NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
Question-1
Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
Solution:
Tea is also an important beverage crop introduced in India, along with coffee. The tea plant grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates. It requires deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year. Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves.
Question-2
Name one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
Solution:
Cotton is one of the staple crops of India. Major cotton-producing states are – Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
More Resources for CBSE Class 10
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Foundation of IT
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Question-3
Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
Solution:
Abolition of zamindari.
Consolidation of smallholdings.
Provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire, and disease.
Establishment of Grameen banks, cooperative societies, Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme, and banks for providing loan facilities to the farmers at lower rates of interest.
Announcement regarding Minimum support prices to ensure farmers did not suffer if the pres crashed due to bumper crops.
Subsidy on agricultural inputs and resources such as power and fertilisers.
Question-4:
The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Solution:
India shall no longer be self-sufficient in its requirements of food grains.
Landless labourers will outweigh the ranks of unskilled – unemployed workers in India.
More farmers will switch over to the cultivation of high-value crops.
Question-5
Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
Solution:
Organic farming is much in vogue today because it is practiced without factor made chemicals such as fertilisers and pesticides. Hence, it does not affect the environment in a negative manner. Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops. This will increase incomes and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously. Because fruits, medicinal herbs, flowers, vegetables, bio-diesel crops like jatropha and jojoba need much less irrigation than rice or sugarcane. India’s diverse climate can be harnessed to grow a wide range of high-value crops.
Question-6
How did the partition of the country in 1947 affect the jute industry?
Solution:
Jute: It is known as the golden fibre. Jute grows well on well-drained fertile soils in the flood plains where soils are renewed every year. High temperature is required during the time of growth. It is used in making gunny bags, mats, ropes, yarn, carpets, and other artifacts. Due to its high cost, it is losing the market to synthetic fibres and packing materials, particularly the nylon.
Question-7
Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Solution:
This Kharif crop requires high temperature, (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall over 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation. Rice is grown in the plains of north and northeastern India, coastal areas, and the deltaic regions. Development of a dense network of canal irrigation and tubewells have made it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh, and parts of Rajasthan.
Multiple Choice Questions
Previous Years’ Questions
1. In which type of soil does maize grow well? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Black
(b) Light domat
(c) Old alluvial
(d) None of the above
2. Which of the following crops are grown with the onset of monsoons and are harvested in the months of September-October? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Rabi
(b) Kharif
(c) Zadi
(d) None of the above
3. Which one of the following is a rabi crop? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Rice
(b) Wheat
(c) Millets
(d) Cotton
4. ‘Slash and burn’ agriculture is a [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Shifting agriculture
(b) Intensive agriculture
(c) Commercial agriculture
(d) None of these
NCERT Questions
5. Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area ?
(a) Shifting Agriculture
(b) Plantation Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive Agriculture
6. Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses
(b) Millet
(c) Jowar
(d) Sesamum
7. Which one of the following is announced by the government in support of a crop ?
(a) Maximum support price
(b) Minimum support price
(c) Moderate support price
(d) Influential support price
Additional Questions
8. Jhumming refers to
(a) Primitive subsistence farming in Brazil.
(b) ‘Slash and burn’ agriculture in North-eastern states of India.
(c) Primitive farming in Malaysia.
(d) Commercial farming in Punjab.
9. Bhoodan – Gramdan movement was initiated by
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Vinoba Bhave
(d) Bal GangadharTilak
10. India is the leading producer and exporter of ………….. in the world.
(a) Rubber
(b) Sugarcane
(c) Tea
(d) Rice
11. Rearing of silkworms is called as
(a) Pisciculture
(b) Agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Sericulture
12. Yellow revolution refers to
(a) increased production of eggs.
(b) increased production of oilseeds.
(c) increased production offish.
(d) increased production of pulses.
13. Cultivation of fruits and vegetables is called
(a) Floriculture
(b) Sericulture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Agriculture
14. The third agricultural season is
(a) Kharif
(b) Rabi
(c) Zaid
(d) Spring
15. India is the ………….. largest producer of sugarcane in the world.
(a) Fifth
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) fourth
16. Which one of the following states is the leading producer of rubber ?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Kerala
(d) Andhra Pradesh
17. White revolution refers to
(a) increased production of flowers.
(b) increased production of eggs.
(c) increased production of milk.
(d) increased production of fish.
18. The leading producer of Jowar is ……………..
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Rajasthan
(c) Assam
(d) Maharashtra
19. Which position does India rank in terms of rice production in the world ?
(a) First
(b) Fifth
(c) Second
(d) Fourth
20. Which one of the following statements is incorrect as regards to commercial farming ?
(a) Use of heavy doses of modern inputs.
(b) Crops are grown for sale.
(c) Family members are involved in growing crops.
(d) Practised on large land holdings.
21. Intensive subsistence farming is practised in area of ……………
(a) high population
(b) low population
(c) deserts
(d) thick forests
22. Punjab and Haryana grow rice mainly due to
(a) availability of cheap labour.
