Page 12 Q1:
Multiple choice questions:
(i) Which one of the following types of resources is iron ore?
a. Renewable
b. Biotic.
c. Flow
d. Non-renewable
(ii) Under which of the following type of resource can tidal energy be put?
a. Replenishable
b. Abiotic
c. Human-made.
d. Non-recyclable
(iii)Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in
Punjab?
a. Intense cultivation
b. Deforestation
c. Over irrigation
d. Overgrazing
(iv) In which one of the following states is the terrace cultivation practiced?
a. Punjab
b. Haryana
c. Plains of Uttar Pradesh
d. Uttaranchal
(v) In which one of the following states is the black soil found?
a. J & K
b. Gujarat
c. Rajasthan
d. Jharkhand
Answers:
(i) (d) Non-renewable
(ii) (a) Replenishable
(iii) (c) Over irrigation
(iv) (d) Uttarakhand
(v) (b) Gujarat
More Resources for CBSE Class 10
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of IT
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Page 13:
Q.2: Answer the following questions in about 30 words:
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the Eastern Coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
(iv) What are biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Answer:
(i) The Black soils are black in colour.
These are also known as regur soils.
This soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan Plateau. They cover the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh and extend in a south-east direction along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
Black soil is ideal for growing cotton.
(ii) Alluvial soil is found in the eastern coastal plan is particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
Three main features of this type of soil are as follows :
- The alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
- These soils are very fertile. Due to its high fertility, regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
- These soils contain an adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid, and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat, and other cereal and pulse crops.
(iii) The soil erosion in the hilly areas can be controlled by taking steps as mentioned below :
- Contour ploughing: Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called contour ploughing.
- Terrace cultivation: Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion.
- Strip cropping: Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This is strip cropping.
(iv) Biotic resources are obtained from the biosphere and have life such as human beings, flora, and fauna, fisheries, livestock, e.g., forests and animals are biotic resources.
Abiotic resources consist of all those things which are composed of non-living things. e.g., rocks and metals. Land, water, and soil are also abiotic resources.
Q3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
(ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer:
(i) Land resources in India are primarily divided into agricultural land, forest land, pasture and grazing land, and wasteland. Wasteland includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land used for non-agricultural purposes like housing, roads, industry, etc.
According to recent data available, the percentage of net sown area (NSA) in India is about 54% of the total reporting area (if, the other than current fallow lands is included). . 22.5% is covered by forests, and 3.45% is used for grazing. The rest is a wasteland, with traces of miscellaneous cultivation.
Improper use of forest land has led to land degradation and made conservation of forests difficult. Human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, mining, quarrying, etc have contributed to the slow growth rate of forests. Thus, land under forest has increased by only about 4% since 1960-61.
(ii) The following factors have been responsible for technical and economic development leading to overconsumption of resources.
In colonial times, imperial powers used their technological and economic superiority to establish control over other countries and thereby gain access to the latter’s resources. One country’s resources were accessible to the citizens of its colonial ruler too, leading to increased consumption. Technical progress also results in inefficient machinery, increased production, and greater consumption of resources.
Technological development and economic progress have led to populations increasing due to low mortality at all ages. With new developments in medicine and health care, fewer people die due to accidents, diseases, childbirth, etc. This too has contributed to higher consumption of resources.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Resources which are surveyed and their quantity and quality have been determined for utilisation is known as [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Potential resources
(b) Stock
(c) Developed resources
(d) Reserves
2. Which one of the following soil is ideal for growing cotton? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Regur soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Desert soil
(d) Mountainous soil
3. In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land degradation? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Jharkhand and Orissa
(b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
4. Which one of the following statements is true about the term resources? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Resources are free gifts of nature.
(b) They are the functions of human activities.
(c) All those things which are found in nature.
(d) Things which cannot be used to fulfill our needs.
5. Which one of the following types of the resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Biotic
(c) Flow
(d) Non-renewable
6. Under which of the following types of resource the tidal energy can be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic
(d) Non-recyclable
7. Soil formed by intense leaching is
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Red soil
(c) Laterite soil
(d) Desert
8. Fallow land refers to
(a) land not under cultivation.
(b) land with many gullies.
(c) a fertile land.
(d) cultivable land not cultivated for a season to regain its fertility.
9. Method of growing long strips of grass between the crops refers to
(a) Contour ploughing
(b) Terrace farming
(c) Strip cropping
(d) Crop rotation
10. Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised.
(a) Renewable
(b) Developed
(c) National
(d) Potential
11. Which of the following factors involves the transformation of things into a resource ?
(i) Physical environment
(ii) Technology
(iii) Human beings
(iv) Institutions
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) All of above
12. Renewable resources are those
(a) which cannot be renewed
(b) which are accessible
(c) which are developed
(d) which are renewed by physical, chemical or mechanical processes.
13. Which one of the following is not a community resource ?
(a) Public parks
(b) A library
(c) A car
(d) A community hall
14. Territorial waters of India extends to
(a) 10 Nautical miles
(b) 15 Nautical miles
(c) 12 Nautical miles
(d) 1900 kilometres
15. Find out which one of the following is a stock?
(a) Biofuels
(b) Coal
(c) Solar energy
(d) Hydro-electricity
16. The first International Earth Summit was held in
(a) Geneva
(b) New York
(c) Japan
(d) Rio de Janeiro
17. “There is enough for everybody’s need but not for anybody’s greed”. Who said this ?
