Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (English + Hindi) NCERT Solutions
- Ex.4.1
- Ex.4.2
- Ex.4.3
- Ex.4.4
- Ch 4 with Solutions Extra Questions
- Ch 4 Quadratic Equations Important Questions
- Ch 4 Quadratic Equations Notes
Ex 4.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
(i) (x+ 1)2=2(x-3)
(ii) x – 2x = (- 2) (3-x)
(iii) (x – 2) (x + 1) = (x – 1) (x + 3)
(iv) (x – 3) (2x + 1) = x (x + 5)
(v) (2x – 1) (x – 3) = (x + 5) (x – 1)
(vi) x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2
(vii) (x + 2)3 = 2x(x2 – 1)
(viii) x3 -4x2 -x + 1 = (x-2)3
Solution:
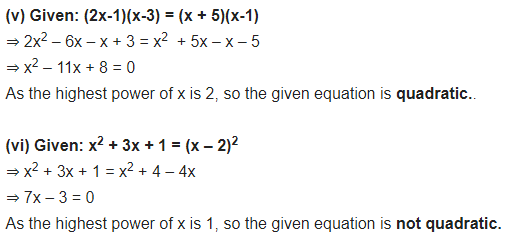
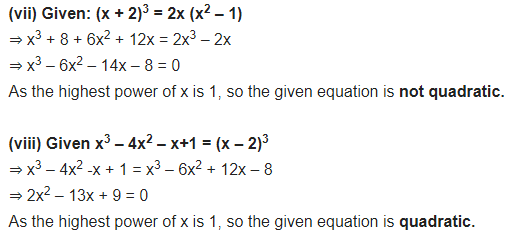
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 4 Quadratic Equations- Video
You can also watch the video solutions of NCERT Class10 Maths chapter 4 Quadratic Equations here.
Ex 4.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Represent the following situations in the form of quadratic equations:
(i) The area of a rectangular plot is 528 m2. The length of the plot (in metres) is one more than twice its breadth. We need to find the length and breadth of the plot.
(ii) The product of two consecutive positive integers is 306. We need to find the integers.
(iii) Rohan’s mother is 26 years older than him. The product of their ages (in years) 3 years from now will be 360. We would like to find Rohan’s present age.
(iv) A train travels a distance of 480 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 8 km/h less, then it would have taken 3 hours more to cover the same distance. We need to find the speed of the train.
Solution:

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (Hindi Medium) Ex 4.1









Class 10 Maths Quadratic Equations Mind Map
Quadratic Equation
Standard form of the quadratic equation in the variable x is an equation of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
Any equation of the form P(x) = 0, Where P(x) is a polynomial of degree 2, is a quadratic equation.
Zero(es)/Root(s) of Quadratic Equation
A real number α is said to be a root of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 if aα2 + bα + c = 0.
We can say that x = α, is a solution of the quadratic equation or that α satisfies the quadratic equation.
The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial ax2 + bx + c = 0 and the roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are same. A quadratic equation has atmost two roots/zeroes.
Relation Between Zeroes and Co-efficient of a Quadratic Equation
If α and β are zeroes of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0 then
Methods of Solving Quadratic Equation
Following are the methods which are used to solve quadratic equations:
(i) Factorisation
(ii) Completing the square
(iii) Quadratic Formula
Methods of Factorisation
In this method we find the roots of a quadratic equation (ax2 + bx + c = 0) by factorising LHS it into two linear factors and equating each factor to zero, e.g.,
6x2 – x – 2 = 0
⇒ 6x2 + 3x – 4x – 2 = 0 …(i)
⇒ 3x (2x + 1) – 2(2x + 1) = 0
⇒ (3x — 2) (2x + 1) = 0
⇒ 3x – 2 = 0 or 2x + 1 = 0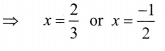
Necessary Condition : Product of 1st and last terms of eq. (i) should be equal to product of 2nd and 3rd terms of the same equation.
Method of Completing the Square
This is the method of converting L.H.S. of a quadratic equation which is not a perfect square into the sum or difference of a perfect square and a constant by adding and subtracting the suitable constant terms. E.g,
(1) x2 + 4x – 5 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2(2)(x) -5 = 0
⇒ x2 + 2(2)(x) + (2)2 – (2)2 – 5 = 0
⇒ (x + 2)2 – 4 – 5 = 0
⇒ (x + 2)2 – 9 = 0
⇒ x + 2 = ± 3
⇒ x = —5, 1
(2) 3x2 – 5x + 2 = 0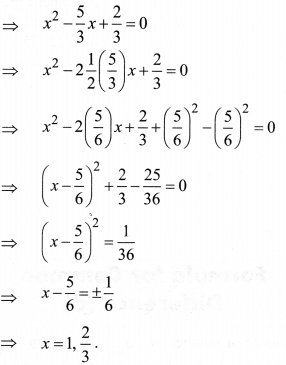
Quadratic Formula
Consider a quadratic equation: ax2 + bx + c = 0.
If b2 – 4ac ≥ 0, then the roots of the above equation are given by: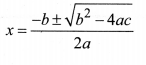
Nature of Roots
For quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0
(a ≠ 0), value of (b2 – 4ac) is called discriminant of the equation and denoted as D.
D = b2 – 4ac
Discriminant is very important in finding nature of the roots.
(i) If D = 0, then roots are real and equal.
(ii) If D > 0, then roots are real and unequal
(iii) If D < 0, then roots are not real.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.2
Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations by factorisation:
(i) x2 -3x – 10 = 0
(ii) 2x2 + x – 6 = 0
(iii) √2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0
(iv) 2x2 – x +
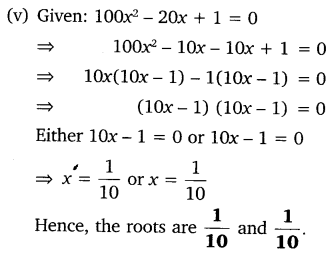
(v) 100 x2 – 20 X + 1 = 0
Solution:

Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Solve the following situations mathematically:
(i) John and Jivanti together have 45 marbles. Both of them lost 5 marbles each and the product of the number of marbles they now have is 124. We would like to find out how many marbles they had to start with.
(ii) A cottage industry produces a certain number of toys in a day. The cost of production of each toy (in rupees) was found to be 55 minus the number of toys produced in a day. On a particular day, the total cost of production was ₹750. We would like to find out the number of toys produced on that day.
Solution: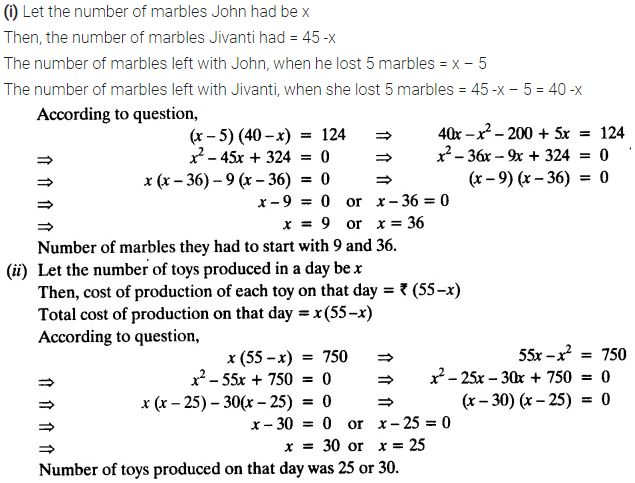
Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
Find two numbers whose sum is 27 and product is 182.
Solution: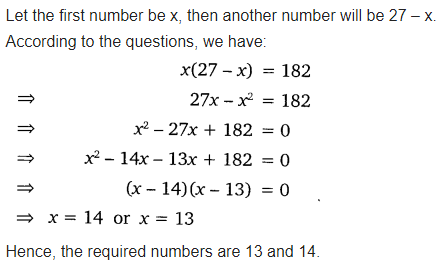
Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
Find two consecutive positive integers, the sum of whose squares is 365.
Solution: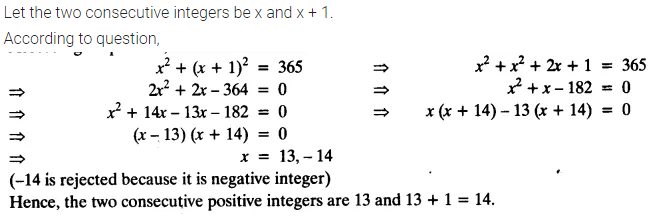
Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
The altitude of a right triangle is 7 cm less than its base. If the hypotenuse is 13 cm, find the other two sides.
Solution: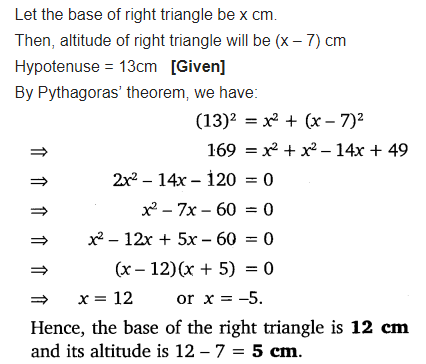
Ex 4.2 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
A cottage industry produces a certain number of pottery articles in a day. It was observed on a particular day that the cost of production of each article (in rupees) was 3 more than twice the number of articles produced on that day. If the total cost of production on that day was ₹90, find the number of articles produced and the cost of each article.
Solution: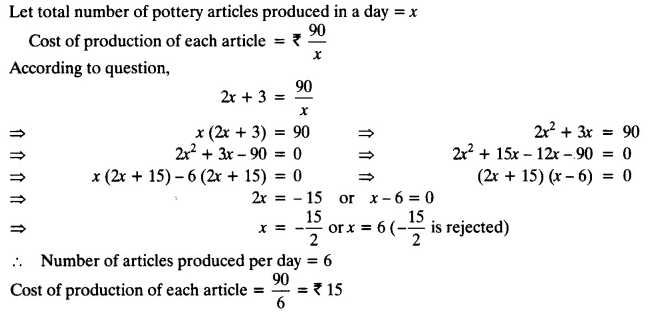
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (Hindi Medium) Ex 4.2

