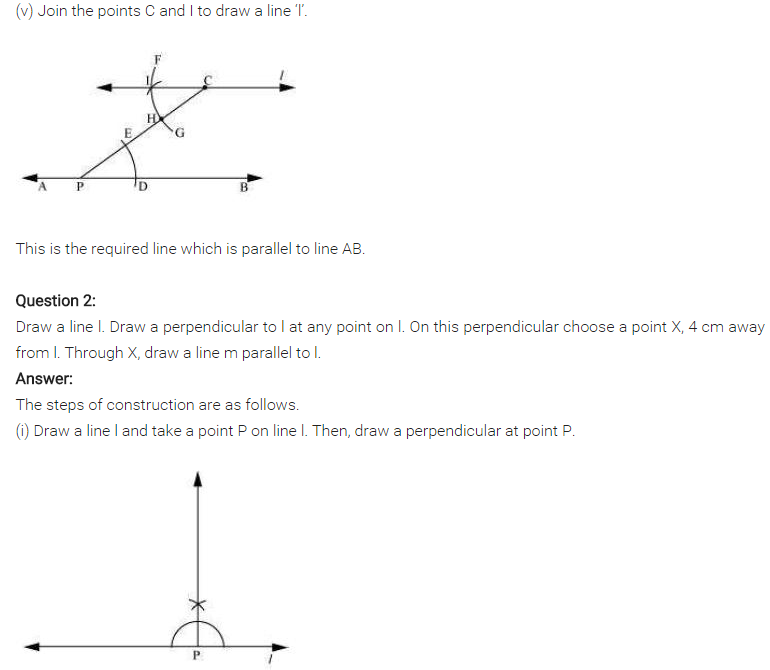
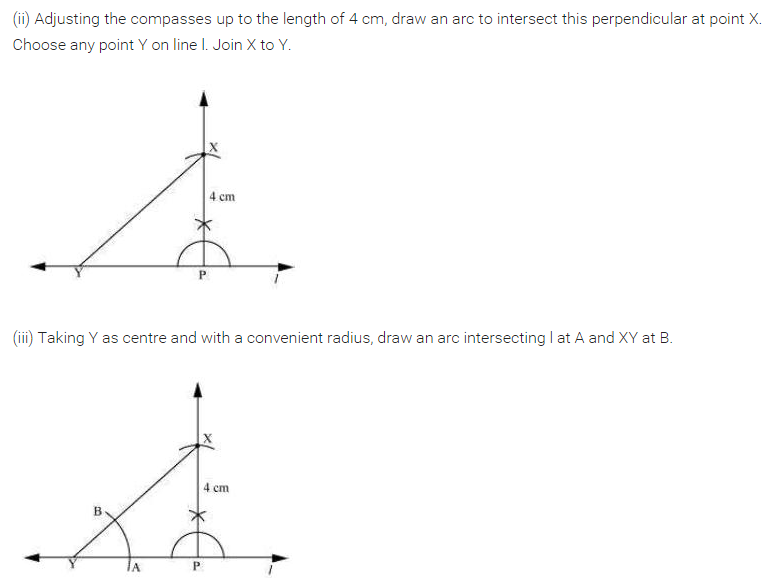
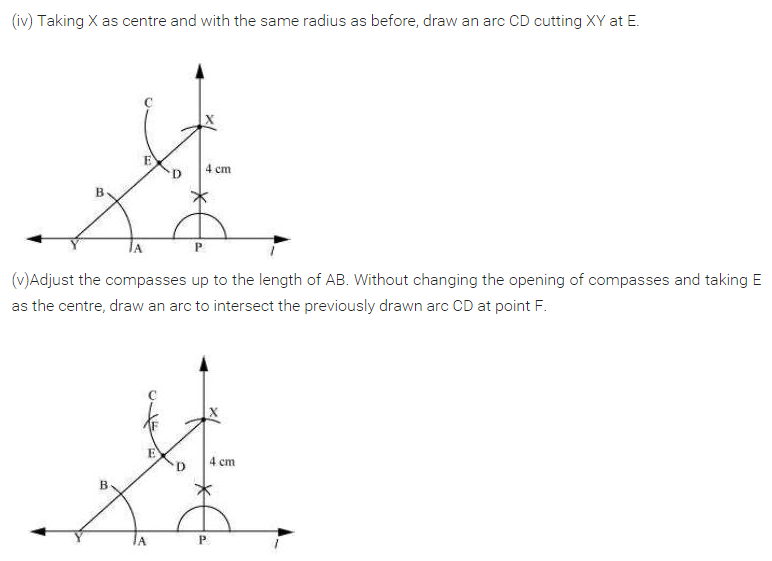
Ex 10.1 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Draw a line Z. Draw a perpendicular to l at any point on l. On this perpendicular choose a point X, 4 cm away from l. Through X, draw a line m parallel to l.