(a) Jawahar Lai Nehru
(b) Atal Bihari Vajpai
(c) M. K. Gandhi
(d) Sunder Lai Bhauguna
18. The area brought under cultivation in a year is called …………….
(a) Fallow land
(b) Cultivable
(c) Net sown area
(d) Gross sown area
19. I am the most widespread soil, covering the Northern Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains-who am I ?
(a) Black soil
(b) Forest soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Alluvial soil
20. Resources which are non-renewable but can be recycled are called
(a) Renewable resources
(b) Non-renewable resources
(c) Recyclable resources
(d) Biotic resources
21. The most widespread relief feature of India is
(a) Mountains
(b) Forests
(c) Plains
(d) Plateaus
22. The current net sown area of India in 2002-03 is
(a) 45 percent
(b) 43.4 percent
(c) 50 percent
(d) 48 percent
23. The state having maximum net sown area in India is ……………
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Punjab
24. Land left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year is called
(a) Culturable waste land
(b) Current fallow land
(c) Waste land
(d) None of the above
25. The present per cent of area under forests is (2002 – 03)
(a) 18 percent
(b) 22.57 percent
(c) 19 percent
(d) 11 percent
26. The factor responsible for maximum land degradation is ………………
(a) Human activities
(b) Wind
(c) Salinity
(d) Soil erosion
27. Which agent is responsible for maximum land degradation ?
(a) Wind
(b) Water
(c) Glaciers
(d) Overgrazing
28. Soil is formed by the process of
(a) Denudation
(b) Gradation
(c) Weathering
(d) Erosion
29. Supply a technical term for the dead and decomposed material found on the top soil.
(a) Bed rock
(b) Fossils
(c) Humidity
(d) Humus
30. The old alluvial soil is known as ………………
(a) Bangar
(b) Bhabbar
(c) Khadar
(d) Regur
31. Which of the following statement(s) is true for black soil ?
(i) It has larger proportion of clay.
(ii) It can retain moisture for a long time.
(iii) It develops cracks during summer which helps in aeration.
(iv) Cotton grows best in this soil.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) All of the above
32. Red colour of soil is due to
(a) it is rich in humus.
(b) it is rich in iron compounds.
(c) it is derived from volcanic origin.
(d) it is rich in potash.
33. The denudation of the soil cover and washing down of soil by various agents are known as ………………
(a) Weathering
(b) Gradation
(c) Soil erosion
(d) Soil conservation
34. The land consisting of many gullies and ravines are called ……………….
(a) Gully erosion
(b) Bed rock
(c) V shaped valleys
(d) Bad land
35. Terrace cultivation can be used to control soil erosion in
(a) Desert regions
(b) Hill slopes
(c) Valleys
(d) Plains
36.Strip cropping refers to
(a) growing of crops in long strips.
(b) growing of trees in long rows.
(c) growing of strips of grass in between the crops.
(d) ploughing along the contour lines.
37. Erosion of the top soil when water flows as a sheet over large areas down the slope is called
(a) Gully erosion
(b) Badlands
(c) Soil erosion
(d) Sheet erosion
38. Which one of the following statements is correct as regards to international resources ?
(a) Resources which are regulated by international institutions.
(b) Resources which lie beyond the territorial waters.
(c) Resources which are found along the international frontier.
(d) Resources which are not yet developed.
39. Which one of the following methods is ideal for controlling land degradation in coastal areas and in deserts ?
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Contour ploughing
(c) Planting of shelter belts
(d) Plugging of gullies
40. Which type of soil is suitable for the growth of cashew nut ?
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Red laterite soil
41. Arid soils are less fertile as
(i) it lacks humus and moisture
(ii) it has high salt content
(iii) it is sandy in nature
(iv) it is rich in Iron
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
42. Ploughing along the contour lines can
(a) accelerate the flow of water.
(b) decelerate the flow of water.
(c) accelerate the force of winds.
(d) decelerate the force of winds.
43. Bad lands or ravines are found in
(a) Chenab basin
(b) Chambal basin
(c) Ganga basin
(d) Godavari basin
ANSWERS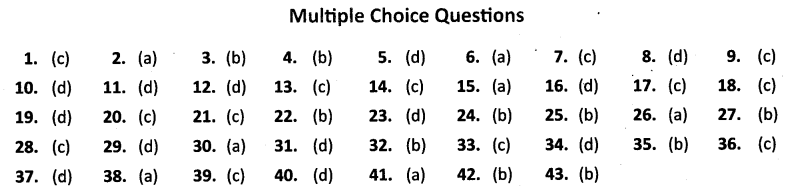
- Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
- Chapter 2 The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China
- Chapter 3 Nationalism in India
- Chapter 4 The Making of Global World
- Chapter 5 The Age of Industrialisation
- Chapter 6 Work, Life and Leisure
- Chapter 7 Print Culture and the Modern World
- Chapter 8 Novels, Society and History
NCERT Class 10 SST Solutions Geography:
- Chapter 1 Resource and Development
- Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Water Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
- Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
- Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
NCERT Solutions Class 10 SST
- Chapter 1 Power Sharing
- Chapter 2 Federalism
- Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity
- Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste
- Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
.png)
.png)