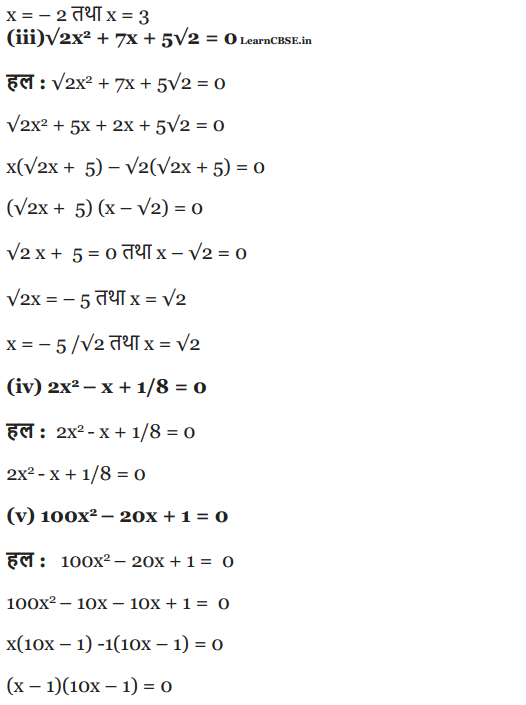









Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.3
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
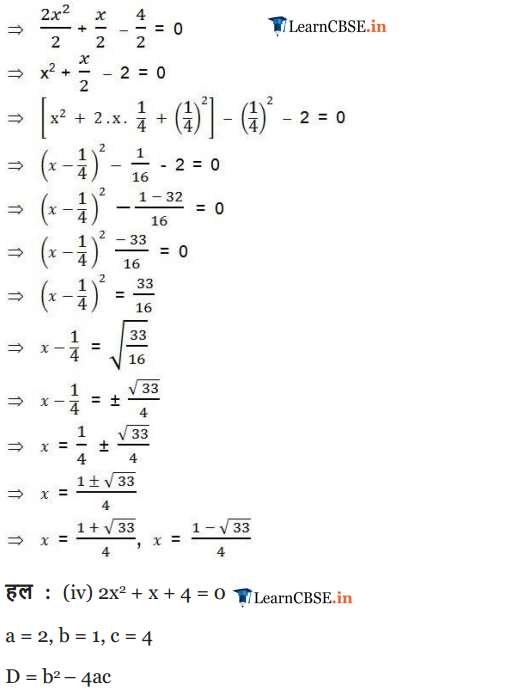
(i) 2x2 – 7x + 3 = 0
(ii) 2x2 + x – 4 = 0
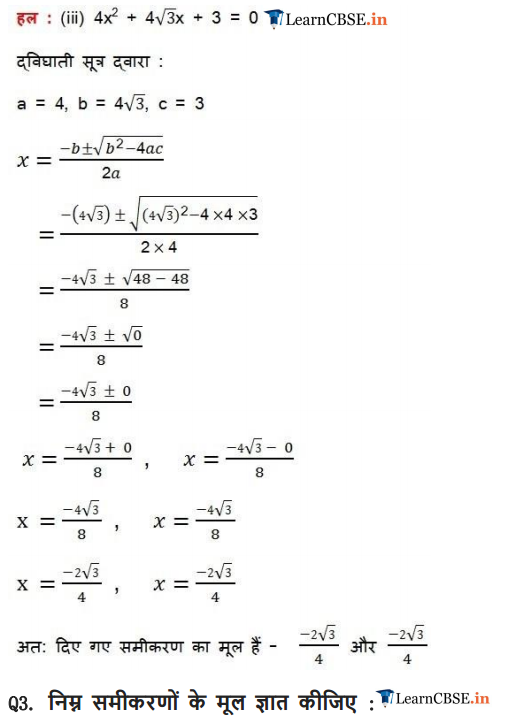
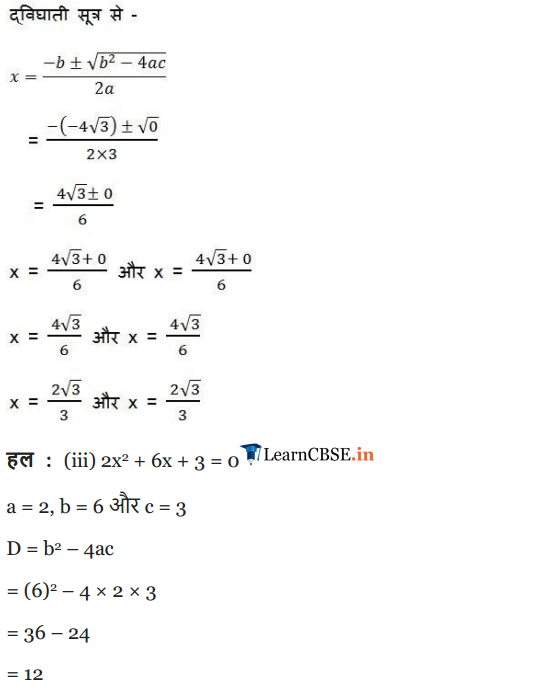
(iii) 4x2 + 4√3x + 3 = 0
(iv) 2x2 + x + 4 = 0
Solution: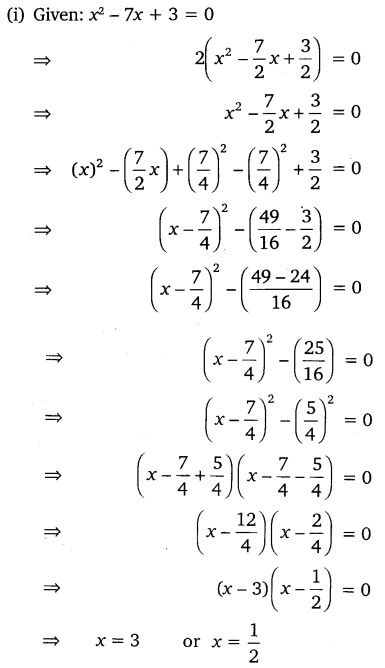
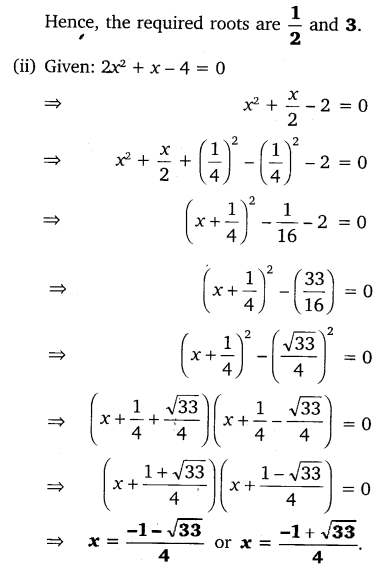
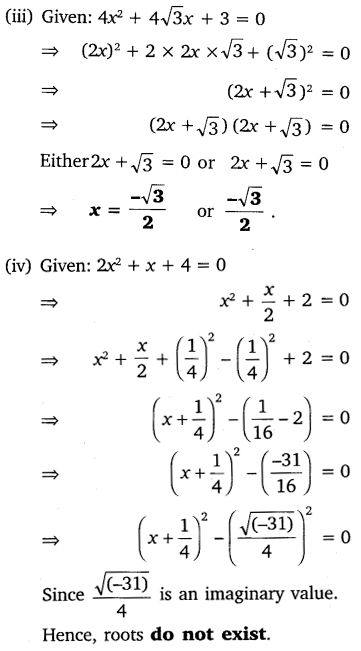
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Find the roots of the quadratic equations by applying the quadratic formula.
(i) 2x2 – 7x + 3 = 0
(ii) 2x2 – x + 4 = 0
(iii) 4x2 – 4√3x + 3 = 0
(iv) 2x2 – x + 4 = 0
Solution: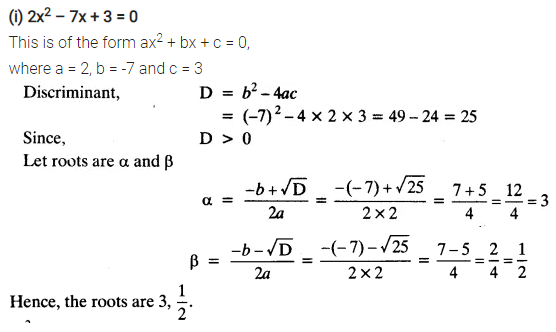


Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
Find the roots of the following equations:![]()
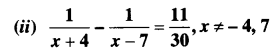
Solution: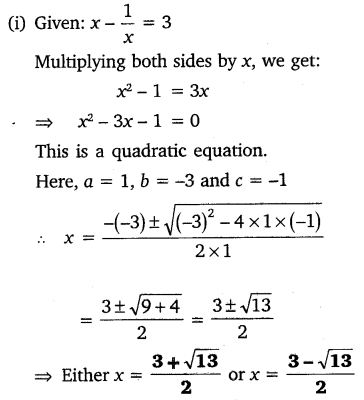
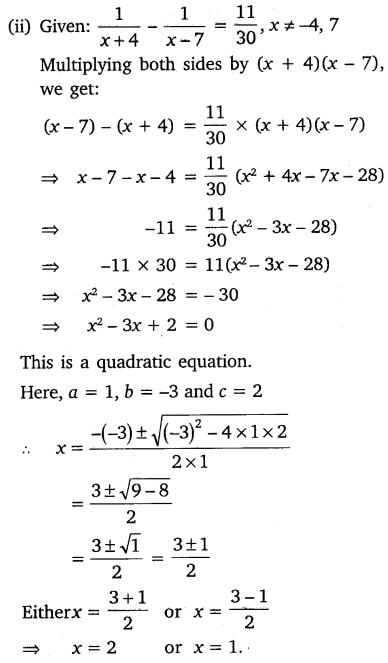
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
The sum of the reciprocals of Rehman’s ages, (in years) 3 years ago and 5 years from now is
Solution:
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
In a class test, the sum of Shefali’s marks in Mathematics and English is 30. Had she got 2 marks more in Mathematics and 3 marks less in English, the product of their marks would have been 210. Find her marks in the two subjects.
Solution: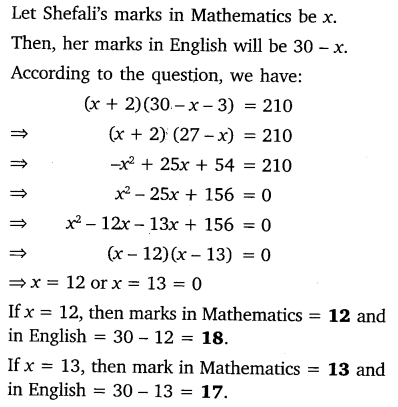
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
The diagonal of a rectangular field is 60 metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 30 metres more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Solution: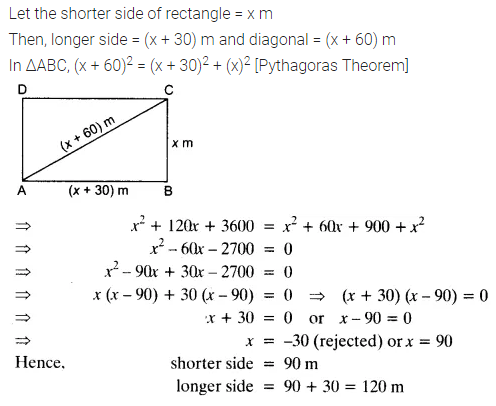
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
The difference of squares of two numbers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger number. Find the two numbers.
Solution:

Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
A train travels 360 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 5 km/h more, it would have taken 1 hour less for the same journey. Find the speed of the train.
Solution:
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
Two water taps together can fill a tank in 9
Solution:
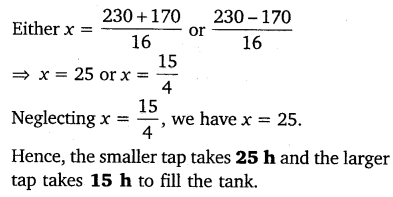
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 10.
An express train takes 1 hour less than a passenger train to travel 132 km between Mysore and Bengaluru (without taking into consideration the time they stop at intermediate stations). If the average speed of the express train is 11 km/h more than that of the passenger train, find the average speed of the two trains.
Solution:
Ex 4.3 Class 10 Maths Question 11.
Sum of the areas of two squares is 468 m2. If the difference of their perimeters is 24 m, find the sides of the two squares.
Solution:
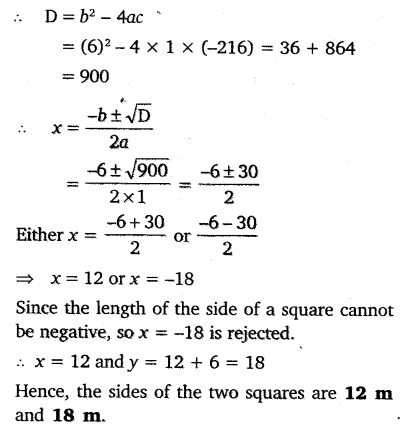
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (Hindi Medium) Ex 4.3
Chapter 4. द्विघात समीकरण

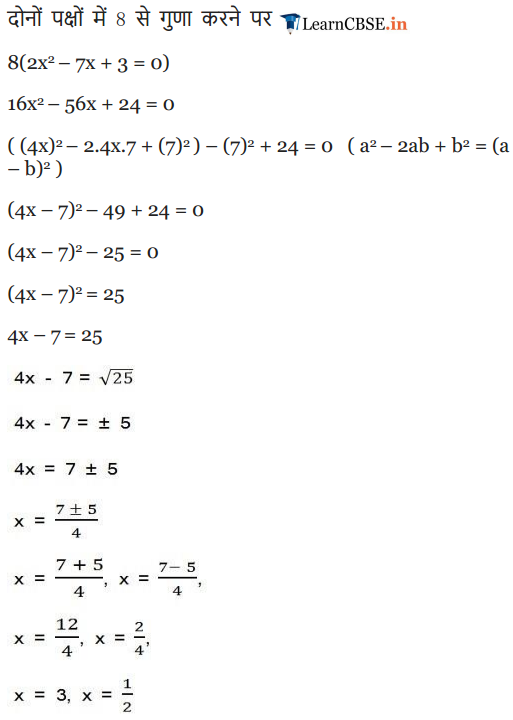




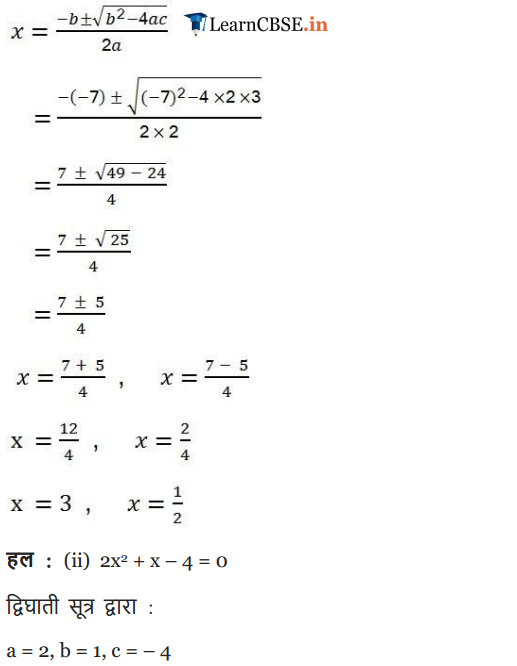


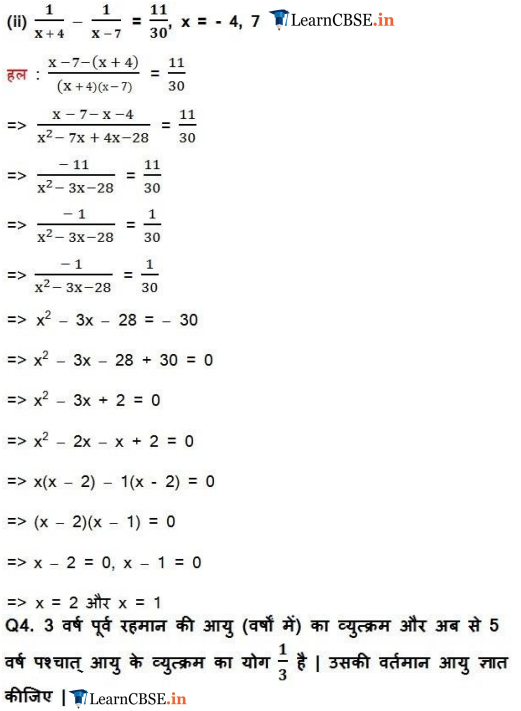






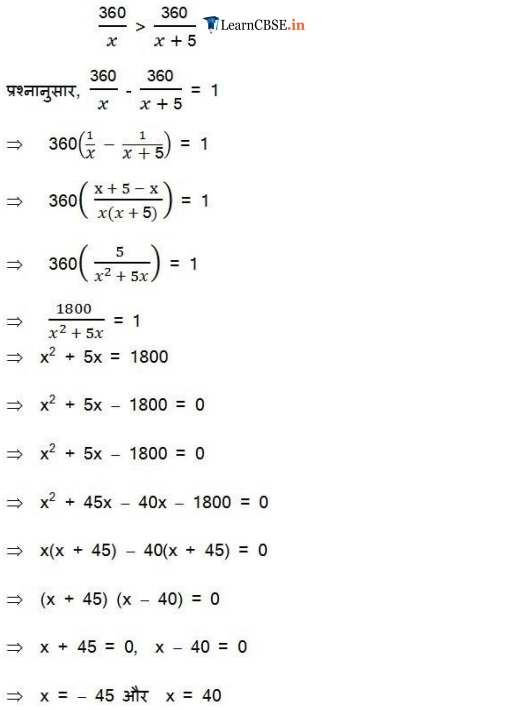






Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.4
Ex 4.4 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If the real roots exist, find them:
(i) 2x² -3x + 5 = 0
(ii) 3x2 – 4√3x + 4 = 0
(iii) 2x2-6x + 3 = 0
Solution:

