Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Applications of Trigonometry (English + Hindi) NCERT Solutions
- Ex.9.1
- Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Extra Questions
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
Ex.9.1
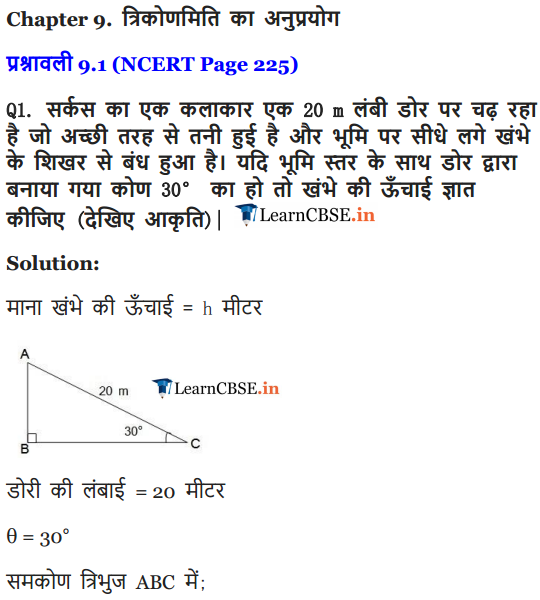
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 1.
A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is 30°.
Solution: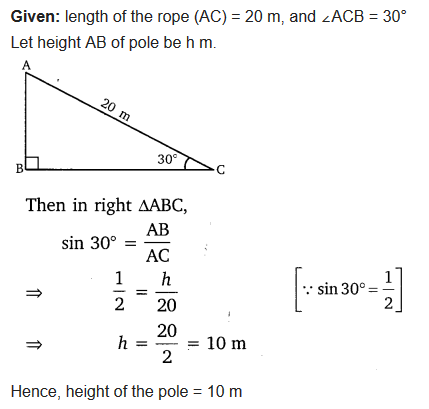
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
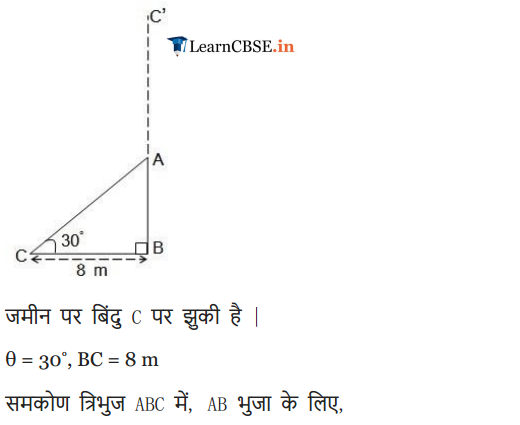
A tree breaks due to storm and the broken part bends so that the top of the tree touches the ground making an angle 30° with it. The distance between the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is 8 m. Find the height of the tree.
Solution: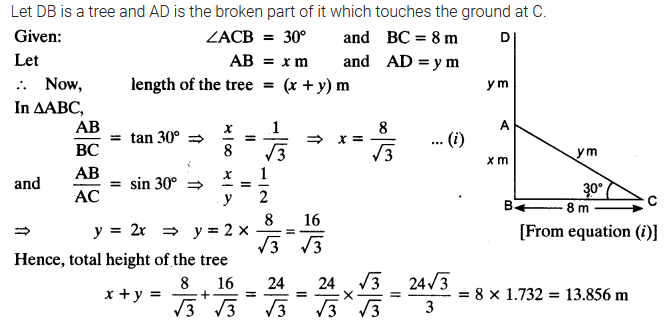
You can also download the free PDF of Ex 9.1 Class 10 Some Applications of Trigonometry NCERT Solutions or save the solution images and take the print out to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
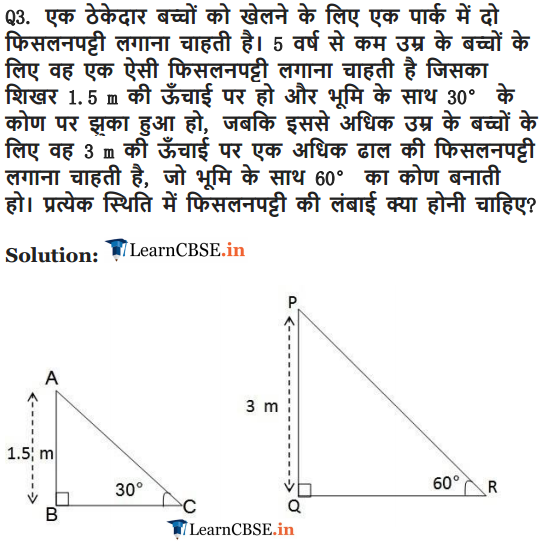
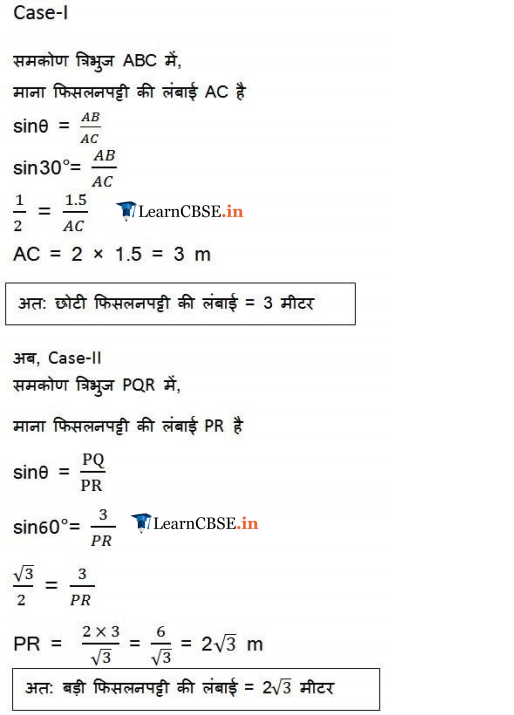
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
A contractor plans to install two slides for the children to play in a park. For the children below the age of 5 years, she prefers to have a slide whose top is at a height of 1.5 m, and is inclined at an angle of 30° to the ground, whereas for elder children, she wants to have a steep slide at a height of 3 m, and inclined at an angle of 60° to the ground. What should be the length of the slide in each case?
Solution: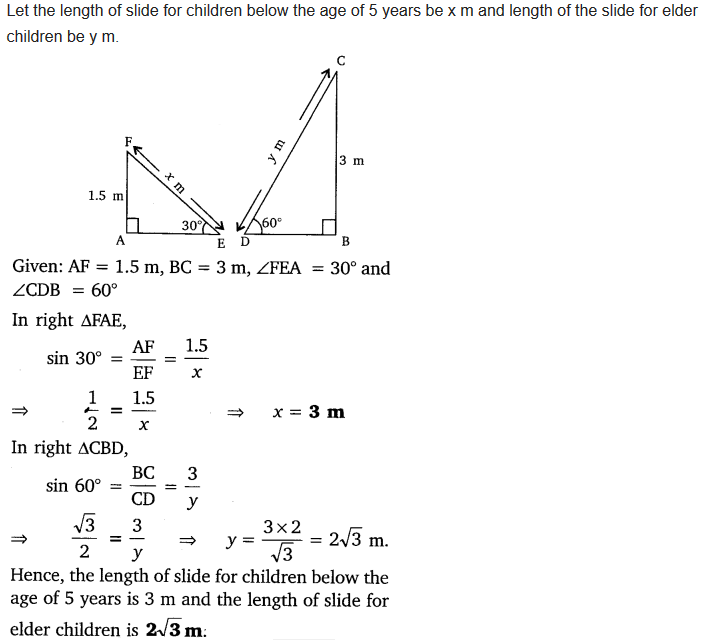
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of the tower is 30°. Find the height of the tower.