Solution: ‘Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a given line Z and take any point P on it.
(ii) Draw a perpendicular line at P to the line Z such that PX = 4 cm.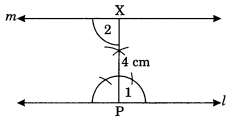
(iii) Draw ∠2 = ∠1 i.e. 90° at PX and produce the line both sides.
(iv) m is the required line parallel to Z through X.
Using Properties of Alternate Angles
Ex 10.1 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
Let l be a line and P be a point not on l. Through P, draw a line m parallel to P. Now join P to any point Q on l. Choose any other point R on m. Through R, draw a line parallel to PQ. Let this meet l at S. What shape do the two sets of parallel lines enclose?
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
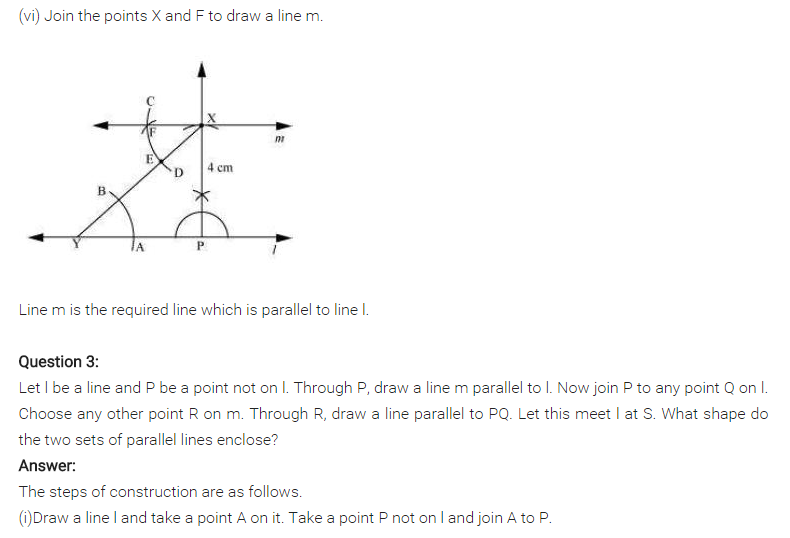
(i) Draw a line l and take any point P not on l.
(ii) Draw a line m parallel to l through P.
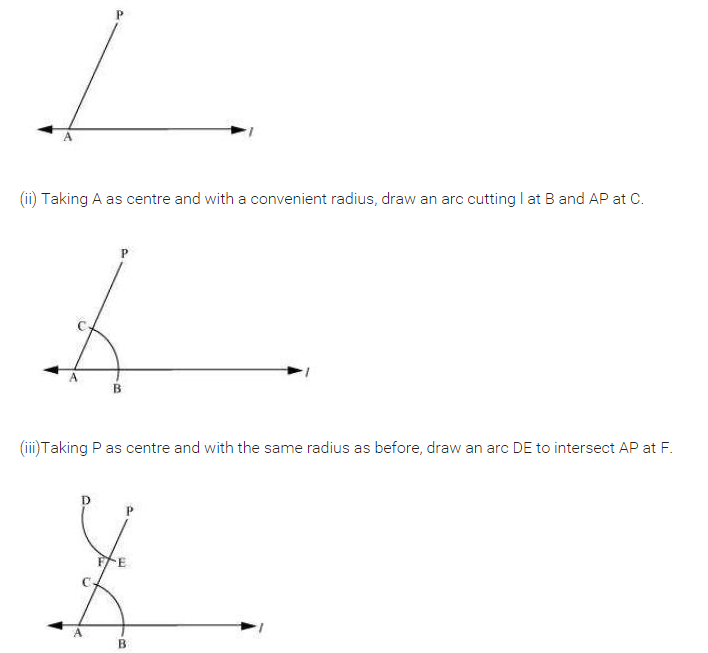
(iii) Join P and Q.
(iv) PQ makes ∠1 with l and ∠2 with m which are equal angles.