(b) development of canals irrigation and tubewells.
(c) fertile soil.
(d) development of transport network.
23. A type of millet rich in iron, calcium, other micro nutrients and roughage is …………..
(a) Bajra
(b) Rajma
(c) Jowar
(d) Ragi
24. Which crop is grown covering 12 per cent of total cropped area ?
(a) Rice
(b) Wheat
(c) Oil seeds
(d) Millets
25. Specialised cultivation of fruits and vegetables is called
(a) Agriculture
(b) Horticulture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Pisciculture
26. Which one of the following countries produce 13 per cent of world’s vegetables ?
(a) France
(b) India
(c) Brazil
(d) Japan
27. Rearing of silk worms to produce raw silk is called ………………
(a) Floriculture
(b) Pisciculture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Viticulture
28. Which crop is used both as food crop and feed crop ?
(a) Rabi
(b) Millet
(c) Maize
(d) Pulses
29. India is the largest producer and consumer of this crop
(a) Millets
(b) Maize
(c) Pulses
(d) Oil seeds
30. Tea is a beverage crop initially introduced by the …………….
(a) Americans
(b) British
(c) Africans
(d) Australians
31. India produces ………. percent of world’s coffee production.
(a) 2 percent
(b) 5 percent
(c) 4 percent
(d) 1 percent
32. Oranges are mainly produced in the state of …………..
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Kerala
(d) Tamil Nadu
33. Grapes are mainly produced in the state of …………..
(a) Meghalaya
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Mizoram
(d) Andhra Pradesh
34. ICAR refers to
(a) International Council of Aeronautical Research
(b) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
(c) Indian Council of Animal Research
(d) International Commission for Agricultural Research
35. Grouping of small land holdings into a bigger one is called
(a) ceiling on land holdings.
(b) collectivisation.
(c) cooperative farming.
(d) consolidation of land holdings.
36. Which one of the following crops is commercial crop in one state while it is subsistence crop in another state ?
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Sugarcane
(d) Rubber
37. Which day is celebrated as World Food Day ?
(a) 11th April
(b) 16th October
(c) 10th November
(d) 15th December
38. The percentage of India’s population engaged in agriculture is
(a) 1/3
(b) 2/3
(c) 1/2
(d) 3/4
39. A type of farming in which crops are grown using primitive tools is …………….
(a) Primitive subsistence farming
(b) Extensive agriculture
(c) Plantation
(d) Commercial farming
40. Rabi crops are sown in
(a) Winter
(b) Summer
(c) Autumn
(d) Spring
41. Which one of the following states is the leading producer of Jute?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Karnataka
(c) Maharashtra
(d) West Bengal
ANSWERS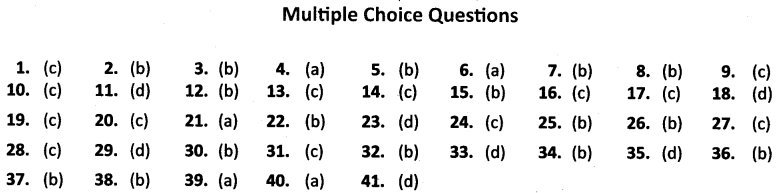
Agriculture CBSE Class 10 SST Geography Extra Questions
Agriculture NCERT Class 10 SST Geography Extra Questions
According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions For Class 10 Social Science with Answers Carries 20 Marks.
Question-1
What is the importance of agriculture in Indian economy?
Solution:
a. India is an agricultural country.
b. Nearly two-thirds of its population depends directly on agriculture for its livelihood.
c. Agriculture is the main stay of India’s economy.
d. It accounts for 26% of the gross domestic product.
e. It ensures food security for the country and produces several raw materials for industries.
f. Agricultural development is therefore, a precondition of our national prosperity.
You can also download NCERT Solutions Class 10 to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Question-2
Name three features of Indian agriculture.
Solution:
a. Farmers own small piece of land and grow crops primarily for their own consumption.
b. Animals play a significant role in the various kinds of agricultural activities.
c. Farmers depend mainly upon monsoon rains.
Question-3
What is plantation agriculture?
Solution:
a. Plantation farming is bush or tree farming
b. The British introduced it in the nineteenth century.
c. It is a single crop farming of rubber, tea, coffee, cocoa, spices, coconut and fruits like apples, grapes, oranges etc.
d. It is capital intensive and demands good managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilizers, irrigation and transport facilities.
e. Some of the plantations like tea, coffee, rubber have a processing factory within the farm itself or close to it.
f. This type of agriculture has developed in hilly areas of north- eastern India, sub-Himalayan, West Bengal and in Nilgiri, Anamalai and Cardamom hills in peninsular India.
Question-4
Name three important wheat-producing states of India.
Solution:
The main wheat producing states are U.P, Haryana, Bihar,and Punjab.