Solution: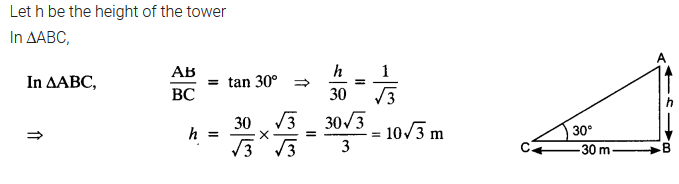
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
A kite is flying at a height of 60 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
Solution: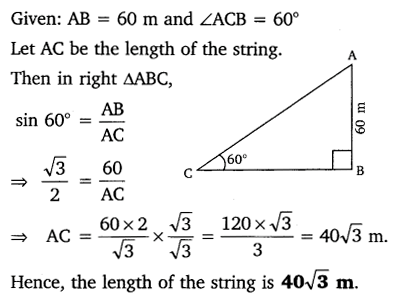
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
A 1.5 m tall boy is standing at some distance from a 30 m tall building. The angle of elevation from his eyes to the top of the building increases from 30° to 60° as he walks towards the building. Find the distance he walked towards the building.
Solution: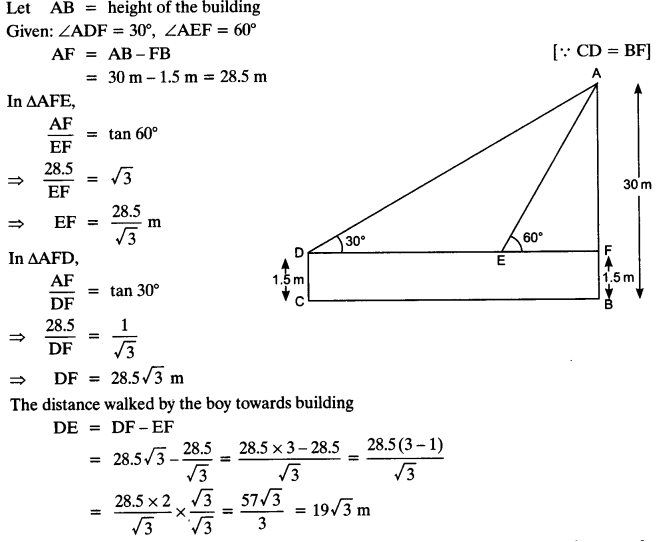
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
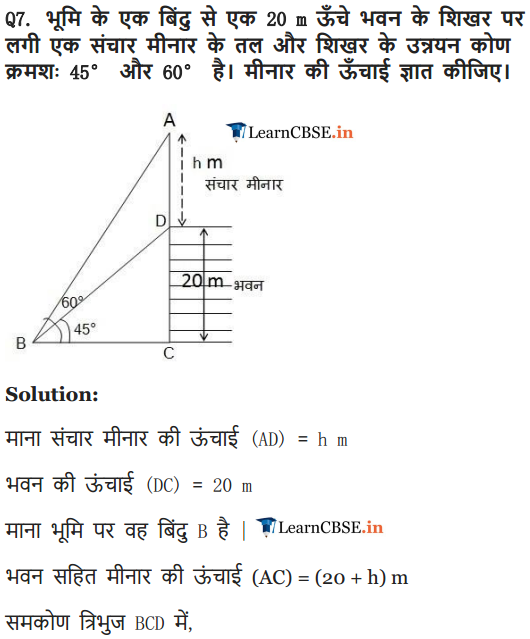
From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and the top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a 20 m high building are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Solution: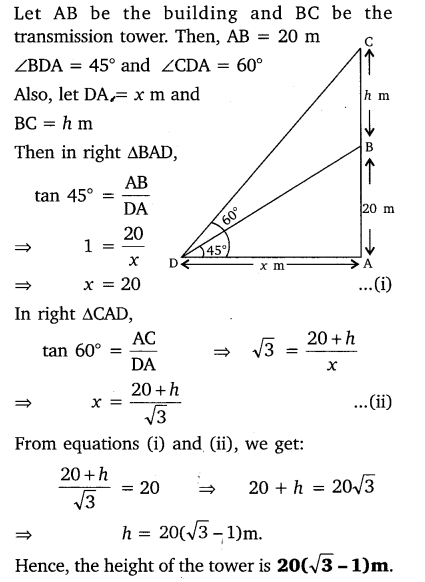
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
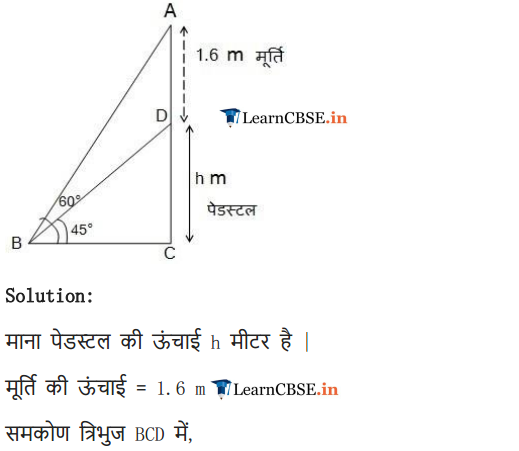
A statue, 1.6 m tall, stands on the top of a pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 45°. Find the height of the pedestal.
Solution: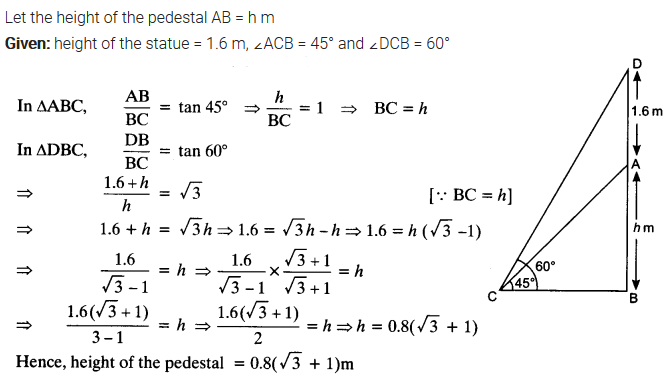
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
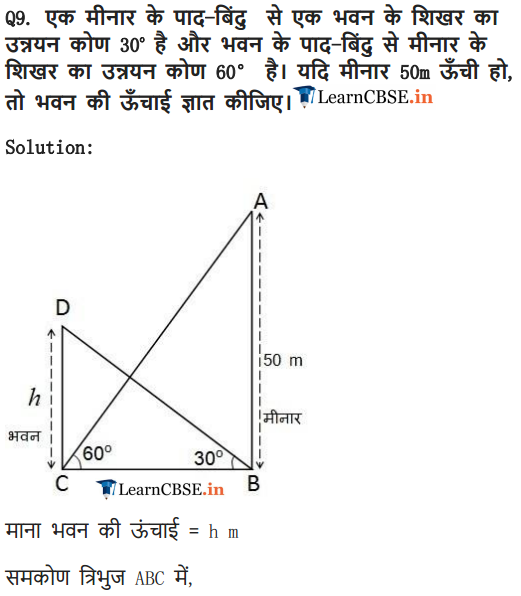
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of a tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the building.
Solution: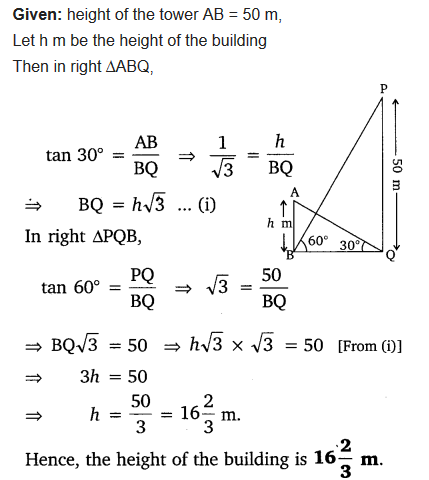
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 10.
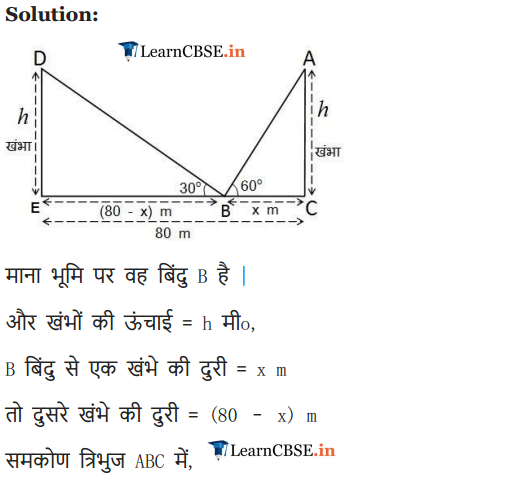
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distance of the point from the poles.