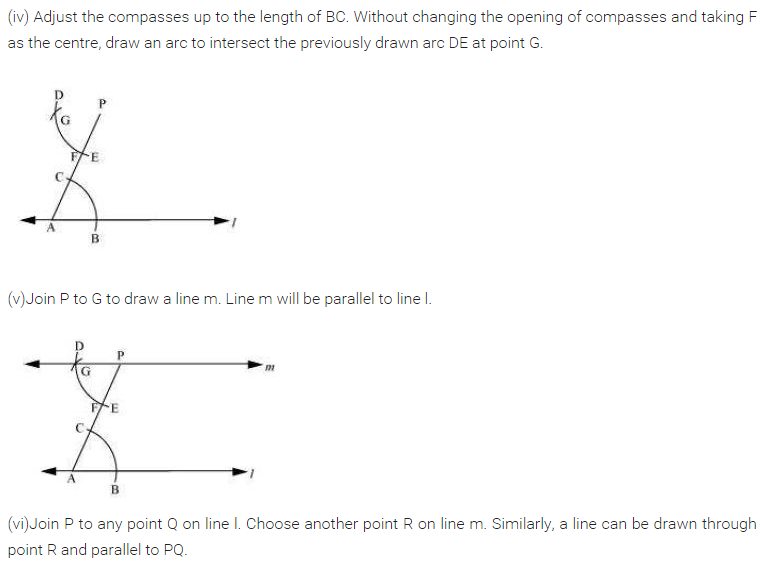
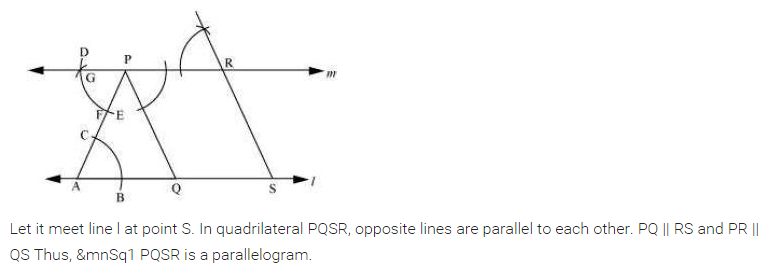
(v) Take any point R on m and draw ∠3 equal to ∠ 2 to meet l at S such that PQ || RS.
(vi) Since l || m and PQ || RS. Therefore, PQSR is a parallelogram.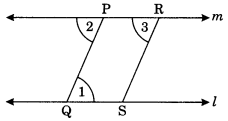
Using the properties of parallel lines and transversal line and alternate angles
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.2
Ex 10.2 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Construct ∆XYZ in which XY = 4.5 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ZX = 6 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw XY = 4.5 cm.
(ii) Draw an arc with centre Y and radius 5 cm.
(iii) Draw another arc with centre X and radius 6 cm to meet the first arc at Z.
(iv) Join ZY and ZX.
(v) XYZ is the required triangle.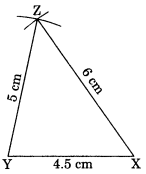
Using SSS criterion
Ex 10.2 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Construct an equilateral triangle of side 5.5 cm. Solution: Steps of construction:
(i) Draw BC = 5.5 cm.
(ii) Draw two arcs with centres B and C and same radius of 5.5 cm to meet each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
(iv) ABC is the required triangle.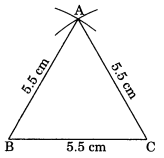
Using SSS criterion
Ex 10.2 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
Draw ∆PQR with PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3.5 cm and PR = 4 cm. What type of triangle is this?
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw QR = 3.5 cm.
(ii) Draw two arcs with centre Q and R and same radius of 4 cm to meet each other at P.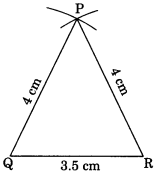
(iii) Join PQ and PR.
(iv) PQR is the required triangle.
(v) Since PQ = PR = 4 cm, therefore APQR is an isosceles triangle.
Using SSS Criterion
Ex 10.2 Class 7 Maths Question 4.
Construct ∆ABC such that AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm. Measure ∠B.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw BC = 6 cm.
(ii) Draw two arcs with centres B and C and radius 2.5 cm and 6.5 cm respectively to meet each other at A.
(iii) Join AB and AC.
(iv) ABC is the required triangle.
[Using SSS criterion]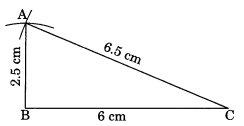





NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.3
Ex 10.3 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Construct ∆DEF such that DE = 5 cm, DF = 3 cm and m ∠DEF = 90°.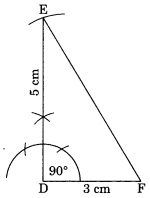
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw DF = 3 cm.
(ii) Draw an angle of 90° at D and cut DE = 5 cm.
(iii) Join EF.
(iv) EPF is the required triangle.