Question-5
Name three sugarcane-producing states of the country.
Solution:
The major sugarcane producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Question-6
Mention three spice-producing states of India.
Solution:
Spice producing areas in India are Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
Question-7
Name three tobacco-producing states of India.
Solution:
Tobacco producing states are Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka.
Question-8
Distinguish between: Rabi and Kharif Crops.
Solution:
Rabi and Kharif crops
Kharif:
1. Cultivation begins with the on set of monsoons in May.
2. Sowing of seeds is done in June or early July.
3. Crops are harvested in September- October.
4. Crops depend on the monsoons.
5. Types: Rice, millets, maize, groundnuts, jute, cotton and various pulses.
Rabi
1 Cultivation begins with the withdrawal of monsoons in October.
2. Sowing of seeds is done in October- November.
3. Crops are harvested in April-May.
4. Crops depend on the sub-soil moisture.
5. Types : Wheat, gram and oil-seeds like mustard and rape- seeds
Question-9:
Distinguish Between Dry and Wet Agriculture.
Solution:
Dry and Wet Agriculture
Dry Agriculture:
Dry farming is a type of farming in which moisture is maintained by raising special type of crops.
Crops such as gram and peas are grown.
There is vast dependence on irrigation.
This is practiced in dry areas of the country
Wet Agriculture:
Wet farming is a type of farming, which depends mainly upon rains.
In this type of farming rice, jute and maize are grown.
There is no irrigation required.
This type of farming is done in Northeastern parts of India.
Question-10
Distinguish between Tea and Coffee Cultivation.
Solution:
Tea and Coffee Cultivation
Tea
Coffee
It requires warm and moist-free climate
It requires hot and humid climate
The British introduced it.
The Arabic variety was brought from Yemen.
It requires 200C to 300C temperatures.
It requires 150C to 280C temperature.
It requires 300 cm rainfall.
It requires 200 cm rainfall.
It is grown in Assam, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
It is grown on hills around Nilgiris, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
Question-11
Describe various technological and institutional reforms, which led to Green and White revolutions in India.
Solution:
The various technological and institutional reforms consist of various measures taken by the Central and State governments from time to time. Flooding of fields with water is now being replaced by drip irrigation and the use of sprinklers. Chemical fertilizers are being used on a large scale, to increase the farm yields. Bio- fertilisers are now supplementing them. High yielding and early maturing quality seeds have been developed. Most of these technology inputs gave birth to Green Revolution in sixties and seventies of twentieth century. White Revolution followed the Green Revolution.
Question-12
What is the importance of animal husbandry in India?
Solution:
Farm animals form an important ecosystem in an agriculture country like India. Farm animals are the partners of the farmers. Ox, he- buffalo and camel are used as drought animals in performing activities like ploughing, sowing, thrashing and transporting farm products. Cows and she- buffalo provide them milk.
Question-13
Describe the distribution of rice cultivation in India.
Solution:
Rice is one of the major food crop in India. India is second largest producer of rice in the world after China. It is grown on about one fourth of the total cropped area and provides food to about half of the country’s population. Rice is a tropical plant. It requires high temperature of about 240C with minor variation during sowing and harvesting. It requires 100cm of rain. It is grown in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, western and eastern coastal strips, Brahmaputra valley and Jammu and Kashmir.
Question-14
How is it possible to grow rice in areas of less rain, like Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan?
Solution:
Development of canal irrigation and tube wells have made possible to grow rice in Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan.
Question-15:
Mention some industries based on agricultural raw materials.
Solution:
Tea, coffee, sugar and cotton industries.
Question-16:
What is the the PDS programme of the government of India?
Solution:
It is a programme that, provides food grains and other essential commodities at subsidized process in rural and urban areas.
Question-17
Mention one reason for big zamindars to offer Bhvadonar Goarrdan.
Solution:
Many offered due to the fear of land ceiling act.
Question-18
Name the movements started by Vinoba Bhave, known as Blood-less revolution?
Solution:
The Bhoodan – Gramdan movements started by Vinoba Bhave are known as Blood – less revolution.
Question-19
What are the 2 important beverage crops of India?
Solution:
They are coffee and tea.
Question-20
Solution:
In shifting agriculture a piece of land is cleared, crops are grown and the patch is deserted when it loses its fertility in order to regain its fertility.
Question-21
Solution:
Agriculture for the production of tropical and sub-tropical crops, like bananas, coffee, cocoa, tea, cotton, palm oil, rubber, spices, sugar and sisal. Is called plantation agriculture.
Question-22
Solution:
The area, which is actually under the cultivation and crops.
Question-23
Solution:
Agriculture with a high level of inputs, capital and labour and high yields.
Question-24
What is gross cultivated area?
Solution:
The total area on which crops are grown. It includes the area on which crops are not raised for 1 to 2 seasons.
Question-25
Define dry land farming?
Solution:
Farming without irrigation, using techniques, which conserve water for the crops.