Solution: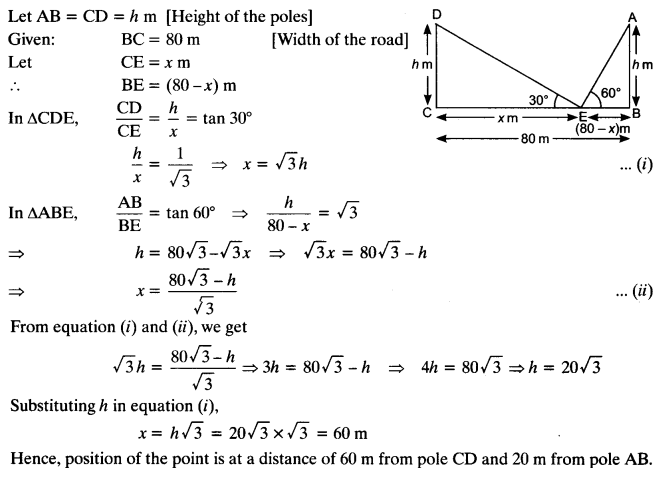
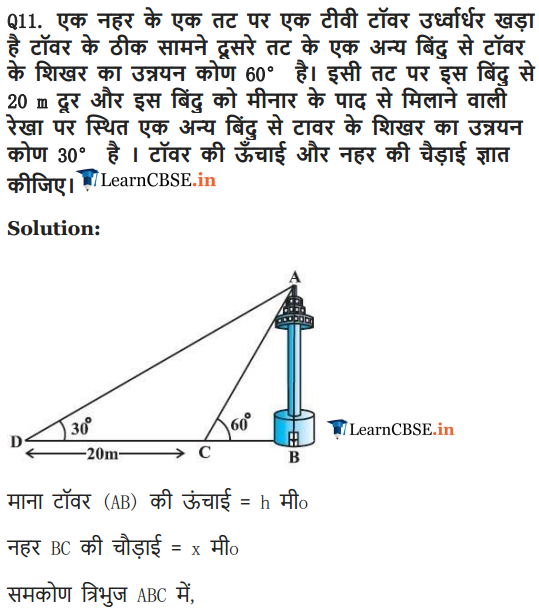
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 11.
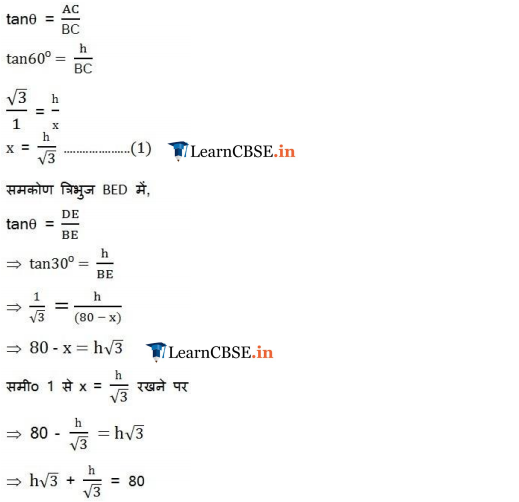
A TV tower stands vertically on a bank of a canal. From a point on the other bank directly opposite the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 60°. From another point 20 m away from this point on the line joining this point to the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30° (see the given figure). Find the height of the tower and the width of the CD and 20 m from pole AB.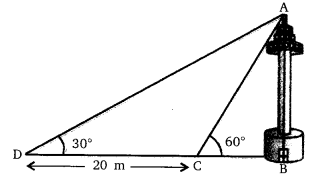
Solution:
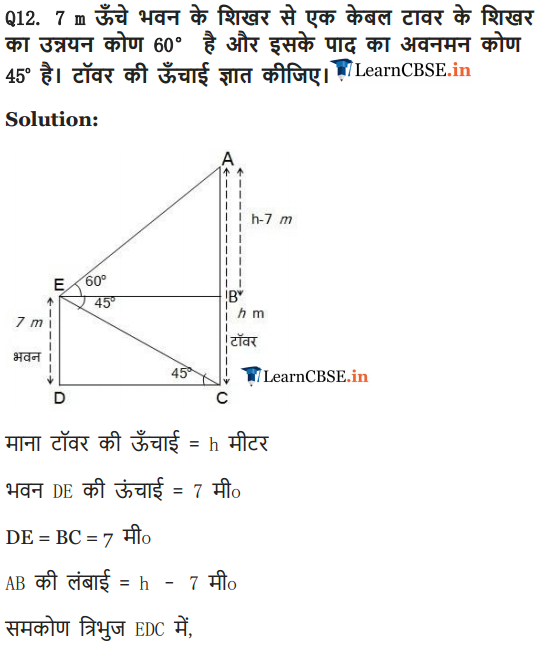
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 12.
From the top of a 7 m high building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower is 60° and the angle of depression of its foot is 45°. Determine the height of the tower.
Solution: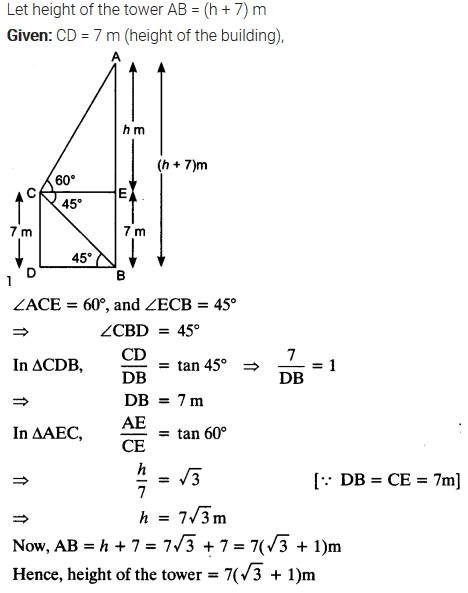
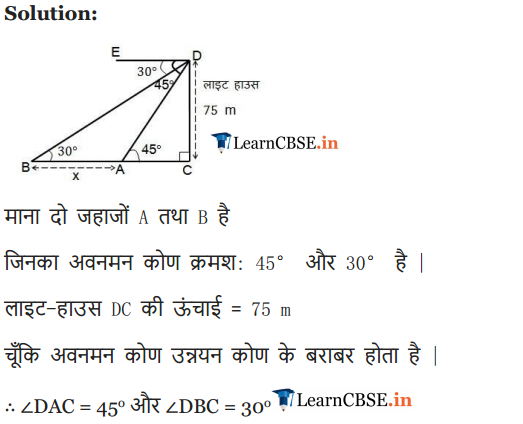
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 13.
As observed from the top of a 75 m high lighthouse from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the lighthouse, find the distance between the two ships.
Solution: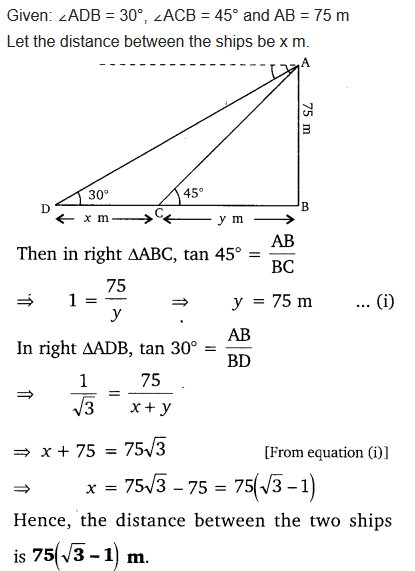
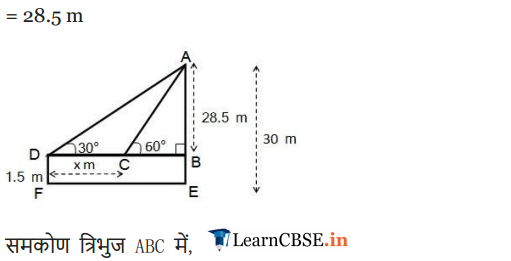
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 14.