Using SAS property
Ex 10.3 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
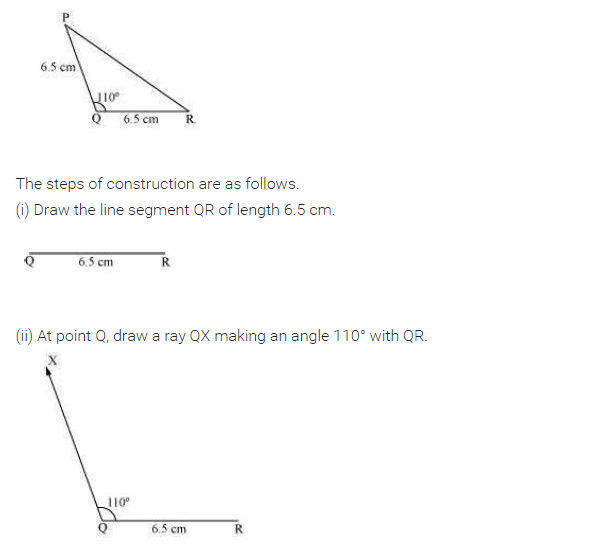
Construct an isosceles triangle in which the lengths of each of its equal sides is 6.5 cm and the angle between them is 110°.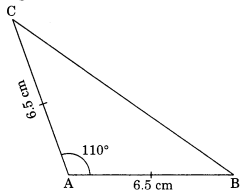
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AB = 6.5 cm.
(ii) Draw angle of 110° at A and cut AC = 6.5 cm.
(iii) Join C to B.
(iv) CAB is the required triangle.
[Using SAS criterion]
Ex 10.3 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
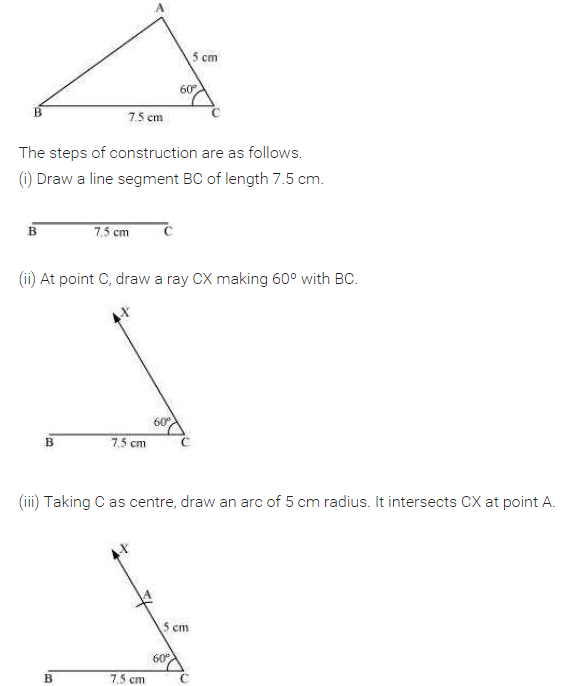
Construct ∆ABC with BC = 7.5 cm, AC = 5 cm and m ∠C = 60°.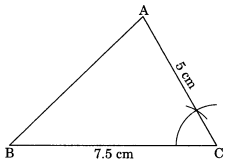
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw BC = 7.5 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠C = 60° such that AC = 5 cm.
(iii) Join A to B.
(iv) ABC is the required triangle.
[Using SAS Criterion]



NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.4
Ex 10.4 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Construct ∆ABC, given m ∠A = 60°, m ∠B = 30° and AB = 5.8 cm.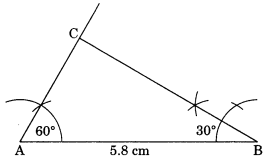
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AB = 5.8 cm.
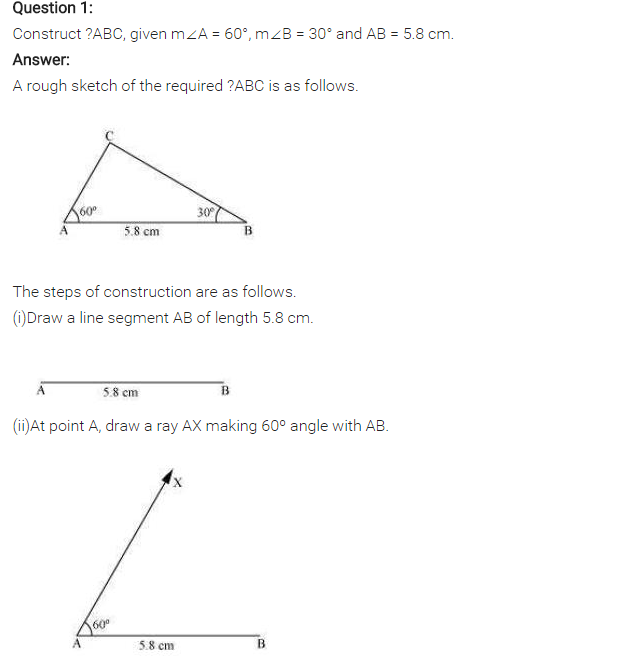
(ii) Draw ∠A = 60° and ∠B = 30° to meet each other at C.