Ex 4.4 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
Find the values of k for each of the following quadratic equations, so that they have two equal roots.
(1) 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0
(2) kx (x – 2) + 6 = 0
Solution:
Ex 4.4 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
Is it possible to design a rectangular mango grove whose length is twice its breadth, and the area is 800 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Solution:
Ex 4.4 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
Is the following situation possible? If so, determine their present ages.
The sum of the ages of two friends is 20 years. Four years ago, the product of their ages in years was 48.
Solution: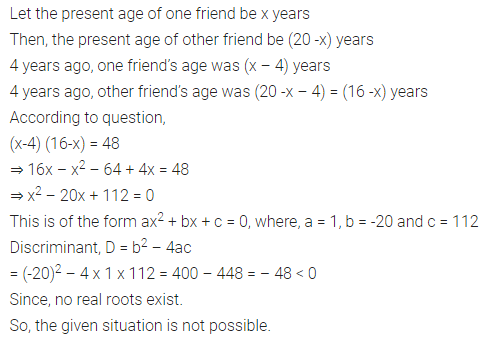
Ex 4.4 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
Is it possible to design a rectangular park of perimeter 80 m and area 400 m2? If so, find its length and breadth.
Solution:
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations (Hindi Medium) Ex 4.4
Chapter 4. द्विघात समीकरण