Question-26
Define agricultural resources?
Solution:
Gifts of nature that include fertile soils, water for irrigation favorable climatic conditions for the growth of plants.
Question-27
Which are the states in India which are famous for commercial farming?
(A) Punjab and Haryana
(B) Orissa and West Bengal
(C) Rajasthan
(D) Himachal Pradesh
Solution:
(A) Punjab and Haryana.
Question-28
Which is helpful in inventing new hybrid varieties of seeds?
(A) Green Revolution
(B) White Revolution
(C) Genetic Engineering
(D) Scientific Research
Solution:
(C) Genetic Engineering .
Question-29
Which industry is based on agricultural raw material?
(A) Food-processing Industry
(B) Marine Industry
(C) Sericulture
(D) Pisiculture
Solution:
(A) Food-processing Industry.
Question-30
Which is not associated with primitive subsistence farming?
(A) Natural fertility of soil
(B) Monsoon
(C) High yield crops or seeds
(D) Involvement of family members
Solution:
(C) High yield crops or seeds.
Question-31
Match the following conditions with the different crops growth:Crop Ideal condition
A. Rice (i) Temperature- 25°C, Rainfall- 100 cm-200 cm.
B. Wheat (ii) Temperature- 20-25°C, Rainfall- 50 cm-75 cm
C. Maize (iii) Temperature- 21-27°C, Rainfall- 50 cm-75 cm
D. Pulses (iv) Temperature- 20-25°C, Rainfall- 50 cm-75 cm
(A) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii)
(B) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i)
(C) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv)
(D) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii)
Solution:
(C) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv)
Question-32
Which is a leguminous crop?
(A) Pulses
(B) Millets
(C) Jowar
(D) Sesamum
Solution:
(A) Pulses.
Question-33
Which is major pulse producing state in India?
(A) Kerala
(B) Goa
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) Punjab
Solution:
(C) Uttar Pradesh.
Question-34
Choose the correct answer
(A) A, C and D are correct
(B) C and D are correct
(C) B, C, and D are correct
(D) All are correct
Solution:
(A) A, C and D are correct.
Question-35
Which country produces more sugarcane than the India?
(A) Australia
(B) Cuba
(C) Brazil
(D) France
Solution:
(C) Brazil.
Question-36
Match the following crops with states in India: Crops States
(A) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv)
(B) A-(i), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(ii)
(C) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii)
(D) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(iii)
Solution:
(B) A-(i), B-(iv), C-(iii), D-(ii).
Question-37
Which crop is grown in shifting cultivation?
(A) Maize
(B) Rice
(C) Wheat
(D) Millet
Solution:
(B) Rice.
Question-38
Which crop is grown in Zaid season?
(A) Rice
(B) Wheat
(C) Millets
(D) Cucumber
Solution:
(D) Cucumber.
Question-39
In which state is intensive subsistence farming largely practiced?
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Gujarat
(C) West Bengal
(D) Punjab
Question-40
What is a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area called?
(A) Shifting Agriculture
(B) Plantation Agriculture
(C) Horticulture
(D) Sericulture
Solution:
(B) Plantation Agriculture.
Question-41
Which are the states which have abundance of rice production?
(A) Punjab, Haryana
(B) Karnataka, Tamil Nadu
(C) Bengal, Bihar
(D) Gujarat, Maharashtra
Solution:
(C) Bengal, Bihar.
Question-42
Which is major producer of the maize in India?
(A) Bihar
(B) Punjab
(C) Haryana
(D) Himachal Pradesh
Solution:
(A) Bihar.
Question-43
Which one of the following institutions established by Government of India, helped in modernization of Agriculture?
(A) Krishidarshan
(B) Doordarshan
(C) Indian council of Agriculture
(D) Indian Institute of Agronomy
Solution:
(C) Indian council of Agriculture.
Question-44
Which system launched by government of India ensure subsidised prices for food grains to poor in rural areas?
(A) FCI
(B) Buffer Stock
(C) PDS
(D) FCD
Solution:
(C) PDS.
Question-45
Which type of farming is not harmful as compared to modern agriculture?
(A) Intensive farming
(B) Extensive farming
(C) Organic farming
(D) Genetic farming
Solution:
(C) Organic farming.
Question-46
Point out the five uses of jute. Why is it losing market?
Solution:
Uses – It is used in making gunny bags, mats robes, yarn, carpets and other artifacts.
Due to its high cost, it is losing market to synthetic fibres, which are much cheaper and are now used for packing materials, particularly nylon.
Question-47
What is the rank, India holds in cotton production in the world? Name the major cotton producing state of India.
Solution:
(1)India ranks third in the cotton production in the world.
(2)Major Cotton producing slates are :- Maharashtra, Gujrat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh.
Question-48
What are the fibre crops of India and from where are there obtained?
Solution:
(1) The four major fibre crops of India are: – Cotton, jute, hemp and natural silk.