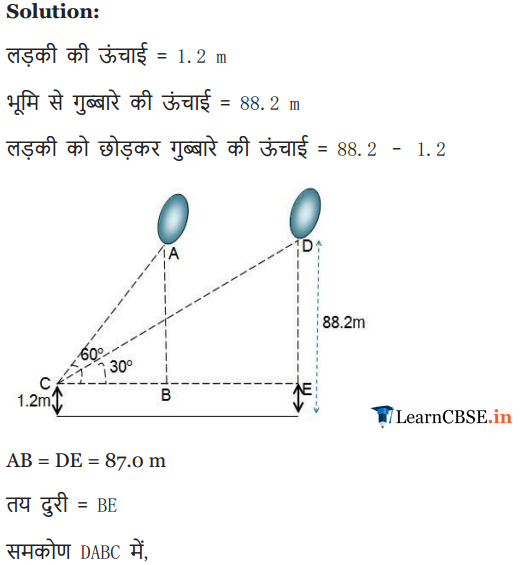
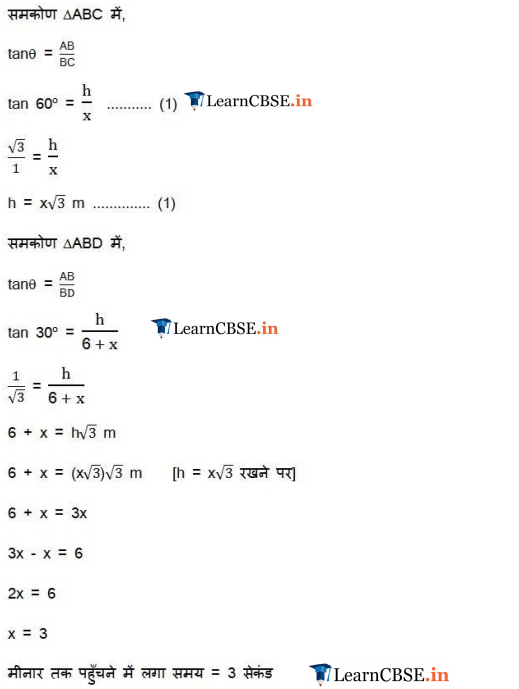
A 1.2 m tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of 88.2 m from the ground. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the eyes of the girl at any instant is 60°. After sometime, the angle of elevation reduces to 30° (see figure). Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval.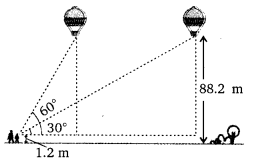
Solution: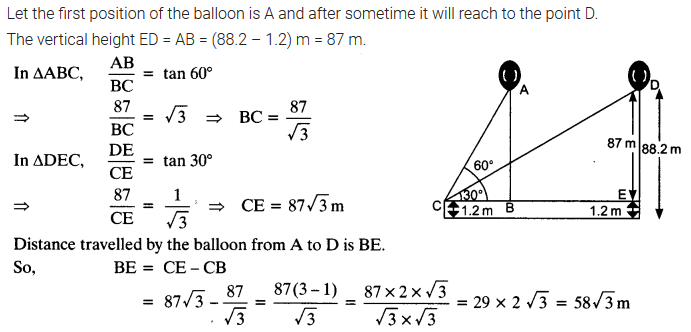
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 15.
A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing at the top of the tower observes a car at an angle of depression of 30°, which is approaching the foot of the tower with a uniform speed. Six seconds later, the angle of depression of the car is found to be 60°. Find the time taken by the car to reach the foot of the tower from this point.
Solution:
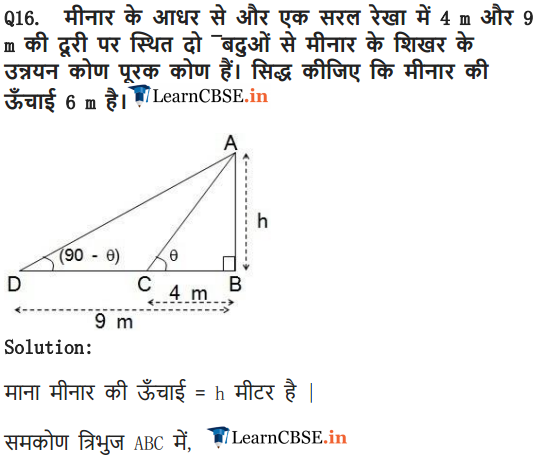
Ex 9.1 Class 10 Maths Question 16.
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is 6 m.
Solution: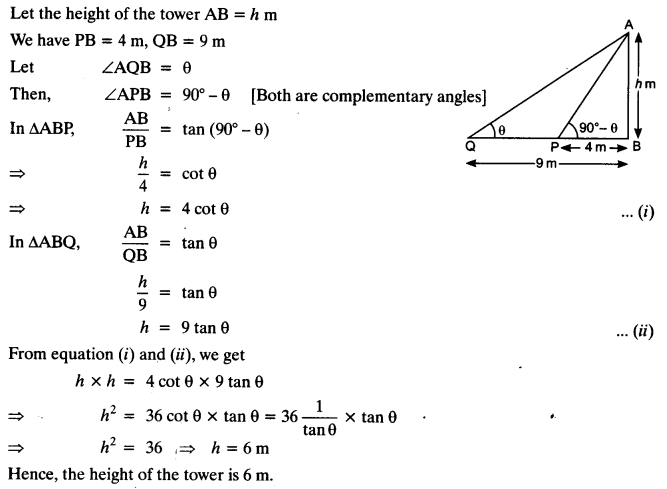
Class 10 Maths Some Application Of Trigonometry Mind Maps
SOME APPLICATION OF TRIGONOMETRY
Introduction
The height or length of an object or the distance between two distinct objects can be determined with the help of trigonometric ratios.
Line of Sight and Angle of Elevation
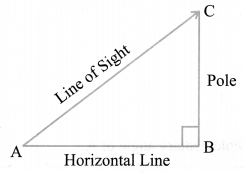
In the above figure, the line AC drawn from the eye of an observer at A to the top of the pole ‘C’ is called the line of sight. The observer is looking at the top of the pole. The angle BAC, so formed by the line of sight with the horizontal, is called the angle of elevation of the top of the pole from the eye of an observer.
Angle of Depression
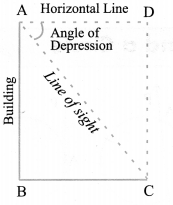
In the above figure, the line AC, is the line of sight as the observer is looking downwards from the top of the building at A towards the object at C. Here angle DAC, so formed by the line of sight with the horizontal, when the observer is lowering his/her head is called Angle of depression.
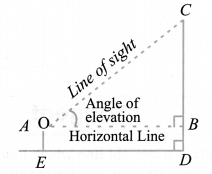
From the above figure, if we want to find the height CD of the pole without actually measuring it, we need the following information:
(i) Distance ED of the observer from the pole.
(ii) the angle of elevation ∠BAC, of the top of the pole.
(iii) the height AE of the observer if it is considerable.
Assuming that the above three conditions are known we can determine the height of the pole in the following way.
In the figure, CD = CB + BD. Here, BD = AE, which is the height of the observer.
To find BC, we will use trigonometric ratios of ∠BAC or ∠A.
In ∆ABC, the side BC is the opposite side to the known ∠A. Now we use either tan A or cot A, as these trigonometric ratios involve AB and BC to find BC.
Therefore, tan A =
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry (Hindi Medium) Ex 9.1
















Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Very Short Answer (1 Mark)
Question 1.
A ladder 15 m long just reaches the top of a vertical wall. If the ladder makes an angle of 60° with the wall, then calculate the height of the wall. (2013OD)
Solution: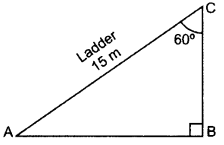
∠BAC = 180° – 90° – 60o = 30°
sin 30° =
2BC = 15
BC =
Question 2.