Quadratic Equations Class 10 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
For what value of V the quadratic equation 9x2 – 3ax + 1 = 0 has equal roots?
Or
If one root of the quadratic equation 2x2 + 2x + k = 0 is –
Answer:
For equal roots D = 0
where D = b2 – 4ac
Here a = 9, b = – 3a, c = 1
∴ (- 3a)2 – 4(9) (1) = 0
⇒ 9a2 – 36 = 0
⇒ 9(a2 – 4) = 0
⇒ a2 = 4
⇒ a = ± 2
Or
Let, p(x) = 2x2 + 2x + k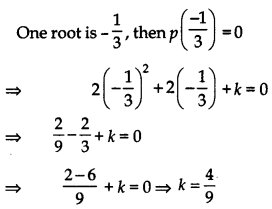
Question 2.
For what values of k, the roots of the equation x2 + 4x + k = 0 are real?
Or
Find the value of k for which the roots of the equation 3x2 – 10x + k = k = 0 are reciprocal of each other. [CBSE 2019]
Answer:
For real roots D ≥ 0 i.e., b2 – 4ac ≥ 0
Here, a = 1, b = 4, c = k
∴ (4)2 – 4(1)k ≥ 0
⇒ 16 – 4k ≥ 0 ⇒ k ≤ A
Or
Roots of the equation 3x2 – 10x + k = 0 are reciprocal of each other
⇒ Product of roots = 1
⇒
Question 3.
If the roots of quadratic equation px2 + 6x + 1 = 0 are real, then find p.
Answer:
Roots are real, D ≥ 0
b2 – 4ac ≥ 0
(62) – 4 × p × 1 ≥ o
9 ≥ p
Question 4.
If 7x2 – (2p2 – 8)x + 16 = 0 has two roots which are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign then find p.
Answer:
Let the roots be α and – α.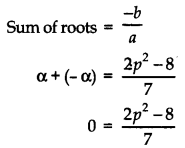
0 = 2p2 – 8
p2 = 4
p = ±2
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Extra Questions Short Answer Type-1
Question 1.
Find the roots of the quadratic equation
√2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0 [CBSE Delhi 2017]
Answer:
√2x2 + 7x + 5√2 = 0
√2x2 + 2x + 5x + 5√2 = 0
⇒ (√2x + 5) (x + √2) = 0
⇒ x =
or
Question 2.
Find the value of k for which the equation x2 + k(2x + k – 1) + 2 = 0 has real and equal roots.
Answer:
Rewriting given equation as
x2 + 2kx + (k2 – k + 2) = 0
Here a = 1, b = 2k, c = k2 – k + 2
For equal roots, b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (2k)2 – 4(1) (k2 – k + 2) = 0![]()
⇒ k = 2
Question 3.
If – 5 is a root of the quadratic equation 2x2 + px – 15 = 0 and the quadratic equation p(x2 + x) + k = 0 has equal roots, find the value of k. [CBSE Outside Delhi 2016]
Answer:
– 5 is root of the equation 2x2 + px – 15 = 0, then
2(-5)2 + p(-5) – 15 = 0
⇒ 50 + (- 5)p – 15 = 0
⇒ p =
p(x2 + x) + k = 0 has equal root
⇒ b2 – 4ac = 0
Here b = p, a = p, c = k
⇒ p2 = 4 pk ………….. (2)
(7)2 – 4 × 7k = 0
(1) and (2) gives,
∴ k =
Question 4.
For what value of k, x2 + 4x + k is a perfect square?
Answer:
A quadratic expression is a perfect square, if and only if corresponding equation has equal roots.
i.e., D = 0
⇒ 16 – 4k = 0
⇒ k = 4
Question 5.
Solve:
[x ≠ 0, x ≠ – (a + b)].
Answer: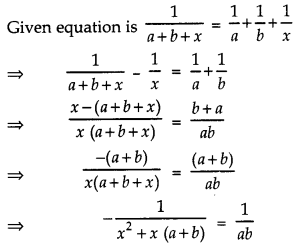
⇒ – ab = x2 + x (a + b)
⇒ x2 + x (a + b) + ab = 0
⇒ x2 + ax + bx + ab = 0
⇒ x (x + a) + b (x + a) = 0
⇒ (x + a) (x + b) = 0
∴ x = – a or x = – b
Hence, – a and – b are roots of given equation.
Question 6.
The product of two consecutive positive integers is 306. Find the integers.
Answer:
Let the consecutive positive integers be x and x + 1.
Then, x (x + 1) = 306
or, x2 + x – 306 = 0
or, x2 + 18x – 17x – 306 = 0
or, x(x + 18) – 17(x + 18) = 0
or, (x + 18) (x – 17) = 0
x = – 18, 17
Neglecting x = – 18
∴ x = 17 and x + 1 = 17 + 1 = 18
Hence, two consecutive positive integers are 17 and 18.
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Extra Questions Short Answer Type-2
Question 1.
If the equation (1 + m2)x2 + 2 mcx + c2 – a2 = 0 has equal roots then show than c2 = a2 (1 + m2). [CBSE 2017]
Answer:
(1 + m2) x2 + 2mcx + c2 – a2 = 0
Here A = (1 + m2), B = 2mc, C = c2 – a2
For equal roots; B2 – 4AC = 0
⇒ (2mc)2 – 4(1 + m2) (c2 – a2) = 0![]()
⇒ c2 – a2(1 + m2) = 0
⇒ c2 = a2(1 + m2)
Question 2.
Solve for x:
Answer:
Given: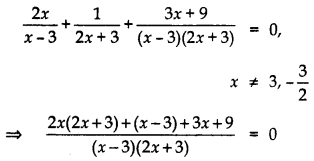
⇒ 4×2 + 6x + x- 3 + 3x + 9 = 0
⇒ 4×2 + lOx + 6 = 0
⇒ 4×2 + 4x+ 6x + 6 = 0
⇒ 4x(x + 1) + 6(x + 1) = 0
⇒ (x +1) (4x + 6) = 0
⇒ x + 1 = 0
or 4x + 6 = 0
⇒ x = – 1, –
But
x ≠ –
Question 3.
A plane left 30 minutes late than its scheduled time and in order to reach the destination 1500 km away in time, it had to increase its speed by 100 km/h from the usual speed. Find its usual speed.
Answer:
Let the usual speed of plane be x km/hr
∴ [Time taken to travel 1500 km with speed × km/hr] – [Time taken to travel 1500 km with speed (x + 100) km/hr] = half an hour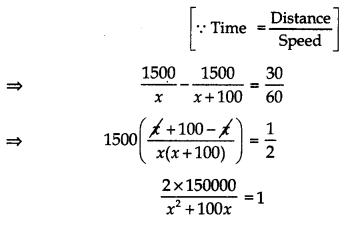
⇒ x2 + 100x – 300000 = 0
x2 + 600x – 500x – 300000 = 0
(x + 600) (x – 500) = 0
x = 500 as x can’t be negative so – 600 is rejected.
∴ usual speed of the plane is 500 km/hr.
Question 4.
Find the value of p for which the quadratic equation (2p + 1)x2 – (7p + 2)x + (7p – 3) = 0 has equal roots. Also find these roots. [S.A-II, 2014]
Answer:
(2p + 1)x2 – (7p + 2)x + (7p – 3) = 0 …(1)
For equal roots D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ [- (7p + 2)]2 – 4(2p + 1) (7p – 3) = 0
⇒ 49p2 + 4 + 28p – 4 (14p2 – 6p + 7p – 3) = 0
⇒ 49p2 + 28p + 4 – 56p2 + 24p – 28p + 12 = 0
⇒ – 7p2 + 24p + 16 = 0
⇒ 7p2 – 24p – 16 = 0
⇒ 7p2 – 28p + 4p – 16 = 0
⇒ 7p (p – 4) + 4 (p – 4) = 0
⇒ (p – 4) (7p + 4) = 0
∴ p = 4,
If p = 4, then (1)
⇒ 9x2 – 30x + 25 = 0
⇒ 9x2 – 15x – 15x + 25 = 0
⇒ 3x(3x – 5) – 5(3x – 5) = 0
⇒ (3x – 5) (3x – 5) = 0
⇒ (3x – 5)2 = 0
⇒ 3x – 5 = 0
∴ x =
∴ Roots are
If P = –
⇒
– x2 + 14x – 49 = 0
x2 – 14x + 49 = 0
(x – 7)2 = 0
∴ x = 7, 7
Question 5.
A journey of 192 km from a town A to town B takes 2 hours more by a ordinary passenger train than a super fast train. If the speed of the faster train is 16 km/h more, find the speeds of the faster and the passenger train.
Answer:
Let the speed of passenger train be x km/h.
Then, speed of faster train = (x + 16) km/h
According to question:
Time taken to complete the journey by faster train (t1) =
According to question,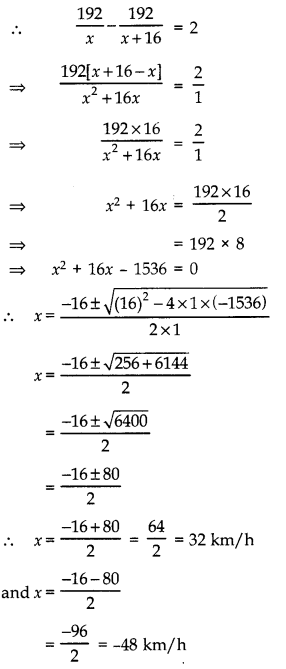
∵ Speed cannot be negative.
∴ Speed of the passenger train = 32 km/h
and speed of faster train = 32 + 16 = 48 km/h
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Extra Questions Long Answer Type 1
Question 1.
Speed of a boat in still water is 15 kn\h. It goes 30 km upstream and returns back at the same point in 4 hours 30 minutes. Find the speed of the stream. [CBSE Delhi 2017]
Answer:
Let speed of boat be xkm/hr
∴ Speed of boat upstream = (15 – x) km/hr.
200 = 225 – x2
⇒ x2 = 25
x = 5 (Rejecting – 5)
∴ Speed of stream = 5 km/hr
Question 2.
Find x in terms of a, b and c:
Answer:
Consider the given equation: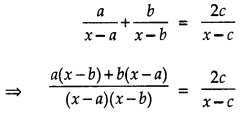
⇒ (x – c)[a(x – b) + b(x – a)] = 2c(x – a)(x – b)
⇒ (x – c)[ax – ab + bx – ab] = 2c(x2 – bx – ax + ab)
⇒ ax2 – 2abx + bx2 – acx + 2abc – bcx = 2cx2 – 2bcx – 2acx + 2abc
⇒ ax2 + bx2 – 2cx2 = 2abx – acx – bcx
⇒ (a + b – 2c)x2 = x(2ab – ac – bc)
⇒ (a + b – 2c)x2 – x(2ab – ac – bc) = 0
⇒ x[(a + b – 2c)x – (2 ab – ac – bc) = 0
⇒ either x = 0
or (a + b – 2c)x – (2ab – ac – bc) = 0
or (a + b – 2c)x = (2ab – ac – bc)
or x =
Thus, the two roots of the given equation are x = 0 and
Question 3.
A train travels at a certain average speed for a distance of 63 km and then travels at a distance of 72 km at an average speed of 6 km/hr more than its original speed. If it takes 3 hours to complete total journey, what is the original average speed ? [CBSE 2018]
Answer:
Let original speed of train be x km/ hr
Distance = 63 km; time (t1) = 63/x hrs
∴ Faster speed = (x + 6) km/hr
[∵ Time =
Distance = 72 km; time (t2) = 72/ (x + 6) hrs.
(t1) + (t2) = 3 hrs
⇒ 63(x + 6) + 72x = 3x (x + 6)
⇒ 63x + 378 + 72x = 3x2 + 18x
⇒ 3x2 – 117x – 378 = 0
⇒ x2 – 39x – 126 = 0
⇒ 7x2 – 42x + 3x + 126 = 0
⇒ (x – 42) (x + 3) = 0
⇒ x = -3
[Rejected as speed can’t be negative]
∴ x = 42
∴ Original speed of train is 42 km/hr.
Question 4.
A motor boat whose speed is 18 km/hr in still water takes 1 hr more to go 24 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream. [CBSE 2018]
Answer:
Let the speed of stream be x km/ hr
∴ The speed of the boat upstream = (18 – x) km/hr
and speed of the boat downstream = (18 + x) km/hr
According to the question: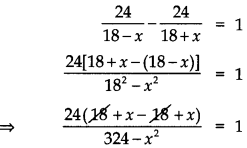
⇒ 48x = 324 – x2
⇒ x2 + 48x – 324 = 0
⇒ x2 + 54x – 6x – 324 = 0
⇒ x(x + 54) – 6(x + 54) = 0
⇒ (x + 54) (x – 6) = 0
⇒ x + 54 = 0
x = – 54
[Rejecting – 54, as speed can’t be negative]
and x – 6 = 0
∴ x = 6 km/h
∴ Speed of the stream = 6 km/hr.
Question 5.
A thief runs with a uniform speed of 100 m/ minute. After one minute, a policeman runs after the thief to catch him. He goes with a speed of 100 m/minute in the first minute and increases his speed by 10 m/minute every succeeding minute. After how many minutes the policeman will catch the thief? [CBSE 2016]
Answer:
Suppose the policeman catches the thief after t minutes.
Uniform speed of the thief = 100 metres/minute
∴ Distance covered by thief in (t + 1) = 100 (t + 1) metres [∵ Distance = Speed × Time]
Distance covered by policeman in t minutes = Sum of t terms of an AP with first term 100 and common difference 10.
= t[100 + 5(t – 1)]
= t(5t + 95) = 5t2 + 95t
When the policeman catches the thief.
5t2 + 95t = 100 (t + 1)
⇒ 5t2 + 95t = 100t + 100
⇒ 5t2 – 5t – 100 = 0
⇒ t2 – t – 20 = 0
⇒ t = – 4 and t = 5
Neglecting -ve time. We get t = 5
Thus, the policeman catches the thief after 5 minutes.
Question 6.
The difference of two natural numbers is 5. If the difference of their reciprocals is
Answer:
Let the number be x and y (x > y).
According to question; x – y = 5 …………… (i)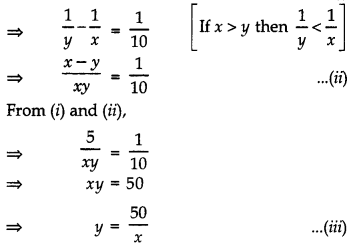
Putting the value of y in (z)
x –
⇒ x2 – 50 = 5x
⇒ x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
⇒ x22 – 10x + 5x – 50 = 0
⇒ x (x – 10) + 5 (x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x – 10) (x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = – 5, 10
When x = – 5, y =
When x = 10, y =
∴ Two natural numbers as 5,10.
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
Solve
Answer:
Let x =
⇒ x =
Squaring both sides, we get
x2 = 5 + x
⇒ x2 – x – 5 = 0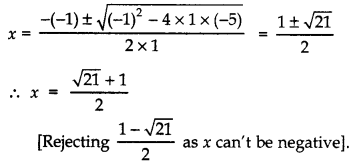
Question 2.
Solve by factorisation: (x – 3) (x – 4) =
Answer:
Question 3.
If the equation (1 + m2) x2 + 2mcx + c2 – a2 = 0 has equal roots, show that c2 = a2 (1 + m2).
Answer:
Given equation is,
(1 + m2) x2 + 2mcx + c2 – a2 = 0
∵ Roots are equal.
∴ D = 0
B2 – 4AC = 0
(2mc)2 – 4 (1 + m2) (c2 – a2) = 0
or 4m2c2 – 4 [c2 – a2 + m2c2 – m2a2] = 0
or 4[m2c2 – c2 + a2 – m2c2 + m2a2] = 0
or – c2 + a2 (1 + m2) = 0
or c2 = a2 (1 + m2).
Question 4.
A person on tour has ₹ 360 for his expenses. If he extends his tour for 4 days, he has to cut down his daily expenses by ₹ 3. Find the original duration of the tour.
Answer:
Let, original duration of tour = x days
Expenditure on tour = ₹ 360
So, expenditure per day = ₹
According to 1st condition,