(2) Cotton, jute and hemp are derived from crops grown in the soil: Natural silk is obtained from the cocoons of silk worms fed on green leaves, especially mulberry.
Question-49
Which variety of Indian coffee is of great demand in the world and from where was it initially brought? Where was its cultivation initially?
Solution:
(1) The Arabic variety of Indian coffee is in great demand in the world.
(2) It was initially brought from Yemen and now produced in the country.
(3) Initially it was cultivated on Baba Budan hills.
Question-50
Give importance of groundnut as an oil seed? Name the largest groundnut producing states in India.
Solution:
(1)Groundnut accounts for about half of the major oil seeds produced in India.
(2)The largest producer of ground nut Is Andhra Pradesh. Other states are Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Question-51
Give the main oil seeds grown in India. Point out 2 to 3 of their uses.
Solution:
The main oil seeds produced in India are groundnut, coconut, mustard, seamum, soya bean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and seen flower.
Uses – Most of these are edible and used in cooking. Some of them are used a raw material in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments.
Question-52
Why are pulses usually grown in rotation with other crops? How is it important in our diet?
Solution:
All pulses except, arhar helps in soil fertility, by fixing nitrogen from the air, that is why they are mostly grown in rotation with other crops.
Role – They are a major source of protein in a vegetarian diet and India has more number of vegetarians. Also non vegetarian food is expensive and most of the Indians depend on vegetarian food.
Question-53
How is maize used? In which season is it grown? Describe briefly the soil, temperature required for the production of maize. Name 4 major maize producing states of India.
Solution:
(1) It is used as food as well as fodder.
(2) It is a Kharif crop, but in some states, like Bihar, its grown in Rabi season.
(3) It requires temperature between 21. c to 27. c, grows well in alluvial soil.
Question-54
How will the change in the cropping pattern affect the Indian Economy?
Solution:
(1) Change in the cropping pattern, for example from cereals to high value-crops will mean that India will have to import food.
(2) If India imports cereals while exporting high value commodities, it will be following successful economies like Italy, Israel and Chile.
Question-55
Why is organic farming in vogue nowadays?
Solution:
(1) It is much in vogue today, because it is practiced without factory made chemicals, such as fertilizers and pesticides.
(2) Therefore it does not affect environment in a negative manner.
Question-56
Mention two reasons for the reduction of net sown area in our country.
Solution:
Using land for non-agricultural purposes like housing, raising factories etc has resulted in reduction in net sown area.
Question-57
The excessive use of fertilizers and water has affected the soil-Explain?
Solution:
Excessive use of fertilizers and water has led to: water logging, salinity and depletion of essential micro nutrients in the soil.
Question-58
Explain the term Food Corporation of India (FCI).
Solution:
The Food Corporation of India focuses and maintains stocks of food grains. It procures food grains from the farmers at the government announced minimum support price (MSP).
Question-59
What is the lack of food security?
Solution:
Food is the basic need of every living being. If any segment of our population does not have access to food, that segment suffers from lack of food security.
Question-60
Solution:
A term coined in late 1960’s, recent developments in agriculture in our country which have led to considerable increase in agricultural yields in certain cereals, specially wheat as a result of new seeds, application of manures, and chemical fertilizers, assured water supply and use of machinery.
Question-61
Why is food Security is a big concern for the small farmers?
Solution:
(1) Free power to a certain section of farmers has encourage them to pump ground water and grow water intensive crops in low rain fall areas also (like rice in Punjab and sugarcane in Maharashtra). As a result water storage has reduced in aquifers tube wells and many wells has run dry, which has pushed small and marginal farmers out of cultivation.
(2) Inadequate storage and marketing facilities also discourage the small farmers. Thus they are badly affected by uncertainties of production and market.
(3) They pay high prices for inputs like H.Y.V seeds; fertilizers etc., but the bargaining power to fix prices in their favour, is very less
(4) All the production reaches the market simultaneously. The higher the supply, the lower the demand. Due to all the above given reason the food scarcity of small farmers is a big concern.
Question-62
Give four measures to increase agricultural production.
Solution:
(1) Each district and block can be made self sufficient in food grain production if government provides proper agricultural infrastructure that is availability of electricity, irrigation facilities, good roads, building etc.
(2) Providing loan facilities on lower interest to cultivator.
(3) Encouraging latest techniques in agricultural and instead of concentrating on rice or wheat, the food crop with a better growth potential in that particular area must be encouraged.
(4) Attract foreign investment in agriculture and also free trade in grains which will not only increase agricultural production but will also create massive employment and reduce poverty in rural areas.
Question-63
Mention the government of India’s efforts to modernize agriculture.
Solution:
(1) Establishment of Indian council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), agricultural universities veterinary services and animal breeding centers.
(2) Horticulture development research and development in the field of metrology and weather forecast etc – have been given priority for improving India’s agriculture.