(iii) ABC is the required triangle.
Using ASA criterion
Ex 10.4 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Construct ∆PQR if PQ = 5 cm, m ∠PQR = 105° and m∠QRP = 40°.
(Hint: Recall angle-sum property of a triangle)
Solution:
Given: m∠PQR = 40°, m∠QRP = 105°
∵ m∠PQR + m∠QRP + ∠QPR = 180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)
105° + 40° + ∠QPR = 180°
145° + ∠QPR = 180°
∴ ∠QPR = 180° – 145° = 35°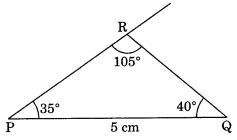
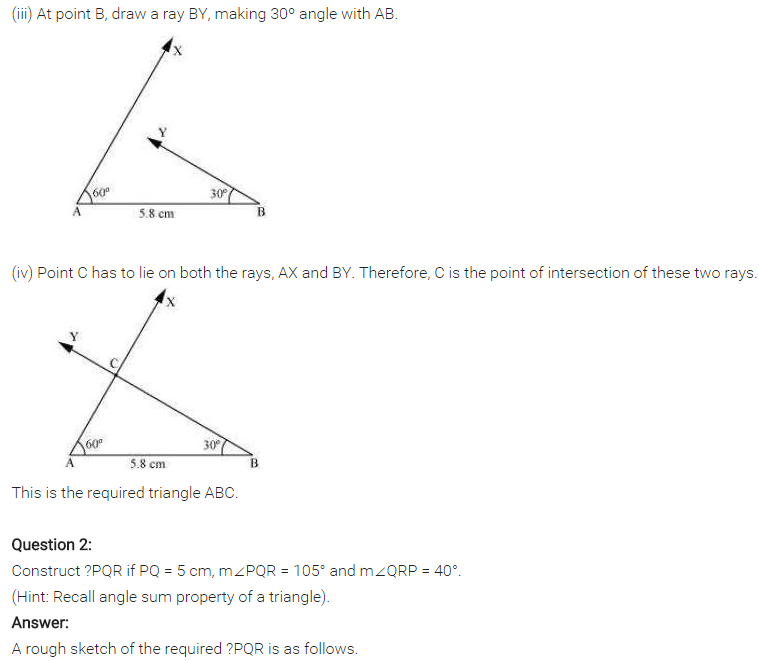
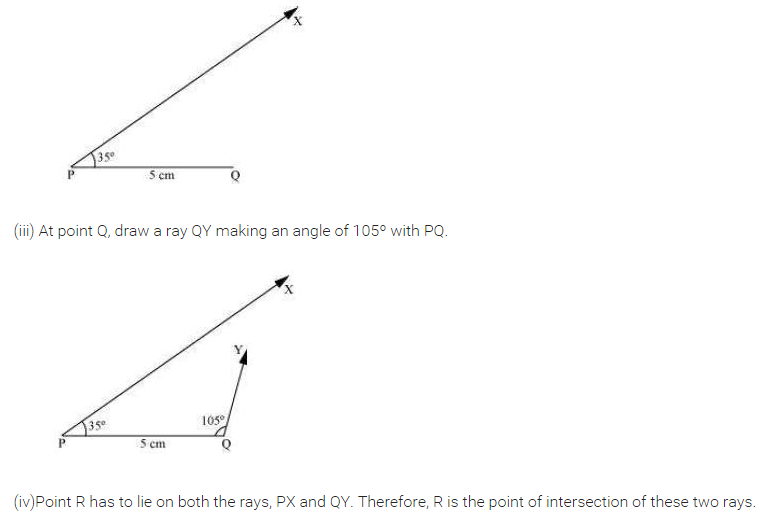
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw PQ = 5 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠QPR = 35° and ∠PQR = 40° to meet each other at R.
(iii) ∆PQR is the required triangle.