In the given figure, a tower AB is 20 m high and BC, its shadow on the ground, is 
Solution:
AB = 20 m, BC = 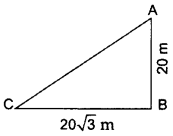
θ = ?
In ∆ABC,
Question 3.
In the figure, AB is a 6 m high pole and CD is a ladder inclined at an angle of 60° to the horizontal and reaches up to a point D of pole. If AD = 2.54 m. Find the length of the ladder. (Use 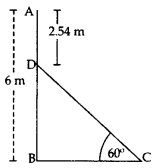
Solution:
BD = AB – AD = 6 – 2.54 = 3.46 m
In rt., ∆DBC, sin 60° =
∴ Length of the ladder, DC =
DC = 4 m
Question 4.
A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes anangle of 60° with the horizontal. If the foot of the ladder is 2.5 m away from the wall, find the length of the ladder. (2016OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the ladder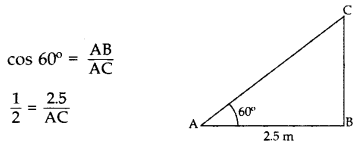
∴ Length of ladder, AC = 5 m 2.5 m
Question 5.
If a tower 30 m high, casts a shadow 10
Solution:
Let required angle be θ.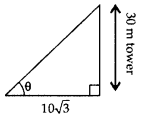
tan θ =
tan θ =
⇒ tan θ = tan 60° ∴ θ = 60°
Question 6.
The tops of two towers of height x and y, standing on level ground, subtend angles of 30° and 60° respectively at the centre of the line joining their feet, then find x : y. (2015D)
Solution:
When base is same for both towers and their heights are given, i.e., x and y respectively
Let the base of towers be k.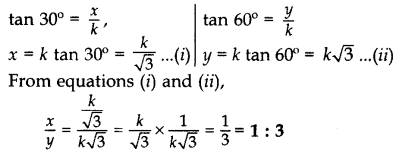
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 7.
The angles of depression of two ships from the top of a light house and on the same side of it are found to be 45° and 30°. If the ships are 200 m apart, find the height of the light house. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the height of the light house,
D and C are two ships and DC = 200 m
Let BC = x m, AB = h m
In rt. ∆ABC,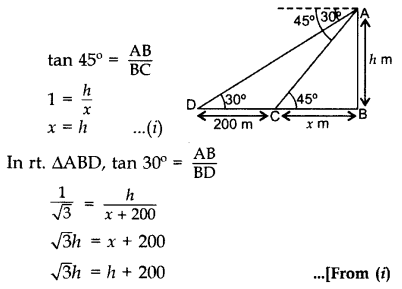
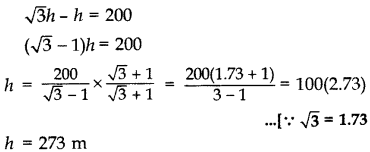
∴ Height of the light house = 273 m
Question 8.
The horizontal distance between two poles is 15 m. The angle of depression of the top of first pole as seen from the top of second pole is 30°. If the height of the second pole is 24 m, find the height of the first pole. [Use
Solution:
Let AB be the 1st pole
and CE = 24 m be the 2nd pole
In ∆ADE,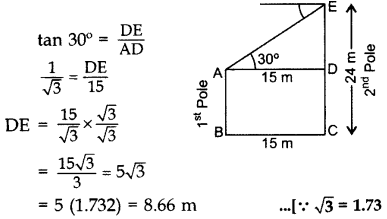
∴ Height of the first pole,
AB = CD = CE – DE
= 24 – 8.66 = 15.34 m
Question 9.
As observed from the top of a 60 m high light house from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the light-house, find the distance between the two ships. (Use
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the height of Light-house and C and D be the two ships.
In right ∆ABC,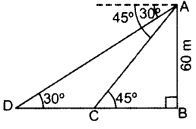
∴ Distance between the two ships,
CD = BD – BC = 103.92 – 60 = 43.92 m
Question 10.
Two ships are there in the sea on either side of a light house in such a way that the ships and the light house are in the same straight line. The angles of depression of two ships as observed from the top of the light house are 60° and 45°. If the height of the light house is 200 m, find the distance between the two ships. [Use
Solution: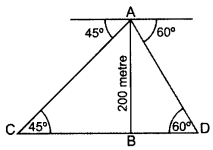
Let AB be the light house and C and D be the two ships,
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = 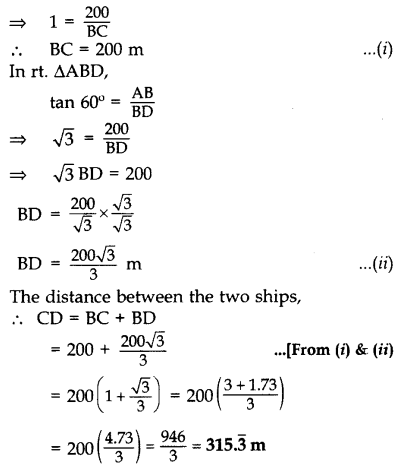
Question 11.
The angle of elevation of an aeroplane from a point on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 30 seconds the angle of elevation becomes 30°. If the aeroplane is flying at a constant height of 3000
Solution:
Let A be the point on the ground and C be the aeroplane.
In rt. ∆ABC,

Question 12.
From the top of a 60 m high building, the angles of depression of the top and the bottom of a tower are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (Take
Solution:
Let AC be the building & DE be the tower.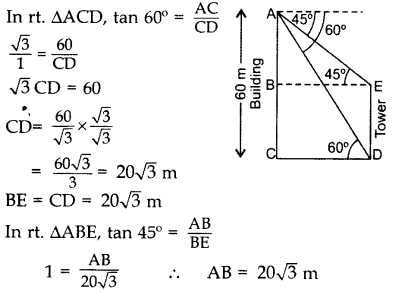
∴ Height of the tower, DE = BC
DE = AC – AB
DE = 60 – 20
DE = 20(3 – 1.73) = 20(1.27)
DE = 25.4 m
Question 13.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 45°. If the tower is 30 m high, find the height of the building. (2015D)
Solution: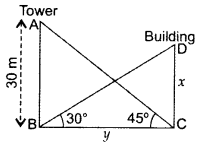
Let height of building be x and the distance between tower and building be y.
In ∆ABC,
∴Height of the building is 10
Question 14.
The angle of elevation of an aeroplane from a point A on the ground is 60°. After a flight of 15 seconds, the angle of elevation changes to 30°. If the aeroplane is flying at a constant height of 1500
Solution:
Let AL = x, BL = CM = 1500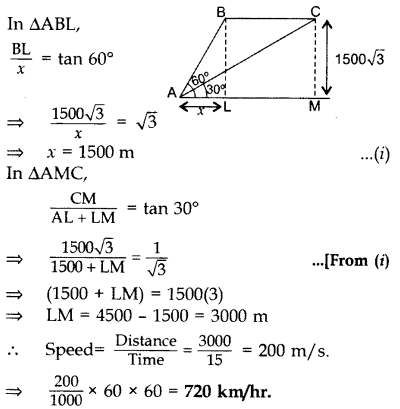
Question 15.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a 50 m high building from the top of a tower are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower and the horizontal distance between the tower and the building. [Use
Solution: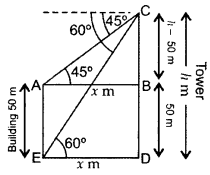
Let AE be the building and CD be the tower. Let height of the tower = h m
and, the horizontal distance between tower and building = x m …[Given
BD = AE = 50 m
∴ BC = CD – BD = (h – 50) m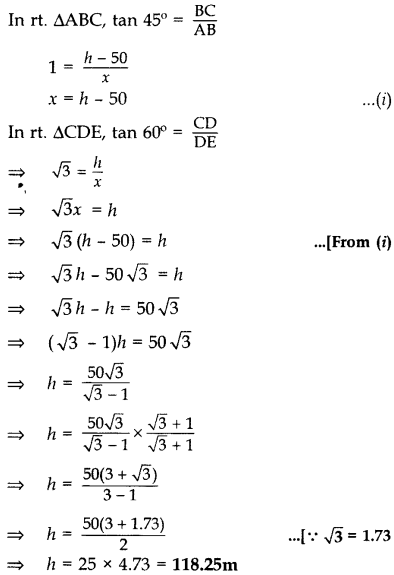
From (i), x = h – 50
= 118.25 – 50 = 68.25 m
Height of the tower, h = 118.25 m
∴ Horizontal distance between tower and Building, x = 68.25 m
Question 16.