(3) Improvement in the rural infrastructure, the basic system the country needs in order to work properly (i.e) transport, communication and banking system.
(4) Encouragement to the care of machines and chemical fertilizers, development of high yielding varieties of seeds.
(5) The government has launched various schemes to protect and save plants from pests and diseases.
(6) Development of various kinds of tools and implements like factors, harvesters, thrashers etc. have led to increased population and time, minimize chances of wastage, fire and rain destroying the grains lying in the few fields.
Question-64
Give the main objectives of food security policy of government of India. What is the role of FCI?
Solution:
(1) The primary objective of India’s food security policy is to ensure availability of food grains to the common people at affordable price.
(2) The forces of the Policy is on growth in agricultural production and on fixing the support price of wheat and rice.
(3) To maintain the stocks of wheat, rice and other food grains
Organizations the FCI that is food Corporation of India is responsible for procuring and stocking food grain whereas the distribution is ensured by public distribution.
Question-65
What factors have hindered the pace of agricultural development in India?
Solution:
(1) Inspite of development of source of irrigation, most of the farmers still depend upon monsoons.
(2) Farmers still depend on natural fertilizer and manures and therefore the land does not gain fertility.
(3) Indian farmers are still using outdated tools and implements and have not implemented the use of modern farming machinery.
(4) They are still using traditional methods of farming and have not made use of new technique of farming, technical and institutional reforms.
(5) Division of land after every generation has led to fragments, allow of the land and smallholdings which have become uneconomic.
Question-66
Which crop is known as golden fibre? Describe the geographical requirements for its growth, and name the major states producing it.
Solution:
(1) Jute is known as the golden fibre.
(2) Geographical requirements: –
(a) Well drained fertile soils in the flood plains where soils are renewed every year.
(b) High temperature during the time of growth.
Question-67
Why is the production of pulses and oil seeds still lagging behind?
Solution:
(1) Though the production of oil seeds and pulses is rising but the population is growing at a greater pace.
(2) The production of pulses and oil seals is subject to fluctuation and market speculations.
(3) They need HYV seeds for high productivity, assured irrigation and chemical fertilizers, which are costly, and India farmers cannot afford them.
(4) Their support price is not attractive.
Question-68
Name the major challenges faced by the Indian farmers today?
Solution:
(1) Though the production of oil seeds and pulses is rising but the population is growing at a greater pace.
(2) The production of pulses and oil seals is subject to fluctuation and market speculations.
(3) They need HYV seeds for high productivity, assured irrigation and chemical fertilizers, which are costly, and India farmers cannot afford them.
(4) Their support price is not attractive.
Question-69
What are the implications of growing population on Indian farming?
Solution:
Following are the implications of growing population on farming:
(1)Almost every step has been taken to increase food production and now there is very little scope for increasing it further.
(2)India’s population is increasing at an alarming rate. Whatever has been advised so far in food production would soon be neutralized by this ever growing population.
Question-70
How has agriculture contributed to the national Income and employment?
Solution:
(1) Agriculture has been the backbone of Indian economy. It provides employment and livelihood to nearly 63% of India’s population (In 2001).
(2) Two thirds of India’s population is engaged in agricultural activities.
(3) Agriculture is a primary activity which produces most of the food that we consume. Besides food grains, it also produces raw materials for many industries. Some agricultural products like tea, coffee, spices etc are exported and they bring in foreign exchange for the country.
Question-71
What are the 3 main problems faced by Indian farmers today?
Solution:
The problems faced by the Indian farmers are :-
(1) There is lack of availability of water for irrigation.
(2) Most of the farmers have small holdings which are uneconomical.
(3) The high yielding variety of seeds, chemical fertilizers, insecticides, pesticides etc are expensive and our farmers find it difficult to purchase these.
(4) The soil is loosing its fertility; due to soil erosion, absence of good forests.
(5) Our farmers have to take heavy loans. Therefore, to payback these, they are compelled to sell their produce at cheap rates.
Question-72
Who introduced tea in India? Why do we say that tea is a labour intensive industry? Where is it mostly produced? Name the major tea producing states.
Solution:
(1) The British introduced tea to India.
(2) Tea is labour intensive industry because it requires abundant, cheap and skilled labour.
(3) Tea is generally processed within the tea gardens to restore its freshness.
(4) Major tea producing states are – Assam, hills of Darjeeling and Jalpaigur districts, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu, Kerala. Besides, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura are also tea producing states.
Question-73
Mention the important millets grown in India. Which of them is the 3rd most important crop with respect to area and production? What is the importance of millets? Give examples.
Solution:
(1) Jowar, bajra and ragi are the most important millets of India.
(2) Jowar is the 3rd most important crop with respect to area and production.
(3) Importance – Millets have high nutritional value. For example, Ragi is very rich in iron, calcium, other micro-nutrients and roughage.
Question-74
Give the second most important cereal crop of India? When is it grown? What is the temperature, soil, rainfall, and irrigation required for its production?