[Using AAS or ASA criterion]
Ex 10.4 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
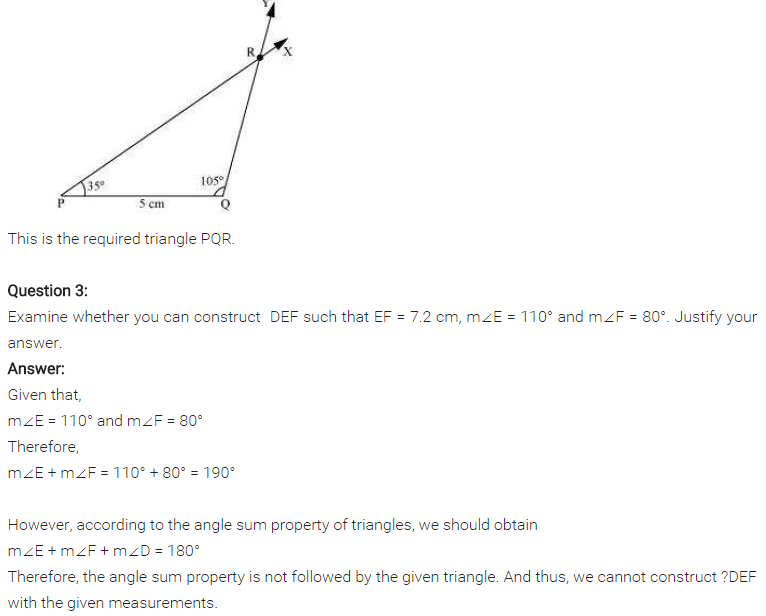
Examine whether you can construct ∆DEF such that EF = 7.2 cm, m∠E = 110° and m∠F = 80°. Justify your answer.
Solution:
To construct ∆DEF with the given measurement, is not possible.
∵ m∠E + m∠F = 110° + 80°
= 190° > 180° [Sum of the angles of a triangle = 180°]
∴ ADEF is not possible to construct.


NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Exercise 10.5
Ex 10.5 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
Construct the right angled ∆PQR, where m∠Q = 90°, QR = 8 cm and PR = 10 cm.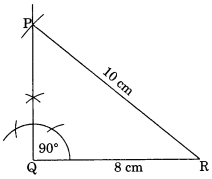
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw QR = 8 cm.
(ii) Draw m∠Q = 90°.
(iii) Draw an arc with centre R and radius 10 cm to cut the perpendicular line at P.
(iv) ∆PQR is the required triangle.
[Using RHS criterion]
Ex 10.5 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
Construct a right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is 6 cm long and one of the legs is 4 cm long.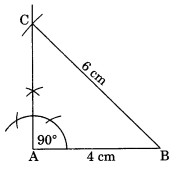
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AB = 4 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠A = 90°.
(iii) Cut BC = 6 cm.
(iv) ∆CAB is the required right-angled triangle.
[Using RHS criterion]
Ex 10.5 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
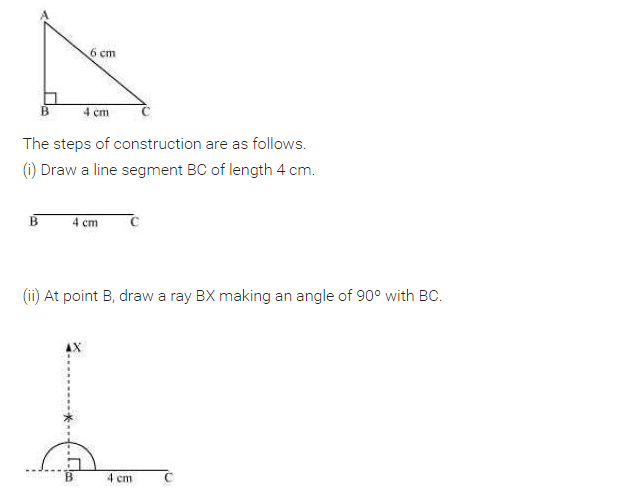
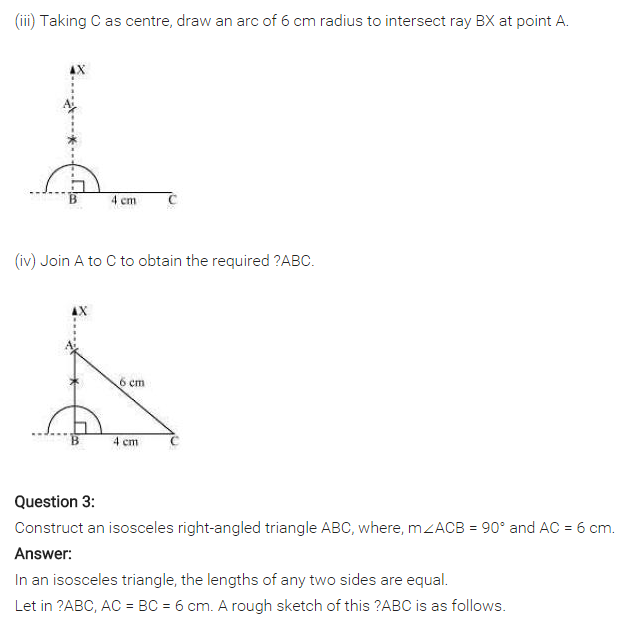
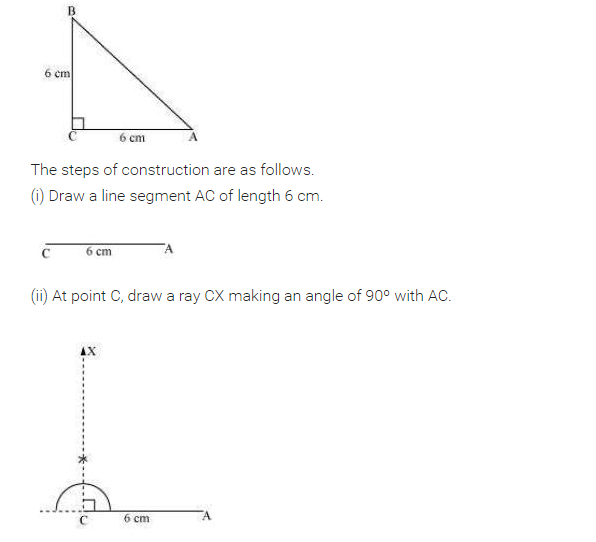
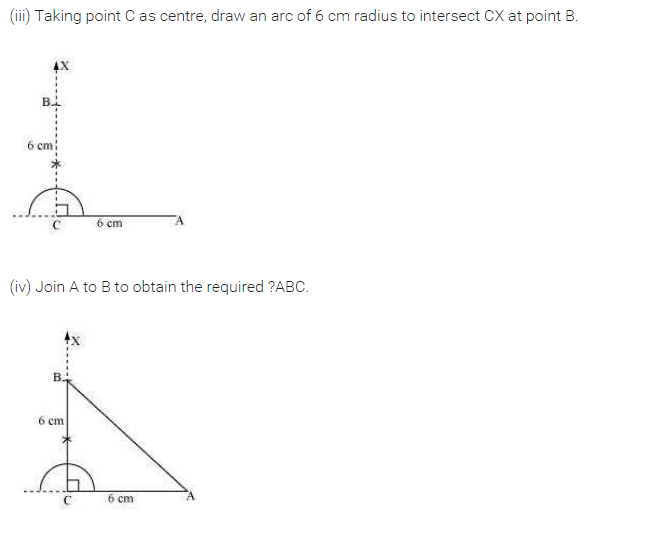