Duration of extended tour = (x + 4) days
Expenditure per day = ₹
According to 2nd condition,
360 (x + 4) – 360x = 3x (x + 4)
360x + 1440 – 360x = 3 (x2 + 4x)
x2 + 4x – 480 = 0, S = 4
x2 + 24x – 20x – 480 = 0, P = – 480
x(x + 24) – 20 (x + 24) = 0
(x + 24) (x – 20) = 0
Either x + 24 = 0 or x – 20 = 0
x = – 24 or x = 20
∵ x cannot be negative so, x = 20
Hence, original duration of tour has 20 days.
Question 5.
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 1 m less than twice the shortest side. If the third side is 1 m more than the shortest side, find the sides of the triangle.
Answer:
Let, shortest side of triangle = x m
Hypotenuse of triangle = (2x – 1) m
Third side of triangle = (x + 1) m By
Pythagoras theorem,
(Hyp.)2 = (Base)2 + (Alt.)2
(2x – 1)2 = (x + 1)2 + (x)2
4x2 + 1 – 4x = x2 + 1 + 2x + x2
2x2 – 6x = 0
2x (x – 3) = 0
Either 2x = 0 or x – 3 = 0
x = 0 or x = 3
But side cannot be zero, so . x = 3
∴ Shortest side = x = 3 m
Hypotenuse = (2x – 1) = [2 (3) – 1] = 5 m
Third side = x + 1 = (3 + 1) = 4 m.
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option for each of the following:
Question 1.
The condition on ‘a’ for ax2 + bx + c = 0 to represent a quadratic equation is:
(a) a = 0
(b) a > 0
(c) a < 0
(d) a ≠ 0
Answer:
(d) a ≠ 0
Question 2.
The value of k for which the expression x2 + 4x + k is a perfect square is :
(a) 4
(b) – 4
(c) 16
(d) 3
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 3.
Which of the following equation has 3 as a root?
(a) x2 – 4x + 2 = 0
(b) x2 + x – 3 = 0
(c) 2x2 – 8x + 6 = 0
(d) 3x2 – 6x – 2 = 0
Answer:
(c) 2x2 – 8x + 6 = 0
Question 4.
If
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) – 3
Answer:
(b)
Question 5.
Which of the following is true about the equation
(a) Its discriminant is not defined
(b) Its discriminant is – 7
(c) Its discriminant is -11
(d) Its discriminant is same as coefficient of x
Answer:
(b) Its discriminant is – 7
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a quadratic equation?
(a)
(b) (x2 – 1)2 = x4& + 31 + 4x2
(c) 2(x – 1)2 = 4x2 – 3x + 1
(d) (√3x + √5)2 + x2 = 4x2 – 5x
Answer:
(d) (√3x + √5)2 + x2 = 4x2 – 5x
Question 7.
The roots of the equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 are non- real, if
(a) b2 – 4ac = 0
(b) b2 – 4ac < 0
(c) b2 – 4ac > 0
(d) coefficient of x is zero
Answer:
(b) b2 – 4ac < 0
Question 8.
The roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 are real, if b2 – 4ac is
(a) = 0
(b) ≥ 0
(c) ≤ 0
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) ≥ 0
Question 9.
If n denotes the number of roots of a quadratic equation, then
(a) n is always equal to 2
(b) n < 2 (c) n ≤ 2 (d) n > 2
Answer:
(c) n ≤ 2
Question 10.
The positive value of /c for which the equation x2 + kx + 9 = 0 and x2 – 12x + k = 0 will both have real roots
(a) 36
(b) 6
(c) 16
(d) 12
Answer:
(b) 6
Question 11.
The equation (a2 + b2)x2 – 2 (ac + bd) x + c2 + d2 = 0 has equal roots, then
(a) ab = cd
(b) ad = bc
(c) ad = √bc
(d) ad = √cd
Answer:
(d) ad = √cd
Question 12.
The sum of a number and its reciprocal is 10/3, then the number is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 13.
The value of k for which – 5 is a root of 2x2 + px – 15 = 0 and the quadratic equation p(x2 + x) + k = 0 has equal roots is
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer:
(c)
Question 14.
What constant should be added or subtracted to solve the quadratic equation x2 –
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Answer:
(b)
Question 15.
The value of k for which roots of kx2 – 3x + 1 = 0 are real is .
(a) k ≥
(b) k ≤
(c) k ≤
(d) k ≤
Answer:
(c) k ≤
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has two _____________ and _____________ roots if b2 – 4ac > 0.
Answer:
real, unequal
Question 2.
Quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has two real and _____________ roots if b2 – 4ac = 0.
Answer:
equal
Question 3.
For a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, the quantity b2 – 4ac is called _____________ .
Answer:
discriminant
Question 4.
Quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has two _____________ roots if b2 – 4ac < 0. Answer: imaginary Question 5. If D > 0 and is a perfect square then roots are _____________ (rational/irrational/imaginary).
Answer:
rational
Question 6.
If D > 0 and it is not a perfect square then roots are _____________ (rational/irrational/imaginary).
Answer:
irrational
Question 7.
If the value of mα2 + nα + p is zero, then a is said to be the _____________ of equation mx2 + nx + p = 0.
Answer:
root
Question 8.
The quadratic formula for finding roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 is given by _____________ .
Answer:
x =
Question 9.
A quadratic equation can have at most _____________ roots.
Answer:
two
Question 10.
The quadratic equation x2 – 3x + 5 = 0 has _____________ roots.
Answer:
imaginary
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Important Questions Very Short Answer (1 Mark)
Question 1.
Find the roots of the equation x2 – 3x – m (m + 3) = 0, where m is a constant. (2011OD)
Solution:
x2 – 3x – m(m + 3) = 0
D = b2 – 4ac
D = (- 3)2 – 4(1) [-m(m + 3)]
= 9 + 4m (m + 3)
= 4m2 + 12m + 9 = (2m + 3)2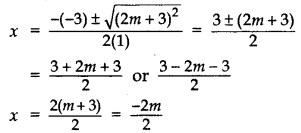
∴ x = m + 3 or -m
Question 2.
If 1 is a root of the equations ay2 + ay + 3 = 0 and y2 + y + b = 0, then find the value of ab. (2012D)
Solution:
ay2 + ay + 3 = 0
a(1)2 + a(1) + 3 = 0
2a = -3
a =
y2 + y + b = 0
12 + 1 + b = 0
b = -2
∴ ab =
Question 3.
If x = –
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as, 3x2 + 2kx – 3 = 0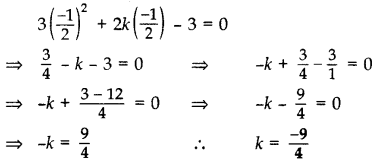
Question 4.
If the quadratic equation px\frac{1}{2} – 2
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as px\frac{1}{2} – 2
Here a = p, b = – 2
For equal roots, D = 0
D = b2 – 4ac – 0 …[∵ Equal roots
0 = (-2
0 = 4 × 5p2 – 60p
0 = 20p2 – 60p => 20p2 = 60p
p =
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 5.
Find the value of p so that the quadratic equation px(x – 3) + 9 = 0 has two equal roots. (2011D, 2014OD)
Solution:
We have, px (x – 3) + 9 = 0
px2 – 3px + 9 = 0 Here a = p, b = -3p,
D = 0
b2 – 4ac = 0 ⇒ (-3p)2 – 4(p)(9) = 0
⇒ 9p2 – 36p = 0
⇒ 9p (p – 4) = 0
⇒ 9p = 0 or p – 4= 0
p = 0 (rejected) or p = 4
∴ p = 4 ……..(∵ Coeff. of x2 cannot be zero
Question 6.
Find the roots of 4x2 + 3x + 5 = 0 by the method of completing the squares. (2011D)
Solution:
Here 4x2 + 3x + 5 = 0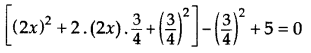
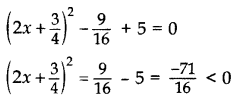
But
Question 7.
Find the value of m so that the quadratic equation mx (x – 7) + 49 = 0 has two equal roots. (2011OD)
Solution:
We have, mx (x – 7) + 49 = 0
mx2 – 7mx + 49 = 0
Here, a = m, b = – 7m, c = 49
D = b2 – 4ac = 0 …[For equal roots
⇒ (-7m)2 – 4(m) (49) = 0
⇒ 49m2 – 4m (49) = 0
⇒ 49m (m – 4) = 0
⇒ 49m = 0 or m – 4 = 0
m = 0 (rejected) or m = 4
∴ m = 4
Question 8.
Solve for x:
36x2 – 12ax + (a2 – b2) = 0 (2011OD)
Solution:
We have, 36x2 – 12ax + (a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ (36x2 – 12ax + a2) – b2 = 0
⇒ [(6x)2 – 2(6x)(a) + (a)2] – b2 = 0
⇒ (6x – a)2 – (b)2 = 0 …[∵ x2 – 2xy + y2 = (x – y)2
⇒ (6x – a + b) (6x – a – b) = 0 „[∵ x2 – y2 = (x + y)(x – y)
⇒ 6x – a + b = 0 or 6x – a – b = 0
⇒ 6x = a – b or 6x = a + b
⇒ x =
Question 9.
Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation x2 – 4kx + k = 0 has equal roots. (2012D)
Solution:
We have, x2 – 4kx + k = 0
Here a = 1, b = -4k:, c = k D = 0 …[Since, Equal roots
As b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (-4k)2 – 4(1) (k) = 0
⇒ 16k2 – 4k = 0 ⇒ 4k(4k – 1) = 0
⇒ 4k = 0 or 4k – 1 = 0
k = 0 (rejected) or 4k = 1
∴ k =
Question 10.
Find the value of k for which the equation x2 + k(2x + k – 1) + 2 = 0 has real and equal roots. (2017D)
Solution:
We have, x2 + k(2x + k – 1) + 2 = 0
x2 + 2kx + k2 – k + 2 = 0
Here a = 1, b = 2k, c = k2 – k + 2
D = 0 …[real and equal roots
∴ b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (2k)2 – 4 × 1(k2 – k + 2) = 0
⇒ 4k2 – 4 (k2 – k + 2) = 0
⇒ 4(k2 – k2 + k – 2) = 0 ⇒ 4(k – 2) = 0
⇒ k – 2 = 0 ⇒ k = 2
Question 11.
Find the value of p for which the roots of the equation px(x – 2) + 6 = 0, are equal. (2012OD)
Solution:
We have , px(x – 2) + 6 = 0
px2 – 2px + 6 = 0, p ≠ 0
Two equal roots …[Given
b2 – 4ac = 0 ….[a = p, b = -2p, c = 6
∴ (-2p)2 – 4(p)(6) = 0
4p2 – 24p = 0 ⇒ 4p(p – 6) = 0
4p = 0 or p – 6 = 0
p = 0 (rejected) or p = 6
Since p cannot be equal to 0.
…[Standard form of a quad. eq. ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0
∴ P = 6
Question 12.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: 4
Solution:
4
4
4x(
(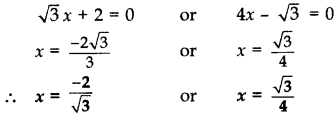
Question 13.
Solve the following for x:
Solution:
⇒
x(
(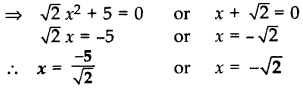
Question 14.
Solve the quadratic equation 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0 for x. (2014D)
Solution:
We have, 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0
2x2 + 2ax – ax – a2 = 0
2x(x + a) – a(x + a) = 0
(x + a) (2x – a) = 0
x + a = 0 or 2x – a = 0
∴ x = -a or x =
Alternatively:
First calculate D = b2 – 4ac
Then apply x =
We get x = -a, x =
Question 15.
Find the values of p for which the quadratic equation 4x2 + px + 3 = 0 has equal roots. (2014OD)
Solution:
Given: 4x2 + px + 3 = 0
Here a = 4, b = p. (= 3 … [Equal roots
D = 0 (Equal roots)
As b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (p)2 – 4(4)(3) = 0
= p2 – 48 = 0 ⇒ p2 = 48
∴ p =
Question 16.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: 4x2– 4a2x + (a4 – b4) = 0. (2015D)
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as,
4x2 – 4a2x + (a44 – b4) = 0
(4x2 – 4a2x + a4) – b4 = 0
or (2x – a2)2 – (b2)2 = 0
⇒ (2x – a2 + b2) (2x – a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ (2x – a2 + b2) = 0 or (2x – a2 – b2) = 0
∴ x =
Question 17.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: 9x2 – 6b2x – (a4 – b4) = 0 (2015D)
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as
(9x2 – 6b2x + b4) – a4 = 0
⇒ (3x – b2)2 – (a2)2 = 0
⇒ (3x – b2 + a2) (3x – b2 – a2) = 0 …[:: x2 – y2 = (x + y) (x – y)
⇒ 3x – b2 + a2 = 0 or 3x – b2 – a2 = 0
⇒ 3x = b2 – a2 or 3x = b2 + a2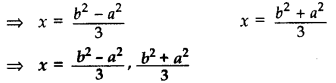
Question 18.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: 4x2 + 4bx – (a2 – b2) = 0 (20150D)
Solution: The given quadratic equation can be written as
4x2 + 4bx + b2 – a22 = 0
⇒ (2x + b)2 – (a)2 = 0
⇒ (2x + b + a) (2x + b – a) = 0 …[x2 – y2 = (x + y)(x – y)
⇒ (2x + b + a) = 0 or (2x + b – a) = 0
⇒ 2x = -(a + b) or 2x = (a – b)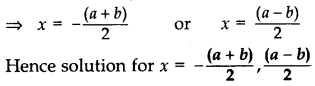
Question 19.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: x2 – 2ax – (4b2 – a2) = 0) (2015OD)