A man standing on the deck of a ship, which is 10 m above water level, observes the angle of elevation of the top of a hill as 60° and the angle of depression of the base of hill as 30°. Find the distance of the hill from the ship and the height of the hill. (2016D)
Solution: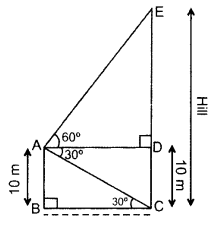
Let the man standing on the deck of a ship be at point A and let CE be the hill.
Here BC is the distance of hill from ship and CE be the height of hill.
In rt. ∠ABC, tan 30° =
BC = 10
BC = 10(1.73) = 17.3 m …[::
AD = BC = 10
In rt. ∆ADE, tan 60° =
⇒
⇒ DE = 10
∴ CE = CD + DE = 10 + 30 = 40 m
Hence, the distance of the hill from the ship is 17.3 m and the height of the hill is 40 m.
Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Important Questions Long Answer (4 Marks)
Question 17.
The angle of elevation of the top of a vertical tower from a point on the ground is 60°. From another point 10 m vertically above the first, its angle of elevation is 30°. Find the height of the tower. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the tower
Let AC = y m
Let DC = EB = x m
In rt. ∆ABE,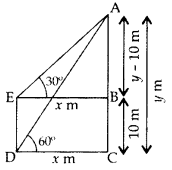
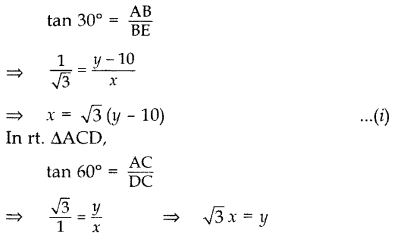
3(y – 10) = y ⇒ 3y – 30 = y
3y – y = 30 ⇒ 2y = 30
∴ Height of the tower, y = 15 m
Question 18.
From the top of a tower 100 m high, a man observes two cars on the opposite sides of the tower with angles of depression 30° and 45° respectively. Find the distance between the cars. (Use
Solution:
Let AB be the tower.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = 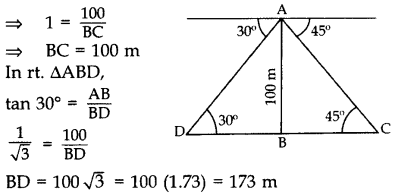
∴ Distance between the cars, CD
= BD + BC
= 173 + 100
= 273 m
Question 19.
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite to each other on either side of the road, which is 100 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles. (2011D)
Solution:
Let AB and DE be the two equal poles and C be the point on BD (road).
Let BC = x m
Then CD = (100 – x) m
Let AB = DE = y m
In rt. ∆ABC,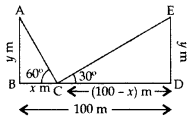
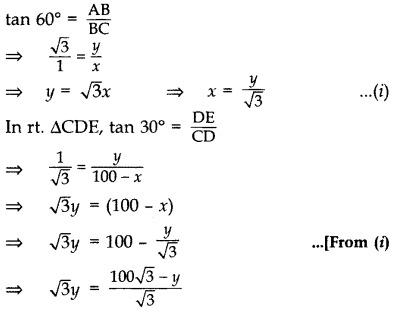
⇒ 3y = 100
⇒ 4y = 100
∴ Height of the poles,
y =
Question 20.
From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a 10 m high building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (2011D)
Solution:
Let BC be the building and CD be the transmission tower. A be the point on the ground.
Let CD = y m
In rt. ∆ABC,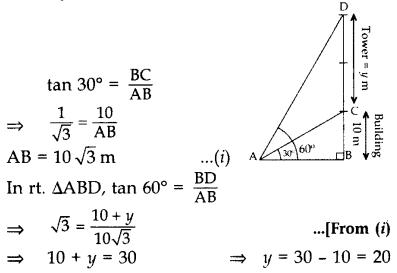
∴ Height of transmission tower = 20 m
Question 21.
From the top of a vertical tower, the angles of depression of two cars, in the same straight line with the base of the tower, at an instant are found to be 45° and 60°. If the cars are 100 m apart and are on the same side of the tower, find the height of the tower. [Use
Solution:
Let AB be the tower
Let AB = h m,
and BC = x m
In rt. ∆ABC,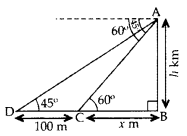
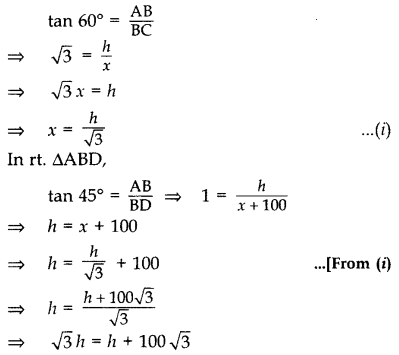
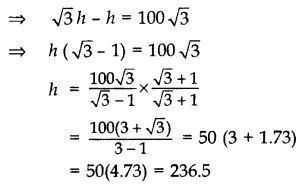
∴ Height of the tower, h = 236.5 m
Question 22.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a 12 m tall building, from the top of a multi-storeyed building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the multistoreyed building. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AC be the multi-storeyed building and DE be the other building.
Let AC = y m,
DC = EB = x m
In rt. ∆ABE,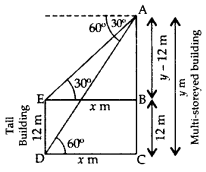
tan 30° =
x =
In rt. ∆ACD, tan
60° =
⇒
⇒
⇒
⇒ 3 (y – 12) = y
⇒ 3y – 36 = y
⇒ 3y – y = 36
⇒ 2y = 36
⇒ y = 18
∴ Height of the multi-storeyed building, y = 18 m
Question 23.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of a tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the building. (2011OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 50 m be the tower
and CD be the building.
In rt. ∆ABC,

Question 24.
The angle of elevation of the top of a hill at the foot of a tower is 60° and the angle of depression from the top of the tower of the foot of the hill is 30°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the hill. (2012D)
Solution:
Let CD = H m, be the height of the hill
AB = 50 be the tower
and Distance between them, BC = x m
In rt. ∆ABC,
tan 30° = 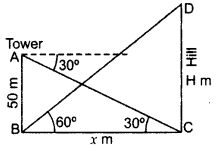
x = 50
In rt. ∆BCD,
tan 60° =
∴ Height of the hill = 150 m
Question 25.
From the top of a hill, the angles of depression of two consecutive kilometre stones due east are found to be 30° and 45°. Find the height of the hill. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the hill of height h km.
Let C and D be two stones due east of the hill at a distance of 1 km from each other.
Let BC = x km
In rt. ∆ABC,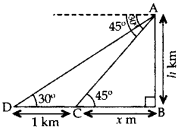
tan 45° =
= 1 =
= h = x … (1)
In rt. ∆ABD, tan 30° =
(
Hence, the height of the hill is 1.365 km.
Question 26.
The shadow of a tower standing on a level ground is found to be 20 m longer when the Sun’s altitude is 45° than when it is 60°. Find the height of the tower. (2012D)
Solution:
Let AB be the tower = h m
BC = x m, DC = 20 m
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = 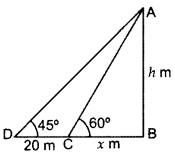

∴ Height of the tower = 47.3 m
Question 27.
A kite is flying at a height of 45 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string assuming that there is no slack in the string. (2012D )
Solution:
Let AB = 45 m be the height of the kite from the ground,
In rt. ∆ABC, sin 60° = 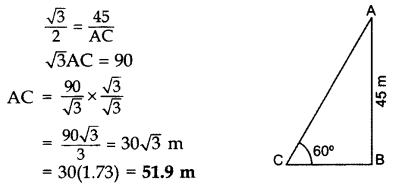
Question 28.