Construct an isosceles right-angled triangle ABC, where m∠ACB = 90° and AC = 6 cm.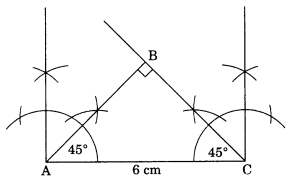
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AC = 6 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠A =∠C = 45° to meet each other at B such that m∠B = 90°.
(iii) ∆ABC is right-angled isosceles triangle which is the required triangle.
[Using RHS criterion]

Practical Geometry Class 7 Extra Questions Maths Chapter 10
Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry
Practical Geometry Class 7 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
State whether the triangle is possible to construct if
(a) In ΔABC, m∠A = 80°, m∠B = 60°, AB = 5.5 cm
(b) In ΔPQR, PQ = 5 cm, QR = 3 cm, PR = 8.8 cm
Solution:
(a) m∠A = 80°, m∠B = 60°
m∠A + m∠B = 80° + 60° = 140° < 180°
So, ΔABC can be possible to construct.
(b) PQ = 5 cm, QR = 3 cm, PR = 8.8 cm
PQ + QR = 5 cm + 3 cm = 8 cm < 8.8 cm
or PQ + QR < PR
So, the ΔPQR can not be constructed.
Question 2.
Draw an equilateral triangle whose each side is 4.5 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AB = 4.5 cm.
(ii) Draw two arcs with centres A and B and same radius of 4.5 cm to meet each other at C.
(iii) Join CA and CB.
(iv) ΔCAB is the required triangle.
Question 3.
Draw a ΔPQR, in which QR = 3.5 cm, m∠Q = 40°, m∠R = 60°.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw QR = 3.5 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠Q = 40°, ∠R = 60° which meet each other at P.
(iii) ΔPQR is the required triangle.
Question 4.