Solution:
Given quadratic equation can be written as
x2 – 2ax – 4b2 + a2 = 0.
(x2 – 2ax + a2) – 4b2 = 0 or (x – a)2 – (2b)2 = 0
As we know,
[a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b)]
∴ (x – a + 2b) (x – a – 2b) = 0
⇒ x – a + 2b = 0 or x – a – 2b = 0
⇒ x = a – 2b or x = a + 2b
⇒ x = a – 2b and x = a + 2b
Question 20.
If x =
Solution:
We have, ax2 + 7x + b = 0
Here ‘a’ = a, ‘b’ = 7, ‘c’ = b
Now, α = 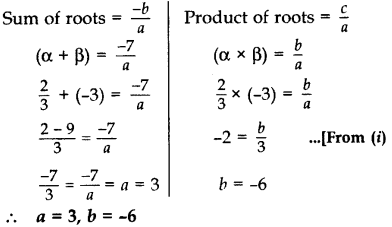
Question 21.
Find the value of p, for which one root of the quadratic equation px2 – 14x + 8 = 0 is 6 times the other. (20170D)
Solution:
Given equation is px2 – 14x + 8 = 0.
Here a = p b = -14 c = 8
Let roots be a and 6α.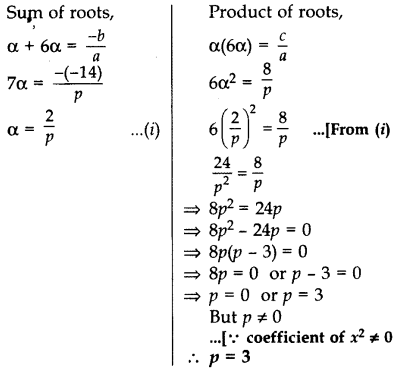
Question 22.
If -5 is a root of the quadratic equation 2x2 + px – 15 = 0 and the quadratic equation p(x2 + x) + k = 0 has equal roots, find the value of k. (2016OD)
Solution:
We have, 2x2 + px – 15 =0
Since (-5) is a root of the given equation
∴ 2(-5)2 + p(-5) – 15 = 0
⇒ 2(25) – 5p – 15 = 0
⇒ 50 – 15 = 5p
⇒ 35 = 5p ⇒ p = 7 …(i)
Now, p(x2 + x) + k ⇒ px2 + px + k = 0
7x2 + 7x + k = 0 …[From (i)
Here, a = 7, b = 7, c = k
D = 0 …[Roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (7)2 – 4(7)k = 0 ⇒ 49 – 28k = 0
⇒ 49 = 28k ∴ k =
Question 23.
Solve for x:
Solution:
⇒
⇒ (
⇒ 2x + 9 = 169 + x22 – 26x
⇒ 0 = 169 + x22 – 26x – 2x – 9
⇒ x2 – 28x + 160 = 0
⇒ x2 – 20x – 8x + 160 = 0
⇒ x(x – 20) – 8(x – 20) = 0
⇒ (x – 20) (x – 8) = 0
⇒ x – 8 = 0 or x – 20 = 0
⇒ x = 8 or x = 20
Checking, When x = 8 in (i)
5 + 8 = 13 ⇒ 13 = 13 …[True
∴ x = 8 is the solution.
Checking, When x = 20 in (i),
7 + 20 ≠ 13 …[False
∴ x = 20 is not a solution.
Therefore, x = 8 is the only solution.
Question 24.
Solve for x:
Solution:
⇒
⇒ (
⇒ 6x + 7 = 4x2 – 28x + 49
⇒ 0 = 4x2 – 28x – 6x – 7 + 49
⇒ 4x2 – 34x + 42 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 17x + 21 = 0 …[Dividing by 2
⇒ 2x2 – 14x – 3x + 21 = 1
⇒ 2x(x – 7) – 3(x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 7) (2x – 3) = 0
⇒ x – 7 = 0 or 2x – 3 = 0 =
x= 7 or x =
Checking: When x = 7 in (i),
7 – 7 = 0 … [True
Checking: When x =
4 + 4 ≠ 0
∴ x = 7 is the only solution.
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-II (3 Marks)
Question 25.
ind the roots of the following quadratic equation: 2
Solution:
We have, 2
Here, a = 2
D = b2 – 4ac
∴ D = (-5)2 – 4 (2
= 25 – 24 = 1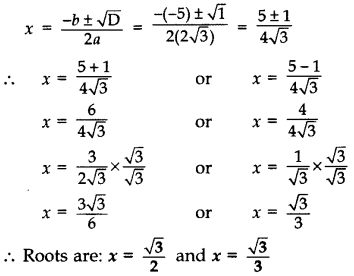
Question 26.
Solve for x: 4x2 – 4ax + (a2 – b2) = 0 (2011OD)
Solution:
4x2 – 4ax + (a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ [4x2 – 4ax + a2] – b2 = 0
⇒ [(2x)2 – 2(2x)(a) + (a)2] – b2 = 0
⇒ (2x – a)2 – (b)2 = 0
⇒ (2x – a + b) (2x – a – b) = 0
⇒ 2x – a + b = 1 or 2x – a – b = 0
2x = a – b or 2x = a + b
∴ x =
Question 27.
Solve for x: 3x2} – 2
Solution:
3x2} – 2
⇒ 3x2 –
⇒
⇒ (
⇒
∴ x =
Question 28.
Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0 has equal roots. (2012D)
Solution:
Given: 2x2 + kx + 3 = 0
Here a = 2, b = k, c= 3
D = 0 … [Since roots are equal
As b2 – 4ac = 0 ∴ K2 – 4(2)(3) = 0
K2 – 24 = 0 or k2 = 24
∴ k =
Question 29.
Find the value(s) of k so that the quadratic equation 3x2 – 2kx + 12 = 0 has equal roots. (2012D)
Solution:
Given: 3x2 – 2kx + 12 = 0
Here a = 3, b = -2k, c = 12
D = 0 … [Since roots are equal As
b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (-2k)2 – 4(3) (12) = 0
⇒ 4k2 – 144 = 0 ⇒ k2 =
∴ k =
Question 30.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: x2 – 4ax – b2 + 4a2 = 0 (2012OD)
Solution:
We have, x2 – 4ax – b2 + 4a2 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4ax + 4a2 – b\frac{144}{4} = 0
⇒ [(x)\frac{144}{4} – 2(x)(2a) + (2a)\frac{144}{4}] – (b)2 = 0
(x – 2a)2 – (b)2 = 0
(x – 2a + b) (x – 2a – b) = 0
x – 2a + b = 0 or x – 2a – b = 0
∴ x = 2a – b or x = 2a + b
Question 31.
Find the value of k for which the roots of the equation kx(3x – 4) + 4 = 0, are equal. (20120D)
Solution:
We have, kx(3x – 4) + 4 = 0
3kx2 – 4kx + 4 = 0
Here a = 3k, b = -4k, c = 4
D = 0 … [Since roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (-4k)2 – 4(3k) (4) = 0
16k2 – 48k = 0
16k (k – 3) = 0
16k = 0 or k – 3 = 0
k = 0 or k = 3
…[Rejecting k = 0, as coeff. of x2 cannot be zero
∴ k = 3
Question 32.
Find the value of m for which the roots of the equation. mx (6x + 10) + 25 = 0, are equal. (2012OD)
Solution:
We have, mx(6x + 10) + 25 = 0
6mx2 + 10mx + 25 = 0
Here a = 6m, b = 10m, c = 25
D = 0 … Since roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (10m)2 – 4(6m) (25) = 0
100m2 – 600m = 0 ⇒ 100m (m – 6) = 0
100m = 0 or m – 6 = 0
m = 0 or m = 6
…[Rejecting m = 0, as coeff. of x2 cannot be zero
∴ m = 6
Question 33.
For what value of k, the roots of the quadratic equation kx(x – 2
Solution:
We have, kx(x – 2
kx2 – 2
Here a = k, b= -2
D = 0 …[∵ Roots are equal
As b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (-2
20k2 – 40k = 0
⇒ 20k(k – 2) = 0
∴ 20k = 0 or k – 2 = 0
k = 0 (rejected) or k = 2
…[∵ Coeff. of x2 cannot be zero
∴ k= 2
Question 34.
For what values of k, the roots of the quadratic equation (k + 4)x2 + (k + 1)x + 1 = 0 are equal? (2013D)
Solution:
We have, (k + 4) x2 + (k + 1) x + 1 = 0
Here, a = k + 4, b = k + 1, c = 1
D =0 …[∵ Roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ (k + 1)2 – 4(k + 4)(1) = 0
k2 + 2k + 1 – 4k – 16 = 0
k2 – 2k – 15 = 0
k2 – 5k + 3k – 15 = 0
k(k – 5) + 3(k – 5) = 0
(k – 5)(k + 3) = 0
k – 5 = 0 or k + 3= 0
k = 5 or k = -3
∴ k = 5 and -3
Question 35.
For what value of k, are the roots of the quadratic equation: (k – 12)x2 + 2(k – 12)x + 2 = 0 equal? (2013OD)
Solution:
We have, (k – 12)x2 + 2(k – 12)x + 2 = 0
The given quadratic equation will have equal roots if D = 0 ⇒ b2 – 4ac = 0
Here a = (k – 12), b = 2(k – 12), c = 2
b2 – 4ac = 0
0 = 4(k – 12)2 – 4 × (k – 12) × 2
0 = (k – 12)[4(k – 12) – 4 × 2]
0 = (k – 12) 4[k – 12 – 2]
0 = 4(k – 12) (k – 14)
∴ 4(k – 12)(k – 14) = 0
∴ k = 12 (rejected) or k = 14
But k cannot be equal to 12 because in that case the given equation will imply 2 = 0 which is not true.
∴ k = 14
Question 36.
For what value of k, are the roots of the quadratic equation y2 + k2 = 2 (k + 1)y equal? (2013OD)
Solution:
y2 + k2 = 2(k + 1)y
y2 – 2(k + 1)y + k2 = 0
Here a = 1, b = -2(k + 1), c = k2
D = 0 … [Roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ [-2(k + 1)]2 – 4 × (1) × (k2) = 0
⇒ 4(k2 + 2k + 1) – 4k2 = 0
⇒ 4k2 + 8k + 4 – 4k2 = 0
⇒ 8k + 4 = 0
⇒ 8k = -4 ∴ k =
Question 37.
Find that non-zero value of k, for which the quadratic equation kx2 + 1 – 2(k – 1)x + x2 = 0 has equal roots. Hence find the roots of the equation. (2015D)
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as
kx2 + x2 – 2(k – 1)x + 1 = 0
(k + 1) x2 – 2 (k – 1) x + 1 = 0 …(i)
Here, a = (k + 1), b = -2(k – 1), c = 1
For equal roots, D = 0
D = b2 – 4ac
⇒ (-2(k – 1)]2 – 4 × (k + 1) × 1 = 0
⇒ 4(k − 1)2 – 4(k + 1) = 0
⇒ 4k2 + 4 – 8k – 4k – 4 = 0
⇒ 4k2 – 12k = 0 ⇒ 4k(k – 3) = 0
k = 3 or k = 0 (rejected)
∴ k = 3
Putting k = 3 put in equation (i), we get
⇒ 4x2 – 4x + 1 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 2x – 2x + 1 = 0
⇒ 2x(2x – 1) – 1(2x – 1) = 0
⇒ (2x – 1) (2x – 1) = 0
⇒ 2x – 1 = 0 or 2x – 1 = 0
⇒ x =
Roots are
Question 38.
Find that value of p for which the quadratic equation (p + 1)x2 – 6(p + 1)x + 3 (p + 9) = 0, p ≠ -1 had equal roots. (2015D(
Solution:
For the given quadratic equation to have equal roots, D = 0
Here a = (p + 1), b = -6(p + 1), c = 3(p + 9)
D = b2 – 4ac
⇒ [-6(p + 1)]2 – 4(p + 1).3 (p + 9) = 0
⇒ 36(p + 1)2 – 12(p + 1) (p + 9) = 0
⇒ 12(p + 1) (3p + 3 – p – 9) = 0
⇒ 12(p + 1)(2p – 6) = 0
⇒ 24(p + 1)(p – 3) = 0
⇒ p + 1 = 0 or p – 3 = 0
⇒ p = -1 (rejected) or p = 3
∴ p = 3
Question 39.
Solve for x:
Solution:
The given quadratic equation can be written as
Here, a =
D = b2 – 4ac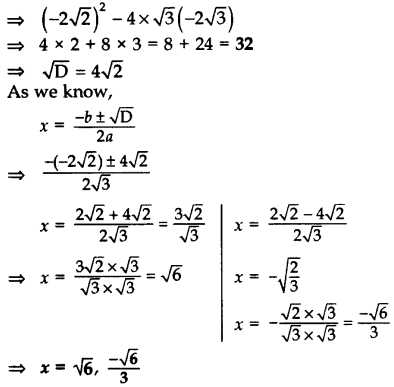
Question 40.
Solve for x: 2x2 + 6
Solution:
Given equation can be written as
2(x2 + 3
x2 + 3
Here, a = 1, b = 3
D = b2 – 4ac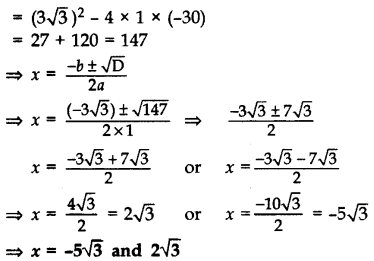
Question 41.
If the roots of the quadratic equation (a – b)x2 + (b – c)x + (c – a) = 0 are equal, prove that 2a = b + c. (2016OD)
Solution:
Here’a’ = a – b, ‘b’ = b – c, ‘c’ = c – a
D = 0 ….[Roots are equal
b2 – 4ac = 0
⇒ (b – c)2 – 4(a – b)(c – a) = 0
⇒ b2 + c2 – 2bc – 4(ac – a2 – bc + ab) = 0
⇒ b2 + c2 – 2bc – 4ac + 4a2 + 4bc – 4ab = 0
⇒ 4a2 + b22 + c2 – 4ab + 2bc – 4ac = 0
⇒ (-2a)2 + (b)2 + (c)22 + 2(-2a)(b) + 2(b)(c) + 2(c)(-2a) = 0
⇒ [(-2a) + (b) + (c)]2 = 0
….[∵ x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2zx = (x + y + z)2
Taking square-root on both sides
-2a + b + c = 0
⇒ b + c = 2a ∴ 2a = b + c
Question 42.
Solve the equation
Solution: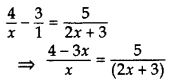
⇒ 5x = (2x + 3) (4 – 3x)
⇒ 5x = 8x – 6x2 + 12 – 9x
⇒ 5x – 8x + 6x2 – 12 + 9x = 0
⇒ 6x2 + 6x – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + x – 2 = 0 …[Dividing by 6
⇒ x2 + 2x – x – 2 = 0
⇒ x(x + 2) – 1(x + 2) = 0
⇒ x – 1 = 0 or x + 2 = 0
∴ x = 1 or x = -2
Question 43.
Solve the equation
Solution: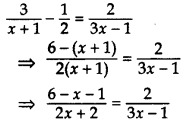
⇒ 2(2x + 2) = (5 – x)(3x – 1)
⇒ 4x + 4 = 15x – 5 – 3x2 + x
⇒ 4x + 4 – 15x + 5 + 3x2 – x = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 12x + 9 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x + 3 = 0 …[Dividing by 3
⇒ x2 – 3x – x + 3 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) – 1(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 1) (x – 3) = 0
⇒ x – 1 = 0 or x – 3 = 0
∴ x = 1 or x = 3
Question 44.
Solve the equation
Solution: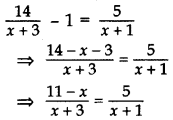
⇒ 5(x + 3) = (11 – x) (x + 1)
⇒ 5x + 15 = 11x + 11 – x2 – x
⇒ 5x + 15 – 11x – 11 + x2 + x = 0
⇒ x2 – 5x + 4 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x – x + 4 = 0
⇒ x(x – 4) – 1(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (x – 1) (x – 4) = 0
⇒ x – 1=0 or x – 4 = 0
⇒ x= 1 or x = 4
Question 45.
Solve for x:
Solution: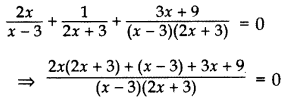
⇒ 4x2 + 6x + x – 3 + 3x + 9 = 0
⇒ 4x2 + 10x + 6 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 5x + 3 = 0 …[Dividing both sides by 2
⇒ 2x2 + 3x + 2x + 3 = 0
⇒ x(2x + 3) + 1(2x + 3) = 0
⇒ (2x + 3) (x + 1) = 0
⇒ 2x + 3 = 0 or x + 1 = 0
⇒ x=
But, x ≠
∴ x= -1 is the only solution.
Question 46.
Solve for x:
Solution: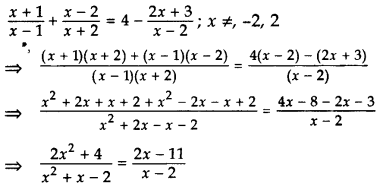
⇒ (2x2 + 4)(x – 2) = (2x – 11)(x2 + x – 2)
⇒ 2x3 – 4x2 + 4x – 8 = 2x3 + 2x2 – 4x – 11x2 – 11x + 22
⇒ 2x3 – 4x2 + 4x – 8 – 2x3 – 2x2 + 4x + 11x2 + 11x – 22 = 0
⇒ 5x2 + 19x – 30 = 0
⇒ 5x2 + 25x – 6x – 30 = 0
⇒ 5x(x + 5) – 6(x + 5) = 0
⇒ (x + 5) (5x – 6) = 0
⇒ x + 5 = 0 or 5x – 6 = 0
⇒ x = -5 or x =
Question 47.
Solve the following quadratic equation for x:
Solution: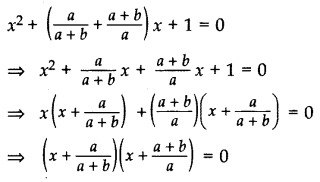