Solution:
(1) Wheat is the second most important cereal crop of India.
(2) This is a rabi crop, its sown in winter from October to December.
(3) It requires a cool growing season and a bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
(4) Requires 50 to 75 cms of annual rainfall, evenly distributed over growing seasons or irrigation facilities.
Question-75
Why has Indian agriculture been transformed from subsistence to commercial farming.
Solution:
Before independence Indian agriculture was mainly that of subsistence farming, but now it has changed to commercial farming. The reasons are –
(1) The small and scattered land holdings have been consolidated and converted to large holding and ploughed on cooperative basis.
(2) The farmers have started using modern techniques of farming and scientific methods; also they have started use of fertilizers and high yielding varieties of seeds and farm machinery.
(3) Irrigation methods have improved, resulting in increased soil fertility.
(4) New methods of agriculture like rotation of crops, inter cropping, strip cropping, multiple cropping, have been adopted for better results.
(5) As a result of production of wheat, rice, sugarcane, millets etc spices, cotton, jute, tea etc has increased many times.
Due to all these reasons Indian agriculture is shifting from subsistence to commercial farming.
Question-76
Distinguish between fertilizers and manures.
Solution:
(1) Fertilizers generally refer to chemical fertilizers which are produced in factories. They contain chemical elements like phosphorus, potassium and nitrogen etc.
(2) Whereas, manures refers to green leaf manures, farm wastes, compost produced by storing cow dung and farm wastes. Manures are of biological origin and are not prepared in factories.
Question-77
What are the differences between intensive agriculture and extensive agriculture/farming.
Solution:
Intensive Agriculture:
(1) To obtain high yields, large capitals and labourers are applied.
(2) The size of land holding is small, production per hectare is high.
(3) Most of the production is consumed locally.
(4) Manual labour and drought animals are mostly used.
Extensive Agriculture:
(1) As compared less capital and labour is applied.
(2) The size of land holding is large and production per hectare is low.
(3) Surplus production is sold in the market.
(4) Mechanized farming is practiced. This type of farming is practiced in sparsely populated areas.
Question-78
Differentiate between settled agriculture and shifting agriculture.
Solution:
Settled Agriculture:
(1) In agricultural farms, it is practiced permanently on a small or big piece of land. In this type of agriculture, size of the field is not paid much attention.
(2) The land / soil is often suitable for agriculture, if not it is made suitable by farmers, by using manures to increase the fertility of land.
Shifting agriculture:
(1) In this type of agriculture the place of cultivation changes after 2 to 3 crops, when there is over growth of grass, weeds etc. It is left fallow to regain its fertility.
(2) The land for this type of agriculture is obtained after burning bushes etc or after cutting down trees or bushes. The farmer does not use manure to regain the fertility of the land.
Question-79
What are the cropping seasons are found in India? When are crops sown & harvested in each of these. With examples.
Solution:
India has 3 cropping seasons Rabi, Kharif and Zaid.
a) Rabi – Crops are sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from april to june. Some of the important crops are – wheat, barley, mustard, peas, grass.
b) Kharif – Crops are grown with the outset of monsoons and harvested in September – October. Important crops are – paddy, maize, jowar, bazra, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, ground nut, soya bean.
c) Zaid – Crops are grown between rabi and kharif, there is a short season during summer known as Zaid season. Important crops are – watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops. Sugar cane takes almost a year to grow.
Question-80
Define plantation farming. What are its main characteristics? Name any five plantation crops of India.
Solution:
Plantation farming is a bush or tree farming. In this type of farming a single crop in grown on a large area. Characteristics –
This type of agriculture is found in:
(1) Hilly areas or North India, Sub Himalayas, W Bengal, Nilgiris, Andaman and cardamom hills.
(2) The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry.
(3) Covers large areas of land.
(4) It is capital intensive, i.e it requires expensive inputs, requires skilled laboureres.
(5) All the production is used as raw material in respective industries. The important crops are tea, coffee, banana, sugarcane etc.
Question-81
Give the characteristics of commercial farming?
Solution:
(1) Use of higher doses of modern inputs, that is high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity.
(2) Agriculture goods are mainly produced for sale.
(3) The main crops are rice, millets, spices, cotton, etc. The farmer can sell them on commercial lines.
(4) The degree of commercialization varies from one region to another. For example, rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Orissa, it is subsistence farming.
Question-82
What is slash and burn agriculture?
Solution:
In this farmers clear a patch of land and produce cereals and other crops to sustain their family, when the soil looses its fertility, the farmers shift and clear a fresh patch of land for cultivation. Nature replenishes the fertility of soil through natural processes. Land productivity in this type of agriculture is low, because the farmers do not use fertilizers or other modern inputs. It is generally known as shifting agriculture, but also known in different names in different parts of the country.
Question-83
Define subsistence farming and give its main characteristics.