There are four options, out of which one is correct. Choose the correct one:
(i) A triangle can be constructed with the given measurement.
(a) 1.5 cm, 3.5 cm, 4.5 cm
(b) 6.5 cm, 7.5 cm, 15 cm
(c) 3.2 cm, 2.3 cm, 5.5 cm
(d) 2 cm, 3 cm, 6 cm
(ii) (a) m∠P = 40°, m∠Q = 60°, AQ = 4 cm
(b) m∠B = 90°, m∠C = 120° , AC = 6.5 cm
(c) m∠L = 150°, m∠N = 70°, MN = 3.5 cm
(d) m∠P = 105°, m∠Q = 80°, PQ = 3 cm
Solution:
(i) Option (a) is possible to construct.
1.5 cm + 3.5 cm > 4.5 cm
(ii) Option (a) is correct.
m∠P + m∠Q = 40° + 60° = 100° < 180°
Question 5.
What will be the other angles of a right-angled isosceles triangle?
Solution:
In right angled isosceles triangle ABC, ∠B = 90°
∠A + ∠C = 180° – 90° = 90°
But ∠A = ∠B
∠A = ∠C =
Hence the required angles are ∠A = ∠C = 45°
Question 6.
What is the measure of an exterior angle of an equilateral triangle?
Solution:
We know that the measure of each interior angle = 60°
Exterior angle = 180° – 60° = 120°
Question 7.
In ΔABC, ∠A = ∠B = 50°. Name the pair of sides which are equal.
Solution:
∠A = ∠B = 50°
AC = BC [∵ Sides opposite to equal angles are equal]
Hence, the required sides are AC and BC.
Question 8.
If one of the other angles of a right-angled triangle is obtuse, whether the triangle is possible to construct.
Solution:
We know that the angles other than right angle of a right-angled triangle are acute angles.
So, such a triangle is not possible to construct.
Question 9.
State whether the given pair of triangles are congruent.
Solution:
Here, AB = PQ = 3.5 cm
AC = PR = 5.2 cm
∠BAC = ∠QPR = 70°
ΔABC = ΔPQR [By SAS rule]
Practical Geometry Class 7 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 10.
Draw a ΔABC in which BC = 5 cm, AB = 4 cm and m∠B = 50°.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw BC = 5 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠B = 50° and cut AB = 4 cm.
(iii) Join AC.
(iv) ΔABC is the required triangle.
Question 11.
Draw ΔPQR in which QR = 5.4 cm, ∠Q = 40° and PR = 6.2 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw QR = 5.4 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠Q = 40°.
(iii) Take R as the centre and with radius 6.2 cm, draw an arc to meet the former angle line at P.
(iv) Join PR.
(v) ΔPQR is the required triangle.
Question 12.
Construct a ΔPQR in which m∠P = 60° and m∠Q = 30°, QR = 4.8 cm.
Solution:
m∠Q = 30°, m∠P = 60°
m∠Q + m∠P + m∠R = 180° (Angle sum property of triangle)
30° + 60° + m∠R = 180°
90° + m∠R = 180°
m∠R = 180° – 90°
m∠R = 90°
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw QR = 4.8 cm.
(ii) Draw ∠Q = 30°.
(iii) Draw ∠R = 90° which meets the former angle line at P.
(iv) ∠P = 180° – (30° + 90°) = 60°
(v) ΔPQR is the required triangle.
Practical Geometry Class 7 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills [HOTS] Type
Question 13.
Draw an isosceles right-angled triangle whose hypotenuse is 5.8 cm.
Solution:
Right angled triangle is an isosceles triangle
Each of its acute angles = 
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw AB = 5.8 cm.
(ii) Construct ∠A = 45° and ∠B = 45° to meet each other at C.
(iii) ∠C = 180° – (45° + 45°) = 90°
(iv) ΔACB is the required isosceles right angle triangle.
Question 14.
Construct a ΔABC such that AB = 6.5 cm, AC = 5 cm and the altitude AP to BC is 4 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw a line l and take any point P on it.
(ii) Construct a perpendicular to l at P.
(iii) Cut AP = 4 cm.
(iv) Draw two arcs with centre A and radii 6.5 cm and 5 cm to cut the line l at B and C respectively.
(v) Join AB and AC.
(vi) ΔABC is the required triangle.
Question 15.
Construct an equilateral triangle whose altitude is 4.5 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
(i) Draw any line l and take a point D on it.
(ii) Construct a perpendicular to l at D and cut AD = 4.5 cm.
(iii) Draw the angle of 30° at on either side of AD to meet the line l at B and C.
(iv) ΔABC is the required equilateral triangle.
.png)
.png)