Question 48.
Solve for x:
Solution: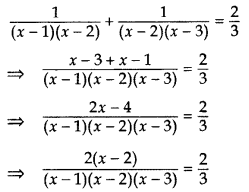
⇒ (x – 1)(x – 3) = 3
⇒ x2 – 3x – x + 3 – 3 = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x = 0 ⇒ x(x – 4) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x – 4 = 0
∴ x = 0 or x = 4
Question 49.
Three consecutive natural numbers are such that the square of the middle number exceeds the difference of the squares of the other two by 60. Find the numbers. (2016OD)
Solution:
Let three consecutive natural numbers are x, x + 1, x + 2.
According to the question,
(x + 1)2 – [(x + 2)2 – x2] = 60
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 – (x2 + 4x + 4 – x2) = 60
⇒ x2 + 2x + 1 – 4x – 4 – 60 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – 63 = 0
⇒ x2 – 9x + 7x – 63 = 0
⇒ x(x – 9) + 7(x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x – 9) (x + 7) = 0
⇒ x – 9 = 0 or x + 7 = 0
⇒ x = 9 or x = -7
Natural nos. can not be -ve, ∴ x = 9
∴ Numbers are 9, 10, 11.
Question 50.
If the sum of two natural numbers is 8 and their product is 15, find the numbers. (2012OD)
Solution:
Let the numbers be x and (8 – x).
According to the Question,
x(8 – x) = 15
⇒ 8x – x2 = 15
⇒ 0 = x2 – 8x + 15
⇒ x2 – 5x – 3x + 15 = 0
⇒ x(x – 5) – 3(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x – 3)(x – 5) = 0
x – 3 = 0 or x – 5 = 0
x = 3 or x = 5
When x = 3, numbers are 3 and 5.
When x = 5, numbers are 5 and 3.
Quadratic Equations Class 10 Important Questions Long Answer (4 Marks)
Question 51.
Find the values of k for which the quadratic equation (3k + 1)x2 + 2(k + 1)x + 1 = 0 has equal roots. Also find the roots. (2014D)
Solution:
(3k + 1)x2 + 2(k + 1) + 1 = 0
Here, a = 3k + 1, b = 2(k + 1), c = 1
D = 0 …[∵ Roots are equal
As b2 – 4ac = 0
∴ [2(k + 1)]2 – 4(3k + 1)(1) = 0
4(k + 1)2 – 4(3k + 1) = 0
4(k2 + 2k + 1 – 3k – 1) = 0
(k2 – k) =
k = 0 or k – 1 = 0
∴ k = 0 or k = 1
Roots are x =
x =
When k = 0, x =
∴ Equal roots are -1 and -1
When k = 1, x =
x=
∴ Equal roots are
Question 52.
Find the value of p for which the quadratic equation (2p + 1)x2 – (7p + 2)x + (7p – 3) = 0 has equal roots. Also find these roots. (2014D)
Solution:
(2p + 1)x2 – (7p + 2)x + (7p – 3) = 0
Here, a = 2p + 1, b = -(7p + 2), c = 7p – 3
D = 0 …[∵ Equal roots As h2 – 4ac = 0
∴ [-(7p + 2)]2 – 4(2p + 1)(7p – 3) = 0
⇒ (7p + 2)2 – 4(14p2 – 6p + 7p – 3) = 0
⇒ 49p2 + 28p + 4 – 56p2 + 24p – 28p + 12 = 0
⇒ -7p2 + 24p + 16 = 0
⇒ 7p2 – 24p – 16 = 0 … [Dividing both sides by -1
⇒ 7p2 – 28p + 4p – 16 = 0
⇒ 7p(p – 4) + 4(p – 4) = 0
⇒ (p – 4) (7p + 4) = 0
⇒ p – 4 = 0 or 7p + 4 = 0
⇒ p = 4 or p = 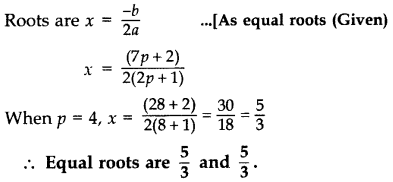
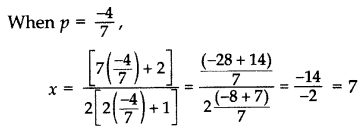
∴ Equal roots are 7 and 7.
Question 53.
Find the roots of the equation
Solution: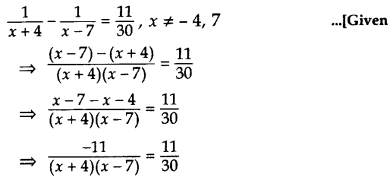
⇒ (x + 4)(x – 7) = – 30
⇒ x2 – 7x + 4x – 28 + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x2 – x – 2x + 2 = 0
⇒ x(x – 1) – 2(x – 1) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(x – 2) = 0
⇒ x – 1 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
∴ x = 1 or x = 2
Question 54.
Find the roots of the equation:
Solution: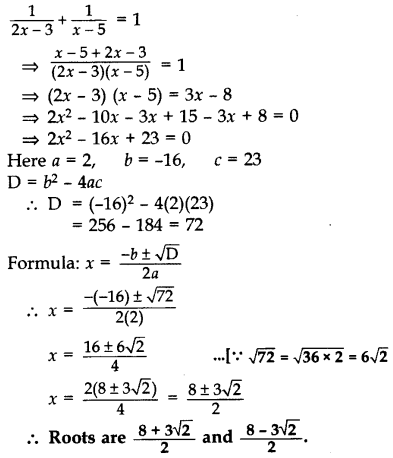
Question 55.
Solve for x:
Solution:![]()
![]()
⇒ 8(x – 3)(x – 2) = x(3x – 8)
⇒ 8(x2 – 3x – 2x +6) = 3x2 – 8x
⇒ 8x2 – 24x – 16x + 48 – 3x2 + 8x = 0
⇒ 5x2 – 32x + 48 = 0
⇒ 5x2 – 20x – 12x + 48 = 0
⇒ 5x(x – 4) – 12(x – 4) = 0
⇒ (x – 4)(5x – 12) = 0
⇒ x – 4 = 0 or 5x – 12 = 0
x = 4 or x =
Question 56.
Solve for x:
Solution: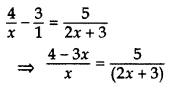
⇒ 5x = (2x + 3 (4 – 3x)
⇒ 5x = 8x – 6x2 + 12 – 9x
⇒ 5x – 8x + 6x2 – 12 + x = 0
⇒ 6x + 6x – 12 = 0
⇒ x2 + x – 2 = 0 …[Dividing by 6
⇒ x2 + 2x – x – 2 = 0
⇒ x(x + 2) – 1(x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 1)(x + 2) = 0
⇒ x – 1 = 0 or x + 2 = 0
∴ x = 1 or x = -2
Question 57.
Solve for x:
Solution: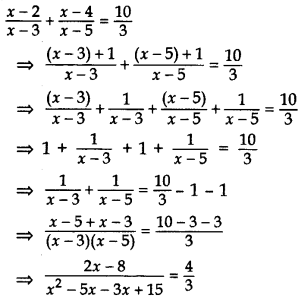
⇒ 4(x2 – 8x + 15) = (6x – 24)
⇒ 4x2 – 32x + 60 – 6x + 24 = 0
⇒ 4x2 – 38x + 84 = 0
⇒ 2x2 – 19x + 42 = 0 …[Dividing by 2
⇒ 2x2 – 12x – 7x + 42 = 0
⇒ 2x(x -6) – 7(x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (2x – 7) = 0
⇒ x – 6 = 0 or 2x – 7 = 0
∴ x = 6 or x =
Question 58.
Solve for x:
Solution: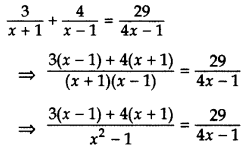
⇒ [3(x – 1) + 4(x + 1)] [4x – 1] = 29(x2 – 1)
⇒ (3x – 3 + 4x + 4) [4x – 1] = 29(x2 – 1)
⇒ (7x + 1) (4x – 1) = 29x2 – 29
⇒ 28x2 – 3x – 1 = 29x2 – 29
⇒ x2 + 3x – 28 = 0
⇒ x2 + 7x – 4x – 28 = 0
⇒ x(x + 7) – 4(x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x + 7) (x – 4) = 0
x = -7 or x = 4
∴ x = -7 and 4
Question 59.
Solve for x:
Solution: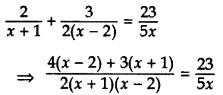
⇒ 5x[4 (x – 2) + 3x + 3) = 46(x + 1) (x – 2)
⇒ 5x[4x – 8 + 3x + 3) = 46[x2 – 1x – 2]
⇒ 5x (7x – 5) = 46 (x2 – x – 2)
⇒ 35x2 – 25x = 46x2 – 46x – 92
⇒ 35x2 – 46x2 – 25x + 46x + 92 = 0
⇒ 11x2 – 21x – 92 = 0
Here, a = 11, b = -21, c = -92
D = b2 – 4ac
= (-21)2 – 4 × 11 × (-92)
= 441 + 4048 = 4489
Question 60.
Find x in terms of a, b and c:
Solution: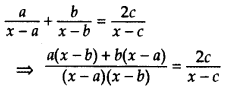
⇒ (x – c)[ax – ab + bx – ab] = 2c(x – a)(x – b)
⇒ (x – c)(ax + bx – 2ab) = 2c(x2 – bx – ax + ab)
⇒ ax2 + bx2 – 2abx – acx – bcx + 2abc = 2cx2 – 2bcx – 2cax + 2abc
⇒ ax2 + bx2 – 2abx – acx – bcx – 2cx2 + 2bcx + 2cax = 0
⇒ ax2 + bx2 – 2cx2 – 2abx + bcx + cax = 0
⇒ x2(a + b – 2c) + x(-2ab + bc + ca) = 0
⇒ x[x (a + b – 2c) + (-2ab + bc + ca)] = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x (a + b – 2c) + (-2ab + bc + ca) = 0
⇒ x = 0 or x (a + b – 2c) = 2ab – bc – ca = 0
∴ x =
Question 61.
Solve the following for x: ![]() (2013D)
(2013D)
Solution: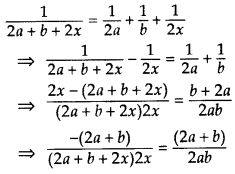
⇒ 2x2 + 2ax + bx + ab = 0
⇒ 2x (x + a) + b(x + a) = 0
⇒ (x + a) (2x + b) = 0
⇒ x + a = 0 or 2x + b = 0
⇒ x = -a or x =
Question 62.
A shopkeeper buys some books for 80. If he had bought 4 more books for the same amount, each book would have cost ₹1 less. Find the number of books he bought. (2012D)
Solution:
Let the number of books he bought = x
Increased number of books he had bought = x +4
Total amount = ₹80
According to the problem,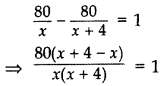
⇒ x(x + 4) = 320
⇒ x2 + 4x – 320 = 0
⇒ x2 + 20x – 16x – 320 = 0
⇒ x(x + 20) – 16(x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x + 20) (x – 16) = 0
⇒ x + 20 = 0 or x – 16 = 0
⇒ x = -20 … (neglected) or x = 16
∴ Number of books he bought = 16
Question 63.
Sum of the areas of two squares is 400 cm2. If the difference of their perimeters is 16 cm, find the sides of the two squares. (2013D)
Solution:
Let the side of Large square = x cm
Let the side of small square = y cm
According to the Question,
x2 + y2 = 400… (i) …[∵ area of square = (side)2
4x – 4y = 16 …[∵ Perimeter of square = 4 sides
⇒ x – y = 4 … [Dividing both sides by 4
⇒ x = 4 + y …(ii)
Putting the value of x in equation (i),
(4 + y)2 + y22 = 400
⇒ y2 + 8y + 16 + y2 – 400 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 8y – 384 = 0
⇒ y2 + 4y – 192 = 0 … [Dividing both sides by 2
⇒ y2 + 16y – 12y – 192 = 0
⇒ y(y + 16) – 12(y + 16) = 0
⇒ (y – 12)(y + 16) = 0
⇒ y – 12 = 0 or y + 16 = 0
⇒ y = 12 or y = -16 … [Neglecting negative value
∴ Side of small square = y = 12 cm
and Side of large square = x = 4 + 12 = 16 cm
Question 64.
The diagonal of a rectangular field is 16 metres more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 14 metres more than the shorter side, then find the lengths of the sides of the field. (2015OD)
Solution:
Let the length of shorter side be x m.
∴ length of diagonal = (x + 16) m
and length of longer side = (x + 14) m
Using pythagoras theorem,
(l)2 + (b)2 = (h)2
∴ x2 + (x + 14)22 = (x + 16)2
⇒ x2 + x2 + 196 + 28x = x2 + 256 + 32x
⇒ x2 – 4x – 60 = 0
⇒ x2 – 10x + 6x – 60 = 0
⇒ x(x – 10) + 6(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (x – 10) (x + 6) = 0
⇒ x – 10 = 0 or x + 6 = 0
⇒ x = 10 or x = -6 (Reject)
⇒ x = 10 m …[As length cannot be negative
Length of shorter side = x = 10 m
Length of diagonal = (x + 16) m = 26 m
Length of longer side = (x + 14)m = 24m
∴ Length of sides are 10 m and 24 m.
Question 65.
The sum of three numbers in A.P. is 12 and sum of their cubes is 288. Find the numbers. (2016D)
Solution:
Let three numbers in A.P. are a – d, a, a + d.
a – d + a + a + d = 12
⇒ 3a = 12 ⇒a = 4
(a – d)3 + (a)3 + (a + d)3 = 288
⇒ a3 – 3a2d + 3ad2 – d3 + a3 + a3 + 3a2d + 3ad2 + d3 = 288
⇒ 3a3 + 6ad2 = 288
⇒ 3a(a2 + 2d2) = 288
⇒ 3 × 4(42 + 2d2) = 288
⇒ (16 + 2d2) =
⇒ 2d2 = 24 – 16 = 8
⇒ d2 = 4 ⇒ d = ± 2
When, a = 4, d = 2, numbers are –
a – d, a, a + d, i.e., 2, 4, 6
When, a = 4, d = -2, numbers are –
a – d, a, a + d, i.e., 6, 4, 2
Question 66.
The perimeter of a right triangle is 60 cm. Its hypotenuse is 25 cm. Find the area of the triangle. (2016D)
Solution: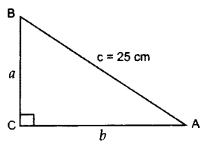
Perimeter of right ∆ = 60 cm …[Given
a + b + c = 60
a + b + 25 = 60
a + b = 60 – 25 = 35 …(i)
In rt. ∆ACB, AC2 + BC2 = AB2
b2 + a2 = (25)2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
a2 + b2 = 625 ….(ii)
From (i), a + b = 35
(a + b)2 = (35) … [Squaring both sides
a2 + b2 + 2ab = 1225
625 + 2ab = 1225 … [From (ii)
2ab = 1225 – 625 = 600 ⇒ ab = 300 … (iii)
Area of ∆ =
=
= 150 cm2
Question 67.
The sum of two numbers is 9 and the sum of their reciprocals is
Solution:
Let the numbers be x and 9 – x.
According to the Question,
⇒ 18 = 9x – x2
⇒ x2 – 9x + 18 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – 6x + 18 = 0
⇒ x(x – 3) – 6(x – 3) = 0
⇒ (x – 3) (x – 6) = 0
⇒ x – 3 = 0 or x – 6 = 0
⇒ x = 3 or x = 6
When x = 3, nos. are 3 and 6.
When x = 6, nos. are 6 and 3.
Question 68.
The numerator of a fraction is 3 less than its denominator. If 1 is added to the denominator, the fraction is decreased by
Solution:
Let the denominator be x and the numerator be x – 3.
∴ Fraction =
New denominator = x + 1
According to the Question,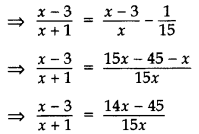
⇒ 15x2 – 45x = 14x2 – 45x + 14x – 45
⇒ 15x2 – 14x2 – 14x + 45 = 0
⇒ x2 – 14x + 45 = 0
⇒ x2 – 5x – 9x + 45 = 0
⇒ x(x – 5) – 9(x – 5) = 0
⇒ (x – 5) (x – 9) = 0
⇒ x – 5 = 0 or x – 9 = 0
⇒ x = 5 or x = 9
When x = 5, fraction =
When x = 9, fraction =
∴ Fraction =
Question 69.
The difference of two natural numbers is 5 and the difference of their reciprocals is
Solution:
Let the larger natural number be x and the smaller natural number be y.
According to the Question,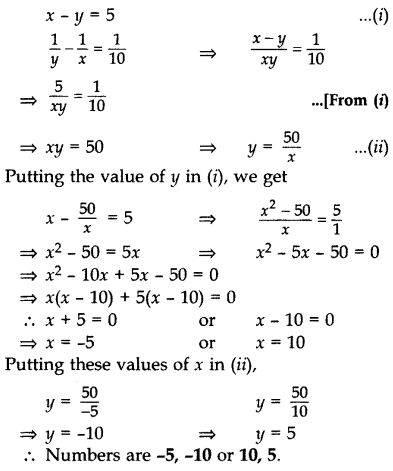
Question 70.
The difference of two natural numbers is 5 and the difference of their reciprocals is
Solution:
Let the larger number be x and the smaller number be y.
According to the Question,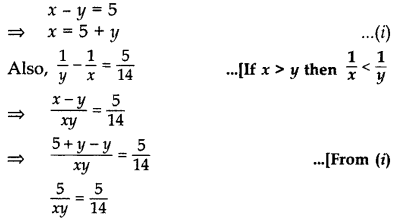
⇒ xy = 14
(5 + y)y = 14 … [From (i)
y2 + 5y – 14 = 0
⇒ y2 + 7y – 2y – 14 = 0
y(y + 7) – 2(y + 7) = 0
(y – 2) (y + 7) = 0
y – 2 = 0 or y + 7 = 0
y = 2 or y = -7
When y = 2, x = 5 + 2 = 7 …[From (1)
∴ Numbers are 7 and 2.
When y = -7, x = 5 + (-7) = -2 …[From (i)
∴ Numbers are -2 and (-7).