Solution:
Refers to an agricultural system where crops are produced for self use or for circulation within the social networks for ritual, ceremonial exchange puposes, and some food may be sold in the market.
Characteristics:-
(a) Small scattered land holding.
(b) Primitive tools.
(c) Farmers being poor do not use fertilizers and high yielding quality seeds as per requirement, facilities like electricity, irrigation, generally is not available to farmers.
(d) It has given way to commercial agriculture to some extent.
Question-84
What are the different types of farming / agriculture practiced in India?
Solution:
(1) Primitive Subsistence Farming – Known by different name in different parts of India,subdivided into shifting agriculture.
(2) Intensive Subsistence Farming – Practiced in areas of high population pressure. It is labour intensive.
(3) Commercial Farming – Includes plantation farming.
Question-85
Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Solution:
It is a kharif crop, which requires –
(a) High Temperature – above 15. C and high humidity.
(b) Rainfall – Annual rainfall above 100cms. In areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
(c) Plains of North and North-eastern India, coastal areas and deltaic regions are suitable for the growth of rice.
Question-86
What type of soil is suited for cultivation of tea?
Solution:
Deep fertile well drained soil rich in humus and organic matter is suited for cultivation of tea.
Question-87
Mention two characteristics of commercial farming.
Solution:
High doses of fertilisers and pesticides are used in commercial farming.
Question-88
Which price is announced by the government in support of a crop?
Solution:
Minimum Support Price is announced by the government in support of a crop.
Question-89
Name four major wheat producing states in India.
Solution:
Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh are the four major wheat producing states in India.
Question-90
How have technological and institutional reforms been able to improve the conditions of Indian farmers?
Solution:
The Zamindari system in which property rights are vested on absentee landlords was abolished after India became independent. Ownership rights were transferred to the actual tillers of the land. The new land owners made improvements on their lands. This led to increase in yields.
Land ceiling acts were passed to ensure that no person could hold agricultural land beyond a specified limit. The excess land was distributed among the landless labourers.
Small land holdings scattered over various places were consolidated through the Consolidation of holdings Acts passed by the State legislatures. This resulted in farmers being able to fence their lands, sink wells and use modern agricultural machinery.
Formation of Corporative societies helped farmers get seeds, pesticides and fertilizers at economical prices. All these helped improve the condition of the Indian farmers.
Question-91
What is the importance of agriculture on Indian economy? Name 3 features of Indian agriculture.
Solution:
a. India is an agricultural country.
b. Nearly two-thirds of its population depends directly on agriculture for its livelihood.
c. Agriculture is the main stay of India’s economy.
d. It accounts for 26% of the gross domestic product.
e. It ensures food security for the country and produces several raw materials for industries.
f. Agricultural development is therefore, a precondition of our national prosperity.
Features
a. Farmers own small piece of land and grow crops primarily for their own consumption.
b. Animals play a significant role in the various kinds of agricultural activities.
c. Farmers depend mainly upon monsoon rains.
Question-92
Solution:
a. Plantation farming is bush or tree farming
b. The British introduced it in the nineteenth century.
c. It is a single crop farming of rubber, tea, coffee, cocoa, spices, coconut and fruits like apples, grapes, oranges etc.
d. It is capital intensive and demands good managerial ability, technical know-how, sophisticated machinery, fertilizers, irrigation and transport facilities.
e. Some of the plantations like tea, coffee, rubber have a processing factory within the farm itself or close to it.
f. This type of agriculture has developed in hilly areas of north- eastern India, sub-Himalayan, West Bengal and in Nilgiri, Anamalai and Cardamom hills in peninsular India.
Question-93:
Describe various technological and institutional reforms, which led to Green and White revolutions in India.
Solution:
The various technological and institutional reforms consist of various measures taken by the Central and State governments from time to time. Flooding of fields with water is now being replaced by drip irrigation and the use of sprinklers. Chemical fertilizers are being used on a large scale, to increase the farm yields. Bio- fertilisers are now supplementing them. High yielding and early maturing quality seeds have been developed. Most of these technology inputs gave birth to Green Revolution in sixties and seventies of twentieth century. White Revolution followed the Green Revolution.
- Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
- Chapter 2 The Nationalist Movement in Indo-China
- Chapter 3 Nationalism in India
- Chapter 4 The Making of Global World
- Chapter 5 The Age of Industrialisation
- Chapter 6 Work, Life and Leisure
- Chapter 7 Print Culture and the Modern World
- Chapter 8 Novels, Society and History
NCERT Class 10 SST Solutions Geography:
- Chapter 1 Resource and Development
- Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources
- Chapter 3 Water Resources
- Chapter 4 Agriculture
- Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
- Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
- Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
NCERT Solutions Class 10 SST
- Chapter 1 Power Sharing
- Chapter 2 Federalism
- Chapter 3 Democracy and Diversity
- Chapter 4 Gender Religion and Caste
- Chapter 5 Popular Struggles and Movements
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
.png)
.png)