The angles of depression of the top and bottom of a tower as seen from the top of a 60
Solution:
Let AB = 60
In rt. ∆ABC,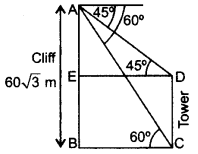
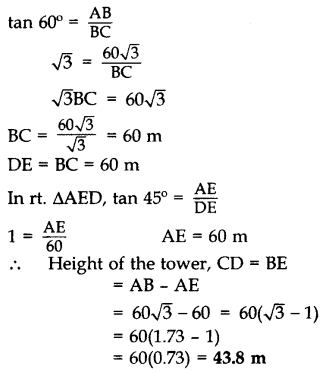
Question 29.
The angles of elevation and depression of the top and bottom of a light-house from the top of a 60 m high building are 30° and 60° respectively. Find:
(i) the difference between the heights of the light-house and the building.
(ii) the distance between the light-house and the building. (2012OD)
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the building
and CE be the light-house.
In rt. ∆ABC,
tan 60° = 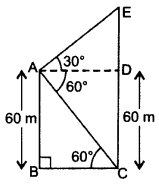


∴ (i) Difference between the heights = 20 m
and (ii) Distance = 34.64 m
Question 30.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 60 m high, find the height of the building. (2013D)
Solution:
Let AB = 60 m be the tower
and let CD be the building.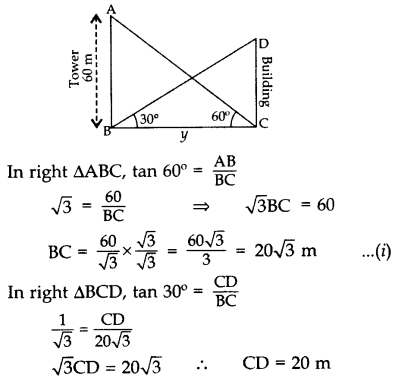
∴Height of the building, CD = 20 m
Question 31.
From a point P on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of a 10m tall building is 30°. A flagstaff is fixed at the top of the building and the angle of elevation of the top of the flagstaff from P is 45°. Find the length of the flagstaff and the distance of the building from the point P. (Take
Solution:
Let QR = 10 m be the building
and RS be the flagstaff.
In right ∆PQR,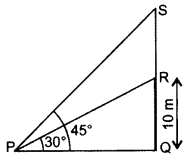

Length of the flagstaff, RS = 17.3 – 10
= 7.3 m
Question 32.
Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles. (2013D)
Solution:
Let AB = DE = y m be the two poles such that
BD = 80 m, CD = x m and BC = 80 – x m
In rt. ∆CDE,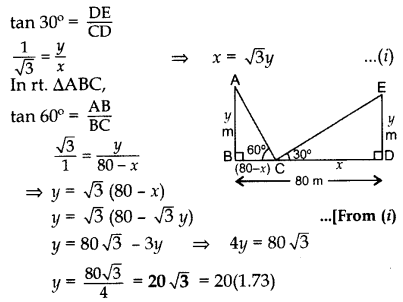
Height of pole = 34.6 m
Puting the value of y in (i),
x =
∴ CD, x = 60 m
Distance of poin from the pole
and BC = 80 – x = 80 – 60 = 20 m
Question 33.
The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of a tower is 30°. The angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 60 m high, find the height of the building. (2013OD)
Solution:
Refer to Question 30, Page 143.
Question 34.
The angles of elevation and depression of the top and the bottom of a tower from the top of a building, 60 m high, are 30° and 60° respectively. Find the difference between the heights of the building and the tower and the distance between them. (2014D)
Solution:
Let AB be the building and CE be the tower.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = 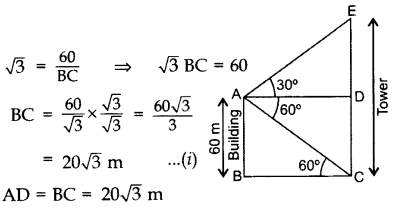

∴ Difference between the heights of the building and the tower, DE = 20 m
Distance between them,
BC= 20
Question 35.
A peacock is sitting on the top of a pillar, which is 9 m high. From a point 27 m away from the bottom of the pillar, a snake is coming to its hole at the base of the pillar. Seeing the snake the peacock pounces on it. If their speeds are equal, at what distance from the hole is the snake caught? (2014D)
Solution: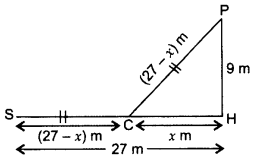
Lęt PH be the pillar. Let the distance from the hole to the place where snake is caught = x m
Let P be the top of the pillar and S be the point where the snake is
∴ SC = (27 – x)m
SC = PC = (27 – x)m …[∵ Their speeds are equal
In rt. ∆PHC
PH2 + CH2 = PC2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
92 + x2 = (27 – x)2
81 + x2 = 729 – 54x + x2
54x = 729 – 81 = 648
x =
Hence, required distance, x =12 m
Question 36.
The angle of elevation of the top of a tower at a distance of 120 m from a point A on the ground is 45°. If the angle of elevation of the top of a flagstaff fixed at the top of the tower, at A is 60°, then find the height of the flagstaff. (Use
Solution:
Let BC be the tower
and CD be the flagstaff.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = 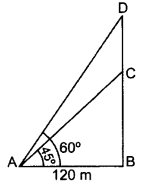
1 =
BC = 120 m …(i)
In rt. ∆ABD,
tan 60° =
BD = 120
Height of the flagstaff,
CD = BD – BC
= 120
= 120(
= 120(1.73 – 1)
= 120(0.73) = 87.6 m
Question 37.
From a point P on the ground the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is 30° and that of the top of a flag staff fixed on the top of the tower, is 60°. If the length of the flag staff is 5m, find the height of the tower. (2015D)
Solution:
In ABCD,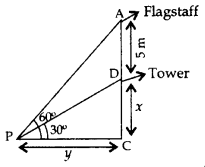
(i)
y =
In ∆ABC,
(ii)
tan 60° =
⇒ 3x = x + 5 or x = 2.5
∴ Height of Tower = x = 2.5 m
Question 38.
At a point A, 20 metres above the level of water in a lake, the angle of elevation of a cloud is 30°. The angle of depression of the reflection of the cloud in the lake, at A is 60°. Find the distance of the cloud from A. (2015OD)
Solution:
In ∆ABC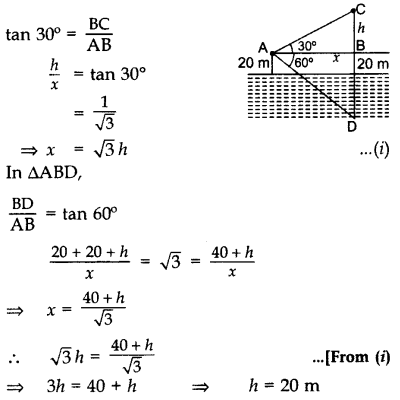
Putting the value of h in equation (i),
∴ x = 20
Using pythagoras’ theorem,
AC =
∴ AC =
Distance of the cloud from A = 40 m.
Question 39.
The angle of elevation of a cloud from a point 60 m above the surface of the water of a lake is 30° and the angle of depression of its shadow in water of lake is 60°. Find the height of the cloud from the surface of water. (2017D)
Solution:
Let the height of the cloud from the surface of lake EC = H m = EF (image in water)
and A be the point, the distance between A and perpendicular of cloud AD = x m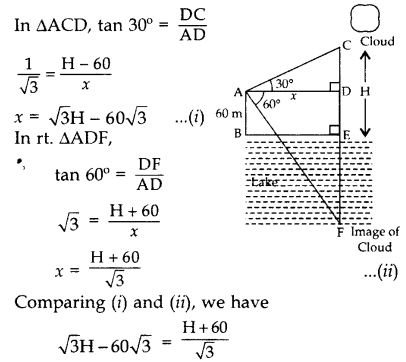
⇒ 3H – 180 = H + 60
⇒ 3H – H = 60 = 180
⇒ 2H = 240
⇒ H = 120
∴ Height of the cloud = 120 m
Question 40.