Question 71.
The numerator of a fraction is 3 less than its denominator. If 2 is added to both the numerator and the denominator, then the sum of the new fraction and original fraction is a
Solution: .
Let the denominator and numerator of the
fraction be x and x – 3 respectively.
Let the fraction be
By the given condition,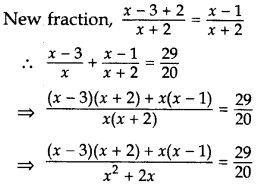
⇒ 20[(x – 3) (x + 2) + x(x – 1)] = 29(x2 + 2x)
⇒ 20(x2 – x – 6 + x2 – x) = 29x2 + 58x
⇒ 20(2x2 – 2x – 6) = 29x2 + 58x
⇒ 40x2 – 29x2 – 40x – 58x = 120
⇒ 11x2 – 98x – 120 = 0
⇒ 11x2 – 110x + 12x – 120 = 0
⇒ 11x(x – 10) + 12(x – 10) = 0
⇒ (11x + 12) (x – 10) = 0
⇒ 11x + 12 = 0 or x – 10 = 0
⇒ x =
Now denominator (x) = 10
then, numerator = x – 3 = 7
∴ The fraction is 1o.
Question 72.
A rectangular park is to be designed whose breadth is 3 m less than its length. Its area is to be 4 square metres more than the area of a park that has already been made in the shape of an isosceles triangle with its base as the breadth of the rectangular park and of altitude 12 m. Find the length and breadth of the rectangular park. (2016OD)
Solution:
Let length of the rectangular park = x m,
breadth of the rectangular park = (x -3)m
∴ Area of the rectangular park = x(x – 3)m2… (i)
Base of an isosceles triangle = (x – 3)m
Altitude of an isosceles triangle = 12 m
∴ Area of isosceles triangle
= 1/2 × base × altitude
= 1/2 × (x – 3) × 12
= 6(x – 3) …(ii)
According to the question,
Ar.(rectangle) – Ar.(isosceles ∆) = 4 m2
⇒ x(x – 3) – 6(x – 3) = 4 … [From (i) & (ii)
⇒ x2 – 3x – 6x + 18 – 4 = 0
⇒ x2 – 9x + 14 = 0
⇒ x2 – 7x – 2x + 14 = 0
⇒ x(x – 7) – 2(x – 7) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (x – 7) = 0
⇒ x – 2 = 0 or x – 7 = 0
⇒ x = 2 or x = 7
When x = 2, breadth of rectangle becomes -ve, so this is not possible.
∴ Length of the rectangular park, x = 7 m
and Breadth = (x – 3) = 4 m.
Question 73.
A train travels 180 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 9 km/hour more, it would have taken 1 hour less for the same journey. Find the speed of the train. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let the speed of the train = x km/hr
Let the increased speed of the train = (x + 9) km/hr
According to the question,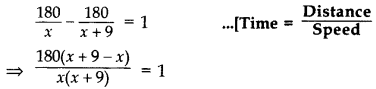
⇒ x(x + 9) = 1620
⇒ x2 + 9x – 1620 = 0
⇒ x2 + 45x – 36x – 1620 = 0
⇒ x(x + 45) – 36(x + 45) = 0
⇒ (x – 36) (x + 45) = 0
⇒ x – 36 = 0 or x + 45 = 0
⇒ x = 36 or x = -45 ….[Rejecting negative value as the speed cannot be -ve
∴ Speed of the train = 36 km/hr
Question 74.
In a flight of 2800 km, an aircraft was slowed down due to bad weather. Its average speed is reduced by 100 km/h and time increased by 30 minutes. Find the original duration of the flight. (2012OD)
Solution:
Let the average speed of the aircraft = x km/hr
the reduced speed of the aircraft = (x – 100 km/hr
Then Distance = 2800 km
According to the Question,
⇒ x2 – 100x = 560000
⇒ x2 – 100x – 560000 = 0
⇒ x2 – 800x + 700x – 560000 = 0
⇒ x(x – 800) + 700(x – 800) = 0
⇒ (x – 800) (x + 700) = 0
⇒ x – 800 = 0 or x + 700 = 0
⇒ x = 800 or x = -700
As speed of the aircraft cannot be -ve.
∴ Speed = 800 km/hr
∴ Original duration/time =
=
= 31/2 hrs. or 3 hrs. 30 mins. or 210 mins.
Question 75.
While boarding an aeroplane, a passenger got hurt. The pilot, showing promptness and concern, made arrangements to hospitalise the injured and so the plane started late by 30 minutes. To reach the destination, 1500 km away in time, the pilot increased the speed by 100 km/hour. Find the original speed/hour of the plane. (2013OD)
Solution:
Let the original speed of the aeroplane = x km/hr
The increased speed of the aeroplane = (x + 100) km/hr
Given: Distance = 1500 km
According to the Question,
⇒ x(x + 100) = 300000
⇒ x2 + 100x – 300000 = 0
⇒ x2 + 600x – 500x – 300000 = 0
⇒ x(x + 600) – 500(x + 600) = 0
⇒ (x – 500) (x + 600) = 0
⇒ x – 500 = 0 or x + 600 = 0
⇒ x = 500 or x = -600 (rejected)
Since speed cannot be negative.
∴ Original speed of the aeroplane = 500 km/hr
Original time =
Question 76.
A train travels at a certain average speed for a distance of 54 km and then travels a distance of 63 km at an average speed of 6 km/h more than the first speed. If it takes 3 hours to complete the total journey, what is its first speed? (2015OD)
Solution:
Let the original average speed of (first) train be x km/hr.
Now, new speed will be = (x + 6) km/hr.
We know,
⇒ 54x + 324 + 63x = 3x (x + 6)
⇒ 117x + 324 = 3x2 + 18x
⇒ 3x2 + 18x – 117x – 324 = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 99x – 324 = 0
⇒ x2 – 33x – 108 = 0
⇒ x2 – 36x + 3x – 108 = 0
⇒ x(x – 36) + 3(x – 36) = 0
⇒ (x – 36) (x + 3) = 0
⇒ x – 36 = 0 or x + 3 = 0
x = 36 or x = -3 (Reject)
∴ First speed of train = 36 km/h.
Question 77.
A bus travels at a certain average speed for a distance of 75 km and then travels a distance of 90 km at an average speed of 10 km/h more than the first speed. If it takes 3 hours to complete the total journey, find its first speed. (2015OD)
Solution:
Let the first average speed of the bus be x km/hr.
Now, new speed of bus = (x + 10) km/hr.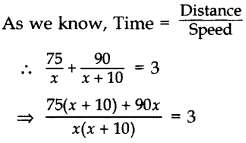
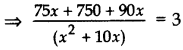
⇒ 75x + 750 + 90x = 3(x2 + 10x)
⇒ 165x + 750 – 3x2 – 30x = 0
⇒ 3x2 – 135x – 750 = 0
⇒ x2 – 45x – 250 = 0
⇒ x2 – 50x + 5x – 250 = 0
⇒ x(x – 50) + 5(x – 50) = 0
⇒ (x – 50) (x + 5) = 0
∴ x = 50 or x = -5 (Reject)
∴ Speed = 50 km/h
Question 78.
A truck covers a distance of 150 km at a certain average speed and then covers another 200 km at an average speed which is 20 km per hour more than the first speed. If the truck covers the total distance in 5 hours, find the first speed of the truck. (2015OD)
Solution:
Let the first average speed of truck be x km/hr.
⇒ 150x + 3000 + 200x = 5(x2 + 20x)
⇒ 350x + 3000 – 5x2 – 100x = 0
⇒ x2 – 50x – 600 = 0
⇒ x2 – 60x + 10x – 600 = 0
⇒ x(x – 60) + 10(x – 60) = 0
⇒ (x – 60) (x + 10) = 0
⇒ x – 60 = 0 or x + 10 = 0
⇒ x = 60 or x = -10 (Reject)
∴ Speed = 60 km/hr.
Question 79.
Two pipes running together can fill a tank in
Solution:
Let the quicker pipe take to fill the cistern = x minutes
Then the slower pipe takes to fill the cistern = (x + 3) minutes
According to Question,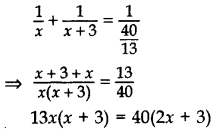
13xv + 39x = 80x + 120
13x2 + 39x – 80x – 120 = 0
13x2 – 41x – 120 = 0
13x2 – 65x + 24x – 120 = 0
13x(x – 5) + 24(x – 5) = 0
(x – 5)(13x + 24) = 0
x – 5 = 0 or 13x + 24 = 0
x = 5 or x =
∴ x = 5 Hence, the faster pipe fills the cistern in 5 minutes, and the slower pipe fills the cistern in 8(5 + 3) minutes.
Question 80.
A motor boat whose speed is 20 km/h in still water, takes 1 hour more to go 48 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream. (2011D)
Solution:
Let the speed of the stream be x km/hr
∴ Speed of the boat upstream = (20 – x) km/hr
and speed of the boat downstream = (20 + x) km/hr
Given, Distance = 48 km
According to the Question,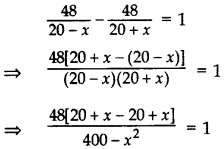
⇒ 96x = 400 – x2
⇒ x2 + 96x – 400 = 0
⇒ x2 + 100x – 4x – 400 = 0
⇒ x (x + 100) – 4 (x + 100) = 0
⇒ (x – 4) (x + 100) = 0
⇒ x – 4 = 0 or x + 100 = 0
⇒ x = 4 or x = – 100 ….[Rejecting negative value as the speed cannot be -ve
∴ Speed of the stream = 4 km/hr
Question 81.
A motorboat whose speed in still water is 18 km/h, takes 1 hour more to go 24 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot.
Find the speed of the stream. (2014OD)
Solution:
Let speed of the stream be x km/hr,
Speed of the boat upstream = (18 – x) km/hr
and Speed of the boat downstream = (18 + x) km/hr
Given, Distance = 24 km
According to the Question,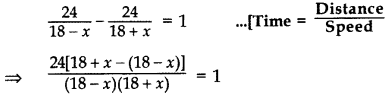
⇒
⇒ 48x = 324 – x2
⇒ x2 + 48x – 324 = 0
⇒ x2 + 54x – 6x – 324 = 0
⇒ x(x + 54) – 6(x + 54) = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (x + 54) = 0
x – 6 = 0 or x + 54 = 0
x = 6 or x= -54 (rejected)
Since speed cannot be negative
∴ Speed of stream, x = 6 km/hr
Question 82.
The time taken by a person to cover 150 km was 2 hours more than the time taken in the return journey. If he returned at a speed of 10 km/hour more than the speed while going, find the speed per hour in each direction. (2016D)
Solution:
Let the speed of a person while going = x km/hr Then the speed of a person while returning = (x + 10) km/hr
Given, Distance = 150 km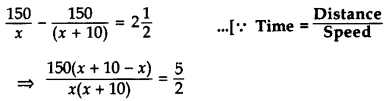
⇒ 5x(x + 10) = 3,000
⇒ x(x + 10) = 600 …[Dividing both sides by 5
⇒ x2 + 10x – 600 = 0
⇒ x2 + 30x – 20x – 600 = 0
⇒ x(x + 30) – 20(x + 30) = 0
⇒ (x + 30) (x – 20) = 0
⇒ x + 30 = 0 or x – 20 = 0
⇒ x = -30 (rejected) or x = 20
Since, speed can not be negative.
∴ Speed x = 20 km/hr.
∴ Speed while going = x = 20 km/hr
and Speed while returning
= (x + 10) = 20 + 10 = 30 km/hr
Question 83.
To fill a swimming pool two pipes are to be used. If the pipe of larger diameter is used for 4 hours and the pipe of smaller diameter for 9 hours, only half the pool can be filled. Find, how long it would take for each pipe to fill the pool separately, if the pipe of smaller diameter takes 10 hours more than the pipe of larger diameter to fill the pool. (2015D)
Solution:
Let the bigger pipe fill the tank in x hrs.
∴ the smaller pipe fills the tanks in (x + 10) hrs.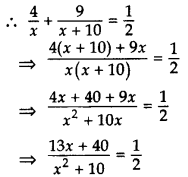
⇒ 2(13x + 40) = x2 + 10x
⇒ 26x + 80 = x2 + 10x
⇒ x2 + 10x – 26x = 80
⇒ x2 – 16x – 80 = 0
⇒ x2 – 20x + 4x – 80 = 0
⇒ x(x – 20) + 4(x – 20) = 0
⇒ (x – 20) (x + 4) = 0
⇒ x – 20 = 0 or x + 4 = 0
x = 20 x = -4 (Reject)
Hence, the pipe with larger diameter fills the tank in 20 hours.
and the pipe with smaller diameter fills the tank in 30 hours.
Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
A quadratic polynomial of the form ax² + bx + c, where a ≠ 0 and a, b, c are real numbers, is called a quadratic equation
when ax² + bx + c = 0.
Here a and b are the coefficients of x² and x respectively and ‘c’ is a constant term.
Any value is a solution of a quadratic equation if and only if it satisfies the quadratic equation.
Quadratic formula: The roots, i.e., α and β of a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0 are given
by
Here, the value b² – 4ac is known as the discriminant and is generally denoted by D. ‘D’ helps us to determine the nature of roots for a given quadratic equation. Thus D = b² – 4ac.
The rules are:
- If D = 0 ⇒ The roots are Real and Equal.
- If D > 0 ⇒ The two roots are Real and Unequal.
- If D < 0 ⇒ No Real roots exist.
If α and β are the roots of the quadratic equation, then Quadratic equation is x² – (α + β) x + αβ = 0 Or x² – (sum of roots) x + product of roots = 0
where, Sum of roots (α + β) =
Product of roots (α x β) =
Here Is The Class 10 Maths All NCERT Solutions In Hindi + English With Extra Questions, Notes And Important Questions
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circle
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
.png)
.png)