A bird is sitting on the top of a 80 m high tree. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the bird is 45°. The bird flies away horizontally in such a way that it remained at a constant height from the ground. After 2 seconds, the angle of elevation of the bird from the same point is 30°. Find the speed of flying of the bird. (Take
Solution: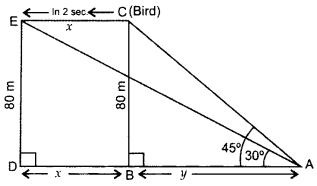
Let BC be the tree
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 45° = 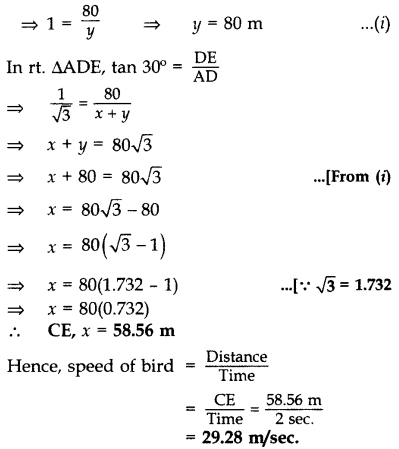
Question 41.
The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the height of the tower. (2016D)
Solution: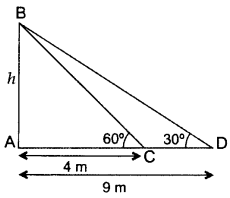
Let the height of the tower, AB = h m
In ∆ABC, tan 60° =
Hence, height of the tower = 473 m
Question 42.
The angle of elevation of the top of a vertical tower PQ from a point X on the ground is 60°. From a point Y, 40 m vertically above X, the angle of elevation of the top Q of tower is 45°. Find the height of the tower PQ and the distance PX. (Use
Solution:
Let QR = x m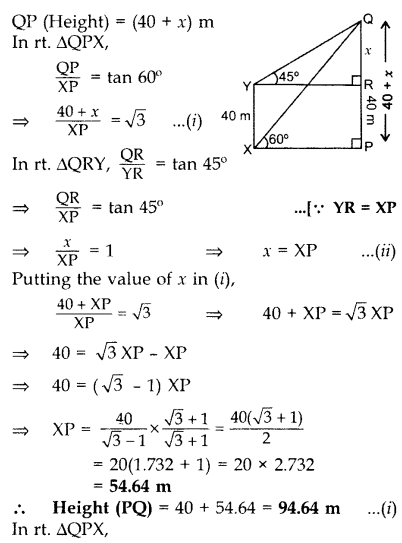
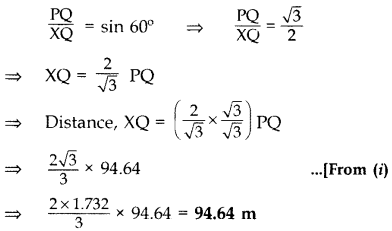
Hence, height of the tower PQ is 96.54 m and the distance PX is 109.3 m.
Question 43.
As observed from the top of a light house, 100 m high above sea level, the angles of depression of a ship, sailing directly towards it, changes from 30° to 60°. Find the distance travelled by the ship during the period of observation. (Use
Solution:
Let AB = 100 m be the light-house and B, C be the two positions of the ship and CD be the distance travelled by ship.
In rt. ∆ABC, tan 60° = 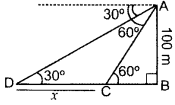
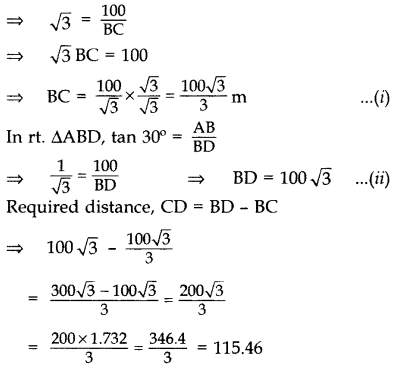
∴ Distance travelled by ship is 115.46 m
Question 44.
An aeroplane is flying at a height of 300 m above the ground. Flying at this height, the angles of depression from the aeroplane of two points on both banks of a river in opposite directions are 45o and 60° respectively. Find the width of the river. [Use
Solution: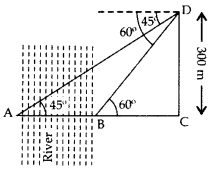
Let CD be height of an aeroplane flying above the ground and AB be the two banks of the river.
In rt. ∆BCD, tan 60° = 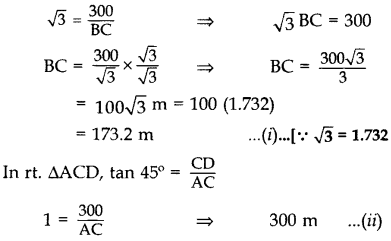
The width of the river, AB = AC – BC
= 300 – 173.2
= 126.8 m
Question 45.
From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of a tower is observed to be 60°. From a point 40 m vertically above the first 300 AC point of observation, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30°. Find the height of the tower and its horizontal distance from the point of observation. (2016OD)
Solution: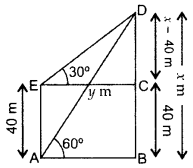
Let BD be the tower, i.e., x m.
In rt. ∆ABD, tan 60° = ![]()
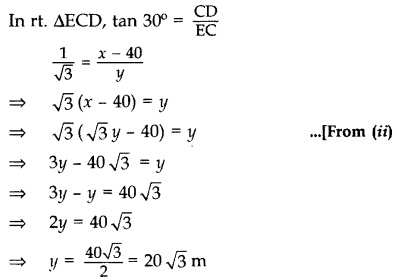
From (i) x =
∴Height of the tower, r = 60 m
Required horizontal distance, y = 20
y = 20(1.73) = 34.6 m …[∵
Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
Line of Sight
When an observer looks from a point E (eye) at object O then the straight line EO between eye E and object O is called the line of sight.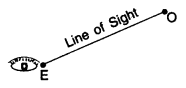
Horizontal
When an observer looks from a point E (eye) to another point Q which is horizontal to E, then the straight line, EQ between E and Q is called the horizontal line.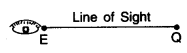
Angle of Elevation
When the eye is below the object, then the observer has to look up from point E to object O. The measure of this rotation (angle θ) from the horizontal line is called the angle of elevation.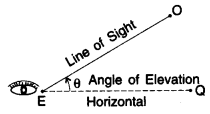
Angle of Depression
When the eye is above the object, then the observer has to look down from point E to the object. The horizontal line is now parallel to the ground. The measure of this rotation (angle θ) from the horizontal line is called the angle of depression.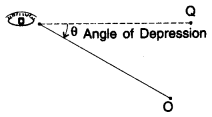
How to convert the above figure into the right triangle.
Case I: Angle of Elevation is known
Draw OX perpendicular to EQ.
Now ∠OXE = 90°
ΔOXE is a rt. Δ, where
OE = hypotenuse
OX = opposite side (Perpendicular)
EX = adjacent side (Base)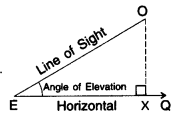
Case II: Angle of Depression is known
(i) Draw OQ’parallel to EQ
(ii) Draw perpendicular EX on OQ’.
(iii) Now ∠QEO = ∠EOX = Interior alternate angles
ΔEXO is an rt. Δ. where
EO = hypotenuse
OX = adjacent side (base)
EX = opposite side (Perpendicular)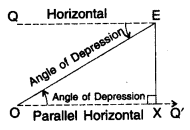
- Choose a trigonometric ratio in such a way that it considers the known side and the side that you wish to calculate.
- The eye is always considered at ground level unless the problem specifically gives the height of the observer.
The object is always considered a point.
Some People Have
Sin θ =
Curly Black Hair
Cos θ =
Turning Permanent Black.
Tan θ =
Here Is The Class 10 Maths All NCERT Solutions In Hindi + English With Extra Questions, Notes And Important Questions
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circle
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability
.png)
.png)